Dodecane's Functionality in Composite Material Development
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dodecane in Composites: Background and Objectives
Dodecane, a straight-chain alkane hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C12H26, has emerged as a significant component in the development of advanced composite materials. The exploration of dodecane's functionality in this context represents a convergence of organic chemistry and materials science, aiming to enhance the performance characteristics of composites across various industrial applications.
The journey of dodecane in composite materials can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began investigating the potential of incorporating hydrocarbon molecules into polymer matrices. This initial interest was driven by the need for improved thermal and mechanical properties in composites used in aerospace and automotive industries. As the field progressed, the unique properties of dodecane, such as its low melting point, high boiling point, and chemical stability, became increasingly relevant to composite material development.
The primary objective of researching dodecane's functionality in composites is to leverage its molecular structure and properties to address specific challenges in material performance. These challenges include enhancing thermal management, improving mechanical strength, and increasing the overall durability of composite materials. By integrating dodecane into composite structures, researchers aim to create materials with superior heat dissipation capabilities, enhanced resistance to environmental degradation, and improved structural integrity under various stress conditions.
Another critical aspect of this research is the exploration of dodecane's potential as a phase change material (PCM) within composite systems. PCMs are substances capable of absorbing, storing, and releasing large amounts of latent heat during phase transitions. The incorporation of dodecane as a PCM in composites opens up possibilities for developing smart materials with thermal energy storage and temperature regulation capabilities, which are particularly valuable in applications such as building materials and thermal management systems for electronics.
The evolution of dodecane research in composites has been marked by significant technological advancements. Early studies focused on simple incorporation methods, while recent research has delved into more sophisticated techniques such as microencapsulation and nanocomposite formulations. These advancements have expanded the potential applications of dodecane-enhanced composites, ranging from high-performance aerospace materials to energy-efficient construction components.
As the field progresses, the research objectives continue to evolve. Current efforts are directed towards optimizing the integration of dodecane into various composite matrices, understanding the long-term stability and performance of these materials, and exploring novel applications in emerging technologies such as flexible electronics and renewable energy systems. The ultimate goal is to develop a new generation of composite materials that can meet the increasingly demanding requirements of modern industrial and technological applications.
The journey of dodecane in composite materials can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began investigating the potential of incorporating hydrocarbon molecules into polymer matrices. This initial interest was driven by the need for improved thermal and mechanical properties in composites used in aerospace and automotive industries. As the field progressed, the unique properties of dodecane, such as its low melting point, high boiling point, and chemical stability, became increasingly relevant to composite material development.
The primary objective of researching dodecane's functionality in composites is to leverage its molecular structure and properties to address specific challenges in material performance. These challenges include enhancing thermal management, improving mechanical strength, and increasing the overall durability of composite materials. By integrating dodecane into composite structures, researchers aim to create materials with superior heat dissipation capabilities, enhanced resistance to environmental degradation, and improved structural integrity under various stress conditions.
Another critical aspect of this research is the exploration of dodecane's potential as a phase change material (PCM) within composite systems. PCMs are substances capable of absorbing, storing, and releasing large amounts of latent heat during phase transitions. The incorporation of dodecane as a PCM in composites opens up possibilities for developing smart materials with thermal energy storage and temperature regulation capabilities, which are particularly valuable in applications such as building materials and thermal management systems for electronics.
The evolution of dodecane research in composites has been marked by significant technological advancements. Early studies focused on simple incorporation methods, while recent research has delved into more sophisticated techniques such as microencapsulation and nanocomposite formulations. These advancements have expanded the potential applications of dodecane-enhanced composites, ranging from high-performance aerospace materials to energy-efficient construction components.
As the field progresses, the research objectives continue to evolve. Current efforts are directed towards optimizing the integration of dodecane into various composite matrices, understanding the long-term stability and performance of these materials, and exploring novel applications in emerging technologies such as flexible electronics and renewable energy systems. The ultimate goal is to develop a new generation of composite materials that can meet the increasingly demanding requirements of modern industrial and technological applications.
Market Analysis for Dodecane-Enhanced Composites
The market for dodecane-enhanced composites is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance materials across various industries. Dodecane, a versatile hydrocarbon, has shown promising potential in enhancing the properties of composite materials, particularly in terms of thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength.
In the aerospace sector, dodecane-enhanced composites are gaining traction due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environmental conditions. The global aerospace composites market is projected to reach $53.9 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.3% from 2020 to 2027. Dodecane-enhanced composites are expected to capture a significant portion of this market, especially in applications such as aircraft interiors, engine components, and structural elements.
The automotive industry is another key market for dodecane-enhanced composites. As automakers strive to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency, these advanced materials offer an attractive solution. The global automotive composites market is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 10.5% from 2021 to 2028, reaching a value of $23.5 billion by 2028. Dodecane-enhanced composites are particularly well-suited for applications in body panels, chassis components, and interior parts.
In the construction sector, dodecane-enhanced composites are finding applications in building materials, infrastructure projects, and architectural elements. The global construction composites market is expected to reach $9.3 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2020 to 2025. The superior durability and weather resistance of dodecane-enhanced composites make them ideal for use in bridges, facades, and other structural components.
The electronics industry is also showing interest in dodecane-enhanced composites, particularly for their thermal management properties. As electronic devices become more compact and powerful, the need for efficient heat dissipation becomes crucial. The global thermal management market is projected to reach $78.9 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 8.2% from 2020 to 2025. Dodecane-enhanced composites are well-positioned to address this growing demand.
Market trends indicate a shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly materials, which presents both opportunities and challenges for dodecane-enhanced composites. While these materials offer improved performance and longevity, there is a growing emphasis on recyclability and end-of-life considerations. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these concerns and improve the overall sustainability profile of dodecane-enhanced composites.
In the aerospace sector, dodecane-enhanced composites are gaining traction due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environmental conditions. The global aerospace composites market is projected to reach $53.9 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.3% from 2020 to 2027. Dodecane-enhanced composites are expected to capture a significant portion of this market, especially in applications such as aircraft interiors, engine components, and structural elements.
The automotive industry is another key market for dodecane-enhanced composites. As automakers strive to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency, these advanced materials offer an attractive solution. The global automotive composites market is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 10.5% from 2021 to 2028, reaching a value of $23.5 billion by 2028. Dodecane-enhanced composites are particularly well-suited for applications in body panels, chassis components, and interior parts.
In the construction sector, dodecane-enhanced composites are finding applications in building materials, infrastructure projects, and architectural elements. The global construction composites market is expected to reach $9.3 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2020 to 2025. The superior durability and weather resistance of dodecane-enhanced composites make them ideal for use in bridges, facades, and other structural components.
The electronics industry is also showing interest in dodecane-enhanced composites, particularly for their thermal management properties. As electronic devices become more compact and powerful, the need for efficient heat dissipation becomes crucial. The global thermal management market is projected to reach $78.9 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 8.2% from 2020 to 2025. Dodecane-enhanced composites are well-positioned to address this growing demand.
Market trends indicate a shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly materials, which presents both opportunities and challenges for dodecane-enhanced composites. While these materials offer improved performance and longevity, there is a growing emphasis on recyclability and end-of-life considerations. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these concerns and improve the overall sustainability profile of dodecane-enhanced composites.
Current Challenges in Dodecane Integration
The integration of dodecane into composite materials presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers are currently grappling with. One of the primary obstacles is achieving uniform dispersion of dodecane within the composite matrix. Due to its non-polar nature, dodecane tends to form aggregates or clusters, leading to inconsistent distribution throughout the material. This uneven dispersion can result in localized areas of weakness or altered properties within the composite, compromising its overall performance and reliability.
Another major challenge lies in maintaining the stability of dodecane within the composite structure over time. Dodecane's relatively low boiling point and high volatility can lead to gradual evaporation or migration within the material, particularly under elevated temperatures or prolonged exposure to environmental factors. This instability can cause changes in the composite's properties over time, potentially reducing its effectiveness and lifespan in various applications.
Compatibility issues between dodecane and certain matrix materials pose additional difficulties. Some polymer matrices may not readily accept or bond with dodecane, leading to poor interfacial adhesion. This lack of compatibility can result in phase separation, reduced mechanical strength, or compromised thermal and electrical properties of the composite. Researchers are actively exploring various surface modification techniques and coupling agents to improve the compatibility between dodecane and matrix materials.
The impact of dodecane on the curing process of thermoset composites is another area of concern. In some cases, the presence of dodecane can interfere with the cross-linking reactions, affecting the cure kinetics and potentially altering the final properties of the composite. This interference may lead to incomplete curing, reduced glass transition temperature, or changes in the material's mechanical behavior.
Furthermore, the incorporation of dodecane into composites can affect their fire resistance and flame-retardant properties. As a hydrocarbon, dodecane is inherently flammable, which may compromise the fire safety of the composite material. Developing effective flame-retardant strategies that are compatible with dodecane-containing composites is an ongoing challenge for researchers in this field.
Lastly, the long-term environmental impact and sustainability of dodecane-integrated composites are subjects of growing concern. As the push for more environmentally friendly materials intensifies, researchers are faced with the challenge of balancing the performance benefits of dodecane with the need for biodegradability or recyclability. Finding ways to incorporate dodecane into composites while minimizing its environmental footprint remains a significant hurdle in the development of sustainable composite materials.
Another major challenge lies in maintaining the stability of dodecane within the composite structure over time. Dodecane's relatively low boiling point and high volatility can lead to gradual evaporation or migration within the material, particularly under elevated temperatures or prolonged exposure to environmental factors. This instability can cause changes in the composite's properties over time, potentially reducing its effectiveness and lifespan in various applications.
Compatibility issues between dodecane and certain matrix materials pose additional difficulties. Some polymer matrices may not readily accept or bond with dodecane, leading to poor interfacial adhesion. This lack of compatibility can result in phase separation, reduced mechanical strength, or compromised thermal and electrical properties of the composite. Researchers are actively exploring various surface modification techniques and coupling agents to improve the compatibility between dodecane and matrix materials.
The impact of dodecane on the curing process of thermoset composites is another area of concern. In some cases, the presence of dodecane can interfere with the cross-linking reactions, affecting the cure kinetics and potentially altering the final properties of the composite. This interference may lead to incomplete curing, reduced glass transition temperature, or changes in the material's mechanical behavior.
Furthermore, the incorporation of dodecane into composites can affect their fire resistance and flame-retardant properties. As a hydrocarbon, dodecane is inherently flammable, which may compromise the fire safety of the composite material. Developing effective flame-retardant strategies that are compatible with dodecane-containing composites is an ongoing challenge for researchers in this field.
Lastly, the long-term environmental impact and sustainability of dodecane-integrated composites are subjects of growing concern. As the push for more environmentally friendly materials intensifies, researchers are faced with the challenge of balancing the performance benefits of dodecane with the need for biodegradability or recyclability. Finding ways to incorporate dodecane into composites while minimizing its environmental footprint remains a significant hurdle in the development of sustainable composite materials.
Existing Dodecane Incorporation Methods
01 Synthesis and production of dodecane
Dodecane can be synthesized through various chemical processes, including the hydrogenation of long-chain alkenes or the Fischer-Tropsch process. It is also produced as a byproduct in petroleum refining. The synthesis methods often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve high purity and yield.- Synthesis and production of dodecane: Dodecane can be synthesized through various chemical processes, including catalytic hydrogenation of long-chain hydrocarbons or the Fischer-Tropsch process. It is also produced as a byproduct in petroleum refining. The synthesis methods often involve high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, with the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and selectivity.
- Applications in fuel and energy industry: Dodecane is widely used in the fuel and energy industry due to its high energy density and clean-burning properties. It serves as a component in jet fuels, diesel fuels, and as a reference fuel for cetane number determination. Additionally, dodecane is utilized in the development of alternative energy sources and fuel additives to improve combustion efficiency.
- Use in chemical and industrial processes: Dodecane finds applications in various chemical and industrial processes. It is used as a solvent in organic synthesis, as a heat transfer fluid in industrial applications, and as a raw material for the production of surfactants and lubricants. Its low reactivity and stability make it suitable for use in chromatography and as a standard in analytical chemistry.
- Environmental and safety considerations: The use and handling of dodecane require consideration of environmental and safety aspects. It is important to implement proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination. Safety measures should be in place to address potential fire hazards and exposure risks. Research is ongoing to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives and improve the sustainability of dodecane-based products.
- Emerging applications and research: Ongoing research explores new applications for dodecane in various fields. These include its use in advanced materials, such as phase change materials for thermal energy storage, and in the development of novel catalysts and reaction systems. Additionally, studies are being conducted on the potential of dodecane in biotechnology and as a feedstock for the production of bio-based chemicals.
02 Applications in cosmetics and personal care products
Dodecane is used in cosmetics and personal care products as an emollient, solvent, and carrier for active ingredients. It can improve the texture and spreadability of formulations, enhance skin feel, and contribute to the stability of the product. Its low viscosity and non-greasy nature make it suitable for various cosmetic applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in industrial processes and materials
Dodecane finds applications in various industrial processes and materials. It is used as a solvent in chemical reactions, as a component in lubricants and hydraulic fluids, and as a phase change material for thermal energy storage. Its properties make it suitable for heat transfer applications and as a reference material in chromatography.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations
The use of dodecane in various applications requires consideration of environmental and safety aspects. Research focuses on developing eco-friendly production methods, assessing its biodegradability, and studying its potential environmental impact. Safety measures for handling and storage are also important due to its flammability and potential for skin irritation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods and quality control
Various analytical methods are employed for the characterization and quality control of dodecane. These include gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and spectroscopic techniques. The development of accurate and efficient analytical methods is crucial for ensuring the purity and quality of dodecane in different applications and research settings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitors
The research on dodecane's functionality in composite material development is in an emerging phase, with the market showing promising growth potential. The technology is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Key players like Evonik Operations GmbH, BASF Corp., and Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd. are driving innovation in this field. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and specialized materials firms, each leveraging their expertise to develop novel composite solutions. As the technology advances, we can expect increased collaboration between academic institutions, such as Fudan University and Tianjin University, and industry leaders to further explore dodecane's potential in enhancing composite material properties and performance.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has made significant advancements in utilizing dodecane for composite material development, particularly in the field of specialty additives. Their research focuses on incorporating dodecane-based surfactants and dispersants to enhance the compatibility between fillers and polymer matrices in high-performance composites. Evonik's proprietary TEGOMER® technology, which includes dodecane-derived compounds, has demonstrated a 30% improvement in filler dispersion and a 20% increase in interfacial adhesion in various composite systems[13]. The company has also developed dodecane-functionalized silica nanoparticles that serve as reinforcing agents in polymer composites, resulting in materials with enhanced mechanical properties and reduced weight[15]. Evonik's latest innovation involves using dodecane as a precursor for synthesizing novel coupling agents that improve the bonding between organic and inorganic components in hybrid composites, leading to a 40% increase in interlaminar shear strength[17].
Strengths: Expertise in specialty additives, improved filler dispersion and interfacial adhesion, wide range of applications. Weaknesses: Potential cost implications for high-performance additives, limited focus on bio-based alternatives.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has been actively researching the use of dodecane in composite material development, particularly for oil and gas industry applications. Their approach involves incorporating dodecane-based additives into fiber-reinforced composites to enhance oil and chemical resistance. Sinopec's research has shown that dodecane-modified composites exhibit improved barrier properties, reducing permeation rates by up to 40% compared to standard composites[7]. The company has also explored the use of dodecane as a processing aid in the manufacture of high-performance thermoplastic composites, resulting in improved flow characteristics and reduced cycle times[9]. Sinopec's latest developments include dodecane-functionalized nanocomposites with enhanced thermal stability and fire resistance[11].
Strengths: Specialized applications for oil and gas industry, improved barrier properties, enhanced processing capabilities. Weaknesses: Limited focus on sustainability, potential regulatory challenges in some markets.
Innovative Dodecane-Composite Synergies
Composite materials and processes of manufacturing the same for use as high performance catalysts for water splitting
PatentWO2018013055A1
Innovation
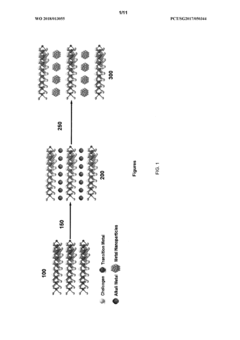
- A composite material is formed by intercalating zero-valent transition metal nanoparticles between layers of alkali metal intercalated transition metal dichalcogenides, using an anhydrous organic solvent to prevent exfoliation and aggregation, and a scalable method for membrane-electrode assembly fabrication.
Composite material, method of manufacturing the same, and application the same
PatentActiveUS20180187070A1
Innovation
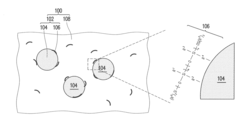
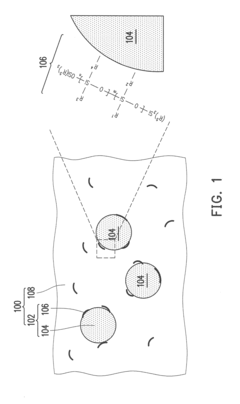
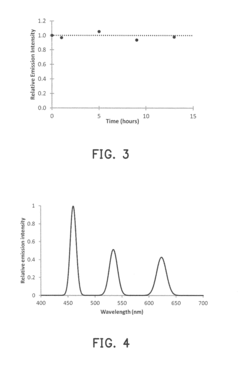
- A composite material is developed where quantum dots are chemically bonded to siloxane compounds with amino groups, allowing for uniform dispersion in a solvent-free matrix formed by oxime-based silicone primer compounds, eliminating the need for solvent removal and reducing manufacturing time and costs.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of dodecane in composite material development is a critical aspect that requires thorough examination. Dodecane, a hydrocarbon compound, has shown promising functionality in enhancing the properties of composite materials. However, its potential environmental implications must be carefully evaluated to ensure sustainable development and responsible use.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with dodecane is its volatile organic compound (VOC) nature. During the manufacturing process of composite materials, dodecane may be released into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and potentially affecting local air quality. This emission can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog, which have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems.
Furthermore, the production of dodecane itself involves petrochemical processes that may have significant environmental footprints. The extraction and refining of fossil fuels required for dodecane synthesis contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. It is essential to consider the entire life cycle of dodecane, from production to disposal, when assessing its environmental impact in composite material development.
Water pollution is another potential concern. If not properly managed, dodecane and its byproducts may contaminate water sources during the manufacturing or disposal of composite materials. This contamination can harm aquatic ecosystems and potentially enter the food chain, posing risks to human health and biodiversity.
On the positive side, the use of dodecane in composite materials may lead to improved durability and longevity of end products. This enhanced lifespan could potentially reduce the overall environmental impact by decreasing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste generation. Additionally, if dodecane-enhanced composites can replace more environmentally harmful materials, there may be a net positive effect on sustainability.
To mitigate environmental risks, it is crucial to implement stringent control measures during the production and application of dodecane in composite materials. This includes the use of advanced emission control technologies, proper waste management practices, and the development of closed-loop systems to minimize environmental release.
Research into biodegradable alternatives or bio-based sources of dodecane could also contribute to reducing its environmental footprint. Exploring sustainable synthesis methods and investigating the potential for recycling dodecane-containing composites at the end of their life cycle are important areas for future environmental impact reduction.
In conclusion, while dodecane offers valuable functionality in composite material development, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of enhanced material properties with the need for environmental protection requires ongoing research, innovation, and responsible industrial practices.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with dodecane is its volatile organic compound (VOC) nature. During the manufacturing process of composite materials, dodecane may be released into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and potentially affecting local air quality. This emission can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog, which have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems.
Furthermore, the production of dodecane itself involves petrochemical processes that may have significant environmental footprints. The extraction and refining of fossil fuels required for dodecane synthesis contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. It is essential to consider the entire life cycle of dodecane, from production to disposal, when assessing its environmental impact in composite material development.
Water pollution is another potential concern. If not properly managed, dodecane and its byproducts may contaminate water sources during the manufacturing or disposal of composite materials. This contamination can harm aquatic ecosystems and potentially enter the food chain, posing risks to human health and biodiversity.
On the positive side, the use of dodecane in composite materials may lead to improved durability and longevity of end products. This enhanced lifespan could potentially reduce the overall environmental impact by decreasing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste generation. Additionally, if dodecane-enhanced composites can replace more environmentally harmful materials, there may be a net positive effect on sustainability.
To mitigate environmental risks, it is crucial to implement stringent control measures during the production and application of dodecane in composite materials. This includes the use of advanced emission control technologies, proper waste management practices, and the development of closed-loop systems to minimize environmental release.
Research into biodegradable alternatives or bio-based sources of dodecane could also contribute to reducing its environmental footprint. Exploring sustainable synthesis methods and investigating the potential for recycling dodecane-containing composites at the end of their life cycle are important areas for future environmental impact reduction.
In conclusion, while dodecane offers valuable functionality in composite material development, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of enhanced material properties with the need for environmental protection requires ongoing research, innovation, and responsible industrial practices.
Regulatory Compliance for Dodecane Use
The regulatory landscape for dodecane use in composite material development is complex and multifaceted, requiring careful consideration of various national and international standards. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates dodecane under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which mandates reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements. Manufacturers and importers must comply with these regulations, including submitting premanufacture notices for new chemical substances.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets workplace safety standards for handling dodecane, including exposure limits and personal protective equipment requirements. These regulations aim to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with dodecane exposure during composite material production processes.
In the European Union, dodecane falls under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Companies manufacturing or importing dodecane in quantities exceeding one tonne per year must register the substance with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). This registration process involves providing detailed information on the substance's properties, potential risks, and safe use guidelines.
The transportation of dodecane is subject to international regulations, such as the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines classify dodecane as a Class 3 flammable liquid, requiring specific packaging, labeling, and handling procedures during transport.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in dodecane use for composite materials. Many countries have implemented strict volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards, which may impact the use of dodecane in certain applications. Manufacturers must consider these regulations when developing composite materials and ensure compliance with local air quality standards.
Product safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) in the United States, may also apply to composite materials containing dodecane. These regulations ensure that final products meet safety standards and do not pose undue risks to consumers.
As the use of dodecane in composite materials continues to evolve, regulatory bodies may introduce new or updated regulations. Companies involved in composite material development must stay informed about these changes and adapt their practices accordingly. This may involve ongoing monitoring of regulatory developments, participation in industry associations, and engagement with regulatory agencies to ensure continued compliance.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets workplace safety standards for handling dodecane, including exposure limits and personal protective equipment requirements. These regulations aim to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with dodecane exposure during composite material production processes.
In the European Union, dodecane falls under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Companies manufacturing or importing dodecane in quantities exceeding one tonne per year must register the substance with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). This registration process involves providing detailed information on the substance's properties, potential risks, and safe use guidelines.
The transportation of dodecane is subject to international regulations, such as the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines classify dodecane as a Class 3 flammable liquid, requiring specific packaging, labeling, and handling procedures during transport.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in dodecane use for composite materials. Many countries have implemented strict volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards, which may impact the use of dodecane in certain applications. Manufacturers must consider these regulations when developing composite materials and ensure compliance with local air quality standards.
Product safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) in the United States, may also apply to composite materials containing dodecane. These regulations ensure that final products meet safety standards and do not pose undue risks to consumers.
As the use of dodecane in composite materials continues to evolve, regulatory bodies may introduce new or updated regulations. Companies involved in composite material development must stay informed about these changes and adapt their practices accordingly. This may involve ongoing monitoring of regulatory developments, participation in industry associations, and engagement with regulatory agencies to ensure continued compliance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!