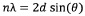Luminol in Leading Innovative Detection Mechanisms
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luminol Detection Background and Objectives
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has been a cornerstone in forensic science and biochemical research for decades. Its ability to emit light when oxidized has made it an invaluable tool in the detection of blood and other biological substances. The history of luminol dates back to 1928 when it was first synthesized by German chemist H. O. Albrecht. However, its potential in forensic applications wasn't fully realized until the 1930s when Walter Specht discovered its reactivity with hemoglobin.
The evolution of luminol-based detection techniques has been driven by the increasing demands for more sensitive, specific, and non-destructive methods in crime scene investigation and medical diagnostics. Traditional luminol tests, while effective, have faced challenges such as false positives and the potential destruction of DNA evidence. These limitations have spurred ongoing research to enhance the specificity and sensitivity of luminol-based detection mechanisms.
In recent years, the field has witnessed significant advancements, particularly in the development of novel formulations and application methods. Researchers have explored modifications to the luminol molecule, investigated alternative oxidizing agents, and experimented with various catalysts to improve the overall performance of luminol-based detection systems. These efforts aim to address the longstanding issues of interference from common household chemicals and the need for more robust and reliable detection in complex environmental conditions.
The objectives of current research on luminol in leading innovative detection mechanisms are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a focus on enhancing the sensitivity of luminol reactions to detect trace amounts of blood and other biological materials. This includes efforts to amplify the chemiluminescent signal and reduce background noise, thereby improving the detection threshold.
Another key objective is to increase the specificity of luminol-based tests. This involves developing methods to differentiate between human blood and animal blood, as well as distinguishing blood from other substances that may trigger a false positive reaction. Researchers are also working on creating luminol formulations that are less likely to interfere with subsequent DNA analysis, addressing a critical concern in forensic investigations.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in expanding the application of luminol beyond its traditional use in crime scene investigation. Scientists are exploring its potential in medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and even in the detection of explosives. These new frontiers present exciting opportunities for innovation and cross-disciplinary collaboration, driving the field towards more versatile and sophisticated detection mechanisms.
The evolution of luminol-based detection techniques has been driven by the increasing demands for more sensitive, specific, and non-destructive methods in crime scene investigation and medical diagnostics. Traditional luminol tests, while effective, have faced challenges such as false positives and the potential destruction of DNA evidence. These limitations have spurred ongoing research to enhance the specificity and sensitivity of luminol-based detection mechanisms.
In recent years, the field has witnessed significant advancements, particularly in the development of novel formulations and application methods. Researchers have explored modifications to the luminol molecule, investigated alternative oxidizing agents, and experimented with various catalysts to improve the overall performance of luminol-based detection systems. These efforts aim to address the longstanding issues of interference from common household chemicals and the need for more robust and reliable detection in complex environmental conditions.
The objectives of current research on luminol in leading innovative detection mechanisms are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a focus on enhancing the sensitivity of luminol reactions to detect trace amounts of blood and other biological materials. This includes efforts to amplify the chemiluminescent signal and reduce background noise, thereby improving the detection threshold.
Another key objective is to increase the specificity of luminol-based tests. This involves developing methods to differentiate between human blood and animal blood, as well as distinguishing blood from other substances that may trigger a false positive reaction. Researchers are also working on creating luminol formulations that are less likely to interfere with subsequent DNA analysis, addressing a critical concern in forensic investigations.
Furthermore, there is a growing interest in expanding the application of luminol beyond its traditional use in crime scene investigation. Scientists are exploring its potential in medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and even in the detection of explosives. These new frontiers present exciting opportunities for innovation and cross-disciplinary collaboration, driving the field towards more versatile and sophisticated detection mechanisms.
Market Analysis for Luminol-based Detection
The market for luminol-based detection technologies has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand in forensic science, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring. Luminol, a chemical compound that exhibits chemiluminescence when oxidized, has become a cornerstone in various detection mechanisms due to its high sensitivity and versatility.
In the forensic science sector, luminol-based detection methods have become indispensable for crime scene investigations, particularly in the detection of trace amounts of blood. The global forensic technologies market, which heavily relies on luminol-based products, is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing many other scientific instrument markets.
The medical diagnostics field has also embraced luminol-based detection techniques, especially in immunoassays and molecular diagnostics. These applications have seen rapid adoption in clinical laboratories worldwide, contributing to the overall market expansion. The ability of luminol-based systems to provide highly sensitive and specific results has made them invaluable in early disease detection and monitoring.
Environmental monitoring represents another growing market segment for luminol-based detection. As concerns about water quality and environmental contamination increase globally, there is a rising demand for sensitive and reliable detection methods. Luminol-based systems have proven effective in detecting various pollutants and heavy metals in water sources, leading to increased adoption by environmental agencies and industrial facilities.
The market landscape for luminol-based detection is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Major scientific instrument manufacturers have invested heavily in developing advanced luminol-based detection systems, while specialized companies focus on niche applications and novel formulations to enhance sensitivity and specificity.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for luminol-based detection technologies, owing to their advanced forensic and healthcare infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing investments in forensic science capabilities and the expansion of healthcare services.
Looking ahead, the market for luminol-based detection is poised for continued growth. Technological advancements, such as the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to improve data analysis and interpretation, are expected to further enhance the capabilities of luminol-based systems. Additionally, the development of portable and field-deployable luminol detection devices is opening up new market opportunities in on-site forensic investigations and environmental monitoring.
In the forensic science sector, luminol-based detection methods have become indispensable for crime scene investigations, particularly in the detection of trace amounts of blood. The global forensic technologies market, which heavily relies on luminol-based products, is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing many other scientific instrument markets.
The medical diagnostics field has also embraced luminol-based detection techniques, especially in immunoassays and molecular diagnostics. These applications have seen rapid adoption in clinical laboratories worldwide, contributing to the overall market expansion. The ability of luminol-based systems to provide highly sensitive and specific results has made them invaluable in early disease detection and monitoring.
Environmental monitoring represents another growing market segment for luminol-based detection. As concerns about water quality and environmental contamination increase globally, there is a rising demand for sensitive and reliable detection methods. Luminol-based systems have proven effective in detecting various pollutants and heavy metals in water sources, leading to increased adoption by environmental agencies and industrial facilities.
The market landscape for luminol-based detection is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Major scientific instrument manufacturers have invested heavily in developing advanced luminol-based detection systems, while specialized companies focus on niche applications and novel formulations to enhance sensitivity and specificity.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for luminol-based detection technologies, owing to their advanced forensic and healthcare infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing investments in forensic science capabilities and the expansion of healthcare services.
Looking ahead, the market for luminol-based detection is poised for continued growth. Technological advancements, such as the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to improve data analysis and interpretation, are expected to further enhance the capabilities of luminol-based systems. Additionally, the development of portable and field-deployable luminol detection devices is opening up new market opportunities in on-site forensic investigations and environmental monitoring.
Current Challenges in Luminol Detection Mechanisms
Despite the widespread use of luminol in forensic science and other fields, several challenges persist in its detection mechanisms, limiting its effectiveness and reliability. One of the primary issues is the lack of specificity in luminol reactions. While luminol is highly sensitive to blood, it can also react with other substances such as certain metals, plant peroxidases, and cleaning agents. This cross-reactivity can lead to false positives, potentially compromising the integrity of forensic investigations.
Another significant challenge is the relatively short duration of the luminol chemiluminescence reaction. The light emission typically lasts only for a few seconds, making it difficult to capture and analyze the results, especially in complex crime scenes. This brevity of the reaction necessitates rapid and precise detection methods, which can be challenging to implement in field conditions.
The sensitivity of luminol to environmental factors also poses a considerable challenge. Factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of contaminants can significantly affect the intensity and duration of the luminescence. This variability makes it difficult to standardize detection protocols across different environments and conditions, potentially leading to inconsistent results.
Furthermore, the potential degradation of DNA evidence due to the application of luminol solutions is a concern in forensic investigations. While luminol itself does not destroy DNA, the water-based solution and the chemicals used in the reaction can potentially dilute or compromise genetic material, complicating subsequent DNA analysis.
The quantification of blood using luminol-based techniques remains challenging. While luminol can detect trace amounts of blood, accurately determining the quantity of blood present based on the intensity of luminescence is complex and often unreliable. This limitation hinders the ability to draw conclusive inferences about the nature and severity of injuries in forensic cases.
Lastly, the development of more sensitive and specific alternatives to luminol has been slow. While research into new chemiluminescent compounds and detection methods is ongoing, finding a solution that matches luminol's sensitivity while overcoming its limitations has proven difficult. This slow progress in innovation has meant that despite its drawbacks, luminol remains a primary tool in many forensic applications, highlighting the need for continued research and development in this field.
Another significant challenge is the relatively short duration of the luminol chemiluminescence reaction. The light emission typically lasts only for a few seconds, making it difficult to capture and analyze the results, especially in complex crime scenes. This brevity of the reaction necessitates rapid and precise detection methods, which can be challenging to implement in field conditions.
The sensitivity of luminol to environmental factors also poses a considerable challenge. Factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of contaminants can significantly affect the intensity and duration of the luminescence. This variability makes it difficult to standardize detection protocols across different environments and conditions, potentially leading to inconsistent results.
Furthermore, the potential degradation of DNA evidence due to the application of luminol solutions is a concern in forensic investigations. While luminol itself does not destroy DNA, the water-based solution and the chemicals used in the reaction can potentially dilute or compromise genetic material, complicating subsequent DNA analysis.
The quantification of blood using luminol-based techniques remains challenging. While luminol can detect trace amounts of blood, accurately determining the quantity of blood present based on the intensity of luminescence is complex and often unreliable. This limitation hinders the ability to draw conclusive inferences about the nature and severity of injuries in forensic cases.
Lastly, the development of more sensitive and specific alternatives to luminol has been slow. While research into new chemiluminescent compounds and detection methods is ongoing, finding a solution that matches luminol's sensitivity while overcoming its limitations has proven difficult. This slow progress in innovation has meant that despite its drawbacks, luminol remains a primary tool in many forensic applications, highlighting the need for continued research and development in this field.
Existing Luminol Detection Solutions
01 Luminol in chemiluminescence detection
Luminol is widely used in chemiluminescence detection methods for various applications. It produces light when oxidized, making it useful for detecting trace amounts of blood, metal ions, or other substances in forensic science, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics.- Luminol in forensic applications: Luminol is widely used in forensic science for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. When mixed with an oxidizing agent, it produces a blue chemiluminescence in the presence of iron from hemoglobin. This reaction is highly sensitive and can detect blood even after cleaning attempts.
- Luminol-based detection systems: Various detection systems incorporate luminol for its chemiluminescent properties. These systems are used in environmental monitoring, food safety testing, and medical diagnostics. The high sensitivity of luminol allows for the detection of minute quantities of target substances.
- Luminol derivatives and modifications: Research focuses on developing luminol derivatives and modifications to enhance its properties. These modifications aim to improve sensitivity, selectivity, and stability of the luminol reaction. Some derivatives offer longer-lasting luminescence or altered emission spectra for specific applications.
- Luminol in analytical chemistry: Luminol is extensively used in analytical chemistry for quantitative and qualitative analysis. It serves as a reagent in flow injection analysis, high-performance liquid chromatography, and other analytical techniques. The chemiluminescent reaction of luminol allows for highly sensitive detection of various analytes.
- Luminol in biomedical research: In biomedical research, luminol is used to study cellular processes and oxidative stress. It can detect reactive oxygen species and serve as a probe for investigating immune cell function. Luminol-based assays are employed in studying inflammation, cancer, and other diseases related to oxidative processes.
02 Luminol-based biosensors and analytical devices
Luminol is incorporated into biosensors and analytical devices for sensitive and specific detection of target analytes. These devices often combine luminol with other reagents or enzymes to enhance sensitivity and selectivity in various fields such as clinical diagnostics, food safety, and environmental monitoring.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luminol in imaging and visualization techniques
Luminol is utilized in imaging and visualization techniques, particularly in forensic science and biomedical research. Its chemiluminescent properties allow for the detection and visualization of latent blood traces, cellular processes, or specific molecules in complex biological samples.Expand Specific Solutions04 Luminol derivatives and modifications
Research focuses on developing luminol derivatives and modifications to enhance its properties or tailor it for specific applications. These modifications may improve sensitivity, stability, or compatibility with different detection systems, expanding the range of luminol's applications in various scientific fields.Expand Specific Solutions05 Luminol in environmental and industrial applications
Luminol finds applications in environmental monitoring and industrial processes. It is used for detecting pollutants, monitoring water quality, or as an indicator in industrial chemical reactions. The chemiluminescent properties of luminol make it valuable for real-time monitoring and rapid detection in these fields.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Luminol Research and Applications
The research on Luminol in leading innovative detection mechanisms is at a critical juncture, with the market showing significant growth potential. The technology is in a transitional phase, moving from early development to more widespread adoption. Market size is expanding as applications in forensics, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring gain traction. Technological maturity varies among key players, with companies like Life Technologies Corp., Olympus Corp., and FUJIFILM Corp. leading in innovation and product development. Smaller firms and research institutions, such as Alverix, Inc. and the Naval Research Laboratory, are also making notable contributions, driving competition and advancing the field.
Alverix, Inc.
Technical Solution: Alverix has developed innovative luminol-based detection mechanisms for point-of-care diagnostics. Their technology utilizes enhanced chemiluminescence reactions with luminol to achieve high sensitivity in rapid tests. The company's approach involves microfluidic chips with optimized reagent formulations to amplify the luminol signal[1]. They have also integrated advanced photodetectors and signal processing algorithms to improve the detection limit and quantification accuracy of luminol-based assays[3]. Alverix's platform enables multiplexed testing for various biomarkers using a single sample, with results available in minutes[5].
Strengths: High sensitivity, rapid results, multiplexing capability. Weaknesses: May require specialized reader devices, potential for interference in complex samples.
Olympus Corp.
Technical Solution: Olympus has incorporated luminol-based chemiluminescence detection into their advanced microscopy and imaging systems. Their approach combines high-sensitivity cameras with microfluidic sample handling to enable real-time visualization of luminol reactions at the cellular level[2]. The company has developed proprietary image processing algorithms to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio and spatial resolution of luminol-generated light emissions[4]. Olympus's technology allows for quantitative analysis of enzyme activity and reactive oxygen species in live cells using luminol probes[6]. They have also explored applications in endoscopic imaging for early cancer detection using targeted luminol derivatives[8].
Strengths: High-resolution imaging, quantitative analysis capabilities. Weaknesses: Expensive equipment, requires expertise to operate and interpret results.
Core Innovations in Luminol Chemistry
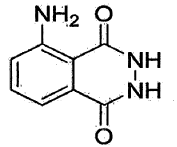
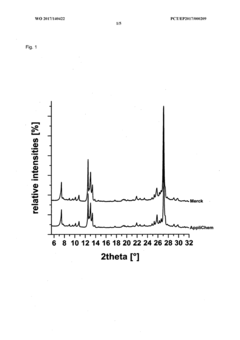
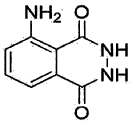
Method for producing a crystalline form of 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione
PatentWO2017140422A1
Innovation
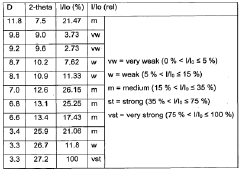
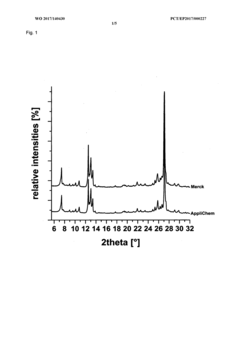
- A method involving dissolving 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione in a refluxing ethanol-water solution, cooling, separating the precipitated crystals, and drying to produce a phase-pure crystalline form of luminol, which can be resuspended and washed for enhanced purity.
Crystalline form of 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione
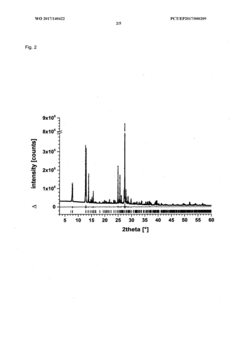
PatentWO2017140430A1
Innovation
- A new crystalline form of luminol (Form II) is produced using a simpler method involving a stirred solution of Na-luminolate in demineralized water, with hydrochloric acid addition, filtration, washing, and drying, which results in phase-pure crystals with improved crystallinity and stability.
Regulatory Framework for Forensic Technologies
The regulatory framework for forensic technologies plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability, admissibility, and ethical use of scientific evidence in criminal investigations and legal proceedings. In the context of luminol and innovative detection mechanisms, this framework encompasses a complex interplay of legal, scientific, and ethical considerations.
At the federal level in the United States, the Federal Rules of Evidence govern the admissibility of scientific evidence in court. The landmark Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals case established key criteria for evaluating the reliability of scientific evidence, including testability, peer review, error rates, and general acceptance within the scientific community. These standards directly impact the use of luminol and other forensic technologies in criminal investigations.
State-level regulations further refine the application of forensic technologies. Many states have adopted variations of the Daubert standard or maintain the older Frye standard, which focuses on general acceptance within the relevant scientific community. These differing standards can lead to variations in the admissibility of luminol-based evidence across jurisdictions.
Accreditation and certification requirements for forensic laboratories and technicians form another critical component of the regulatory framework. Organizations such as the American Society of Crime Laboratory Directors/Laboratory Accreditation Board (ASCLD/LAB) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide guidelines and standards for forensic laboratories. These standards ensure that luminol and other detection technologies are used in accordance with established protocols and quality control measures.
Ethical considerations are also integral to the regulatory framework. Guidelines from professional organizations like the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS) address issues such as maintaining chain of custody, avoiding contamination, and ensuring the proper interpretation of results. These ethical standards are particularly relevant to luminol testing, given its potential to alter crime scene evidence.
Privacy regulations, such as those outlined in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), may also impact the use of forensic technologies when dealing with biological evidence. Balancing the need for thorough investigation with individual privacy rights presents ongoing challenges in the regulatory landscape.
As forensic technologies continue to advance, regulatory frameworks must evolve to keep pace. The development of more sensitive and specific detection methods based on luminol and related compounds necessitates ongoing review and updating of regulations to ensure their appropriate use and interpretation in legal contexts.
At the federal level in the United States, the Federal Rules of Evidence govern the admissibility of scientific evidence in court. The landmark Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals case established key criteria for evaluating the reliability of scientific evidence, including testability, peer review, error rates, and general acceptance within the scientific community. These standards directly impact the use of luminol and other forensic technologies in criminal investigations.
State-level regulations further refine the application of forensic technologies. Many states have adopted variations of the Daubert standard or maintain the older Frye standard, which focuses on general acceptance within the relevant scientific community. These differing standards can lead to variations in the admissibility of luminol-based evidence across jurisdictions.
Accreditation and certification requirements for forensic laboratories and technicians form another critical component of the regulatory framework. Organizations such as the American Society of Crime Laboratory Directors/Laboratory Accreditation Board (ASCLD/LAB) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide guidelines and standards for forensic laboratories. These standards ensure that luminol and other detection technologies are used in accordance with established protocols and quality control measures.
Ethical considerations are also integral to the regulatory framework. Guidelines from professional organizations like the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS) address issues such as maintaining chain of custody, avoiding contamination, and ensuring the proper interpretation of results. These ethical standards are particularly relevant to luminol testing, given its potential to alter crime scene evidence.
Privacy regulations, such as those outlined in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), may also impact the use of forensic technologies when dealing with biological evidence. Balancing the need for thorough investigation with individual privacy rights presents ongoing challenges in the regulatory landscape.
As forensic technologies continue to advance, regulatory frameworks must evolve to keep pace. The development of more sensitive and specific detection methods based on luminol and related compounds necessitates ongoing review and updating of regulations to ensure their appropriate use and interpretation in legal contexts.
Environmental Impact of Luminol Usage
The environmental impact of luminol usage in innovative detection mechanisms is a crucial aspect to consider in the development and application of this technology. Luminol, a chemical compound widely used in forensic science and crime scene investigations, has both positive and negative implications for the environment.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with luminol usage is its potential to contaminate soil and water systems. When luminol is applied to surfaces during crime scene investigations, excess solution can seep into the ground or be washed away by rain, potentially entering nearby water bodies. This contamination may affect aquatic ecosystems and potentially harm marine life.
However, it is important to note that the concentrations of luminol typically used in forensic applications are relatively low, which may mitigate some of the environmental risks. Additionally, the compound is known to degrade relatively quickly when exposed to sunlight and air, further reducing its long-term environmental impact.
The production of luminol and its associated chemicals also raises environmental concerns. The manufacturing process involves the use of various chemicals and solvents, which may contribute to industrial pollution if not properly managed. Responsible production practices and adherence to environmental regulations are essential to minimize these impacts.
On the positive side, the use of luminol in detection mechanisms can indirectly benefit the environment by aiding in the investigation and prevention of environmental crimes. For instance, luminol can be used to detect blood traces in cases of illegal wildlife poaching or to identify contamination sources in environmental pollution incidents.
Research into more environmentally friendly alternatives to luminol is ongoing. Scientists are exploring bio-based luminescent compounds and developing more sustainable production methods. These efforts aim to maintain the effectiveness of luminol-based detection while reducing its environmental footprint.
The disposal of luminol-containing waste is another area of environmental concern. Proper protocols for the handling and disposal of luminol solutions and contaminated materials are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Training forensic personnel in environmentally responsible practices is essential for minimizing the ecological impact of luminol usage.
In conclusion, while luminol plays a vital role in innovative detection mechanisms, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of its use in forensic science with the need for environmental protection requires ongoing research, responsible practices, and the development of more sustainable alternatives.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with luminol usage is its potential to contaminate soil and water systems. When luminol is applied to surfaces during crime scene investigations, excess solution can seep into the ground or be washed away by rain, potentially entering nearby water bodies. This contamination may affect aquatic ecosystems and potentially harm marine life.
However, it is important to note that the concentrations of luminol typically used in forensic applications are relatively low, which may mitigate some of the environmental risks. Additionally, the compound is known to degrade relatively quickly when exposed to sunlight and air, further reducing its long-term environmental impact.
The production of luminol and its associated chemicals also raises environmental concerns. The manufacturing process involves the use of various chemicals and solvents, which may contribute to industrial pollution if not properly managed. Responsible production practices and adherence to environmental regulations are essential to minimize these impacts.
On the positive side, the use of luminol in detection mechanisms can indirectly benefit the environment by aiding in the investigation and prevention of environmental crimes. For instance, luminol can be used to detect blood traces in cases of illegal wildlife poaching or to identify contamination sources in environmental pollution incidents.
Research into more environmentally friendly alternatives to luminol is ongoing. Scientists are exploring bio-based luminescent compounds and developing more sustainable production methods. These efforts aim to maintain the effectiveness of luminol-based detection while reducing its environmental footprint.
The disposal of luminol-containing waste is another area of environmental concern. Proper protocols for the handling and disposal of luminol solutions and contaminated materials are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Training forensic personnel in environmentally responsible practices is essential for minimizing the ecological impact of luminol usage.
In conclusion, while luminol plays a vital role in innovative detection mechanisms, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of its use in forensic science with the need for environmental protection requires ongoing research, responsible practices, and the development of more sustainable alternatives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!