Solenoid Valve Integration in Robotic Automation for Assembly Lines
JUL 23, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Solenoid Valve Robotics Background and Objectives
Solenoid valves have played a crucial role in industrial automation for decades, serving as essential components in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. As manufacturing processes evolve towards greater automation and efficiency, the integration of solenoid valves with robotic systems has become a focal point of technological advancement. This convergence aims to enhance the precision, speed, and flexibility of assembly line operations.
The historical development of solenoid valve technology can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant improvements in design and materials occurring over the years. Initially used in simple on-off control applications, solenoid valves have since evolved to accommodate more complex fluid control scenarios. The advent of robotics in manufacturing during the 1960s and 1970s set the stage for the eventual integration of these two technologies.
In recent years, the push towards Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing has accelerated the need for more sophisticated automation solutions. The integration of solenoid valves with robotic systems represents a critical step in this direction, offering the potential for improved process control, reduced downtime, and enhanced overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
The primary objective of research in this field is to develop seamless integration methodologies that optimize the synergy between solenoid valves and robotic systems. This involves addressing challenges such as response time synchronization, precision control, and system reliability. Additionally, researchers aim to explore novel valve designs that are specifically tailored for robotic applications, considering factors like size, weight, and energy efficiency.
Another key goal is to leverage advanced sensing and communication technologies to create intelligent valve-robot systems. This includes the implementation of predictive maintenance strategies, real-time performance monitoring, and adaptive control algorithms. By incorporating these features, manufacturers can anticipate potential issues, minimize unplanned downtime, and maximize production efficiency.
Furthermore, the research seeks to expand the application scope of solenoid valve-integrated robotic systems beyond traditional assembly lines. Potential areas of exploration include flexible manufacturing cells, collaborative robotics, and even emerging fields like additive manufacturing. This broadened perspective aims to unlock new possibilities for automation across various industries.
As environmental concerns gain prominence, an additional objective is to develop eco-friendly solutions that reduce energy consumption and minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. This involves investigating alternative materials, optimizing valve designs for energy efficiency, and exploring ways to reduce fluid waste in pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
The historical development of solenoid valve technology can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant improvements in design and materials occurring over the years. Initially used in simple on-off control applications, solenoid valves have since evolved to accommodate more complex fluid control scenarios. The advent of robotics in manufacturing during the 1960s and 1970s set the stage for the eventual integration of these two technologies.
In recent years, the push towards Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing has accelerated the need for more sophisticated automation solutions. The integration of solenoid valves with robotic systems represents a critical step in this direction, offering the potential for improved process control, reduced downtime, and enhanced overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
The primary objective of research in this field is to develop seamless integration methodologies that optimize the synergy between solenoid valves and robotic systems. This involves addressing challenges such as response time synchronization, precision control, and system reliability. Additionally, researchers aim to explore novel valve designs that are specifically tailored for robotic applications, considering factors like size, weight, and energy efficiency.
Another key goal is to leverage advanced sensing and communication technologies to create intelligent valve-robot systems. This includes the implementation of predictive maintenance strategies, real-time performance monitoring, and adaptive control algorithms. By incorporating these features, manufacturers can anticipate potential issues, minimize unplanned downtime, and maximize production efficiency.
Furthermore, the research seeks to expand the application scope of solenoid valve-integrated robotic systems beyond traditional assembly lines. Potential areas of exploration include flexible manufacturing cells, collaborative robotics, and even emerging fields like additive manufacturing. This broadened perspective aims to unlock new possibilities for automation across various industries.
As environmental concerns gain prominence, an additional objective is to develop eco-friendly solutions that reduce energy consumption and minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. This involves investigating alternative materials, optimizing valve designs for energy efficiency, and exploring ways to reduce fluid waste in pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
Market Demand Analysis for Automated Assembly
The global market for automated assembly systems in manufacturing is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness in production processes. The integration of solenoid valves in robotic automation for assembly lines represents a significant segment of this market, as these components play a crucial role in controlling fluid and gas flow within automated systems.
Recent market research indicates that the automated assembly equipment market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by the automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries, which are increasingly adopting advanced automation technologies to streamline their production processes and maintain competitive advantages.
The demand for solenoid valve integration in robotic automation is particularly strong in the automotive sector, where assembly lines require precise control of pneumatic and hydraulic systems. As automakers strive to increase production efficiency and reduce costs, the adoption of advanced robotic systems with integrated solenoid valves is becoming more prevalent. This trend is further accelerated by the shift towards electric vehicle production, which requires new assembly line configurations and more sophisticated automation solutions.
In the electronics industry, the miniaturization of components and the need for high-precision assembly have led to increased demand for robotic automation systems with integrated solenoid valves. These systems enable manufacturers to achieve the level of accuracy and repeatability required for assembling complex electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology.
The aerospace industry is another key driver of market demand for automated assembly systems incorporating solenoid valves. As aircraft manufacturers seek to increase production rates and improve quality control, they are investing in advanced robotic systems that can handle complex assembly tasks with high precision. The integration of solenoid valves in these systems allows for precise control of pneumatic tools and positioning equipment, essential for assembling aircraft components.
Market analysis also reveals a growing trend towards the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, which is further boosting the demand for smart, connected automated assembly systems. Solenoid valves equipped with sensors and communication capabilities are becoming increasingly important in this context, as they enable real-time monitoring and control of assembly processes, predictive maintenance, and data-driven optimization of production lines.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for automated assembly systems, including those with integrated solenoid valves. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization in countries like China and India, as well as the presence of major electronics and automotive manufacturing hubs in the region. North America and Europe are also significant markets, driven by the need for technological upgrades in existing manufacturing facilities and the push towards reshoring of production capabilities.
Recent market research indicates that the automated assembly equipment market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by the automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries, which are increasingly adopting advanced automation technologies to streamline their production processes and maintain competitive advantages.
The demand for solenoid valve integration in robotic automation is particularly strong in the automotive sector, where assembly lines require precise control of pneumatic and hydraulic systems. As automakers strive to increase production efficiency and reduce costs, the adoption of advanced robotic systems with integrated solenoid valves is becoming more prevalent. This trend is further accelerated by the shift towards electric vehicle production, which requires new assembly line configurations and more sophisticated automation solutions.
In the electronics industry, the miniaturization of components and the need for high-precision assembly have led to increased demand for robotic automation systems with integrated solenoid valves. These systems enable manufacturers to achieve the level of accuracy and repeatability required for assembling complex electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology.
The aerospace industry is another key driver of market demand for automated assembly systems incorporating solenoid valves. As aircraft manufacturers seek to increase production rates and improve quality control, they are investing in advanced robotic systems that can handle complex assembly tasks with high precision. The integration of solenoid valves in these systems allows for precise control of pneumatic tools and positioning equipment, essential for assembling aircraft components.
Market analysis also reveals a growing trend towards the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, which is further boosting the demand for smart, connected automated assembly systems. Solenoid valves equipped with sensors and communication capabilities are becoming increasingly important in this context, as they enable real-time monitoring and control of assembly processes, predictive maintenance, and data-driven optimization of production lines.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for automated assembly systems, including those with integrated solenoid valves. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization in countries like China and India, as well as the presence of major electronics and automotive manufacturing hubs in the region. North America and Europe are also significant markets, driven by the need for technological upgrades in existing manufacturing facilities and the push towards reshoring of production capabilities.
Current Challenges in Solenoid Valve Integration
The integration of solenoid valves in robotic automation for assembly lines presents several significant challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the precise control and synchronization of multiple solenoid valves within complex robotic systems. As assembly lines become increasingly sophisticated, the demand for precise timing and coordination between various components grows, putting pressure on solenoid valve integration to meet these exacting requirements.
Another challenge lies in the miniaturization of solenoid valves to accommodate the compact designs of modern robotic systems. As robots become smaller and more agile, the need for equally compact valve solutions becomes crucial. However, reducing the size of solenoid valves while maintaining their performance and reliability is a complex engineering task that requires innovative approaches in materials science and design.
The durability and longevity of solenoid valves in high-speed, high-cycle assembly line environments pose another significant challenge. The constant actuation and exposure to various environmental factors can lead to wear and tear, potentially resulting in system downtime and reduced productivity. Developing solenoid valves that can withstand these demanding conditions without compromising on performance or requiring frequent maintenance is a key area of focus for manufacturers and researchers alike.
Energy efficiency is another critical concern in solenoid valve integration. As industrial automation strives for greater sustainability, there is a growing need for solenoid valves that consume less power while maintaining their operational effectiveness. This challenge is compounded by the fact that many assembly lines operate continuously, making even small improvements in energy consumption significant over time.
The integration of smart technologies and IoT capabilities into solenoid valves presents both opportunities and challenges. While these advancements can greatly enhance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and overall system efficiency, they also introduce complexities in terms of data management, cybersecurity, and interoperability with existing systems. Ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between smart solenoid valves and other components of the robotic automation system is a significant hurdle that needs to be overcome.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of solenoid valve integration remains a persistent challenge. As assembly lines strive for greater automation and precision, the demand for high-performance solenoid valves increases. However, balancing the cost of these advanced components with the overall budget constraints of assembly line projects requires careful consideration and innovative solutions. Manufacturers must find ways to produce high-quality, reliable solenoid valves at competitive prices to make their integration economically viable for a wide range of applications in robotic automation.
Another challenge lies in the miniaturization of solenoid valves to accommodate the compact designs of modern robotic systems. As robots become smaller and more agile, the need for equally compact valve solutions becomes crucial. However, reducing the size of solenoid valves while maintaining their performance and reliability is a complex engineering task that requires innovative approaches in materials science and design.
The durability and longevity of solenoid valves in high-speed, high-cycle assembly line environments pose another significant challenge. The constant actuation and exposure to various environmental factors can lead to wear and tear, potentially resulting in system downtime and reduced productivity. Developing solenoid valves that can withstand these demanding conditions without compromising on performance or requiring frequent maintenance is a key area of focus for manufacturers and researchers alike.
Energy efficiency is another critical concern in solenoid valve integration. As industrial automation strives for greater sustainability, there is a growing need for solenoid valves that consume less power while maintaining their operational effectiveness. This challenge is compounded by the fact that many assembly lines operate continuously, making even small improvements in energy consumption significant over time.
The integration of smart technologies and IoT capabilities into solenoid valves presents both opportunities and challenges. While these advancements can greatly enhance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and overall system efficiency, they also introduce complexities in terms of data management, cybersecurity, and interoperability with existing systems. Ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between smart solenoid valves and other components of the robotic automation system is a significant hurdle that needs to be overcome.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of solenoid valve integration remains a persistent challenge. As assembly lines strive for greater automation and precision, the demand for high-performance solenoid valves increases. However, balancing the cost of these advanced components with the overall budget constraints of assembly line projects requires careful consideration and innovative solutions. Manufacturers must find ways to produce high-quality, reliable solenoid valves at competitive prices to make their integration economically viable for a wide range of applications in robotic automation.
Existing Solenoid Valve Integration Solutions
01 Solenoid valve design improvements
Various design improvements have been made to solenoid valves to enhance their performance and reliability. These include optimizing the valve body structure, improving the plunger mechanism, and refining the electromagnetic coil design. Such enhancements can lead to better flow control, reduced power consumption, and increased durability of the valve.- Solenoid valve design improvements: Various design improvements have been made to solenoid valves to enhance their performance and reliability. These include optimizing the valve body structure, improving the plunger mechanism, and refining the electromagnetic coil design. Such enhancements can lead to better flow control, reduced power consumption, and increased durability of the valve.
- Control systems for solenoid valves: Advanced control systems have been developed for solenoid valves to improve their precision and responsiveness. These systems may incorporate electronic controllers, sensors, and feedback mechanisms to regulate valve operation. Such control systems can enable more accurate flow control, faster response times, and better integration with other automated systems.
- Energy-efficient solenoid valve solutions: Efforts have been made to develop energy-efficient solenoid valve solutions. These may include low-power designs, energy recovery mechanisms, and smart power management systems. Such innovations can reduce the overall power consumption of solenoid valves, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective for long-term operation.
- Miniaturization of solenoid valves: There is a trend towards miniaturization of solenoid valves for use in compact systems and portable devices. This involves developing smaller valve components, integrating multiple functions into a single unit, and utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques. Miniaturized solenoid valves can offer space-saving benefits while maintaining performance characteristics.
- Application-specific solenoid valve designs: Solenoid valves are being customized for specific applications across various industries. This includes developing valves for high-pressure systems, corrosive environments, medical devices, and automotive applications. Such specialized designs can offer improved performance, reliability, and safety in their respective fields of use.
02 Control systems for solenoid valves
Advanced control systems have been developed for solenoid valves to improve their precision and responsiveness. These systems may incorporate electronic controllers, sensors, and feedback mechanisms to regulate valve operation. Such control systems can enable more accurate flow control, faster response times, and better integration with other automated systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy-efficient solenoid valve designs
Efforts have been made to develop energy-efficient solenoid valve designs that reduce power consumption without compromising performance. These designs may include improved magnetic circuits, low-power actuators, or energy recovery mechanisms. Such innovations can lead to significant energy savings in applications where solenoid valves are used extensively.Expand Specific Solutions04 Miniaturization of solenoid valves
There has been a trend towards miniaturization of solenoid valves to meet the demands of compact and portable applications. This involves developing smaller valve components, integrating multiple functions into a single valve assembly, and using advanced manufacturing techniques. Miniaturized solenoid valves can offer space savings and improved performance in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Specialized solenoid valves for specific applications
Solenoid valves have been developed for specialized applications in various industries. These may include high-pressure valves for hydraulic systems, corrosion-resistant valves for chemical processing, or high-temperature valves for industrial furnaces. Such specialized designs address specific operational requirements and environmental conditions in different sectors.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Robotic Assembly and Solenoid Valves
The integration of solenoid valves in robotic automation for assembly lines is in a growth phase, with increasing market size due to the rising demand for automation in manufacturing. The technology is maturing rapidly, driven by advancements in precision control and IoT integration. Key players like Robert Bosch GmbH, Eaton Corp., and BorgWarner, Inc. are leading innovation in this field, developing more efficient and reliable solenoid valve systems. Emerging companies such as Robotphoenix LLC and Solero Technologies LLC are also contributing to the competitive landscape, focusing on specialized applications and novel designs. The market is characterized by a mix of established industrial giants and agile tech-focused firms, indicating a dynamic and evolving sector.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed advanced solenoid valve integration systems for robotic automation in assembly lines. Their solution incorporates smart sensors and actuators, enabling precise control and real-time monitoring of fluid flow and pressure. The system utilizes a network of miniaturized solenoid valves, each equipped with integrated diagnostics and predictive maintenance capabilities[1]. This allows for dynamic adjustment of valve parameters based on production requirements, enhancing overall system flexibility and efficiency. Bosch's approach also includes a centralized control unit that coordinates multiple valves simultaneously, optimizing energy consumption and reducing response times in complex assembly processes[3].
Strengths: High precision control, advanced diagnostics, and energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial cost and complexity in implementation.
Eaton Corp.
Technical Solution: Eaton's solenoid valve integration for robotic automation focuses on modular and scalable solutions. Their system employs a series of compact, high-flow solenoid valves that can be easily integrated into existing robotic systems. Eaton's valves feature advanced materials and coatings to enhance durability and reduce wear in high-cycle applications[2]. The company has also developed a proprietary control algorithm that optimizes valve switching times, reducing energy consumption and improving overall system responsiveness. Eaton's solution includes a user-friendly interface for easy programming and monitoring of valve operations, facilitating seamless integration with various robotic platforms used in assembly lines[4].
Strengths: Modular design, easy integration, and optimized energy efficiency. Weaknesses: May require specific training for optimal utilization of proprietary systems.
Core Innovations in Valve-Robot Integration
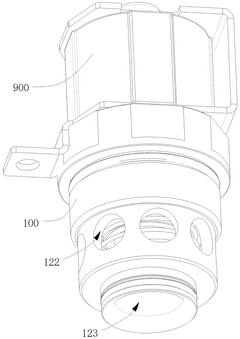
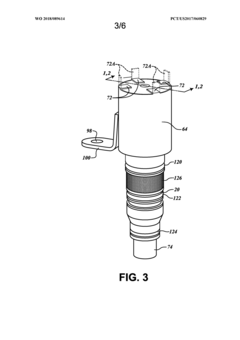
Solenoid valve and assembly method therefor
PatentWO2025067352A1
Innovation
- By providing a second elastic member between the first iron core and the second iron core, and passing the valve stem part into the first cavity and the second cavity in sequence, then installing a sealing part, and finally providing the first elastic member, the first iron core, the second iron core, the valve stem and the sealing part are assembled together by using the limiting effect of the valve core assembly.
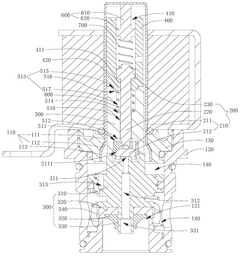
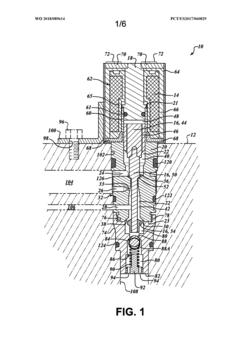
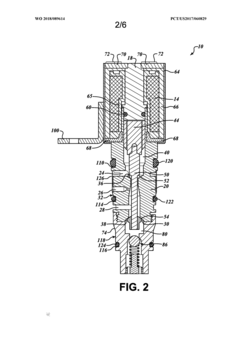
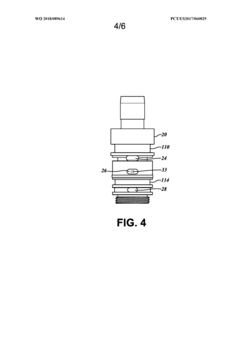
Solenoid valve assembly with pilot pressure control
PatentWO2018089614A1
Innovation
- A solenoid valve assembly with a selectively energizable coil, valve body, and armature assembly that maintains a continuous pilot pressure in the control passage, utilizing a regulator valve to prevent air leaks and ensure fluid flow at predetermined pressures, and an intentional fluid leak path to detect seal issues.
Safety Standards for Robotic Assembly Systems
Safety standards for robotic assembly systems are crucial in ensuring the protection of workers, equipment, and the overall integrity of automated production processes. These standards encompass a wide range of considerations, from mechanical safeguards to advanced electronic safety systems. In the context of solenoid valve integration in robotic automation for assembly lines, safety standards play a pivotal role in mitigating risks associated with the operation of these components.
One of the primary safety standards applicable to robotic assembly systems is ISO 10218, which provides guidelines for the design and integration of industrial robots. This standard emphasizes the importance of risk assessment and the implementation of appropriate safety measures. For solenoid valve integration, this may include ensuring proper shielding of electrical components, implementing fail-safe mechanisms, and incorporating emergency stop functions.
Another relevant standard is IEC 61508, which focuses on functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems. This standard is particularly important for the control systems governing solenoid valves in robotic applications. It outlines requirements for system design, verification, and validation to ensure reliable and safe operation throughout the system's lifecycle.
The Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, applicable in the European Union, sets out essential health and safety requirements for machinery, including robotic assembly systems. This directive mandates the use of safety components and protective devices, which is highly relevant for the integration of solenoid valves in automated assembly lines.
ANSI/RIA R15.06 is a standard specific to industrial robots and robot systems, providing safety requirements for the manufacture, remanufacture, and integration of these systems. It addresses issues such as safeguarding, control reliability, and risk assessment, all of which are pertinent to the safe integration of solenoid valves in robotic automation.
When integrating solenoid valves into robotic assembly systems, compliance with these safety standards typically involves implementing various safety features. These may include pressure relief valves to prevent over-pressurization, flow control mechanisms to regulate fluid movement, and redundant control systems to ensure fail-safe operation. Additionally, proper electrical isolation and grounding are essential to prevent electrical hazards and electromagnetic interference.
Regular maintenance and inspection protocols are also mandated by safety standards to ensure the continued safe operation of robotic assembly systems. This includes periodic checks of solenoid valve functionality, integrity of electrical connections, and verification of safety interlocks and emergency stop systems.
As robotic assembly systems become more advanced and interconnected, cybersecurity considerations are increasingly being incorporated into safety standards. This is particularly relevant for systems utilizing networked solenoid valves or those controlled by programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Standards such as IEC 62443 address the cybersecurity aspects of industrial automation and control systems, providing guidelines for securing networked components against potential cyber threats.
One of the primary safety standards applicable to robotic assembly systems is ISO 10218, which provides guidelines for the design and integration of industrial robots. This standard emphasizes the importance of risk assessment and the implementation of appropriate safety measures. For solenoid valve integration, this may include ensuring proper shielding of electrical components, implementing fail-safe mechanisms, and incorporating emergency stop functions.
Another relevant standard is IEC 61508, which focuses on functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems. This standard is particularly important for the control systems governing solenoid valves in robotic applications. It outlines requirements for system design, verification, and validation to ensure reliable and safe operation throughout the system's lifecycle.
The Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, applicable in the European Union, sets out essential health and safety requirements for machinery, including robotic assembly systems. This directive mandates the use of safety components and protective devices, which is highly relevant for the integration of solenoid valves in automated assembly lines.
ANSI/RIA R15.06 is a standard specific to industrial robots and robot systems, providing safety requirements for the manufacture, remanufacture, and integration of these systems. It addresses issues such as safeguarding, control reliability, and risk assessment, all of which are pertinent to the safe integration of solenoid valves in robotic automation.
When integrating solenoid valves into robotic assembly systems, compliance with these safety standards typically involves implementing various safety features. These may include pressure relief valves to prevent over-pressurization, flow control mechanisms to regulate fluid movement, and redundant control systems to ensure fail-safe operation. Additionally, proper electrical isolation and grounding are essential to prevent electrical hazards and electromagnetic interference.
Regular maintenance and inspection protocols are also mandated by safety standards to ensure the continued safe operation of robotic assembly systems. This includes periodic checks of solenoid valve functionality, integrity of electrical connections, and verification of safety interlocks and emergency stop systems.
As robotic assembly systems become more advanced and interconnected, cybersecurity considerations are increasingly being incorporated into safety standards. This is particularly relevant for systems utilizing networked solenoid valves or those controlled by programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Standards such as IEC 62443 address the cybersecurity aspects of industrial automation and control systems, providing guidelines for securing networked components against potential cyber threats.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Valve Integration
The integration of solenoid valves in robotic automation for assembly lines presents a significant opportunity for cost savings and efficiency improvements. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis reveals several key advantages that justify the investment in this technology. Firstly, the implementation of solenoid valves can lead to substantial reductions in energy consumption. Traditional pneumatic systems often suffer from air leakage and inefficient pressure regulation, resulting in wasted energy. Solenoid valves, with their precise control and rapid response times, can optimize air usage, potentially reducing energy costs by 15-20% in typical assembly line applications.
Labor costs represent another area where solenoid valve integration can yield significant benefits. By automating valve operations that were previously manually controlled, companies can reallocate human resources to more value-added tasks. This reallocation can lead to a 10-15% reduction in direct labor costs associated with valve management and maintenance. Additionally, the increased precision and consistency of automated valve control can reduce error rates and improve product quality, potentially decreasing rework and scrap costs by up to 8%.
Maintenance expenses are also positively impacted by solenoid valve integration. These valves typically have longer operational lifespans compared to traditional mechanical valves, with some models boasting up to 50 million cycles before requiring replacement. This longevity can translate to a 30-40% reduction in valve-related maintenance costs over a five-year period. Furthermore, the predictive maintenance capabilities enabled by smart solenoid valves can prevent unexpected downtime, potentially saving thousands of dollars per hour in lost production.
However, the initial investment in solenoid valve integration can be substantial. The cost of high-quality solenoid valves, associated control systems, and integration expenses can range from $50,000 to $200,000 for a medium-sized assembly line, depending on the complexity and scale of the operation. This upfront cost must be carefully weighed against the projected long-term savings and productivity gains.
The return on investment (ROI) for solenoid valve integration typically ranges from 18 to 36 months, depending on the specific application and scale of implementation. Factors such as production volume, energy costs, and labor rates significantly influence the ROI timeline. Companies operating in regions with high energy costs or facing labor shortages may see faster returns on their investment.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of solenoid valve integration in robotic automation for assembly lines can be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of energy savings, labor efficiency, maintenance reduction, and quality improvements present a compelling case for investment. As technology continues to advance and costs potentially decrease, the value proposition for solenoid valve integration is likely to become even more attractive for a wider range of manufacturing operations.
Labor costs represent another area where solenoid valve integration can yield significant benefits. By automating valve operations that were previously manually controlled, companies can reallocate human resources to more value-added tasks. This reallocation can lead to a 10-15% reduction in direct labor costs associated with valve management and maintenance. Additionally, the increased precision and consistency of automated valve control can reduce error rates and improve product quality, potentially decreasing rework and scrap costs by up to 8%.
Maintenance expenses are also positively impacted by solenoid valve integration. These valves typically have longer operational lifespans compared to traditional mechanical valves, with some models boasting up to 50 million cycles before requiring replacement. This longevity can translate to a 30-40% reduction in valve-related maintenance costs over a five-year period. Furthermore, the predictive maintenance capabilities enabled by smart solenoid valves can prevent unexpected downtime, potentially saving thousands of dollars per hour in lost production.
However, the initial investment in solenoid valve integration can be substantial. The cost of high-quality solenoid valves, associated control systems, and integration expenses can range from $50,000 to $200,000 for a medium-sized assembly line, depending on the complexity and scale of the operation. This upfront cost must be carefully weighed against the projected long-term savings and productivity gains.
The return on investment (ROI) for solenoid valve integration typically ranges from 18 to 36 months, depending on the specific application and scale of implementation. Factors such as production volume, energy costs, and labor rates significantly influence the ROI timeline. Companies operating in regions with high energy costs or facing labor shortages may see faster returns on their investment.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of solenoid valve integration in robotic automation for assembly lines can be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of energy savings, labor efficiency, maintenance reduction, and quality improvements present a compelling case for investment. As technology continues to advance and costs potentially decrease, the value proposition for solenoid valve integration is likely to become even more attractive for a wider range of manufacturing operations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!