Role of Glycerol in Modulating Cellular Metabolism
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol Metabolism Background and Objectives
Glycerol, a simple polyol compound, has been a subject of increasing interest in cellular metabolism research over the past few decades. Its role in modulating cellular processes has evolved from being considered merely a byproduct of triglyceride breakdown to a key player in various metabolic pathways. The historical perspective of glycerol metabolism dates back to the early 20th century when its involvement in glucose production was first recognized.
The evolution of our understanding of glycerol's metabolic significance has been marked by several key discoveries. In the 1950s, researchers identified glycerol kinase, an enzyme crucial for glycerol utilization. This finding paved the way for further investigations into glycerol's metabolic fate. The 1970s and 1980s saw a surge in research focusing on glycerol's role in osmoregulation, particularly in yeast and other microorganisms.
Recent advancements in molecular biology and metabolomics have shed light on the complex interplay between glycerol and cellular metabolism. Studies have revealed its importance in energy production, lipid synthesis, and cellular redox balance. The discovery of aquaglyceroporins, membrane proteins facilitating glycerol transport, has further expanded our understanding of glycerol's cellular dynamics.
The objectives of current glycerol metabolism research are multifaceted. One primary goal is to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms controlling glycerol utilization and production in various cell types. This includes investigating the signaling pathways that respond to changes in glycerol levels and how these pathways integrate with broader metabolic networks.
Another critical objective is to explore the therapeutic potential of modulating glycerol metabolism. This includes studying its role in metabolic disorders, such as obesity and diabetes, where altered glycerol metabolism has been implicated. Researchers are also investigating how glycerol metabolism can be manipulated to enhance cellular resilience under stress conditions, such as hypoxia or nutrient deprivation.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in understanding glycerol's role in cancer metabolism. Cancer cells often exhibit altered metabolic profiles, and recent studies suggest that glycerol metabolism may play a significant role in tumor growth and metastasis. Elucidating these mechanisms could lead to novel therapeutic strategies targeting cancer metabolism.
In the biotechnology sector, researchers aim to harness glycerol metabolism for industrial applications. This includes developing more efficient methods for biofuel production and utilizing glycerol as a renewable feedstock for various chemical processes. The potential for engineered microorganisms to convert glycerol into high-value products is an area of active research and development.
The evolution of our understanding of glycerol's metabolic significance has been marked by several key discoveries. In the 1950s, researchers identified glycerol kinase, an enzyme crucial for glycerol utilization. This finding paved the way for further investigations into glycerol's metabolic fate. The 1970s and 1980s saw a surge in research focusing on glycerol's role in osmoregulation, particularly in yeast and other microorganisms.
Recent advancements in molecular biology and metabolomics have shed light on the complex interplay between glycerol and cellular metabolism. Studies have revealed its importance in energy production, lipid synthesis, and cellular redox balance. The discovery of aquaglyceroporins, membrane proteins facilitating glycerol transport, has further expanded our understanding of glycerol's cellular dynamics.
The objectives of current glycerol metabolism research are multifaceted. One primary goal is to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms controlling glycerol utilization and production in various cell types. This includes investigating the signaling pathways that respond to changes in glycerol levels and how these pathways integrate with broader metabolic networks.
Another critical objective is to explore the therapeutic potential of modulating glycerol metabolism. This includes studying its role in metabolic disorders, such as obesity and diabetes, where altered glycerol metabolism has been implicated. Researchers are also investigating how glycerol metabolism can be manipulated to enhance cellular resilience under stress conditions, such as hypoxia or nutrient deprivation.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in understanding glycerol's role in cancer metabolism. Cancer cells often exhibit altered metabolic profiles, and recent studies suggest that glycerol metabolism may play a significant role in tumor growth and metastasis. Elucidating these mechanisms could lead to novel therapeutic strategies targeting cancer metabolism.
In the biotechnology sector, researchers aim to harness glycerol metabolism for industrial applications. This includes developing more efficient methods for biofuel production and utilizing glycerol as a renewable feedstock for various chemical processes. The potential for engineered microorganisms to convert glycerol into high-value products is an area of active research and development.
Market Analysis for Glycerol-Based Products
The glycerol-based products market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and bio-based alternatives across various industries. Glycerol, a versatile compound derived from renewable sources, has found applications in pharmaceuticals, personal care, food and beverages, and industrial sectors.
In the pharmaceutical industry, glycerol-based products have gained traction due to their role in drug formulations and as a key ingredient in cough syrups and topical medications. The personal care sector has also embraced glycerol for its moisturizing properties, leading to its widespread use in skincare and haircare products. The food and beverage industry utilizes glycerol as a humectant and sweetener, contributing to the market's expansion.
The industrial sector has witnessed a surge in glycerol demand for applications such as lubricants, antifreeze, and polymer production. This diversification of applications has significantly broadened the market scope for glycerol-based products.
Market analysis indicates a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% for the glycerol market from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to the increasing awareness of sustainable alternatives and the rising demand for bio-based products across industries. The global glycerol market size was valued at $2.7 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2026.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the glycerol market, accounting for the largest share due to the rapid industrialization and growing consumer awareness of eco-friendly products. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by stringent regulations promoting the use of bio-based materials and the presence of key market players.
The market landscape is characterized by both established players and new entrants, fostering innovation and competition. Key market players are focusing on research and development to expand their product portfolios and cater to evolving customer needs. Strategic partnerships and collaborations are becoming increasingly common as companies seek to strengthen their market position and access new technologies.
However, the market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and the need for substantial investments in production facilities. Despite these obstacles, the growing emphasis on sustainable development and the circular economy is expected to drive further market expansion for glycerol-based products in the coming years.
In the pharmaceutical industry, glycerol-based products have gained traction due to their role in drug formulations and as a key ingredient in cough syrups and topical medications. The personal care sector has also embraced glycerol for its moisturizing properties, leading to its widespread use in skincare and haircare products. The food and beverage industry utilizes glycerol as a humectant and sweetener, contributing to the market's expansion.
The industrial sector has witnessed a surge in glycerol demand for applications such as lubricants, antifreeze, and polymer production. This diversification of applications has significantly broadened the market scope for glycerol-based products.
Market analysis indicates a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% for the glycerol market from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to the increasing awareness of sustainable alternatives and the rising demand for bio-based products across industries. The global glycerol market size was valued at $2.7 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2026.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the glycerol market, accounting for the largest share due to the rapid industrialization and growing consumer awareness of eco-friendly products. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by stringent regulations promoting the use of bio-based materials and the presence of key market players.
The market landscape is characterized by both established players and new entrants, fostering innovation and competition. Key market players are focusing on research and development to expand their product portfolios and cater to evolving customer needs. Strategic partnerships and collaborations are becoming increasingly common as companies seek to strengthen their market position and access new technologies.
However, the market faces challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and the need for substantial investments in production facilities. Despite these obstacles, the growing emphasis on sustainable development and the circular economy is expected to drive further market expansion for glycerol-based products in the coming years.
Current Understanding and Challenges in Glycerol Metabolism
Glycerol metabolism plays a crucial role in cellular energy production and biosynthesis. Current understanding of glycerol's metabolic pathways has expanded significantly in recent years, revealing its complex interactions with various cellular processes. The primary route of glycerol metabolism involves its conversion to glycerol-3-phosphate by glycerol kinase, followed by oxidation to dihydroxyacetone phosphate by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. This process integrates glycerol into glycolysis and gluconeogenesis pathways, highlighting its importance in glucose homeostasis.
Recent research has uncovered glycerol's involvement in lipid metabolism, particularly in triglyceride synthesis and breakdown. During fasting or high-energy demand states, glycerol serves as a crucial substrate for gluconeogenesis in the liver, contributing to blood glucose regulation. Additionally, glycerol has been identified as a key player in osmoregulation, helping cells maintain volume and protect against osmotic stress.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in fully understanding glycerol metabolism. One major hurdle is the complexity of glycerol transport mechanisms across cellular membranes. While aquaglyceroporins have been identified as facilitators of glycerol movement, the regulation and tissue-specific expression of these transporters remain poorly understood. This gap in knowledge hinders our ability to predict and manipulate glycerol distribution in various physiological states.
Another significant challenge lies in elucidating the intricate regulatory networks governing glycerol metabolism. The interplay between hormonal signals, nutrient availability, and cellular energy status in modulating glycerol utilization is not fully mapped. This complexity makes it difficult to develop targeted interventions for metabolic disorders involving glycerol dysregulation.
Furthermore, the role of glycerol in non-canonical metabolic pathways is an emerging area of research with many unanswered questions. Recent studies suggest glycerol's involvement in epigenetic regulation through its contribution to one-carbon metabolism and DNA methylation. However, the extent and mechanisms of this involvement require further investigation.
The impact of glycerol metabolism on mitochondrial function and cellular redox balance presents another frontier for research. While glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle is known to contribute to mitochondrial redox homeostasis, the full scope of glycerol's influence on mitochondrial metabolism and energy production remains to be explored.
Lastly, the therapeutic potential of modulating glycerol metabolism in various diseases, including diabetes, obesity, and cancer, poses both opportunities and challenges. Developing targeted approaches to manipulate glycerol pathways without disrupting other essential metabolic processes requires a more comprehensive understanding of glycerol's multifaceted roles in cellular metabolism.
Recent research has uncovered glycerol's involvement in lipid metabolism, particularly in triglyceride synthesis and breakdown. During fasting or high-energy demand states, glycerol serves as a crucial substrate for gluconeogenesis in the liver, contributing to blood glucose regulation. Additionally, glycerol has been identified as a key player in osmoregulation, helping cells maintain volume and protect against osmotic stress.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in fully understanding glycerol metabolism. One major hurdle is the complexity of glycerol transport mechanisms across cellular membranes. While aquaglyceroporins have been identified as facilitators of glycerol movement, the regulation and tissue-specific expression of these transporters remain poorly understood. This gap in knowledge hinders our ability to predict and manipulate glycerol distribution in various physiological states.
Another significant challenge lies in elucidating the intricate regulatory networks governing glycerol metabolism. The interplay between hormonal signals, nutrient availability, and cellular energy status in modulating glycerol utilization is not fully mapped. This complexity makes it difficult to develop targeted interventions for metabolic disorders involving glycerol dysregulation.
Furthermore, the role of glycerol in non-canonical metabolic pathways is an emerging area of research with many unanswered questions. Recent studies suggest glycerol's involvement in epigenetic regulation through its contribution to one-carbon metabolism and DNA methylation. However, the extent and mechanisms of this involvement require further investigation.
The impact of glycerol metabolism on mitochondrial function and cellular redox balance presents another frontier for research. While glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle is known to contribute to mitochondrial redox homeostasis, the full scope of glycerol's influence on mitochondrial metabolism and energy production remains to be explored.
Lastly, the therapeutic potential of modulating glycerol metabolism in various diseases, including diabetes, obesity, and cancer, poses both opportunities and challenges. Developing targeted approaches to manipulate glycerol pathways without disrupting other essential metabolic processes requires a more comprehensive understanding of glycerol's multifaceted roles in cellular metabolism.
Current Approaches to Studying Glycerol's Metabolic Effects
01 Glycerol metabolism in microorganisms
Research focuses on the cellular metabolism of glycerol in various microorganisms, including bacteria and yeast. Studies explore the pathways and enzymes involved in glycerol utilization, as well as the genetic modifications that can enhance glycerol metabolism for biotechnological applications.- Glycerol metabolism in microorganisms: Research focuses on the cellular metabolism of glycerol in various microorganisms, including bacteria and yeast. Studies explore the pathways and enzymes involved in glycerol utilization, as well as the genetic modifications that can enhance glycerol metabolism for biotechnological applications.
- Glycerol as a carbon source for cellular growth: Investigations into the use of glycerol as a primary carbon source for cellular growth and metabolism. This includes studies on optimizing growth conditions, metabolic engineering strategies, and the development of strains capable of efficient glycerol utilization for various industrial applications.
- Glycerol metabolism in plants: Research on glycerol metabolism in plants, including studies on glycerol kinase and other enzymes involved in glycerol utilization. This area explores the role of glycerol in plant cellular processes, stress responses, and potential applications in crop improvement.
- Glycerol metabolism in mammalian cells: Studies on glycerol metabolism in mammalian cells, focusing on the pathways involved in glycerol uptake, utilization, and its role in various cellular processes. This includes research on glycerol's involvement in energy metabolism, lipid synthesis, and potential therapeutic applications.
- Metabolic engineering for enhanced glycerol utilization: Development of metabolic engineering strategies to improve glycerol utilization in various organisms. This includes genetic modifications to enhance glycerol uptake, optimize metabolic pathways, and increase the production of valuable compounds from glycerol as a substrate.
02 Glycerol as a carbon source for cellular growth
Investigations into the use of glycerol as a primary carbon source for cellular growth and metabolism in different organisms. This includes optimizing growth conditions, understanding metabolic fluxes, and developing strategies to improve biomass production using glycerol-based media.Expand Specific Solutions03 Genetic engineering for enhanced glycerol metabolism
Development of genetically engineered organisms with improved glycerol metabolism capabilities. This involves modifying genes related to glycerol uptake, catabolism, and regulatory pathways to increase the efficiency of glycerol utilization in cellular processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glycerol metabolism in lipid biosynthesis
Exploration of the role of glycerol in lipid biosynthesis and cellular membrane formation. Research focuses on understanding the metabolic pathways connecting glycerol to lipid production and developing methods to manipulate these pathways for biotechnological applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Glycerol metabolism in energy production
Investigation of glycerol's role in cellular energy production through various metabolic pathways. This includes studying the conversion of glycerol to ATP, its integration into the electron transport chain, and its potential as an alternative energy source in different cellular systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Glycerol Metabolism Research
The role of glycerol in modulating cellular metabolism is an emerging field with growing interest from both academia and industry. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing research activities and potential applications in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals. Key players like Novo Nordisk, Janssen Pharmaceutica, and Chr. Hansen are investing in this area, leveraging their expertise in metabolic processes and fermentation technologies. Universities such as MIT and Xiamen University are contributing to fundamental research, while companies like DuPont and Suntory Holdings are exploring industrial applications. The technology is still evolving, with a focus on understanding glycerol's impact on cellular pathways and developing novel bioprocessing strategies.
Novo Nordisk A/S
Technical Solution: Novo Nordisk has developed innovative approaches to leverage glycerol's role in cellular metabolism, particularly in diabetes treatment. Their research focuses on how glycerol modulates insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis. They have engineered novel insulin analogs that incorporate glycerol molecules to enhance stability and prolong action [1]. Additionally, they are exploring glycerol's potential in improving mitochondrial function and energy metabolism in diabetic patients. Their studies have shown that glycerol supplementation can increase fat oxidation and reduce lipid accumulation in liver cells, potentially addressing fatty liver disease in diabetics [3].
Strengths: Extensive expertise in diabetes research, large-scale clinical trial capabilities, and established market presence. Weaknesses: Narrow focus primarily on diabetes may limit broader applications of glycerol in cellular metabolism.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT researchers have made significant strides in understanding glycerol's role in cellular metabolism. They have developed advanced metabolomics techniques to track glycerol flux through various metabolic pathways [2]. Their studies have revealed that glycerol serves as a crucial node in cellular energy metabolism, connecting lipid metabolism with glucose utilization. MIT's team has also engineered yeast strains with enhanced glycerol utilization capabilities, demonstrating potential applications in biofuel production [4]. Furthermore, they are investigating glycerol's role in cellular stress responses, particularly in relation to osmotic stress and cell volume regulation. Their research has shown that glycerol accumulation is a key mechanism for cell survival under hyperosmotic conditions [5].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research facilities, interdisciplinary approach combining biology, engineering, and computational methods. Weaknesses: Research may be more focused on fundamental science rather than immediate clinical or industrial applications.
Breakthrough Studies on Glycerol's Cellular Impact
System and method for diagnosis and treatment
PatentActiveUS20210361675A1
Innovation
- The use of ORG 34517, a specific GR antagonist, in combination with other therapeutic agents such as radiation therapy, peptides, or PARP inhibitors, to block GR activity, thereby reducing toxicities and enhancing the effectiveness of treatments for neoplasia while minimizing side effects.
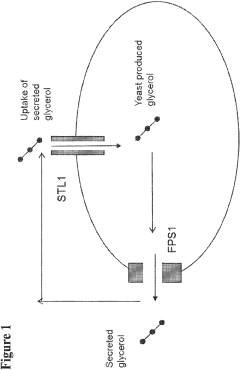
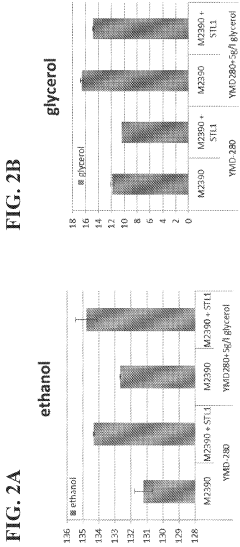
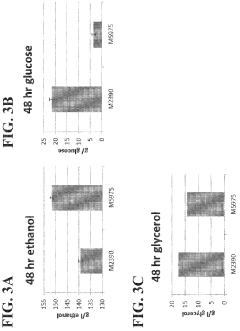
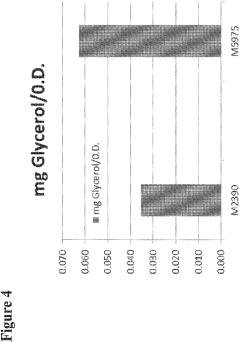
Recombinant yeast expressing heterologous STL1 protein
PatentInactiveUS20230159962A1
Innovation
- Engineering recombinant microorganisms to uptake extracellular glycerol, modulate its production, and utilize alternative electron acceptors to reduce glycerol levels, thereby increasing ethanol yield by redirecting carbon flow to desired end-products.
Regulatory Aspects of Glycerol in Biotechnology
The regulatory landscape surrounding glycerol in biotechnology is complex and multifaceted, reflecting its widespread use and importance in various industrial applications. Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and standards for the production, use, and disposal of glycerol, particularly in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
In the food industry, glycerol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) when used as a food additive. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated glycerol and deemed it safe for use in food applications. However, manufacturers must adhere to specific purity standards and usage limits set by these regulatory agencies.
For pharmaceutical applications, glycerol is subject to stringent quality control measures. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provide detailed specifications for pharmaceutical-grade glycerol, including purity requirements and acceptable levels of contaminants. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure the quality and safety of glycerol used in drug formulations.
In the cosmetics industry, glycerol is regulated under the EU Cosmetics Regulation and the FDA's Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. These regulations outline safety requirements and labeling guidelines for cosmetic products containing glycerol.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in glycerol production and utilization. The increasing use of glycerol as a byproduct of biodiesel production has led to the development of specific guidelines for its disposal and recycling. Many countries have implemented policies to promote the sustainable use of glycerol and minimize its environmental impact.
As glycerol finds new applications in biotechnology, regulatory frameworks are evolving to address emerging concerns. For instance, the use of glycerol in cell culture media and as a cryoprotectant in biobanking has prompted discussions on standardization and quality control measures specific to these applications.
Regulatory bodies are also focusing on the potential health impacts of glycerol exposure, particularly in occupational settings. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and similar agencies in other countries have established exposure limits and safety guidelines for workers handling glycerol in industrial settings.
As research continues to uncover new roles for glycerol in modulating cellular metabolism, regulatory agencies are likely to update their guidelines to reflect these findings. This may include reassessing safety profiles, adjusting usage limits, or implementing new quality control measures to ensure the safe and effective use of glycerol in various biotechnological applications.
In the food industry, glycerol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) when used as a food additive. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated glycerol and deemed it safe for use in food applications. However, manufacturers must adhere to specific purity standards and usage limits set by these regulatory agencies.
For pharmaceutical applications, glycerol is subject to stringent quality control measures. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provide detailed specifications for pharmaceutical-grade glycerol, including purity requirements and acceptable levels of contaminants. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure the quality and safety of glycerol used in drug formulations.
In the cosmetics industry, glycerol is regulated under the EU Cosmetics Regulation and the FDA's Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. These regulations outline safety requirements and labeling guidelines for cosmetic products containing glycerol.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in glycerol production and utilization. The increasing use of glycerol as a byproduct of biodiesel production has led to the development of specific guidelines for its disposal and recycling. Many countries have implemented policies to promote the sustainable use of glycerol and minimize its environmental impact.
As glycerol finds new applications in biotechnology, regulatory frameworks are evolving to address emerging concerns. For instance, the use of glycerol in cell culture media and as a cryoprotectant in biobanking has prompted discussions on standardization and quality control measures specific to these applications.
Regulatory bodies are also focusing on the potential health impacts of glycerol exposure, particularly in occupational settings. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and similar agencies in other countries have established exposure limits and safety guidelines for workers handling glycerol in industrial settings.
As research continues to uncover new roles for glycerol in modulating cellular metabolism, regulatory agencies are likely to update their guidelines to reflect these findings. This may include reassessing safety profiles, adjusting usage limits, or implementing new quality control measures to ensure the safe and effective use of glycerol in various biotechnological applications.
Glycerol's Potential in Metabolic Engineering
Glycerol, a simple polyol compound, has emerged as a promising candidate in metabolic engineering due to its unique properties and versatile applications. Its potential in modulating cellular metabolism offers exciting opportunities for biotechnological advancements and industrial applications.
One of the key aspects of glycerol's potential in metabolic engineering lies in its ability to serve as a carbon source for various microorganisms. Many bacteria and yeasts can efficiently metabolize glycerol, making it an attractive substrate for the production of value-added compounds. This characteristic opens up possibilities for developing novel bioprocesses and improving existing ones.
Glycerol's role as an osmolyte is another crucial factor in its potential for metabolic engineering. It can help cells maintain osmotic balance and protect against environmental stresses, such as high salt concentrations or extreme temperatures. By manipulating glycerol metabolism, researchers can enhance the stress tolerance of engineered microorganisms, potentially improving their performance in industrial fermentation processes.
The integration of glycerol into cellular metabolism also offers opportunities for redirecting metabolic fluxes. By introducing or modifying pathways that utilize glycerol, it is possible to channel carbon flow towards desired products. This approach has been successfully employed in the production of various chemicals, including 1,3-propanediol, succinic acid, and biofuels.
Furthermore, glycerol's potential extends to the field of synthetic biology. Its metabolism can be engineered to create novel pathways or to optimize existing ones, enabling the production of non-natural compounds or improving the yield of target molecules. This aspect of glycerol's potential in metabolic engineering holds promise for developing more efficient and sustainable bioprocesses.
The abundance of glycerol as a byproduct of biodiesel production adds to its attractiveness in metabolic engineering applications. Utilizing this readily available and low-cost substrate can contribute to the development of more economically viable and environmentally friendly bioprocesses.
In conclusion, glycerol's potential in metabolic engineering is multifaceted and far-reaching. Its ability to serve as a carbon source, osmolyte, and metabolic flux modulator, combined with its availability and compatibility with various microorganisms, positions it as a valuable tool in the ongoing efforts to develop more efficient and sustainable biotechnological processes.
One of the key aspects of glycerol's potential in metabolic engineering lies in its ability to serve as a carbon source for various microorganisms. Many bacteria and yeasts can efficiently metabolize glycerol, making it an attractive substrate for the production of value-added compounds. This characteristic opens up possibilities for developing novel bioprocesses and improving existing ones.
Glycerol's role as an osmolyte is another crucial factor in its potential for metabolic engineering. It can help cells maintain osmotic balance and protect against environmental stresses, such as high salt concentrations or extreme temperatures. By manipulating glycerol metabolism, researchers can enhance the stress tolerance of engineered microorganisms, potentially improving their performance in industrial fermentation processes.
The integration of glycerol into cellular metabolism also offers opportunities for redirecting metabolic fluxes. By introducing or modifying pathways that utilize glycerol, it is possible to channel carbon flow towards desired products. This approach has been successfully employed in the production of various chemicals, including 1,3-propanediol, succinic acid, and biofuels.
Furthermore, glycerol's potential extends to the field of synthetic biology. Its metabolism can be engineered to create novel pathways or to optimize existing ones, enabling the production of non-natural compounds or improving the yield of target molecules. This aspect of glycerol's potential in metabolic engineering holds promise for developing more efficient and sustainable bioprocesses.
The abundance of glycerol as a byproduct of biodiesel production adds to its attractiveness in metabolic engineering applications. Utilizing this readily available and low-cost substrate can contribute to the development of more economically viable and environmentally friendly bioprocesses.
In conclusion, glycerol's potential in metabolic engineering is multifaceted and far-reaching. Its ability to serve as a carbon source, osmolyte, and metabolic flux modulator, combined with its availability and compatibility with various microorganisms, positions it as a valuable tool in the ongoing efforts to develop more efficient and sustainable biotechnological processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!