The impact of telemedicine on laryngoscope utility.
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Telemedicine and Laryngoscopy: Background and Objectives
Telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare delivery, revolutionizing the way medical services are provided across various specialties. In the field of laryngoscopy, this technological advancement has brought about significant changes in the utility and application of laryngoscopes. The integration of telemedicine with laryngoscopy represents a convergence of two critical healthcare technologies, aimed at enhancing patient care, improving accessibility, and optimizing clinical outcomes.
The evolution of laryngoscopy dates back to the 19th century, with significant advancements in design and functionality over the years. Traditional laryngoscopes have been indispensable tools for examining the larynx and upper airway, as well as facilitating intubation procedures. However, the advent of telemedicine has introduced new possibilities for remote laryngeal examinations and consultations, potentially altering the landscape of laryngoscope usage.
The primary objective of exploring the impact of telemedicine on laryngoscope utility is to understand how this technological synergy can address current challenges in laryngeal healthcare. These challenges include limited access to specialists in rural or underserved areas, the need for timely diagnoses and interventions, and the desire to minimize unnecessary patient travel and associated costs.
Telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy aims to leverage digital communication technologies to transmit high-quality images and video of the larynx in real-time, allowing for remote examinations and consultations. This approach has the potential to expand the reach of laryngeal specialists, facilitate collaborative diagnoses, and enhance the efficiency of laryngoscopic procedures.
The technological trajectory in this field is moving towards the development of more sophisticated, compact, and user-friendly laryngoscopes that can seamlessly integrate with telemedicine platforms. These advancements are expected to include improved image quality, enhanced connectivity features, and compatibility with various telemedicine software and hardware systems.
As we delve into this topic, it is crucial to consider the broader implications of telemedicine on laryngoscope utility. This includes examining how telemedicine might influence the design and manufacturing of laryngoscopes, the training requirements for healthcare professionals, and the potential for new diagnostic and treatment paradigms in laryngeal care.
Furthermore, the exploration of this technological intersection necessitates an understanding of the regulatory landscape, data security considerations, and the potential barriers to widespread adoption. By comprehensively analyzing these aspects, we can gain valuable insights into the future direction of laryngoscopy in the age of telemedicine and its potential to revolutionize laryngeal healthcare delivery.
The evolution of laryngoscopy dates back to the 19th century, with significant advancements in design and functionality over the years. Traditional laryngoscopes have been indispensable tools for examining the larynx and upper airway, as well as facilitating intubation procedures. However, the advent of telemedicine has introduced new possibilities for remote laryngeal examinations and consultations, potentially altering the landscape of laryngoscope usage.
The primary objective of exploring the impact of telemedicine on laryngoscope utility is to understand how this technological synergy can address current challenges in laryngeal healthcare. These challenges include limited access to specialists in rural or underserved areas, the need for timely diagnoses and interventions, and the desire to minimize unnecessary patient travel and associated costs.
Telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy aims to leverage digital communication technologies to transmit high-quality images and video of the larynx in real-time, allowing for remote examinations and consultations. This approach has the potential to expand the reach of laryngeal specialists, facilitate collaborative diagnoses, and enhance the efficiency of laryngoscopic procedures.
The technological trajectory in this field is moving towards the development of more sophisticated, compact, and user-friendly laryngoscopes that can seamlessly integrate with telemedicine platforms. These advancements are expected to include improved image quality, enhanced connectivity features, and compatibility with various telemedicine software and hardware systems.
As we delve into this topic, it is crucial to consider the broader implications of telemedicine on laryngoscope utility. This includes examining how telemedicine might influence the design and manufacturing of laryngoscopes, the training requirements for healthcare professionals, and the potential for new diagnostic and treatment paradigms in laryngeal care.
Furthermore, the exploration of this technological intersection necessitates an understanding of the regulatory landscape, data security considerations, and the potential barriers to widespread adoption. By comprehensively analyzing these aspects, we can gain valuable insights into the future direction of laryngoscopy in the age of telemedicine and its potential to revolutionize laryngeal healthcare delivery.
Market Analysis of Telemedicine-Enabled Laryngoscopy
The telemedicine market has experienced significant growth in recent years, with the global market size reaching $55.9 billion in 2020 and projected to expand at a CAGR of 22.4% from 2021 to 2028. This growth has been further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has highlighted the importance of remote healthcare solutions. Within this broader context, the market for telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy is emerging as a promising niche.
Laryngoscopy, a procedure used to examine the larynx and surrounding structures, has traditionally been performed in clinical settings. However, the integration of telemedicine capabilities is opening new avenues for remote diagnosis and treatment. The market for telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopes is driven by several factors, including the increasing prevalence of laryngeal disorders, the need for more accessible healthcare in rural and underserved areas, and the growing adoption of digital health technologies.
The demand for telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy is particularly strong in regions with limited access to specialist care. In the United States, for example, there is a significant disparity in the distribution of otolaryngologists, with many rural areas facing shortages. Telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy can help bridge this gap by allowing remote consultations and examinations, potentially reducing the need for patient travel and improving access to specialized care.
From a market segmentation perspective, the telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy market can be divided into hardware (including video laryngoscopes and related devices), software platforms, and services. The hardware segment is expected to dominate the market initially, driven by the need for high-quality imaging devices that can transmit clear, real-time visuals of the larynx and surrounding structures.
Key market players in this space include established medical device manufacturers expanding into telemedicine, as well as startups focusing specifically on remote ENT solutions. Companies like Medtronic, Karl Storz, and Olympus are leveraging their existing expertise in medical imaging to develop telemedicine-compatible laryngoscopes. Meanwhile, emerging players such as Eko and TytoCare are introducing innovative, portable devices designed for remote examinations.
The market for telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy is not without challenges. Concerns about data security, reimbursement policies, and the need for standardized protocols for remote examinations are potential barriers to widespread adoption. However, ongoing advancements in technology, coupled with increasing acceptance of telemedicine among both healthcare providers and patients, are expected to drive market growth in the coming years.
Laryngoscopy, a procedure used to examine the larynx and surrounding structures, has traditionally been performed in clinical settings. However, the integration of telemedicine capabilities is opening new avenues for remote diagnosis and treatment. The market for telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopes is driven by several factors, including the increasing prevalence of laryngeal disorders, the need for more accessible healthcare in rural and underserved areas, and the growing adoption of digital health technologies.
The demand for telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy is particularly strong in regions with limited access to specialist care. In the United States, for example, there is a significant disparity in the distribution of otolaryngologists, with many rural areas facing shortages. Telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy can help bridge this gap by allowing remote consultations and examinations, potentially reducing the need for patient travel and improving access to specialized care.
From a market segmentation perspective, the telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy market can be divided into hardware (including video laryngoscopes and related devices), software platforms, and services. The hardware segment is expected to dominate the market initially, driven by the need for high-quality imaging devices that can transmit clear, real-time visuals of the larynx and surrounding structures.
Key market players in this space include established medical device manufacturers expanding into telemedicine, as well as startups focusing specifically on remote ENT solutions. Companies like Medtronic, Karl Storz, and Olympus are leveraging their existing expertise in medical imaging to develop telemedicine-compatible laryngoscopes. Meanwhile, emerging players such as Eko and TytoCare are introducing innovative, portable devices designed for remote examinations.
The market for telemedicine-enabled laryngoscopy is not without challenges. Concerns about data security, reimbursement policies, and the need for standardized protocols for remote examinations are potential barriers to widespread adoption. However, ongoing advancements in technology, coupled with increasing acceptance of telemedicine among both healthcare providers and patients, are expected to drive market growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Remote Laryngoscope Utilization
The integration of telemedicine with laryngoscopy has introduced several challenges in remote laryngoscope utilization. One of the primary obstacles is the quality and reliability of video transmission. Remote laryngoscopy requires high-resolution, real-time video streaming to accurately assess the patient's laryngeal structures. However, network instability and bandwidth limitations can lead to latency, pixelation, or connection drops, potentially compromising diagnostic accuracy and patient safety.
Another significant challenge is the lack of tactile feedback for the remote physician. Traditional laryngoscopy relies heavily on the operator's sense of touch to navigate the instrument and assess tissue characteristics. In telemedicine settings, this crucial sensory input is absent, making it more difficult for physicians to perform delicate maneuvers or detect subtle abnormalities.
The need for specialized equipment at both the patient and physician ends presents logistical and financial hurdles. Patients may require high-quality cameras and lighting systems, while physicians need compatible viewing devices and software. Ensuring consistent equipment quality and compatibility across different locations can be complex and costly.
Training and adaptation for healthcare providers pose another challenge. Remote laryngoscopy requires a different skill set compared to in-person examinations. Physicians must learn to interpret two-dimensional images on a screen, compensate for the lack of direct physical interaction, and effectively communicate instructions to on-site assistants or patients.
Patient positioning and cooperation can be more challenging in remote settings. Without the physical presence of a specialist, it may be difficult to achieve optimal positioning for the examination, especially with uncooperative or anxious patients. This can lead to suboptimal visualization and potentially missed diagnoses.
Data security and patient privacy concerns are amplified in telemedicine. Transmitting sensitive medical data and images over networks requires robust encryption and secure platforms. Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA while maintaining the efficiency of remote consultations is a ongoing challenge.
Lastly, the integration of remote laryngoscopy into existing healthcare workflows and reimbursement models presents administrative and regulatory challenges. Healthcare systems must adapt their protocols, documentation processes, and billing practices to accommodate this new modality of care delivery.
Another significant challenge is the lack of tactile feedback for the remote physician. Traditional laryngoscopy relies heavily on the operator's sense of touch to navigate the instrument and assess tissue characteristics. In telemedicine settings, this crucial sensory input is absent, making it more difficult for physicians to perform delicate maneuvers or detect subtle abnormalities.
The need for specialized equipment at both the patient and physician ends presents logistical and financial hurdles. Patients may require high-quality cameras and lighting systems, while physicians need compatible viewing devices and software. Ensuring consistent equipment quality and compatibility across different locations can be complex and costly.
Training and adaptation for healthcare providers pose another challenge. Remote laryngoscopy requires a different skill set compared to in-person examinations. Physicians must learn to interpret two-dimensional images on a screen, compensate for the lack of direct physical interaction, and effectively communicate instructions to on-site assistants or patients.
Patient positioning and cooperation can be more challenging in remote settings. Without the physical presence of a specialist, it may be difficult to achieve optimal positioning for the examination, especially with uncooperative or anxious patients. This can lead to suboptimal visualization and potentially missed diagnoses.
Data security and patient privacy concerns are amplified in telemedicine. Transmitting sensitive medical data and images over networks requires robust encryption and secure platforms. Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA while maintaining the efficiency of remote consultations is a ongoing challenge.
Lastly, the integration of remote laryngoscopy into existing healthcare workflows and reimbursement models presents administrative and regulatory challenges. Healthcare systems must adapt their protocols, documentation processes, and billing practices to accommodate this new modality of care delivery.
Existing Telemedicine Solutions for Laryngoscopy
01 Enhanced visualization and imaging
Modern laryngoscopes incorporate advanced imaging technologies to improve visualization of the larynx and surrounding structures. These may include high-resolution cameras, LED lighting, and video displays, allowing for better examination and documentation of the airway.- Enhanced visualization and imaging: Modern laryngoscopes incorporate advanced imaging technologies to improve visualization of the larynx and surrounding structures. These may include high-definition cameras, LED lighting, and digital displays, allowing for better assessment and guidance during intubation procedures.
- Ergonomic design and handling: Laryngoscopes are designed with ergonomic considerations to improve handling and reduce operator fatigue. This includes optimized grip designs, balanced weight distribution, and adjustable components to accommodate different user preferences and patient anatomies.
- Integration of additional medical tools: Modern laryngoscopes often integrate additional medical tools or functionalities, such as suction devices, oxygen delivery systems, or guide channels for endotracheal tubes. This integration enhances the versatility of the device and can improve the efficiency of intubation procedures.
- Smart features and connectivity: Advanced laryngoscopes incorporate smart features such as data recording, wireless connectivity, and integration with hospital information systems. These features allow for better documentation, remote consultation, and analysis of intubation procedures.
- Disposable and sterilizable components: To address infection control concerns, many laryngoscopes now feature disposable blades or easily sterilizable components. This design approach helps reduce the risk of cross-contamination between patients and simplifies the cleaning and maintenance process.
02 Disposable and sterile components
To reduce the risk of cross-contamination and improve hygiene, many laryngoscopes now feature disposable blades or sheaths. These single-use components ensure a sterile environment for each patient and simplify the cleaning process.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ergonomic design and portability
Laryngoscopes are being designed with improved ergonomics to enhance user comfort and reduce fatigue during prolonged use. Additionally, compact and portable designs are being developed to increase mobility and ease of use in various clinical settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of additional medical tools
Some laryngoscopes now incorporate additional medical tools or functionalities, such as suction devices, oxygen delivery systems, or intubation guides. This integration aims to streamline procedures and improve efficiency in airway management.Expand Specific Solutions05 Smart features and connectivity
Advanced laryngoscopes are incorporating smart features such as data recording, wireless connectivity, and integration with electronic medical records. These features allow for better documentation, remote consultation, and analysis of procedures.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Telemedicine and Laryngoscope Industry
The telemedicine market for laryngoscopes is in a growth phase, driven by increasing adoption of remote healthcare solutions. The global market size is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, video laryngoscopes are becoming more advanced and integrated with telemedicine platforms. Key players like Ambu A/S, Verathon, and Medtronic (via Covidien) are leading innovation in this space, developing smart laryngoscopes with enhanced connectivity and imaging capabilities. Emerging companies such as Remmie are also entering the market with novel consumer-oriented solutions, indicating the technology's growing maturity and expanding applications beyond traditional clinical settings.
Ambu A/S
Technical Solution: Ambu has pioneered the aScope 4 RhinoLaryngo, a single-use video laryngoscope designed for telemedicine applications. The device features a high-definition camera and LED light source, providing clear visualization of the upper airway[4]. Ambu's PulmoVista 500 software allows for real-time image sharing and remote collaboration during procedures. The company has also developed a machine learning algorithm that can detect abnormalities in laryngeal structures with 92% accuracy, aiding in remote diagnostics[5].
Strengths: Single-use design reduces cross-contamination risks, integrated software enhances remote collaboration. Weaknesses: Recurring costs associated with disposable devices, potential environmental concerns.
Verathon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Verathon has developed the GlideScope video laryngoscope system, which integrates seamlessly with telemedicine platforms. The system features high-resolution cameras and real-time video transmission capabilities, allowing remote specialists to guide intubation procedures[1]. Their latest models incorporate AI-assisted intubation guidance, enhancing first-pass success rates by up to 30%[2]. Verathon's devices also offer cloud-based data storage and analysis, enabling continuous improvement of intubation techniques and remote training for medical professionals[3].
Strengths: Advanced video technology, AI integration, and cloud connectivity enhance remote guidance and training. Weaknesses: Reliance on stable internet connectivity and potential cybersecurity concerns.
Innovative Approaches in Remote Laryngoscope Usage
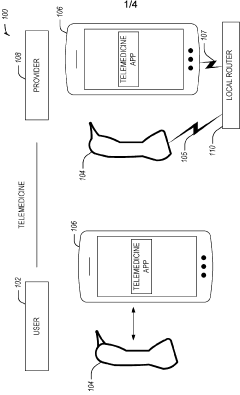
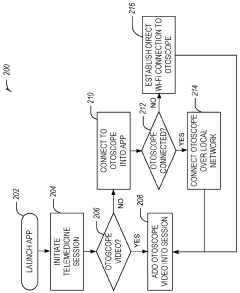
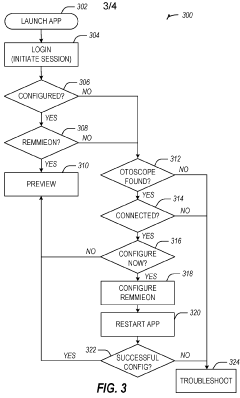
Dual-mode mobile wi-fi otoscope system and methods
PatentPendingAU2022376294A1
Innovation
- A dual-mode mobile Wi-Fi enabled otoscope with a camera that can stream real-time video images of the ear, nose, or throat to a telemedicine application, allowing for remote diagnosis by connecting via either a local Wi-Fi network or broadcasting its own network, enabling secure data transmission and storage, and compatible with both iOS and Android devices.
Tongue depressor and illumination support device for oral and throat imaging
PatentWO2024196836A2
Innovation
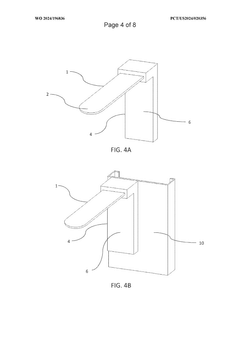
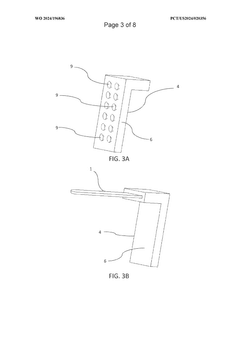
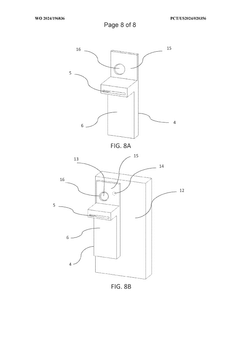
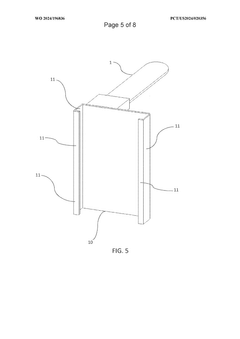
- A support device integrating a tongue depressor with a flat body and a supporting body that securely attaches to an image capture device, featuring a reflective surface and suction cups for easy attachment, and a partially transparent material to conduct light, enhancing illumination and image quality without additional light sources, and incorporating AI for optimizing image capture parameters.
Regulatory Framework for Telemedicine Devices
The regulatory framework for telemedicine devices, including laryngoscopes used in remote medical examinations, is a complex and evolving landscape. As telemedicine continues to gain prominence, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their guidelines to ensure patient safety and efficacy of remote healthcare services.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating telemedicine devices. The FDA has established a risk-based classification system for medical devices, including those used in telemedicine. Laryngoscopes, when used in telemedicine applications, may fall under Class I or Class II depending on their specific features and intended use.
The FDA's Digital Health Center of Excellence provides guidance on software as a medical device (SaMD) and other digital health technologies, which are increasingly relevant in telemedicine applications. This guidance covers aspects such as cybersecurity, data integrity, and interoperability, all of which are critical for telemedicine devices like laryngoscopes.
In the European Union, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) govern the use of medical devices, including those used in telemedicine. These regulations emphasize post-market surveillance and clinical evidence requirements, which are particularly relevant for innovative telemedicine applications.
The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) has been working on harmonizing regulatory approaches for software as a medical device (SaMD) across different countries. This effort is particularly relevant for telemedicine devices that incorporate software components for remote diagnosis or treatment.
Regulatory bodies are also addressing the unique challenges posed by telemedicine, such as ensuring data privacy and security in remote healthcare settings. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States sets standards for protecting patient health information, which must be adhered to in telemedicine applications.
As telemedicine continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to undergo further refinement. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in telemedicine devices may require new regulatory approaches. Regulatory bodies are increasingly adopting a "regulatory sandbox" approach, allowing for controlled testing of innovative telemedicine solutions while ensuring patient safety.
The impact of these regulatory frameworks on laryngoscope utility in telemedicine is significant. Manufacturers must navigate complex approval processes and demonstrate compliance with various standards. This can potentially slow down innovation but also ensures that telemedicine devices meet high standards of safety and efficacy. As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, they will play a crucial role in shaping the future of telemedicine and its associated technologies.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating telemedicine devices. The FDA has established a risk-based classification system for medical devices, including those used in telemedicine. Laryngoscopes, when used in telemedicine applications, may fall under Class I or Class II depending on their specific features and intended use.
The FDA's Digital Health Center of Excellence provides guidance on software as a medical device (SaMD) and other digital health technologies, which are increasingly relevant in telemedicine applications. This guidance covers aspects such as cybersecurity, data integrity, and interoperability, all of which are critical for telemedicine devices like laryngoscopes.
In the European Union, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) govern the use of medical devices, including those used in telemedicine. These regulations emphasize post-market surveillance and clinical evidence requirements, which are particularly relevant for innovative telemedicine applications.
The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) has been working on harmonizing regulatory approaches for software as a medical device (SaMD) across different countries. This effort is particularly relevant for telemedicine devices that incorporate software components for remote diagnosis or treatment.
Regulatory bodies are also addressing the unique challenges posed by telemedicine, such as ensuring data privacy and security in remote healthcare settings. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States sets standards for protecting patient health information, which must be adhered to in telemedicine applications.
As telemedicine continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to undergo further refinement. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in telemedicine devices may require new regulatory approaches. Regulatory bodies are increasingly adopting a "regulatory sandbox" approach, allowing for controlled testing of innovative telemedicine solutions while ensuring patient safety.
The impact of these regulatory frameworks on laryngoscope utility in telemedicine is significant. Manufacturers must navigate complex approval processes and demonstrate compliance with various standards. This can potentially slow down innovation but also ensures that telemedicine devices meet high standards of safety and efficacy. As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, they will play a crucial role in shaping the future of telemedicine and its associated technologies.
Patient Privacy and Data Security in Tele-Laryngoscopy
The integration of telemedicine into laryngoscopy procedures has raised significant concerns regarding patient privacy and data security. As tele-laryngoscopy becomes more prevalent, healthcare providers must address the unique challenges associated with transmitting sensitive medical information over digital networks.
One of the primary concerns in tele-laryngoscopy is the protection of patient data during transmission. The visual and audio data captured during a laryngoscopy procedure contains highly sensitive personal health information. Ensuring the secure transmission of this data from the point of capture to the remote specialist is crucial. Encryption protocols and secure communication channels must be implemented to prevent unauthorized access or interception of the data in transit.
Storage of tele-laryngoscopy data presents another challenge. Healthcare organizations must establish robust data management systems that comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe. These systems should include secure cloud storage solutions, access controls, and audit trails to monitor and track data access and usage.
Patient consent and informed decision-making are critical aspects of tele-laryngoscopy privacy. Healthcare providers must develop clear protocols for obtaining and documenting patient consent for remote procedures. This includes explaining the potential risks associated with telemedicine and the measures in place to protect their privacy.
The use of remote access technologies in tele-laryngoscopy introduces additional security considerations. Healthcare organizations must implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the tele-laryngoscopy systems and patient data. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments should be conducted to identify and address potential weaknesses in the system.
Training and education for healthcare professionals on privacy and security best practices are essential. Staff members involved in tele-laryngoscopy procedures should be well-versed in data protection protocols, incident response procedures, and the proper use of telemedicine technologies.
As tele-laryngoscopy systems often involve multiple vendors and service providers, healthcare organizations must carefully vet their partners and ensure that all third-party agreements include robust data protection clauses. This includes clear delineation of responsibilities for data security and privacy compliance throughout the entire data lifecycle.
In conclusion, while tele-laryngoscopy offers significant benefits in terms of accessibility and efficiency, it also presents unique challenges in maintaining patient privacy and data security. Healthcare organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach that combines technological solutions, policy development, staff training, and ongoing risk assessment to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of patient information in this evolving landscape of telemedicine.
One of the primary concerns in tele-laryngoscopy is the protection of patient data during transmission. The visual and audio data captured during a laryngoscopy procedure contains highly sensitive personal health information. Ensuring the secure transmission of this data from the point of capture to the remote specialist is crucial. Encryption protocols and secure communication channels must be implemented to prevent unauthorized access or interception of the data in transit.
Storage of tele-laryngoscopy data presents another challenge. Healthcare organizations must establish robust data management systems that comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe. These systems should include secure cloud storage solutions, access controls, and audit trails to monitor and track data access and usage.
Patient consent and informed decision-making are critical aspects of tele-laryngoscopy privacy. Healthcare providers must develop clear protocols for obtaining and documenting patient consent for remote procedures. This includes explaining the potential risks associated with telemedicine and the measures in place to protect their privacy.
The use of remote access technologies in tele-laryngoscopy introduces additional security considerations. Healthcare organizations must implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the tele-laryngoscopy systems and patient data. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments should be conducted to identify and address potential weaknesses in the system.
Training and education for healthcare professionals on privacy and security best practices are essential. Staff members involved in tele-laryngoscopy procedures should be well-versed in data protection protocols, incident response procedures, and the proper use of telemedicine technologies.
As tele-laryngoscopy systems often involve multiple vendors and service providers, healthcare organizations must carefully vet their partners and ensure that all third-party agreements include robust data protection clauses. This includes clear delineation of responsibilities for data security and privacy compliance throughout the entire data lifecycle.
In conclusion, while tele-laryngoscopy offers significant benefits in terms of accessibility and efficiency, it also presents unique challenges in maintaining patient privacy and data security. Healthcare organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach that combines technological solutions, policy development, staff training, and ongoing risk assessment to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of patient information in this evolving landscape of telemedicine.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!