The synergy between laryngoscopes and telehealth innovations.
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Laryngoscope-Telehealth Integration Background
The integration of laryngoscopes with telehealth innovations represents a significant advancement in medical technology, combining traditional diagnostic tools with modern communication systems. This synergy has its roots in the early 2000s when telemedicine began to gain traction in healthcare delivery. Laryngoscopes, devices used to examine the larynx and vocal cords, have been a staple in medical practice for over a century. However, their integration with telehealth platforms has opened new avenues for remote diagnosis and treatment.
The evolution of this technology has been driven by the increasing demand for accessible healthcare services, particularly in rural and underserved areas. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth solutions, creating a fertile ground for innovative applications of laryngoscopy in remote settings. This convergence addresses the critical need for specialized care in locations where access to ENT specialists is limited.
Technologically, the integration has been facilitated by advancements in high-definition imaging, secure data transmission, and cloud-based storage systems. Early attempts at remote laryngoscopy were hampered by poor image quality and unreliable connectivity. However, the development of 4G and 5G networks, coupled with improvements in camera miniaturization and image processing, has significantly enhanced the feasibility of remote examinations.
The primary goal of laryngoscope-telehealth integration is to provide real-time, high-quality visualization of the larynx and surrounding structures to remote specialists. This enables accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up care without the need for in-person visits. Additionally, it aims to improve patient outcomes by reducing delays in diagnosis and treatment, particularly in emergency situations where immediate expert consultation is crucial.
From a clinical perspective, this integration supports a wide range of applications, including initial screenings, post-operative follow-ups, and ongoing management of chronic conditions affecting the throat and vocal cords. It also plays a vital role in medical education, allowing trainees to observe procedures and examinations conducted by experienced practitioners from anywhere in the world.
As this technology continues to evolve, the focus is shifting towards enhancing the user experience for both patients and healthcare providers. This includes developing more intuitive interfaces, improving the ergonomics of remote-enabled laryngoscopes, and incorporating artificial intelligence for automated image analysis and preliminary diagnostics. The ultimate vision is to create a seamless, reliable, and widely accessible platform that bridges the gap between specialized care and remote patients, revolutionizing the field of otolaryngology and beyond.
The evolution of this technology has been driven by the increasing demand for accessible healthcare services, particularly in rural and underserved areas. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth solutions, creating a fertile ground for innovative applications of laryngoscopy in remote settings. This convergence addresses the critical need for specialized care in locations where access to ENT specialists is limited.
Technologically, the integration has been facilitated by advancements in high-definition imaging, secure data transmission, and cloud-based storage systems. Early attempts at remote laryngoscopy were hampered by poor image quality and unreliable connectivity. However, the development of 4G and 5G networks, coupled with improvements in camera miniaturization and image processing, has significantly enhanced the feasibility of remote examinations.
The primary goal of laryngoscope-telehealth integration is to provide real-time, high-quality visualization of the larynx and surrounding structures to remote specialists. This enables accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up care without the need for in-person visits. Additionally, it aims to improve patient outcomes by reducing delays in diagnosis and treatment, particularly in emergency situations where immediate expert consultation is crucial.
From a clinical perspective, this integration supports a wide range of applications, including initial screenings, post-operative follow-ups, and ongoing management of chronic conditions affecting the throat and vocal cords. It also plays a vital role in medical education, allowing trainees to observe procedures and examinations conducted by experienced practitioners from anywhere in the world.
As this technology continues to evolve, the focus is shifting towards enhancing the user experience for both patients and healthcare providers. This includes developing more intuitive interfaces, improving the ergonomics of remote-enabled laryngoscopes, and incorporating artificial intelligence for automated image analysis and preliminary diagnostics. The ultimate vision is to create a seamless, reliable, and widely accessible platform that bridges the gap between specialized care and remote patients, revolutionizing the field of otolaryngology and beyond.
Telehealth Market Demand for Laryngoscopy
The telehealth market for laryngoscopy has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for remote healthcare services. This trend has been further accelerated by the global COVID-19 pandemic, which has highlighted the importance of telemedicine in providing safe and accessible healthcare.
The market demand for telehealth laryngoscopy solutions is primarily fueled by the need for improved access to specialized care, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Many regions face a shortage of otolaryngologists and other specialists capable of performing laryngoscopic examinations, leading to long wait times and delayed diagnoses. Telehealth laryngoscopy offers a solution by enabling remote consultations and examinations, reducing the need for patients to travel long distances for specialized care.
Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the benefits of telehealth laryngoscopy in terms of cost-effectiveness and efficiency. By implementing these solutions, hospitals and clinics can optimize their resources, reduce overhead costs, and increase patient throughput. This is particularly valuable in managing chronic conditions that require regular follow-ups, such as laryngeal cancer or vocal cord disorders.
The aging population in many countries is another key driver of market demand. As the prevalence of age-related voice and swallowing disorders increases, so does the need for accessible laryngoscopic examinations. Telehealth solutions offer a convenient and less intimidating option for elderly patients who may have mobility issues or prefer to avoid frequent hospital visits.
Technological advancements in laryngoscope design and imaging quality have significantly enhanced the feasibility and reliability of remote examinations. High-definition cameras, improved lighting systems, and real-time image transmission capabilities have made it possible for specialists to conduct thorough assessments remotely, with image quality comparable to in-person examinations.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into telehealth laryngoscopy platforms is opening up new possibilities for automated analysis and decision support. These technologies can assist in detecting abnormalities, tracking changes over time, and providing preliminary diagnoses, thereby enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of remote consultations.
As healthcare systems worldwide strive to improve patient outcomes while managing costs, the demand for telehealth laryngoscopy solutions is expected to continue growing. The market is likely to see further innovations in portable and user-friendly devices, as well as more sophisticated software platforms for seamless integration with existing healthcare IT systems.
The market demand for telehealth laryngoscopy solutions is primarily fueled by the need for improved access to specialized care, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Many regions face a shortage of otolaryngologists and other specialists capable of performing laryngoscopic examinations, leading to long wait times and delayed diagnoses. Telehealth laryngoscopy offers a solution by enabling remote consultations and examinations, reducing the need for patients to travel long distances for specialized care.
Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the benefits of telehealth laryngoscopy in terms of cost-effectiveness and efficiency. By implementing these solutions, hospitals and clinics can optimize their resources, reduce overhead costs, and increase patient throughput. This is particularly valuable in managing chronic conditions that require regular follow-ups, such as laryngeal cancer or vocal cord disorders.
The aging population in many countries is another key driver of market demand. As the prevalence of age-related voice and swallowing disorders increases, so does the need for accessible laryngoscopic examinations. Telehealth solutions offer a convenient and less intimidating option for elderly patients who may have mobility issues or prefer to avoid frequent hospital visits.
Technological advancements in laryngoscope design and imaging quality have significantly enhanced the feasibility and reliability of remote examinations. High-definition cameras, improved lighting systems, and real-time image transmission capabilities have made it possible for specialists to conduct thorough assessments remotely, with image quality comparable to in-person examinations.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into telehealth laryngoscopy platforms is opening up new possibilities for automated analysis and decision support. These technologies can assist in detecting abnormalities, tracking changes over time, and providing preliminary diagnoses, thereby enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of remote consultations.
As healthcare systems worldwide strive to improve patient outcomes while managing costs, the demand for telehealth laryngoscopy solutions is expected to continue growing. The market is likely to see further innovations in portable and user-friendly devices, as well as more sophisticated software platforms for seamless integration with existing healthcare IT systems.
Current Challenges in Remote Laryngoscopy
Remote laryngoscopy, while promising, faces several significant challenges in its current implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the limitation of existing telecommunication infrastructure, particularly in rural or underserved areas. The high-quality video transmission required for accurate laryngeal examination often exceeds the capabilities of standard internet connections, leading to potential misdiagnoses or delayed treatments.
Another critical challenge lies in the design and functionality of remote laryngoscopy devices. Current models often struggle to replicate the tactile feedback and precise control that physicians rely on during in-person examinations. This lack of haptic response can hinder the ability to detect subtle abnormalities or perform delicate procedures, potentially compromising patient care.
The issue of image quality and resolution also presents a significant hurdle. While advancements in camera technology have improved, the need for extremely high-resolution imaging to detect minute laryngeal changes remains a challenge. Factors such as lighting, focus, and color accuracy can significantly impact the diagnostic accuracy of remote laryngoscopy examinations.
Data security and patient privacy concerns pose another set of challenges. The transmission of sensitive medical information over networks requires robust encryption and secure data handling protocols. Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA while maintaining the efficiency of telehealth services is a complex balancing act.
The integration of remote laryngoscopy into existing healthcare systems and workflows presents logistical challenges. Many healthcare providers lack the necessary training to effectively conduct or interpret remote laryngoscopic examinations. Additionally, the absence of standardized protocols for remote laryngoscopy procedures can lead to inconsistencies in care delivery and interpretation of results.
Cost remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption of remote laryngoscopy technologies. The initial investment in equipment, software, and training can be substantial, particularly for smaller healthcare facilities or individual practitioners. This financial hurdle often slows the integration of these innovative technologies into routine clinical practice.
Lastly, there are challenges related to patient acceptance and comfort with remote laryngoscopy procedures. Some patients may feel apprehensive about the accuracy of remote examinations or may struggle with the technical aspects of participating in a telehealth session. Overcoming these psychological barriers and ensuring patient confidence in remote laryngoscopy is crucial for its successful implementation and widespread adoption.
Another critical challenge lies in the design and functionality of remote laryngoscopy devices. Current models often struggle to replicate the tactile feedback and precise control that physicians rely on during in-person examinations. This lack of haptic response can hinder the ability to detect subtle abnormalities or perform delicate procedures, potentially compromising patient care.
The issue of image quality and resolution also presents a significant hurdle. While advancements in camera technology have improved, the need for extremely high-resolution imaging to detect minute laryngeal changes remains a challenge. Factors such as lighting, focus, and color accuracy can significantly impact the diagnostic accuracy of remote laryngoscopy examinations.
Data security and patient privacy concerns pose another set of challenges. The transmission of sensitive medical information over networks requires robust encryption and secure data handling protocols. Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA while maintaining the efficiency of telehealth services is a complex balancing act.
The integration of remote laryngoscopy into existing healthcare systems and workflows presents logistical challenges. Many healthcare providers lack the necessary training to effectively conduct or interpret remote laryngoscopic examinations. Additionally, the absence of standardized protocols for remote laryngoscopy procedures can lead to inconsistencies in care delivery and interpretation of results.
Cost remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption of remote laryngoscopy technologies. The initial investment in equipment, software, and training can be substantial, particularly for smaller healthcare facilities or individual practitioners. This financial hurdle often slows the integration of these innovative technologies into routine clinical practice.
Lastly, there are challenges related to patient acceptance and comfort with remote laryngoscopy procedures. Some patients may feel apprehensive about the accuracy of remote examinations or may struggle with the technical aspects of participating in a telehealth session. Overcoming these psychological barriers and ensuring patient confidence in remote laryngoscopy is crucial for its successful implementation and widespread adoption.
Existing Laryngoscope-Telehealth Solutions
01 Design improvements for better visualization
Laryngoscopes have undergone various design improvements to enhance visualization during intubation. These include modifications to the blade shape, incorporation of fiber optic technology, and adjustable viewing angles. Such improvements aim to provide clearer views of the larynx and surrounding structures, facilitating easier and more accurate intubation procedures.- Illuminated laryngoscopes: Laryngoscopes equipped with illumination systems to improve visibility during intubation procedures. These devices typically incorporate LED or fiber optic light sources to provide clear visualization of the larynx and surrounding structures.
- Disposable laryngoscope blades: Single-use laryngoscope blades designed to reduce the risk of cross-contamination between patients. These disposable blades are often made of lightweight, cost-effective materials and can be easily attached to reusable handles.
- Video laryngoscopes: Advanced laryngoscopes incorporating small cameras and video displays to provide real-time imaging of the airway during intubation. These devices often feature adjustable screens and recording capabilities for training and documentation purposes.
- Flexible laryngoscopes: Laryngoscopes with flexible shafts or blades that can be manipulated to navigate difficult airways or accommodate patients with limited neck mobility. These devices often incorporate steering mechanisms for precise control during intubation procedures.
- Laryngoscope blade design improvements: Innovations in laryngoscope blade design to enhance performance and patient comfort. These improvements may include ergonomic shapes, specialized coatings to reduce friction, or integrated suction channels for clearing secretions during intubation.
02 Integration of video technology
Modern laryngoscopes often incorporate video technology, allowing for real-time imaging of the airway. This advancement enables medical professionals to view the intubation process on a screen, improving precision and potentially reducing the risk of complications. Video laryngoscopes may also include features such as recording capabilities for documentation and training purposes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Disposable and sterile components
To address concerns about cross-contamination and infection control, many laryngoscopes now feature disposable blades or covers. These single-use components ensure a sterile environment for each patient, reducing the risk of nosocomial infections. Some designs also incorporate easily sterilizable materials for reusable parts.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ergonomic handle designs
Laryngoscope handles have been redesigned with ergonomics in mind to improve user comfort and control during procedures. These improvements may include textured grips, balanced weight distribution, and adjustable angles. Ergonomic designs aim to reduce hand fatigue and enhance the overall ease of use for medical professionals.Expand Specific Solutions05 Illumination enhancements
Advancements in illumination technology have been incorporated into laryngoscopes to provide better visibility during intubation. This includes the use of LED lights, adjustable brightness settings, and optimized light placement. Improved illumination helps medical professionals navigate the airway more effectively, especially in challenging anatomical situations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Laryngoscope-Telehealth Industry
The synergy between laryngoscopes and telehealth innovations is at a pivotal stage of development, with the market showing significant growth potential. This convergence is driven by the increasing demand for remote healthcare solutions and advanced visualization technologies in airway management. The market is characterized by a mix of established medical device manufacturers like Medtronic (Covidien), Karl Storz, and Philips, alongside innovative startups such as Caregility and Remmie. These companies are focusing on integrating laryngoscopes with telehealth platforms, enhancing remote diagnostic capabilities and improving patient outcomes. The technology is maturing rapidly, with advancements in video laryngoscopy and AI-assisted diagnosis, indicating a shift towards more sophisticated and interconnected healthcare solutions.
Verathon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Verathon has developed the GlideScope® Video Laryngoscope system, which integrates seamlessly with telehealth platforms. This system uses high-resolution cameras and real-time video transmission to provide clear airway visualization during intubation procedures. The device can stream live video to remote experts, enabling real-time guidance and consultation during difficult intubations. Verathon has also implemented AI-assisted intubation guidance, which can help less experienced practitioners perform intubations more safely and effectively[1][3]. The company has recently introduced cloud-based data management systems that allow for the secure storage and sharing of intubation videos and patient data, facilitating remote training and quality improvement initiatives[5].
Strengths: Advanced video technology, AI-assisted guidance, and seamless telehealth integration. Weaknesses: Reliance on stable internet connectivity for remote features, potential cybersecurity concerns with cloud-based data storage.
Karl Storz SE & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Karl Storz has developed the C-MAC® video laryngoscope system with telehealth capabilities. This system features high-definition cameras and a robust telemedicine interface that allows for real-time video streaming and remote consultation. The company has also introduced the C-HUB® II, a central unit that enables seamless integration of various endoscopic devices, including laryngoscopes, with hospital information systems and telehealth platforms. Karl Storz has implemented advanced image enhancement technologies, such as CLARA and CHROMA, which improve visualization in challenging anatomical situations[2]. Additionally, they have developed software solutions for remote device control and collaborative decision-making during procedures[4].
Strengths: High-quality imaging, comprehensive integration with hospital systems, and advanced image enhancement technologies. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to traditional laryngoscopes, potential learning curve for new users.
Innovative Remote Laryngoscopy Techniques
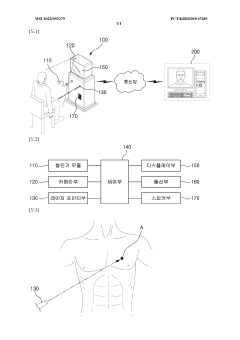
Telemedicine system using stethoscope
PatentWO2022092379A1
Innovation
- A remote medical treatment system equipped with a stethoscope module, camera unit, laser pointer unit, and control unit that allows a medical practitioner to designate the auscultation site on the patient's body using a laser pointer, ensuring the stethoscope is placed correctly, and filters auscultation sounds to isolate respiratory sounds for accurate transmission.
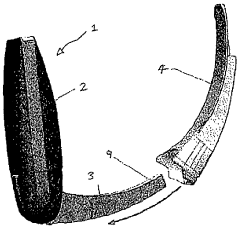
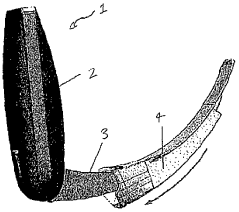
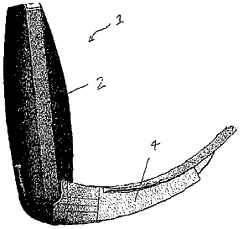
Laryngoscope
PatentInactiveAU2015218566A1
Innovation
- A laryngoscope design featuring a handle with an elongate blade holding element and interchangeable blades, including a 'difficult' blade with a distal extension and adjustable viewing means, such as prisms or movable cameras, to accommodate different intubation needs with a single device.
Regulatory Framework for Tele-Laryngoscopy
The regulatory framework for tele-laryngoscopy is a complex and evolving landscape that intersects healthcare, telecommunications, and medical device regulations. As the integration of laryngoscopes with telehealth technologies advances, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their guidelines to ensure patient safety, data privacy, and quality of care in remote laryngoscopic examinations.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating tele-laryngoscopy devices. These devices are typically classified as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) clearance. The FDA has issued specific guidance for telemedicine devices, emphasizing the importance of cybersecurity, interoperability, and clinical validation for remote use.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets stringent standards for protecting patient data in telehealth applications, including tele-laryngoscopy. Healthcare providers must ensure that all transmissions of laryngoscopic images and video are encrypted and that patient information is securely stored and accessed only by authorized personnel.
In the European Union, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) governs the use of tele-laryngoscopy equipment. The MDR places a strong emphasis on post-market surveillance and requires manufacturers to implement rigorous quality management systems. Additionally, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on the handling of patient data in telehealth applications.
Regulatory bodies are also addressing the issue of cross-border telemedicine, which is particularly relevant for tele-laryngoscopy consultations involving international expertise. The World Health Organization has provided guidelines to help countries develop their telemedicine regulations, emphasizing the need for harmonized standards to facilitate global collaboration in healthcare.
Reimbursement policies for tele-laryngoscopy services vary widely across different healthcare systems. In the United States, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has expanded coverage for telehealth services, including certain laryngoscopic procedures, particularly in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, long-term reimbursement strategies for tele-laryngoscopy are still evolving.
As artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are increasingly integrated into tele-laryngoscopy systems, regulators are grappling with how to assess and approve these advanced features. The FDA has released a proposed regulatory framework for AI/ML-based Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), which will likely impact future tele-laryngoscopy innovations.
Standardization efforts are underway to ensure interoperability and consistency in tele-laryngoscopy practices. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) are working on developing technical standards for telehealth devices and data transmission protocols specific to remote laryngoscopic examinations.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating tele-laryngoscopy devices. These devices are typically classified as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) clearance. The FDA has issued specific guidance for telemedicine devices, emphasizing the importance of cybersecurity, interoperability, and clinical validation for remote use.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets stringent standards for protecting patient data in telehealth applications, including tele-laryngoscopy. Healthcare providers must ensure that all transmissions of laryngoscopic images and video are encrypted and that patient information is securely stored and accessed only by authorized personnel.
In the European Union, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) governs the use of tele-laryngoscopy equipment. The MDR places a strong emphasis on post-market surveillance and requires manufacturers to implement rigorous quality management systems. Additionally, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on the handling of patient data in telehealth applications.
Regulatory bodies are also addressing the issue of cross-border telemedicine, which is particularly relevant for tele-laryngoscopy consultations involving international expertise. The World Health Organization has provided guidelines to help countries develop their telemedicine regulations, emphasizing the need for harmonized standards to facilitate global collaboration in healthcare.
Reimbursement policies for tele-laryngoscopy services vary widely across different healthcare systems. In the United States, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has expanded coverage for telehealth services, including certain laryngoscopic procedures, particularly in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, long-term reimbursement strategies for tele-laryngoscopy are still evolving.
As artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are increasingly integrated into tele-laryngoscopy systems, regulators are grappling with how to assess and approve these advanced features. The FDA has released a proposed regulatory framework for AI/ML-based Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), which will likely impact future tele-laryngoscopy innovations.
Standardization efforts are underway to ensure interoperability and consistency in tele-laryngoscopy practices. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) are working on developing technical standards for telehealth devices and data transmission protocols specific to remote laryngoscopic examinations.
Data Security in Remote Laryngoscopy
The integration of laryngoscopes with telehealth innovations has brought about significant advancements in remote medical examinations. However, this synergy also introduces critical data security concerns that must be addressed to ensure patient privacy and maintain the integrity of medical information.
Remote laryngoscopy involves the transmission of sensitive patient data, including high-resolution images and videos of the larynx, as well as patient identification information. This data must be protected throughout its lifecycle, from capture to transmission, storage, and analysis.
Encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding data during transmission. Advanced encryption protocols, such as AES-256, are employed to secure data as it travels across networks. Additionally, end-to-end encryption ensures that only authorized recipients can access the information, preventing interception by malicious actors.
Secure authentication mechanisms are essential to verify the identities of healthcare professionals accessing remote laryngoscopy systems. Multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and secure token-based access control systems are implemented to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive patient data.
Data storage presents another security challenge. Remote laryngoscopy systems must comply with healthcare data protection regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States. Secure cloud storage solutions with robust access controls and regular security audits are utilized to protect stored patient information.
Anonymization and pseudonymization techniques are employed to protect patient privacy when data is used for research or analysis purposes. These methods ensure that individual patients cannot be identified from the collected data, while still maintaining its scientific value.
Regular security assessments and penetration testing are conducted to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in remote laryngoscopy systems. This proactive approach helps to stay ahead of emerging threats and ensures the ongoing protection of patient data.
Training and awareness programs for healthcare professionals are crucial in maintaining data security. These programs educate users on best practices for handling sensitive information, recognizing potential security threats, and adhering to data protection protocols.
As telehealth continues to evolve, emerging technologies such as blockchain are being explored to enhance data security in remote laryngoscopy. Blockchain's decentralized and immutable nature could provide additional layers of security and traceability for patient data.
Remote laryngoscopy involves the transmission of sensitive patient data, including high-resolution images and videos of the larynx, as well as patient identification information. This data must be protected throughout its lifecycle, from capture to transmission, storage, and analysis.
Encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding data during transmission. Advanced encryption protocols, such as AES-256, are employed to secure data as it travels across networks. Additionally, end-to-end encryption ensures that only authorized recipients can access the information, preventing interception by malicious actors.
Secure authentication mechanisms are essential to verify the identities of healthcare professionals accessing remote laryngoscopy systems. Multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and secure token-based access control systems are implemented to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive patient data.
Data storage presents another security challenge. Remote laryngoscopy systems must comply with healthcare data protection regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States. Secure cloud storage solutions with robust access controls and regular security audits are utilized to protect stored patient information.
Anonymization and pseudonymization techniques are employed to protect patient privacy when data is used for research or analysis purposes. These methods ensure that individual patients cannot be identified from the collected data, while still maintaining its scientific value.
Regular security assessments and penetration testing are conducted to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in remote laryngoscopy systems. This proactive approach helps to stay ahead of emerging threats and ensures the ongoing protection of patient data.
Training and awareness programs for healthcare professionals are crucial in maintaining data security. These programs educate users on best practices for handling sensitive information, recognizing potential security threats, and adhering to data protection protocols.
As telehealth continues to evolve, emerging technologies such as blockchain are being explored to enhance data security in remote laryngoscopy. Blockchain's decentralized and immutable nature could provide additional layers of security and traceability for patient data.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!