Understanding Global LDPE Market Dynamics
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Market Overview
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in various applications, including packaging, construction, and consumer goods. The global LDPE market has experienced significant growth and evolution over the past decades, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries and regions.
The LDPE market is characterized by its cyclical nature, influenced by factors such as raw material prices, economic conditions, and technological advancements. The primary feedstock for LDPE production is ethylene, derived from petroleum or natural gas, making the market sensitive to fluctuations in oil and gas prices. This dependency on fossil fuels has led to increased interest in bio-based alternatives and recycling initiatives to address sustainability concerns.
Geographically, the LDPE market exhibits regional variations in terms of production capacity, consumption patterns, and regulatory landscapes. Asia-Pacific has emerged as a dominant player, with China leading in both production and consumption. North America and Europe remain significant markets, although growth rates have moderated compared to emerging economies. The Middle East has also become a key player, leveraging its abundant petrochemical resources to establish a strong presence in the global LDPE trade.
Market dynamics are further shaped by the ongoing consolidation within the industry, as major petrochemical companies seek to optimize their portfolios and achieve economies of scale. This trend has led to the formation of larger, more integrated players capable of weathering market volatility and investing in research and development.
The LDPE market faces both opportunities and challenges in the coming years. On the one hand, the material's excellent properties, such as flexibility, transparency, and moisture resistance, continue to drive demand in packaging applications. The growth of e-commerce and changes in consumer behavior have further boosted the need for flexible packaging solutions, benefiting LDPE producers.
On the other hand, environmental concerns and regulatory pressures pose significant challenges to the industry. The push for circular economy principles and the reduction of single-use plastics have led to increased scrutiny of LDPE usage, particularly in packaging. This has spurred innovation in recycling technologies and the development of more sustainable alternatives, including bio-based LDPE and advanced recycling processes.
The competitive landscape of the LDPE market is characterized by a mix of global petrochemical giants and regional players. Key market participants include companies such as ExxonMobil, SABIC, Dow Chemical, and LyondellBasell, among others. These companies are increasingly focusing on product differentiation, technological innovation, and sustainability initiatives to maintain their competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
The LDPE market is characterized by its cyclical nature, influenced by factors such as raw material prices, economic conditions, and technological advancements. The primary feedstock for LDPE production is ethylene, derived from petroleum or natural gas, making the market sensitive to fluctuations in oil and gas prices. This dependency on fossil fuels has led to increased interest in bio-based alternatives and recycling initiatives to address sustainability concerns.
Geographically, the LDPE market exhibits regional variations in terms of production capacity, consumption patterns, and regulatory landscapes. Asia-Pacific has emerged as a dominant player, with China leading in both production and consumption. North America and Europe remain significant markets, although growth rates have moderated compared to emerging economies. The Middle East has also become a key player, leveraging its abundant petrochemical resources to establish a strong presence in the global LDPE trade.
Market dynamics are further shaped by the ongoing consolidation within the industry, as major petrochemical companies seek to optimize their portfolios and achieve economies of scale. This trend has led to the formation of larger, more integrated players capable of weathering market volatility and investing in research and development.
The LDPE market faces both opportunities and challenges in the coming years. On the one hand, the material's excellent properties, such as flexibility, transparency, and moisture resistance, continue to drive demand in packaging applications. The growth of e-commerce and changes in consumer behavior have further boosted the need for flexible packaging solutions, benefiting LDPE producers.
On the other hand, environmental concerns and regulatory pressures pose significant challenges to the industry. The push for circular economy principles and the reduction of single-use plastics have led to increased scrutiny of LDPE usage, particularly in packaging. This has spurred innovation in recycling technologies and the development of more sustainable alternatives, including bio-based LDPE and advanced recycling processes.
The competitive landscape of the LDPE market is characterized by a mix of global petrochemical giants and regional players. Key market participants include companies such as ExxonMobil, SABIC, Dow Chemical, and LyondellBasell, among others. These companies are increasingly focusing on product differentiation, technological innovation, and sustainability initiatives to maintain their competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
Global Demand Analysis
The global demand for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) has been steadily increasing over the past decade, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. LDPE's unique properties, including flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance, make it a preferred choice in packaging, agriculture, and construction sectors.
In the packaging industry, LDPE remains a dominant material for flexible packaging solutions. The growing e-commerce sector has significantly boosted the demand for LDPE in protective packaging and shipping materials. Additionally, the food and beverage industry's expansion, particularly in emerging economies, has further fueled the need for LDPE in food packaging applications.
The agricultural sector represents another significant driver of LDPE demand. Greenhouse films, mulch films, and silage bags made from LDPE are widely used to improve crop yields and reduce water consumption. As global food demand rises and sustainable farming practices gain traction, the agricultural use of LDPE is expected to grow substantially.
Construction and infrastructure development also contribute to the increasing demand for LDPE. Its application in geomembranes for landfills, reservoirs, and canal linings has seen steady growth, especially in regions focusing on environmental protection and water conservation projects.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific leads the global LDPE market, with China and India being the major consumers. The rapid industrialization, urbanization, and population growth in these countries have led to increased demand across various end-use industries. North America and Europe, while mature markets, continue to show stable demand, primarily driven by innovations in packaging and sustainability initiatives.
However, the LDPE market faces challenges from environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The growing awareness of plastic pollution has led to stricter regulations on single-use plastics in many countries, potentially impacting LDPE demand in certain applications. This has spurred research and development efforts towards more sustainable and recyclable LDPE formulations.
The automotive industry presents an emerging opportunity for LDPE demand. As vehicle manufacturers focus on lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency, LDPE finds increasing applications in automotive interiors and under-the-hood components.
Looking ahead, the global LDPE market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, albeit at a moderated pace. Factors such as technological advancements in production processes, the development of bio-based LDPE, and the expansion of end-use industries in developing economies are likely to shape the future demand landscape for LDPE.
In the packaging industry, LDPE remains a dominant material for flexible packaging solutions. The growing e-commerce sector has significantly boosted the demand for LDPE in protective packaging and shipping materials. Additionally, the food and beverage industry's expansion, particularly in emerging economies, has further fueled the need for LDPE in food packaging applications.
The agricultural sector represents another significant driver of LDPE demand. Greenhouse films, mulch films, and silage bags made from LDPE are widely used to improve crop yields and reduce water consumption. As global food demand rises and sustainable farming practices gain traction, the agricultural use of LDPE is expected to grow substantially.
Construction and infrastructure development also contribute to the increasing demand for LDPE. Its application in geomembranes for landfills, reservoirs, and canal linings has seen steady growth, especially in regions focusing on environmental protection and water conservation projects.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific leads the global LDPE market, with China and India being the major consumers. The rapid industrialization, urbanization, and population growth in these countries have led to increased demand across various end-use industries. North America and Europe, while mature markets, continue to show stable demand, primarily driven by innovations in packaging and sustainability initiatives.
However, the LDPE market faces challenges from environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The growing awareness of plastic pollution has led to stricter regulations on single-use plastics in many countries, potentially impacting LDPE demand in certain applications. This has spurred research and development efforts towards more sustainable and recyclable LDPE formulations.
The automotive industry presents an emerging opportunity for LDPE demand. As vehicle manufacturers focus on lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency, LDPE finds increasing applications in automotive interiors and under-the-hood components.
Looking ahead, the global LDPE market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, albeit at a moderated pace. Factors such as technological advancements in production processes, the development of bio-based LDPE, and the expansion of end-use industries in developing economies are likely to shape the future demand landscape for LDPE.
Production Challenges
The production of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) faces several significant challenges that impact the global market dynamics. One of the primary issues is the high energy consumption required for the production process. LDPE manufacturing involves high-pressure polymerization, which demands substantial energy inputs, leading to increased production costs and environmental concerns.
Raw material volatility presents another major challenge. The primary feedstock for LDPE production is ethylene, derived from petroleum or natural gas. Fluctuations in oil and gas prices directly affect the cost of ethylene, creating uncertainty in production costs and potentially squeezing profit margins for manufacturers.
Capacity utilization is a critical factor in LDPE production efficiency. Many plants struggle to maintain optimal utilization rates due to various factors, including market demand fluctuations, maintenance requirements, and supply chain disruptions. Underutilization can lead to increased per-unit production costs, affecting competitiveness in the global market.
Environmental regulations pose increasing challenges for LDPE producers. Stringent emissions standards and waste management requirements necessitate significant investments in cleaner technologies and processes. This regulatory pressure is particularly acute in developed markets, potentially creating disparities in production costs across different regions.
Quality control remains a persistent challenge in LDPE production. Maintaining consistent product properties, such as melt index and density, is crucial for meeting customer specifications. Variations in raw material quality, process conditions, and equipment performance can lead to product inconsistencies, potentially resulting in rejected batches and increased costs.
Technological obsolescence is an ongoing concern for LDPE manufacturers. As newer, more efficient production technologies emerge, older plants face the challenge of remaining competitive. Upgrading existing facilities or investing in new plants requires substantial capital expenditure, which can be challenging for smaller producers or those operating in economically uncertain environments.
Supply chain management presents logistical challenges for LDPE production. Efficient transportation and storage of both raw materials and finished products are crucial for maintaining production schedules and meeting customer demands. Disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to geopolitical events, natural disasters, or transportation issues, can significantly impact production capabilities and market supply.
Lastly, the growing competition from alternative polyethylene types, such as Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), poses a strategic challenge for LDPE producers. These alternatives offer improved properties for certain applications, potentially eroding LDPE's market share in specific sectors and necessitating continuous innovation and market repositioning for LDPE manufacturers.
Raw material volatility presents another major challenge. The primary feedstock for LDPE production is ethylene, derived from petroleum or natural gas. Fluctuations in oil and gas prices directly affect the cost of ethylene, creating uncertainty in production costs and potentially squeezing profit margins for manufacturers.
Capacity utilization is a critical factor in LDPE production efficiency. Many plants struggle to maintain optimal utilization rates due to various factors, including market demand fluctuations, maintenance requirements, and supply chain disruptions. Underutilization can lead to increased per-unit production costs, affecting competitiveness in the global market.
Environmental regulations pose increasing challenges for LDPE producers. Stringent emissions standards and waste management requirements necessitate significant investments in cleaner technologies and processes. This regulatory pressure is particularly acute in developed markets, potentially creating disparities in production costs across different regions.
Quality control remains a persistent challenge in LDPE production. Maintaining consistent product properties, such as melt index and density, is crucial for meeting customer specifications. Variations in raw material quality, process conditions, and equipment performance can lead to product inconsistencies, potentially resulting in rejected batches and increased costs.
Technological obsolescence is an ongoing concern for LDPE manufacturers. As newer, more efficient production technologies emerge, older plants face the challenge of remaining competitive. Upgrading existing facilities or investing in new plants requires substantial capital expenditure, which can be challenging for smaller producers or those operating in economically uncertain environments.
Supply chain management presents logistical challenges for LDPE production. Efficient transportation and storage of both raw materials and finished products are crucial for maintaining production schedules and meeting customer demands. Disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to geopolitical events, natural disasters, or transportation issues, can significantly impact production capabilities and market supply.
Lastly, the growing competition from alternative polyethylene types, such as Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), poses a strategic challenge for LDPE producers. These alternatives offer improved properties for certain applications, potentially eroding LDPE's market share in specific sectors and necessitating continuous innovation and market repositioning for LDPE manufacturers.
Current Production Methods
01 Composition and properties of LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, low water absorption, and excellent electrical insulation properties.- Composition and properties of LDPE: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, moisture barrier properties, and processability, making it suitable for various applications.
- Manufacturing processes for LDPE: LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE. These may include modifications to reactor design, catalyst systems, and process conditions to achieve desired molecular weight distribution and branching characteristics.
- Applications of LDPE in packaging: LDPE is widely used in packaging applications due to its flexibility, transparency, and sealing properties. It is commonly employed in the production of plastic bags, food packaging films, and shrink wraps. Innovations in LDPE packaging focus on improving barrier properties, enhancing recyclability, and developing biodegradable alternatives to address environmental concerns.
- LDPE blends and composites: To enhance the performance of LDPE, it is often blended with other polymers or reinforced with various fillers and additives. These blends and composites aim to improve mechanical properties, thermal stability, or introduce specific functionalities such as flame retardancy or UV resistance. Research in this area focuses on optimizing blend ratios and developing novel compatibilization techniques.
- Recycling and sustainability of LDPE: As environmental concerns grow, there is increasing focus on the recycling and sustainability of LDPE products. Research efforts are directed towards developing efficient recycling processes, improving the quality of recycled LDPE, and exploring bio-based alternatives. Additionally, there are initiatives to reduce the environmental impact of LDPE production and enhance its biodegradability.
02 Manufacturing processes for LDPE
LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE, including the use of different catalysts, reactor designs, and process conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of LDPE
LDPE finds widespread use in various industries due to its unique properties. Common applications include packaging materials, plastic bags, containers, tubing, and agricultural films. It is also used in the production of wire and cable insulation, toys, and household items.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modifications and blends of LDPE
To enhance its properties and expand its applications, LDPE is often modified or blended with other materials. This includes the incorporation of additives, crosslinking, and blending with other polymers to improve strength, thermal stability, or specific functional properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and environmental considerations of LDPE
As a widely used plastic, the recycling and environmental impact of LDPE are important considerations. Research and development efforts focus on improving recycling processes, developing biodegradable alternatives, and reducing the environmental footprint of LDPE production and disposal.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Market Players
The global LDPE market is in a mature stage, characterized by steady growth and established players. The market size is substantial, with major petrochemical companies like Dow Global Technologies, ExxonMobil Chemical, and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp dominating the landscape. Technologically, LDPE production is well-established, but ongoing research by companies and institutions such as Zhejiang University and LG Chem Ltd. focuses on improving efficiency and developing new grades. The presence of diverse players, from global giants to regional specialists like Formosa Plastics and Sinopec, indicates a competitive and technologically advanced market with opportunities for innovation in product quality and manufacturing processes.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced catalyst systems for LDPE production, focusing on improving product quality and process efficiency. Their proprietary UNIPOL™ PE Process technology enables the production of a wide range of LDPE grades with enhanced physical properties[1]. The company has also invested in sustainable production methods, including the use of renewable feedstocks and circular economy initiatives to reduce the environmental impact of LDPE manufacturing[2]. Dow's research efforts have led to innovations in LDPE applications, such as improved packaging materials with better barrier properties and durability[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, diverse product portfolio, and focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: High capital investment requirements for new technologies and potential vulnerability to fluctuations in raw material prices.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed proprietary metallocene catalyst technology for LDPE production, allowing for precise control over polymer structure and properties[4]. Their Exceed™ XP performance polymers offer enhanced toughness, flex-crack resistance, and processability for demanding LDPE applications[5]. The company has also invested in advanced process control systems to optimize LDPE production efficiency and reduce energy consumption. ExxonMobil's research efforts have led to the development of LDPE grades with improved optical properties and seal strength for packaging applications[6].
Strengths: Advanced catalyst technology, strong global presence, and integrated supply chain. Weaknesses: Reliance on fossil fuel-based feedstocks and potential regulatory challenges related to environmental concerns.
Innovative LDPE Processes
Lldpe-LDPE blown film blend
PatentInactiveUS20130245201A1
Innovation
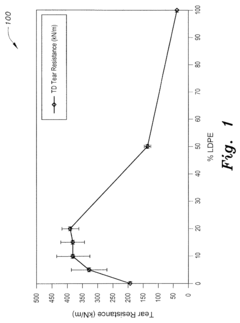
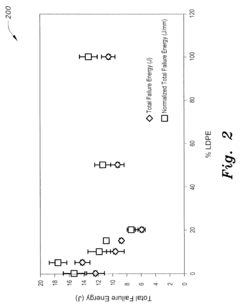
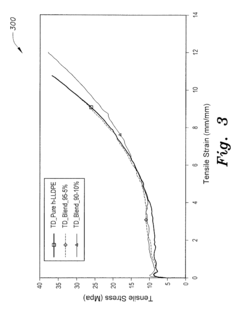
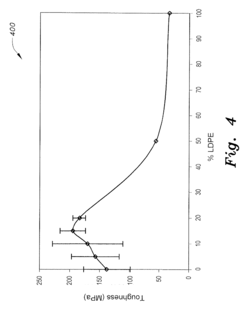
- A blown film blend of unimodal hexene-LLDPE and LDPE with a blend ratio of 2%-10% LDPE to 98%-90% h-LLDPE, which increases transverse direction tear resistance by 100%, impact failure energy by 20%, and toughness and yield strength in the machine direction, while reducing energy consumption in film production.
Composition for Odor Suppression
PatentActiveUS20220169839A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising an olefin-based polymer with 0.15 wt % to 15 wt % of an odor suppressant, including 0.05 wt % to 2 wt % of a metal oxide with a band gap greater than 5.0 eV and 0.1 wt % to 13 wt % of an acid copolymer, which synergistically reduces volatile hetero-carbonyl species without compromising processability or film properties.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the global Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) market dynamics. These regulations, aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting sustainability, have significant implications for LDPE production, consumption, and disposal practices worldwide.
In recent years, many countries have implemented stringent policies to address plastic pollution. The European Union, for instance, has introduced the Single-Use Plastics Directive, which bans certain single-use plastic items and sets targets for recycling and reuse. This directive has led to increased pressure on LDPE manufacturers to develop more sustainable alternatives and improve recycling capabilities.
Similarly, China's National Sword Policy, implemented in 2018, has dramatically altered the global plastic waste trade. This policy restricts the import of plastic waste, forcing many countries to reassess their plastic waste management strategies. As a result, there is growing emphasis on domestic recycling and circular economy initiatives, which directly impact LDPE demand and production patterns.
The United States has also seen increased regulatory activity at both federal and state levels. Several states have implemented plastic bag bans or fees, while others are considering extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws for plastic packaging. These regulations are driving innovation in LDPE alternatives and recycling technologies.
In developing economies, environmental regulations are evolving rapidly. India, for example, has pledged to phase out single-use plastics by 2022, which is expected to significantly impact LDPE consumption in the region. Similarly, many African countries are implementing plastic bag bans, reflecting a global trend towards stricter plastic regulations.
The impact of these environmental regulations on the LDPE market is multifaceted. On one hand, they create challenges for traditional LDPE producers, potentially reducing demand in certain applications. On the other hand, they drive innovation in bio-based and recyclable LDPE alternatives, opening new market opportunities.
Moreover, these regulations are accelerating the development of advanced recycling technologies. Chemical recycling, for instance, is gaining traction as a method to break down LDPE into its chemical components, allowing for the production of virgin-quality recycled plastics. This technological advancement could potentially reshape the LDPE supply chain and market dynamics.
In response to these regulatory pressures, many LDPE producers are adopting sustainability strategies. These include increasing the use of recycled content in their products, investing in bio-based LDPE production, and participating in industry-wide initiatives to improve plastic waste collection and recycling infrastructure.
In recent years, many countries have implemented stringent policies to address plastic pollution. The European Union, for instance, has introduced the Single-Use Plastics Directive, which bans certain single-use plastic items and sets targets for recycling and reuse. This directive has led to increased pressure on LDPE manufacturers to develop more sustainable alternatives and improve recycling capabilities.
Similarly, China's National Sword Policy, implemented in 2018, has dramatically altered the global plastic waste trade. This policy restricts the import of plastic waste, forcing many countries to reassess their plastic waste management strategies. As a result, there is growing emphasis on domestic recycling and circular economy initiatives, which directly impact LDPE demand and production patterns.
The United States has also seen increased regulatory activity at both federal and state levels. Several states have implemented plastic bag bans or fees, while others are considering extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws for plastic packaging. These regulations are driving innovation in LDPE alternatives and recycling technologies.
In developing economies, environmental regulations are evolving rapidly. India, for example, has pledged to phase out single-use plastics by 2022, which is expected to significantly impact LDPE consumption in the region. Similarly, many African countries are implementing plastic bag bans, reflecting a global trend towards stricter plastic regulations.
The impact of these environmental regulations on the LDPE market is multifaceted. On one hand, they create challenges for traditional LDPE producers, potentially reducing demand in certain applications. On the other hand, they drive innovation in bio-based and recyclable LDPE alternatives, opening new market opportunities.
Moreover, these regulations are accelerating the development of advanced recycling technologies. Chemical recycling, for instance, is gaining traction as a method to break down LDPE into its chemical components, allowing for the production of virgin-quality recycled plastics. This technological advancement could potentially reshape the LDPE supply chain and market dynamics.
In response to these regulatory pressures, many LDPE producers are adopting sustainability strategies. These include increasing the use of recycled content in their products, investing in bio-based LDPE production, and participating in industry-wide initiatives to improve plastic waste collection and recycling infrastructure.
Trade Policy Impacts
Trade policies play a significant role in shaping the global Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) market dynamics. These policies, including tariffs, quotas, and trade agreements, can have far-reaching effects on the production, distribution, and consumption of LDPE across different regions. The impact of trade policies on the LDPE market is multifaceted and can lead to shifts in market competitiveness, supply chain restructuring, and price fluctuations.
One of the primary ways trade policies affect the LDPE market is through the imposition of tariffs. When countries implement tariffs on LDPE imports, it can lead to increased costs for manufacturers and consumers in the importing country. This, in turn, may stimulate domestic production but potentially at higher costs. Conversely, exporting countries may face reduced demand for their LDPE products, leading to oversupply and potential price pressures in their domestic markets.
Trade agreements and free trade zones can significantly influence LDPE market dynamics by creating preferential access to certain markets. For instance, regional trade agreements like NAFTA (now USMCA) have facilitated the flow of LDPE between North American countries, fostering regional integration in the petrochemical industry. Similarly, the European Union's single market has allowed for seamless trade of LDPE among member states, promoting efficiency and competition within the bloc.
Export restrictions and quotas implemented by major LDPE-producing countries can also have substantial impacts on global supply chains. Such policies may be implemented to protect domestic industries or in response to geopolitical tensions. These restrictions can lead to supply shortages in importing countries, driving up prices and potentially spurring investments in alternative sources or materials.
The global nature of the LDPE market means that trade disputes between major economies can have ripple effects throughout the industry. For example, trade tensions between the United States and China have led to shifts in LDPE trade flows, with Chinese buyers seeking alternative suppliers and U.S. producers exploring new export markets. Such geopolitical factors can introduce uncertainty and volatility into the LDPE market, affecting investment decisions and long-term strategic planning for industry participants.
Furthermore, trade policies intersect with environmental regulations, particularly in the context of plastic waste management. Restrictions on the import of plastic waste by countries like China have forced exporting nations to reconsider their recycling and waste management strategies, potentially impacting the demand for virgin LDPE and driving innovation in recycling technologies.
One of the primary ways trade policies affect the LDPE market is through the imposition of tariffs. When countries implement tariffs on LDPE imports, it can lead to increased costs for manufacturers and consumers in the importing country. This, in turn, may stimulate domestic production but potentially at higher costs. Conversely, exporting countries may face reduced demand for their LDPE products, leading to oversupply and potential price pressures in their domestic markets.
Trade agreements and free trade zones can significantly influence LDPE market dynamics by creating preferential access to certain markets. For instance, regional trade agreements like NAFTA (now USMCA) have facilitated the flow of LDPE between North American countries, fostering regional integration in the petrochemical industry. Similarly, the European Union's single market has allowed for seamless trade of LDPE among member states, promoting efficiency and competition within the bloc.
Export restrictions and quotas implemented by major LDPE-producing countries can also have substantial impacts on global supply chains. Such policies may be implemented to protect domestic industries or in response to geopolitical tensions. These restrictions can lead to supply shortages in importing countries, driving up prices and potentially spurring investments in alternative sources or materials.
The global nature of the LDPE market means that trade disputes between major economies can have ripple effects throughout the industry. For example, trade tensions between the United States and China have led to shifts in LDPE trade flows, with Chinese buyers seeking alternative suppliers and U.S. producers exploring new export markets. Such geopolitical factors can introduce uncertainty and volatility into the LDPE market, affecting investment decisions and long-term strategic planning for industry participants.
Furthermore, trade policies intersect with environmental regulations, particularly in the context of plastic waste management. Restrictions on the import of plastic waste by countries like China have forced exporting nations to reconsider their recycling and waste management strategies, potentially impacting the demand for virgin LDPE and driving innovation in recycling technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!