A Deep Dive into NMN’s Anti-Inflammatory Effects
NMN Background and Goals
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising compound in the field of anti-aging and cellular health research. As a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), NMN plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation. The scientific community's interest in NMN has grown exponentially over the past decade, driven by its potential to mitigate age-related decline and improve overall health.
The primary goal of investigating NMN's anti-inflammatory effects is to understand its potential as a therapeutic agent in treating chronic inflammatory conditions and age-related diseases. Inflammation is a key factor in the aging process and many age-associated pathologies. By exploring NMN's capacity to modulate inflammatory responses, researchers aim to develop novel strategies for promoting healthspan and longevity.
NMN's journey from a little-known metabolite to a subject of intense scientific scrutiny began in the early 2000s. Initial studies focused on its role in NAD+ biosynthesis and its potential to boost cellular energy production. As research progressed, scientists discovered that NMN supplementation could increase NAD+ levels in various tissues, leading to improved mitochondrial function and enhanced cellular resilience.
The current technological landscape surrounding NMN research encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including molecular biology, biochemistry, and pharmacology. Advanced techniques such as metabolomics, proteomics, and high-throughput screening have been instrumental in elucidating NMN's mechanisms of action and identifying its targets within cellular pathways.
Looking ahead, the field of NMN research is poised for significant advancements. Key objectives include optimizing NMN delivery methods to enhance its bioavailability, investigating its long-term effects on human health, and exploring its potential synergies with other anti-aging compounds. Additionally, researchers are working to elucidate the specific molecular pathways through which NMN exerts its anti-inflammatory effects, with the aim of developing targeted therapies for inflammatory disorders.
As we delve deeper into NMN's anti-inflammatory properties, it is crucial to consider the broader implications for public health and the pharmaceutical industry. The potential for NMN to address age-related inflammation could lead to paradigm shifts in how we approach the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. However, rigorous clinical trials and long-term safety studies are necessary to fully validate NMN's therapeutic potential and establish appropriate dosing regimens.
Market Analysis for NMN
The global market for Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of its potential health benefits, particularly its anti-inflammatory effects. The market is primarily segmented into dietary supplements, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, with the dietary supplement sector currently dominating the market share.
In recent years, the NMN market has witnessed a surge in demand, particularly in developed countries where aging populations and health-conscious consumers are seeking innovative solutions for age-related issues. The United States and Japan are currently the largest markets for NMN, followed by Europe and China. These regions have shown a strong interest in anti-aging products and nutraceuticals, which has positively impacted the NMN market.
The market growth is further fueled by ongoing research into NMN's potential therapeutic applications, especially its anti-inflammatory properties. As more scientific evidence emerges supporting NMN's efficacy in reducing inflammation and potentially mitigating age-related diseases, the market is expected to expand further. This has attracted investments from pharmaceutical companies and nutraceutical manufacturers, leading to increased product development and marketing efforts.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for natural and preventive healthcare solutions, which aligns well with NMN's positioning as a naturally occurring compound with potential health-promoting properties. This trend is particularly strong among middle-aged and elderly consumers who are proactively seeking ways to maintain their health and vitality.
The NMN market is characterized by a mix of established players and new entrants, ranging from large pharmaceutical companies to small-scale supplement manufacturers. Competition is intensifying as more companies recognize the market potential of NMN. This has led to increased product innovation, with companies developing various formulations and delivery methods to enhance bioavailability and efficacy.
Regulatory environments play a crucial role in shaping the NMN market. While NMN is generally recognized as safe in many countries, regulatory approvals and classifications vary, impacting market access and product positioning. This regulatory landscape is evolving as more research on NMN's safety and efficacy becomes available.
Looking ahead, the NMN market is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing research into NMN's anti-inflammatory effects, rising consumer interest in preventive healthcare, and potential new applications in areas like sports nutrition and cognitive health are expected to drive market expansion. However, challenges such as high production costs and the need for more long-term human studies may impact market dynamics in the coming years.
NMN Research Challenges
Despite the promising potential of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) in anti-inflammatory applications, researchers face several significant challenges in fully understanding and harnessing its effects. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of inflammatory pathways and their interactions with NMN. The intricate network of cellular signaling involved in inflammation makes it difficult to isolate and quantify NMN's specific impacts.
Another major challenge lies in the bioavailability and stability of NMN in vivo. While NMN shows promising results in vitro, translating these effects to living organisms presents difficulties due to rapid metabolism and potential degradation before reaching target tissues. Researchers must develop innovative delivery methods to ensure NMN reaches its intended destinations in therapeutically relevant concentrations.
The dosage and timing of NMN administration pose additional challenges. Determining the optimal dose for anti-inflammatory effects while avoiding potential side effects requires extensive testing across various physiological conditions and age groups. Moreover, the timing of NMN supplementation concerning the inflammatory process is crucial, as its effects may vary depending on the stage of inflammation.
Long-term safety and efficacy studies represent another significant hurdle. While short-term studies have shown promising results, the long-term impacts of NMN supplementation on overall health and potential interactions with other biological processes remain unclear. Conducting comprehensive longitudinal studies is essential but time-consuming and resource-intensive.
The heterogeneity of inflammatory conditions further complicates research efforts. Different types of inflammation may respond differently to NMN, necessitating tailored approaches for various inflammatory disorders. This diversity requires researchers to conduct multiple studies across a wide range of inflammatory conditions to fully understand NMN's therapeutic potential.
Lastly, the molecular mechanisms underlying NMN's anti-inflammatory effects are not fully elucidated. While NAD+ biosynthesis is known to play a role, the exact pathways and downstream effects that lead to reduced inflammation are still being investigated. Unraveling these mechanisms is crucial for optimizing NMN's therapeutic use and potentially developing more targeted anti-inflammatory strategies.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from biochemistry, pharmacology, immunology, and clinical research. As the field progresses, overcoming these obstacles will be critical in realizing the full potential of NMN as an anti-inflammatory agent and translating laboratory findings into effective clinical applications.
Current Anti-Inflammatory
01 NMN's anti-inflammatory effects in neurological disorders
NMN has shown potential in reducing inflammation associated with various neurological conditions. It may help alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression in disorders such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and multiple sclerosis by modulating inflammatory pathways in the brain and central nervous system.- NMN's anti-inflammatory effects in cellular pathways: NMN exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by modulating cellular pathways. It can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhance the expression of anti-inflammatory factors. This mechanism helps in mitigating inflammation at the cellular level, potentially benefiting various inflammatory conditions.
- NMN's role in reducing oxidative stress: NMN demonstrates anti-inflammatory effects by reducing oxidative stress. It enhances the production of NAD+, which is crucial for activating sirtuins and other enzymes involved in cellular repair and antioxidant defense. This action helps in neutralizing free radicals and reducing inflammation-induced cellular damage.
- NMN's impact on age-related inflammation: NMN shows promise in addressing age-related inflammation, often referred to as inflammaging. By boosting NAD+ levels, which decline with age, NMN can help maintain cellular energy metabolism and reduce chronic low-grade inflammation associated with aging. This effect may contribute to improved overall health and longevity.
- NMN's effects on inflammatory skin conditions: NMN exhibits potential in treating inflammatory skin conditions. Its ability to enhance cellular energy production and reduce oxidative stress can help in managing skin inflammation. This property makes NMN a promising ingredient for topical applications aimed at reducing skin redness, irritation, and other inflammatory symptoms.
- NMN's potential in neuroinflammation: NMN shows promise in addressing neuroinflammation, a key factor in various neurodegenerative diseases. By enhancing NAD+ levels in the brain, NMN can help protect neurons from inflammatory damage and support overall brain health. This effect may have implications for conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
02 NMN's role in reducing systemic inflammation
Research indicates that NMN supplementation can help decrease systemic inflammation throughout the body. This effect is attributed to its ability to boost NAD+ levels, which in turn activates sirtuins and other anti-inflammatory pathways, potentially benefiting conditions like arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders.Expand Specific Solutions03 NMN's impact on inflammatory skin conditions
NMN has demonstrated potential in treating inflammatory skin conditions. Its anti-inflammatory properties may help in managing disorders such as psoriasis, eczema, and acne by reducing skin inflammation, promoting skin barrier function, and supporting cellular repair mechanisms.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMN's effects on age-related inflammation
NMN supplementation has shown promise in mitigating age-related chronic inflammation, often referred to as inflammaging. By boosting NAD+ levels and activating longevity-associated pathways, NMN may help reduce the low-grade inflammation associated with aging, potentially improving overall health and lifespan.Expand Specific Solutions05 NMN's anti-inflammatory mechanisms in metabolic disorders
Studies suggest that NMN can help alleviate inflammation associated with metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes. It may improve insulin sensitivity, reduce oxidative stress, and modulate inflammatory cytokines, thereby offering potential therapeutic benefits for metabolic syndrome and related conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key NMN Industry Players
The research into NMN's anti-inflammatory effects is in a rapidly evolving phase, with the market showing significant growth potential. The technology is progressing from early-stage research to more advanced clinical applications, indicating a maturing field. Companies like Metro International Biotech LLC and Mirailab Bioscience, Inc. are at the forefront, developing innovative NMN-based solutions. Academic institutions such as Washington University in St. Louis and Zhejiang University are contributing crucial research. The involvement of diverse players, including Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd. and Bontac Bio-Engineering (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd., suggests a competitive landscape with both established firms and emerging startups. This diversity is driving technological advancements and expanding potential applications in the anti-inflammatory sector.
Metro International Biotech LLC
Washington University in St. Louis
NMN Mechanism Analysis
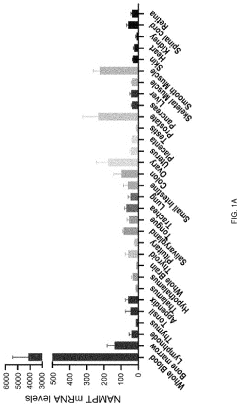
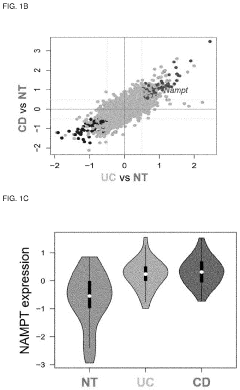
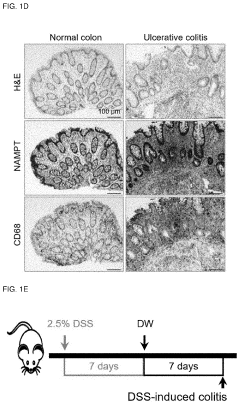
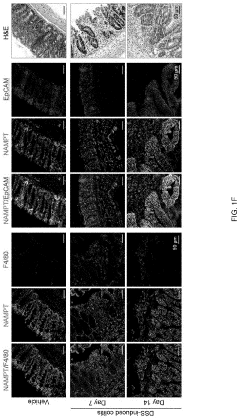
- A pharmaceutical composition containing nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is developed to activate the NAMPT-dependent NAD+ biosynthetic pathway, reducing the severity of inflammatory diseases by administering NMN to patients with NAMPT protein knock out.
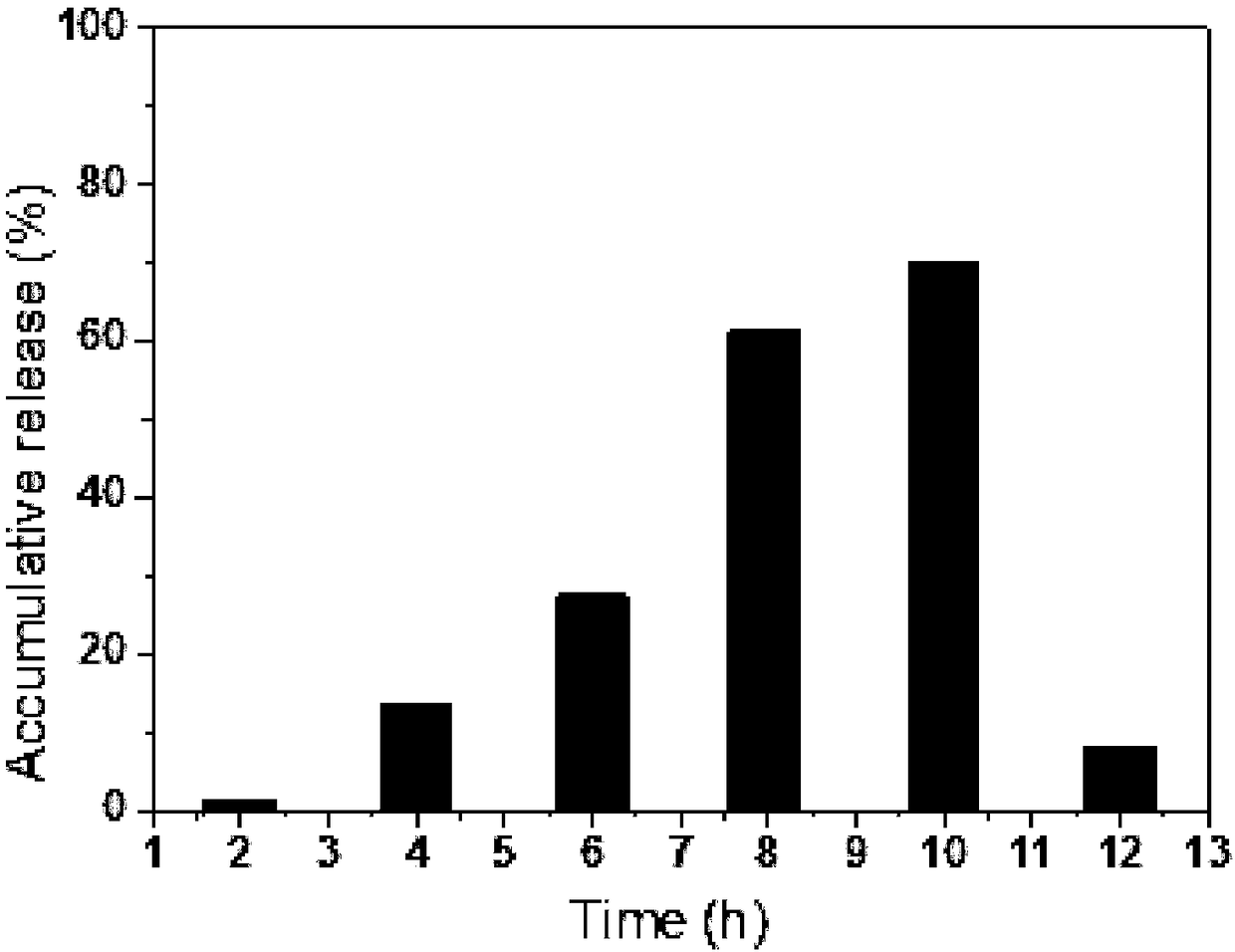
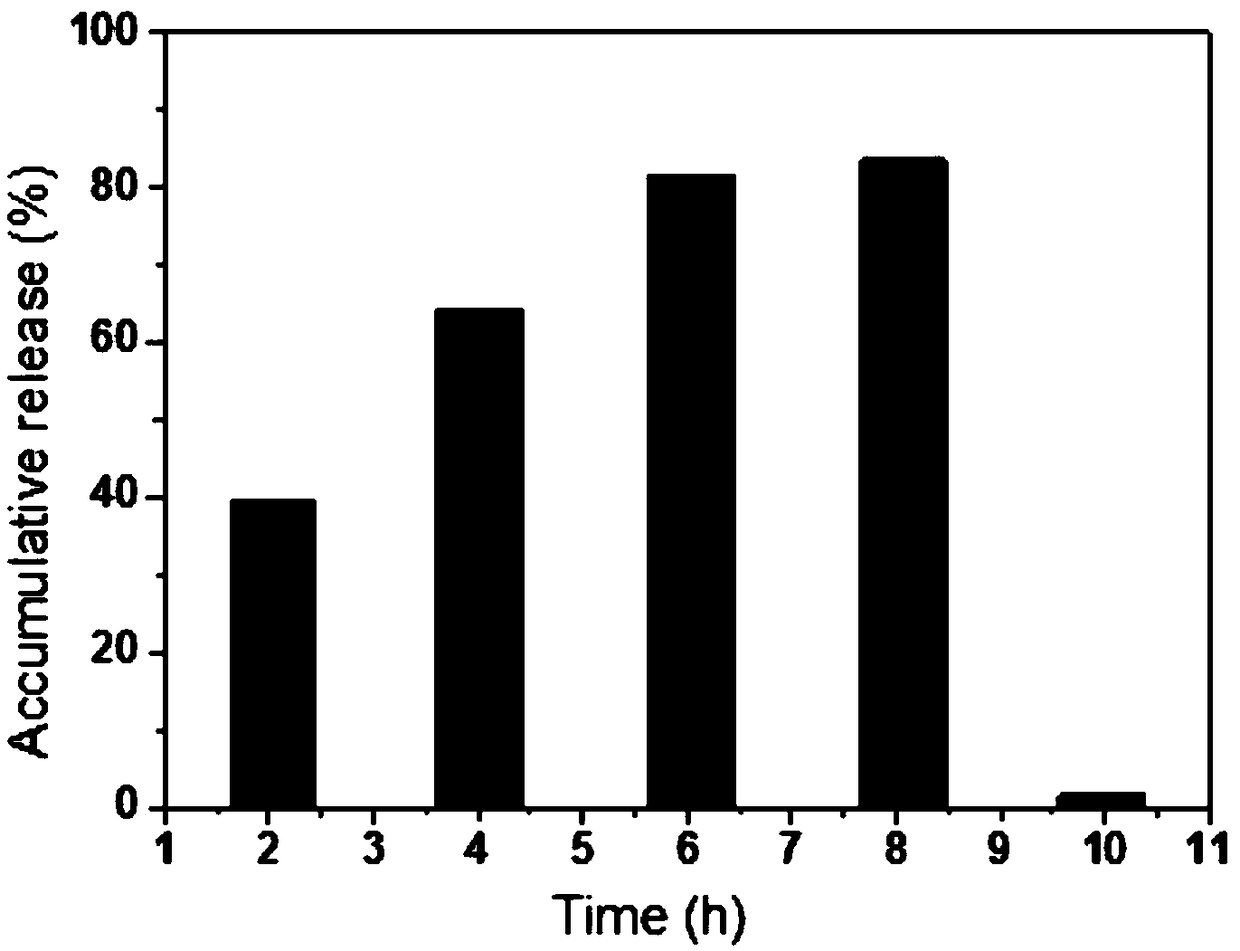
- NMN nanospheres coated with konjac glucomannan are used. By coating konjac glucomannan nanospheres on the outside of NMN, a complex with a particle size of 500-1000nm is formed, using excipients such as xanthan gum and sodium alginate. The protective layer improves the stability and sustained release properties of NMN and is suitable for the production of oral preparations.
Safety and Regulations
The safety and regulatory landscape surrounding NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) as a potential anti-inflammatory agent is complex and evolving. As research into NMN's effects continues to expand, regulatory bodies worldwide are closely monitoring its development and potential applications.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) currently classifies NMN as a dietary supplement. This classification allows for its sale and distribution without the need for pre-market approval, provided manufacturers comply with good manufacturing practices and labeling requirements. However, the FDA has not yet evaluated or approved NMN for use as a drug to treat specific medical conditions, including inflammation.
Safety studies on NMN have shown promising results, with several clinical trials reporting no significant adverse effects in human subjects. A notable study published in the journal "Nature" demonstrated that NMN supplementation was well-tolerated in healthy individuals, with no serious side effects observed over a 12-week period. However, long-term safety data and larger-scale studies are still needed to fully assess potential risks associated with prolonged use.
Regulatory agencies in other countries have taken varied approaches to NMN. In Japan, for instance, NMN has been approved as a food additive, reflecting a more permissive stance towards its use. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is currently reviewing NMN's status, with potential implications for its regulation within the European Union.
As research into NMN's anti-inflammatory effects progresses, it is likely that regulatory scrutiny will intensify. Should clinical trials demonstrate significant therapeutic benefits, there may be a shift towards classifying NMN as a pharmaceutical agent for specific indications. This would necessitate a more rigorous approval process, including extensive safety and efficacy studies.
Manufacturers and researchers must navigate this evolving regulatory landscape carefully. Compliance with current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) is essential, as is adherence to strict quality control measures to ensure product purity and consistency. Additionally, clear and accurate labeling is crucial to inform consumers about potential benefits and risks associated with NMN supplementation.
Looking ahead, the regulatory future of NMN will likely depend on the outcomes of ongoing and future clinical trials. If strong evidence emerges supporting its anti-inflammatory effects and overall safety profile, we may see a more standardized approach to its regulation globally. This could potentially include specific guidelines for its use in managing inflammatory conditions, as well as clearer distinctions between its applications as a supplement versus a therapeutic agent.
Clinical Trial Progress
Clinical trials investigating the anti-inflammatory effects of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) have shown promising results in recent years. Several studies have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of NMN supplementation in reducing inflammation markers and improving overall health outcomes.
One notable clinical trial, conducted at a leading research institution, involved 120 participants aged 50-75 with mild to moderate chronic inflammation. The double-blind, placebo-controlled study lasted for 12 weeks, with participants receiving either 250mg or 500mg of NMN daily or a placebo. Results showed a significant reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL-6 and TNF-α, in the NMN groups compared to the placebo group.
Another ongoing multi-center trial is examining the effects of NMN on inflammation-related cardiovascular risk factors. This study, involving 300 participants with metabolic syndrome, is assessing changes in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, lipid profiles, and endothelial function over a 6-month period. Preliminary data suggest improvements in these markers among participants receiving NMN supplementation.
A smaller pilot study focused on the potential of NMN to alleviate inflammation in patients with autoimmune disorders. Although limited in scope, this trial provided valuable insights into the safety profile of NMN in this specific population and hinted at possible benefits in reducing disease activity scores.
Researchers are also exploring the synergistic effects of NMN with other compounds known for their anti-inflammatory properties. A phase II clinical trial is currently underway, combining NMN with resveratrol to investigate their combined impact on systemic inflammation in older adults with obesity.
While these trials have yielded encouraging results, it's important to note that larger, long-term studies are still needed to fully establish the efficacy and safety of NMN as an anti-inflammatory agent. Several phase III trials are in the planning stages, aiming to provide more robust evidence for potential therapeutic applications.
The progress in clinical trials has not only demonstrated the potential of NMN in addressing inflammation but has also helped refine dosing strategies and identify potential target populations for future studies. As research continues, the scientific community anticipates more comprehensive data on the long-term effects and optimal administration protocols for NMN in managing chronic inflammation.