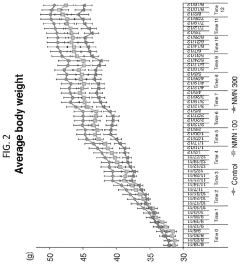
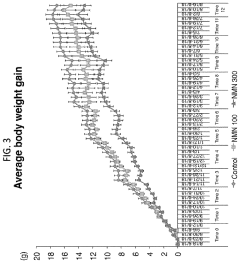
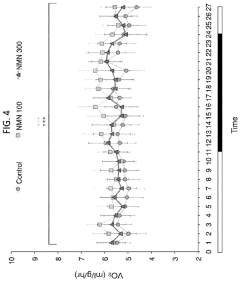
NMN in Obesity Management: Efficacy Studies
NMN and Obesity: Background and Objectives
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising compound in the field of metabolic health, particularly in the context of obesity management. As a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), NMN plays a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism and has garnered significant attention for its potential to mitigate age-related metabolic decline.
The global obesity epidemic has reached alarming proportions, with over 650 million adults classified as obese worldwide. This health crisis has spurred intense research into novel therapeutic approaches, with NMN supplementation representing a cutting-edge avenue of investigation. The primary objective of exploring NMN in obesity management is to harness its metabolic-enhancing properties to combat weight gain, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall metabolic health.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in scientific interest regarding NMN's efficacy in addressing obesity-related complications. Preclinical studies have demonstrated promising results, showing that NMN supplementation can increase NAD+ levels, enhance mitochondrial function, and improve glucose tolerance in animal models of obesity. These findings have paved the way for human clinical trials, which aim to translate these benefits to real-world applications in obesity management.
The technological evolution of NMN production and delivery methods has been a key factor in advancing research in this field. Improved synthesis techniques have made it possible to produce high-purity NMN at scale, facilitating more extensive and rigorous studies. Additionally, innovative formulations and delivery systems are being developed to enhance NMN's bioavailability and efficacy in human subjects.
As research progresses, the scientific community is focusing on several critical objectives. These include determining optimal dosing regimens for NMN supplementation in obese individuals, investigating potential synergistic effects with other compounds or lifestyle interventions, and elucidating the long-term safety profile of NMN administration. Furthermore, researchers are exploring the molecular mechanisms by which NMN influences adipose tissue metabolism, energy expenditure, and appetite regulation.
The intersection of NMN research and obesity management represents a convergence of multiple scientific disciplines, including biochemistry, endocrinology, and nutritional science. This multidisciplinary approach is essential for comprehensively addressing the complex nature of obesity and developing targeted interventions that leverage NMN's metabolic benefits.
Market Analysis for NMN-based Obesity Solutions
The market for NMN-based obesity solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing global obesity rates and a growing consumer interest in health and wellness products. The obesity management market, valued at approximately $2.4 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3%. Within this broader market, NMN-based solutions are carving out a niche, appealing to consumers seeking innovative, science-backed approaches to weight management.
The demand for NMN-based obesity solutions is primarily fueled by the rising prevalence of obesity worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, global obesity rates have nearly tripled since 1975, with over 1.9 billion adults classified as overweight or obese in 2016. This alarming trend has created a substantial market opportunity for effective weight management solutions, including those based on NMN.
Consumer awareness and interest in NMN as a potential obesity management tool have been growing steadily. This is partly due to increased media coverage and scientific research highlighting the potential benefits of NMN in metabolic health and weight management. The global NMN supplement market, which includes obesity management applications, was valued at $253 million in 2020 and is expected to reach $386 million by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.3%.
The target demographic for NMN-based obesity solutions primarily consists of middle-aged and older adults, as NMN's potential anti-aging properties align well with this group's health concerns. However, there is also growing interest among younger health-conscious consumers looking for preventive measures against obesity and related metabolic disorders.
Geographically, North America and Asia-Pacific regions are the largest markets for NMN-based obesity solutions. The United States leads in market share, driven by high obesity rates and a strong consumer appetite for dietary supplements. Japan and China are also significant markets, with a cultural emphasis on longevity and wellness contributing to the demand for NMN products.
The competitive landscape for NMN-based obesity solutions is becoming increasingly crowded, with both established nutraceutical companies and startups entering the market. Key players are focusing on product differentiation through formulation improvements, clinical studies, and marketing strategies emphasizing the scientific basis of NMN's efficacy in weight management.
Current Challenges in NMN Obesity Research
Despite the promising potential of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) in obesity management, researchers face several significant challenges in conducting efficacy studies. One primary obstacle is the lack of standardized dosing protocols for NMN supplementation in humans. Current studies utilize varying doses, making it difficult to establish optimal therapeutic levels for obesity treatment.
Another challenge lies in the limited understanding of NMN's long-term effects on metabolic health. While short-term studies have shown positive outcomes, the sustained impact of NMN supplementation on weight management and related metabolic parameters remains unclear. This gap in knowledge necessitates extended clinical trials, which are both time-consuming and resource-intensive.
The bioavailability and stability of NMN pose additional hurdles. NMN is rapidly metabolized in the body, and its absorption can vary significantly between individuals. Researchers struggle to develop effective delivery methods that ensure consistent and adequate NMN levels reach target tissues, particularly in the context of obesity where metabolic alterations may affect drug absorption and distribution.
Heterogeneity in obesity phenotypes further complicates NMN research. Obesity is a multifactorial condition with diverse underlying causes, and the efficacy of NMN may vary depending on individual metabolic profiles, genetic factors, and lifestyle variables. This diversity makes it challenging to design studies that can accurately assess NMN's effectiveness across different obesity subtypes.
The placebo effect and lifestyle confounders present additional challenges in NMN obesity research. Given the heightened awareness of health and wellness, participants in NMN studies may inadvertently alter their behaviors, potentially skewing results. Controlling for these factors while maintaining ecological validity is a delicate balance that researchers must strike.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding NMN as a potential therapeutic agent for obesity is complex and evolving. The classification of NMN as a dietary supplement in some regions and a drug candidate in others creates inconsistencies in research protocols and regulatory requirements. This variability hampers the standardization of clinical trials and complicates the translation of research findings into clinical practice.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including the development of more sensitive biomarkers for NMN efficacy, improved study designs that account for individual variability, and collaborative efforts to establish standardized research protocols. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial in advancing our understanding of NMN's potential in obesity management and realizing its therapeutic promise.
Existing NMN-based Obesity Treatment Approaches
01 Anti-aging effects of NMN
NMN has shown promising anti-aging effects by increasing NAD+ levels in the body. It may help improve cellular energy production, enhance DNA repair, and promote longevity. Studies have demonstrated potential benefits in reducing age-related decline in various physiological functions.- Anti-aging effects of NMN: NMN has shown potential in combating age-related decline by boosting NAD+ levels in the body. Research indicates that NMN supplementation may improve cellular energy production, enhance DNA repair, and promote longevity. Studies have demonstrated positive effects on various age-related biomarkers and physiological functions.
- Metabolic health improvements: NMN supplementation has been associated with improvements in metabolic health. Studies suggest that it may enhance insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, and lipid metabolism. These effects could potentially benefit individuals with metabolic disorders or those at risk of developing such conditions.
- Cardiovascular health benefits: Research indicates that NMN may have positive effects on cardiovascular health. Studies have shown improvements in vascular function, blood flow, and cardiac performance with NMN supplementation. These findings suggest potential applications in preventing or managing cardiovascular diseases.
- Neuroprotective properties: NMN has demonstrated neuroprotective effects in various studies. It may help maintain cognitive function, protect against neurodegenerative diseases, and support brain health. Research suggests potential applications in conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and other age-related cognitive decline.
- Enhanced physical performance and muscle function: Studies have shown that NMN supplementation may improve physical performance and muscle function. It has been associated with increased endurance, enhanced muscle strength, and improved recovery from exercise. These effects could be beneficial for athletes and individuals looking to maintain physical fitness as they age.
02 Metabolic health improvements
NMN supplementation has been associated with improvements in metabolic health. Research indicates potential benefits in glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and lipid profiles. It may help in managing obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders by enhancing mitochondrial function and energy metabolism.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cardiovascular health benefits
Studies suggest that NMN may have positive effects on cardiovascular health. It has been shown to improve vascular function, reduce oxidative stress, and potentially protect against heart diseases. NMN may help maintain healthy blood pressure and support overall heart function.Expand Specific Solutions04 Neuroprotective properties
NMN has demonstrated neuroprotective properties in various studies. It may help improve cognitive function, protect against neurodegenerative diseases, and support brain health. Research suggests potential benefits in memory enhancement, neuroplasticity, and reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enhanced physical performance and muscle function
NMN supplementation has been linked to improvements in physical performance and muscle function. Studies indicate potential benefits in increasing endurance, reducing fatigue, and supporting muscle strength and recovery. It may also help in maintaining muscle mass during aging.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in NMN and Obesity Research
The research on NMN in obesity management is in its early stages, with the market showing significant growth potential. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies, indicating a balance between basic research and commercial development. Key players like Washington University in St. Louis, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., and AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP are at the forefront, suggesting a high level of interest from both academia and industry. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with ongoing efficacy studies and clinical trials. The involvement of diverse entities, including universities, biotech firms, and established pharmaceutical companies, points to a dynamic and competitive field with substantial investment in research and development.
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Merck & Co., Inc.
Critical NMN Efficacy Studies in Obesity Management
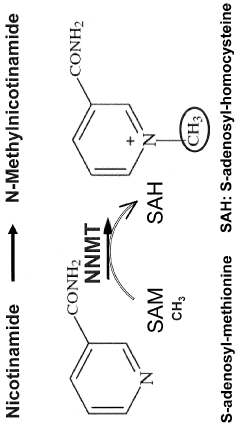
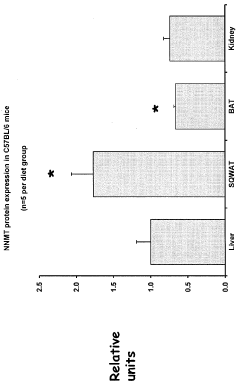
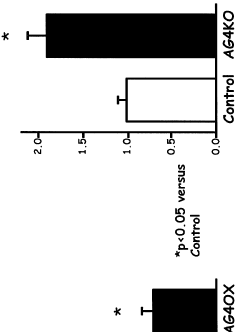
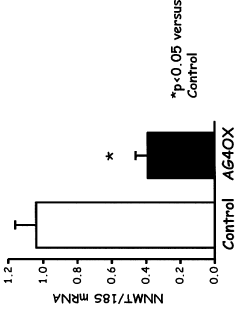
- Inhibiting the expression or activity of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) protein using NNMT antagonists, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, to reduce obesity and improve glucose homeostasis in subjects.
- Administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) through various compositions and routes, including oral and intraocular administration, to treat and prevent age-associated degenerative changes by enhancing NAD+ levels and promoting cellular health.
Regulatory Landscape for NMN in Obesity Treatment
The regulatory landscape for NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) in obesity treatment is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in this compound's potential therapeutic applications. Currently, NMN is primarily regulated as a dietary supplement in many countries, including the United States, where it falls under the purview of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In the U.S., NMN is not approved as a drug for obesity treatment. The FDA has classified it as a New Dietary Ingredient (NDI), requiring manufacturers to submit safety data before marketing products containing NMN. This classification presents challenges for companies seeking to develop NMN-based obesity treatments, as it limits the health claims that can be made about the product.
Internationally, the regulatory status of NMN varies. In Japan, for instance, NMN has been approved as a food additive, allowing for broader use in functional foods. The European Union, however, has a more stringent approach, classifying NMN as a novel food ingredient that requires safety assessment and authorization before market entry.
For NMN to be considered as a pharmaceutical treatment for obesity, extensive clinical trials would be necessary to demonstrate its safety and efficacy. This process would involve multiple phases of human trials, potentially taking several years and significant investment. Regulatory bodies would require robust evidence of NMN's mechanisms of action in obesity management, its long-term safety profile, and its superiority or complementarity to existing obesity treatments.
The path to regulatory approval for NMN as an obesity treatment would likely involve engagement with multiple regulatory agencies. In the U.S., this would mean working closely with the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Similar processes would be required in other major markets, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the EU and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan.
One of the key regulatory challenges for NMN in obesity treatment is the need to establish a clear distinction between its use as a dietary supplement and as a pharmaceutical product. This distinction is crucial for determining the appropriate regulatory pathway and the level of evidence required for approval.
As research on NMN progresses, regulatory agencies may need to adapt their frameworks to accommodate this and similar compounds that blur the line between supplements and pharmaceuticals. This could potentially lead to the development of new regulatory categories or pathways specifically designed for metabolic modulators like NMN.
Safety and Long-term Effects of NMN Supplementation
The safety and long-term effects of NMN supplementation are crucial considerations in evaluating its potential for obesity management. While short-term studies have shown promising results, the long-term implications of NMN use require further investigation.
Current research indicates that NMN supplementation is generally well-tolerated in the short term. Clinical trials have reported minimal adverse effects, with the most common being mild gastrointestinal discomfort. However, these studies have typically been conducted over relatively short periods, ranging from a few weeks to several months.
Long-term safety data on NMN supplementation is limited, and this gap in knowledge presents a significant challenge for its widespread adoption in obesity management. Concerns have been raised about the potential for unintended consequences of long-term NAD+ elevation, including possible effects on cellular senescence and cancer risk.
One area of focus for long-term safety assessment is the impact of NMN on metabolic parameters. While short-term studies have shown improvements in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, the sustained effects of long-term NMN supplementation on these markers remain unclear. Researchers are investigating whether prolonged use could lead to adaptive responses that might diminish its efficacy over time.
Another critical aspect of long-term safety is the potential interaction of NMN with other medications commonly used in obesity management. As NMN influences fundamental cellular processes, its interaction with drugs targeting metabolism, inflammation, or hormonal pathways needs thorough examination to prevent unforeseen complications in long-term use.
The dosage and duration of NMN supplementation for optimal safety and efficacy in obesity management are still under investigation. Current studies have used a wide range of doses, and determining the ideal long-term dosing strategy that balances efficacy with safety is a key research priority.
Regulatory bodies are closely monitoring the emerging data on NMN safety. While NMN is currently available as a dietary supplement in some countries, its status as a potential therapeutic agent for obesity may require more stringent safety evaluations before receiving regulatory approval for long-term use in clinical settings.
In conclusion, while short-term safety data for NMN supplementation is encouraging, comprehensive long-term studies are essential to establish its safety profile for obesity management. These studies should focus on metabolic effects, potential drug interactions, and optimal dosing strategies to ensure that the benefits of NMN in obesity treatment outweigh any potential risks associated with long-term use.