Personalizing NMN Supplementation: Linking NAD⁺ Bioavailability to Individual Health Metrics
NMN Supplementation Background and Objectives
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation has emerged as a promising approach to enhance NAD+ levels in the body, potentially offering a range of health benefits. The field of NMN research has evolved rapidly over the past decade, driven by the growing understanding of NAD+'s crucial role in cellular metabolism and its decline with age. This technological advancement aims to address age-related health issues and improve overall well-being through targeted supplementation.
The primary objective of personalizing NMN supplementation is to optimize its efficacy by tailoring dosages and regimens to individual health profiles. This approach recognizes that NAD+ bioavailability and metabolism can vary significantly among individuals due to factors such as age, genetics, lifestyle, and existing health conditions. By linking NAD+ bioavailability to individual health metrics, researchers and healthcare providers can develop more effective and precise supplementation strategies.
Recent technological developments have enabled more accurate measurement of NAD+ levels in various tissues, providing a foundation for personalized approaches. These advancements include improved metabolomics techniques, wearable devices for continuous health monitoring, and sophisticated data analysis algorithms. The integration of these technologies allows for a more comprehensive understanding of how NMN supplementation affects NAD+ levels and overall health in real-time.
The evolution of NMN supplementation technology is closely tied to broader trends in personalized medicine and preventive healthcare. As the global population ages, there is an increasing focus on interventions that can maintain health and vitality in later life. NMN supplementation represents a cutting-edge approach in this field, with the potential to address multiple aspects of age-related decline simultaneously.
Key technological goals in this area include developing more bioavailable forms of NMN, creating targeted delivery systems to enhance its efficacy in specific tissues, and establishing reliable biomarkers for monitoring the effects of supplementation. Additionally, there is a push towards integrating NMN supplementation with other interventions, such as exercise regimens and dietary modifications, to create holistic, personalized health optimization strategies.
The pursuit of personalized NMN supplementation also aligns with the growing trend of consumer-driven healthcare. As individuals become more proactive about their health, there is increasing demand for customizable solutions that can be tailored to personal health goals and genetic predispositions. This shift is driving innovation in both product development and service delivery models within the NMN supplementation industry.
Market Analysis for Personalized NMN Products
The market for personalized NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the potential health benefits associated with NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) boosting supplements. This market segment is part of the broader personalized nutrition industry, which is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years.
Consumer demand for personalized NMN products is primarily fueled by the growing interest in anti-aging solutions and preventive healthcare approaches. As more individuals seek ways to maintain their health and vitality as they age, personalized NMN supplementation offers a tailored approach to addressing individual health needs and optimizing NAD+ levels.
The target demographic for personalized NMN products primarily consists of health-conscious consumers aged 40 and above, who are proactively managing their health and are willing to invest in premium, science-backed supplements. This demographic typically has higher disposable income and is more likely to adopt innovative health solutions.
Market research indicates that the personalized nutrition market, which encompasses personalized NMN products, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% in the next five years. This growth is attributed to advancements in nutrigenomics, increased accessibility of genetic testing, and a shift towards preventive healthcare.
The personalized NMN product market is still in its early stages, with significant potential for expansion. Current market offerings range from basic NMN supplements to more sophisticated personalized formulations based on individual biomarkers and genetic profiles. As the technology for assessing NAD+ bioavailability improves, there is an opportunity for more precise and effective personalized NMN supplementation regimens.
Key market drivers include the aging global population, rising healthcare costs, and a growing emphasis on personalized medicine. Additionally, the increasing prevalence of age-related diseases and conditions that may be influenced by NAD+ levels is creating a strong demand for targeted NMN supplementation strategies.
However, the market also faces challenges, such as regulatory hurdles, the need for more extensive clinical research to support personalization claims, and consumer education on the benefits of tailored NMN supplementation. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for sustained market growth and widespread adoption of personalized NMN products.
In conclusion, the market for personalized NMN products shows promising growth potential, driven by consumer demand for tailored health solutions and advancements in personalized nutrition technology. As research continues to elucidate the relationship between NAD+ bioavailability and individual health metrics, the market is poised for further innovation and expansion in the coming years.
Current Challenges in NAD+ Bioavailability
Despite significant advancements in NAD+ research, several challenges persist in optimizing NAD+ bioavailability for personalized supplementation. One of the primary obstacles is the variability in individual responses to NAD+ precursors like NMN. Factors such as age, genetics, lifestyle, and existing health conditions can significantly influence how effectively the body converts these precursors into bioavailable NAD+.
Another challenge lies in accurately measuring NAD+ levels in different tissues and organs. Current methods often rely on blood samples, which may not accurately reflect NAD+ concentrations in specific cellular compartments or organs. This limitation hampers the ability to precisely tailor supplementation regimens to individual needs and monitor their effectiveness over time.
The complex interplay between NAD+ metabolism and various physiological processes further complicates personalization efforts. NAD+ is involved in numerous cellular functions, including energy production, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation. Understanding how changes in NAD+ levels affect these processes in different individuals remains a significant challenge, making it difficult to predict the optimal supplementation strategy for each person.
Dosage optimization presents another hurdle. While studies have shown the potential benefits of NAD+ precursor supplementation, determining the ideal dosage for individual health outcomes is challenging. Factors such as absorption rates, metabolic efficiency, and potential side effects at higher doses must be carefully considered.
The long-term effects of sustained NAD+ supplementation are not yet fully understood. As NAD+ plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism, there are concerns about potential unintended consequences of prolonged elevation of NAD+ levels. This uncertainty necessitates careful monitoring and long-term studies to ensure the safety and efficacy of personalized supplementation strategies.
Lastly, the development of more efficient delivery methods for NAD+ precursors remains an ongoing challenge. Current oral supplementation methods may result in significant degradation of compounds like NMN before they reach target tissues. Improving bioavailability through novel formulations or delivery systems is crucial for maximizing the potential benefits of NAD+ supplementation.
Existing NMN Dosage Strategies
01 NMN formulations for enhanced NAD+ bioavailability
Various formulations of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) have been developed to improve its absorption and increase NAD+ bioavailability in the body. These formulations may include specific delivery systems, encapsulation techniques, or combinations with other compounds to enhance stability and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.- NMN formulations for enhanced NAD+ bioavailability: Various formulations of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) have been developed to improve its absorption and increase NAD+ bioavailability in the body. These formulations may include specific delivery systems, encapsulation techniques, or combinations with other compounds to enhance stability and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Combination of NMN with other NAD+ precursors: Research has shown that combining NMN with other NAD+ precursors or cofactors can potentially enhance its effectiveness in increasing NAD+ levels. These combinations may include nicotinamide riboside (NR), niacin, or other compounds that work synergistically with NMN to boost NAD+ production and bioavailability.
- Novel delivery methods for NMN supplementation: Innovative delivery methods have been developed to improve the absorption and bioavailability of NMN. These may include sublingual tablets, transdermal patches, or nanoparticle-based delivery systems that aim to bypass the digestive system and enhance direct cellular uptake of NMN.
- Time-release and sustained-release NMN formulations: Time-release and sustained-release formulations of NMN have been developed to maintain consistent NAD+ levels over extended periods. These formulations may use specialized coatings or matrix systems to control the release of NMN in the body, potentially improving its overall effectiveness and reducing the frequency of dosing.
- Genetic and enzymatic approaches to enhance NMN utilization: Research has explored genetic and enzymatic approaches to enhance the body's ability to utilize NMN and increase NAD+ bioavailability. This may involve modifying enzymes involved in NAD+ biosynthesis or developing compounds that can activate or enhance the activity of these enzymes, leading to more efficient conversion of NMN to NAD+.
02 Combination of NMN with other NAD+ precursors
Research has shown that combining NMN with other NAD+ precursors or cofactors can synergistically enhance NAD+ bioavailability. These combinations may include nicotinamide riboside, niacin, or other compounds that support NAD+ biosynthesis pathways, potentially leading to more efficient NAD+ production in cells.Expand Specific Solutions03 Time-release and sustained-release NMN formulations
Time-release and sustained-release formulations of NMN have been developed to maintain consistent NAD+ levels over extended periods. These formulations may use specialized coatings, matrices, or delivery systems to control the release of NMN in the body, potentially improving its overall bioavailability and effectiveness.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMN delivery methods for improved absorption
Various delivery methods have been explored to enhance NMN absorption and subsequent NAD+ bioavailability. These may include sublingual, transdermal, or liposomal delivery systems, as well as novel formulations designed to protect NMN from degradation in the digestive system and improve its uptake in the bloodstream.Expand Specific Solutions05 Genetic and enzymatic approaches to enhance NMN utilization
Research has focused on genetic and enzymatic approaches to enhance the body's ability to utilize NMN and increase NAD+ bioavailability. This may involve modulating the expression of key enzymes involved in NAD+ biosynthesis or developing genetically modified probiotics that can more efficiently convert NMN to NAD+ in the gut.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in NMN Supplement Industry
The field of personalized NMN supplementation for NAD⁺ bioavailability is in its early growth stage, with increasing market potential as awareness of NAD⁺'s role in health grows. The global NAD⁺ supplement market is expanding, driven by aging populations and interest in longevity. Technologically, it's evolving from general supplementation to personalized approaches. Key players like Elysium Health, Metro International Biotech, and Life BioScience are advancing research, while established entities such as Nestlé and emerging companies like JumpStart Fertility are exploring applications. Academic institutions like Harvard and Washington University in St. Louis contribute to the scientific foundation, indicating a collaborative ecosystem of industry and academia pushing the boundaries of this promising field.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Metro International Biotech LLC
Innovations in NAD+ Bioavailability Assessment
- Development of novel NR and NAR derivatives with improved stability and bioavailability, including specific chemical formulas that can increase NAD+ levels in cells and mitochondria, and their use in pharmaceutical compositions for treating mitochondrial and related diseases.
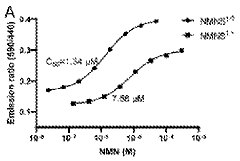
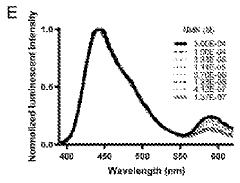
- A fully genetically encoded NMN protein probe based on resonance energy transfer is used to express it in living cells and perform quantitative detection of NMN through the dual-wavelength light intensity ratio. The phenomenon of resonance energy transfer between NMN response protein and luciferase or fluorescent protein is used to optimize Probe structure to maximize dynamic range.
Regulatory Framework for Nutraceuticals
The regulatory framework for nutraceuticals, including NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements, plays a crucial role in ensuring product safety, efficacy, and consumer protection. In the context of personalizing NMN supplementation and linking NAD+ bioavailability to individual health metrics, understanding the regulatory landscape is essential for both manufacturers and consumers.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates dietary supplements, including NMN products, under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This framework allows for the sale of dietary supplements without pre-market approval, provided they contain ingredients that were marketed prior to 1994 or have been deemed safe through a New Dietary Ingredient (NDI) notification process.
For NMN supplements, manufacturers must ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and adhere to labeling requirements set forth by the FDA. These include accurate ingredient listing, serving size information, and appropriate health claims. It's important to note that while structure/function claims are permitted, disease claims are strictly prohibited without FDA approval.
In the European Union, NMN supplements fall under the jurisdiction of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and are regulated as novel foods. This classification requires manufacturers to submit comprehensive safety data and obtain pre-market authorization before introducing NMN products to the market.
Japan, a pioneer in NMN research and development, has a unique regulatory system for functional foods and nutraceuticals. The Foods with Function Claims (FFC) system allows for certain health claims on products, provided they are supported by scientific evidence. This framework has facilitated the growth of the NMN market in Japan and serves as a model for other countries considering similar approaches.
As personalized supplementation gains traction, regulatory bodies are grappling with how to address individualized dosing and health claims based on personal biomarkers. Currently, there is no specific regulatory framework for personalized nutraceuticals, which presents both challenges and opportunities for innovation in the field.
The lack of standardized testing methods for NAD+ bioavailability and its correlation with individual health metrics further complicates the regulatory landscape. Developing validated biomarkers and standardized testing protocols will be crucial for advancing personalized NMN supplementation within existing regulatory frameworks.
Moving forward, regulatory agencies will need to adapt to the emerging field of personalized nutrition. This may involve creating new categories for personalized supplements, establishing guidelines for using individual health data in product recommendations, and developing frameworks for evaluating the safety and efficacy of personalized supplementation regimens.
Ethical Considerations in Personalized Supplementation
The personalization of NMN supplementation raises significant ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. One primary concern is the potential for exacerbating health disparities. As personalized supplementation becomes more sophisticated and potentially more effective, there is a risk that it may become accessible only to those with higher socioeconomic status, further widening the gap in health outcomes between different social groups.
Privacy and data protection present another critical ethical challenge. The process of personalizing NMN supplementation requires collecting and analyzing sensitive individual health data. Ensuring the security and confidentiality of this information is paramount, as breaches could lead to discrimination or misuse of personal health information.
The concept of informed consent takes on new dimensions in the context of personalized supplementation. Individuals must fully understand the implications of sharing their health data and the potential risks and benefits of tailored NMN regimens. This requires clear communication and transparency from healthcare providers and supplement manufacturers.
There are also concerns about the long-term effects of personalized NMN supplementation. While short-term benefits may be apparent, the ethical implications of potentially altering an individual's NAD+ metabolism over an extended period are not yet fully understood. This uncertainty raises questions about the responsibility of healthcare providers and supplement companies in monitoring and managing long-term outcomes.
The issue of autonomy and choice in health decisions is another ethical consideration. While personalization aims to optimize health outcomes, there is a fine line between providing tailored recommendations and potentially limiting an individual's freedom to make their own health choices. Striking the right balance between expert guidance and personal autonomy is crucial.
Lastly, the ethical use of predictive health models in personalizing NMN supplementation must be considered. These models, often based on machine learning algorithms, may inadvertently perpetuate biases present in their training data. Ensuring fairness and equity in these predictive models is essential to avoid discriminatory practices in personalized health recommendations.