NMN's Role in Metabolic Disorders: Latest Findings
NMN and Metabolism: Background and Objectives
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as an effective compound in the field of metabolic health research. As a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), NMN plays a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism and has garnered significant attention for its potential therapeutic applications in metabolic disorders.
The exploration of NMN's role in metabolism dates back to the early 2000s when researchers began to unravel the intricate connections between NAD+ levels, cellular energy production, and overall metabolic health. Since then, the scientific community has witnessed a surge in studies investigating the effects of NMN supplementation on various aspects of metabolism, particularly in the context of age-related metabolic decline and disorders.
Recent findings have shed light on NMN's ability to enhance mitochondrial function, improve insulin sensitivity, and regulate glucose metabolism. These discoveries have opened up new avenues for potential interventions in metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
The primary objective of current research in this field is to elucidate the mechanisms by which NMN influences metabolic processes and to assess its efficacy as a therapeutic agent for metabolic disorders. Researchers aim to determine optimal dosages, delivery methods, and potential synergistic effects with other compounds to maximize NMN's beneficial impact on metabolic health.
Another critical goal is to investigate the long-term safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in human subjects. While animal studies have shown promising results, translating these findings to human clinical applications requires rigorous testing and evaluation. Researchers are working to design and conduct large-scale, long-term clinical trials to establish the safety profile and therapeutic potential of NMN in diverse populations.
Furthermore, scientists are exploring the potential of NMN to address specific metabolic challenges associated with aging, such as sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss) and cognitive decline. By targeting these age-related metabolic changes, researchers hope to develop interventions that can improve overall health span and quality of life in aging populations.
As the field progresses, there is a growing interest in understanding the interplay between NMN and other metabolic regulators, such as sirtuins and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). This holistic approach aims to uncover potential synergies and develop more comprehensive strategies for addressing metabolic disorders.
Market Analysis for NMN-based Therapies
The market for NMN-based therapies is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of metabolic disorders and the potential benefits of NMN supplementation. As research continues to unveil the role of NMN in addressing metabolic issues, the demand for NMN-based products and treatments is expected to rise substantially in the coming years.
The global market for NMN-based therapies is primarily segmented into dietary supplements, pharmaceuticals, and functional foods. Currently, the dietary supplement segment dominates the market, with numerous products available over the counter. However, the pharmaceutical segment is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate as clinical trials progress and regulatory approvals are obtained for NMN-based drugs targeting specific metabolic disorders.
Geographically, North America leads the market for NMN-based therapies, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, has seen a surge in demand for NMN supplements, driven by a health-conscious population and a high prevalence of metabolic disorders. Japan, known for its aging population and advanced research in longevity, is another key market for NMN-based products.
The target demographic for NMN-based therapies primarily includes middle-aged and elderly individuals concerned about age-related metabolic decline. However, there is a growing interest among younger adults seeking preventive measures against metabolic disorders. This expanding consumer base is expected to contribute significantly to market growth.
Key factors driving the market include the rising prevalence of metabolic disorders such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases. The increasing body of scientific evidence supporting NMN's potential in improving metabolic health is also fueling market expansion. Additionally, the growing trend towards preventive healthcare and personalized nutrition is creating new opportunities for NMN-based therapies.
However, the market faces challenges such as high production costs of NMN, which translates to premium pricing of end products. Regulatory hurdles in certain regions, particularly for pharmaceutical applications, may also impact market growth. Moreover, competition from other NAD+ precursors and alternative metabolic health solutions poses a challenge to market players.
Looking ahead, the market for NMN-based therapies is poised for substantial growth. Advancements in production technologies are expected to reduce costs, making NMN more accessible to a broader consumer base. The potential expansion into new application areas, such as sports nutrition and cognitive health, could further boost market growth. As research continues to uncover the full potential of NMN in addressing metabolic disorders, the market is likely to witness increased investment in R&D and clinical trials, paving the way for innovative therapies and expanded market opportunities.
Current State of NMN Research in Metabolic Disorders
Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in the research of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and its potential role in addressing metabolic disorders. NMN, a precursor to NAD+, has emerged as a promising compound in the field of metabolic health and aging research.
Current studies focus on NMN's ability to boost NAD+ levels, which decline with age and are associated with various metabolic dysfunctions. Researchers have observed that NMN supplementation can improve insulin sensitivity, enhance glucose tolerance, and reduce body weight in animal models of obesity and diabetes.
One of the key areas of investigation is NMN's impact on mitochondrial function. Several studies have demonstrated that NMN can enhance mitochondrial biogenesis and improve energy metabolism in various tissues, including skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue. This improvement in cellular energy production is thought to be a crucial mechanism by which NMN may alleviate metabolic disorders.
In the context of cardiovascular health, NMN has shown potential in reducing arterial stiffness and improving endothelial function, both of which are often compromised in metabolic disorders. These effects are believed to be mediated through the activation of SIRT1, a key regulator of metabolic homeostasis.
Recent clinical trials have begun to translate these findings to human subjects. While still in early stages, preliminary results suggest that NMN supplementation may improve measures of insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism in overweight or obese individuals. However, larger and more comprehensive studies are needed to confirm these effects and establish optimal dosing regimens.
Researchers are also exploring the synergistic effects of NMN with other compounds, such as resveratrol and metformin, in the treatment of metabolic disorders. These combination therapies aim to enhance the metabolic benefits of NMN while potentially addressing multiple aspects of metabolic dysfunction simultaneously.
Despite the promising results, challenges remain in NMN research for metabolic disorders. These include optimizing delivery methods to enhance bioavailability, understanding the long-term effects of NMN supplementation, and identifying specific patient populations that may benefit most from NMN-based interventions.
As research progresses, there is growing interest in elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying NMN's metabolic effects. This includes investigating its impact on gene expression, epigenetic modifications, and cellular signaling pathways involved in metabolism and energy homeostasis.
Existing NMN Interventions for Metabolic Disorders
01 NMN for treating metabolic disorders
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has shown potential in treating various metabolic disorders. It acts as a precursor to NAD+, which plays a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism. Research indicates that NMN supplementation may help improve insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, and lipid metabolism, making it a promising candidate for addressing metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and obesity.- NMN for treating metabolic disorders: Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has shown potential in treating various metabolic disorders. It is believed to improve metabolic function by enhancing NAD+ levels in the body, which plays a crucial role in cellular energy production and metabolism regulation. Research indicates that NMN supplementation may help in managing conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and age-related metabolic decline.
- NMN formulations and delivery methods: Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of NMN for treating metabolic disorders. These include oral supplements, transdermal patches, injectable solutions, and sustained-release formulations. The different delivery methods aim to optimize NMN absorption and distribution in the body, potentially leading to improved therapeutic outcomes for metabolic conditions.
- Combination therapies with NMN: Research has explored the potential of combining NMN with other compounds or therapies to enhance its effects on metabolic disorders. These combinations may include other NAD+ precursors, antioxidants, or complementary metabolic regulators. The synergistic effects of such combinations could potentially lead to more comprehensive treatment approaches for complex metabolic conditions.
- NMN's impact on specific metabolic pathways: Studies have investigated the specific metabolic pathways and mechanisms through which NMN exerts its effects on metabolic disorders. This includes its role in mitochondrial function, glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. Understanding these pathways can lead to more targeted therapeutic approaches and potentially expand the application of NMN to a broader range of metabolic conditions.
- Safety and long-term effects of NMN supplementation: Research has been conducted to assess the safety profile and long-term effects of NMN supplementation for metabolic disorders. This includes evaluating potential side effects, optimal dosing regimens, and the impact of prolonged use on various physiological systems. Understanding these aspects is crucial for developing safe and effective NMN-based therapies for chronic metabolic conditions.
02 NMN formulations and delivery methods
Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of NMN. These include oral supplements, transdermal patches, and injectable forms. Some formulations combine NMN with other compounds to improve its stability and absorption. Novel delivery systems aim to target specific tissues or organs affected by metabolic disorders.Expand Specific Solutions03 NMN in combination therapies
Research explores the use of NMN in combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance its effects on metabolic disorders. These combinations may include other NAD+ precursors, antioxidants, or established medications for metabolic diseases. The synergistic effects of these combinations are being studied to develop more effective treatment strategies for complex metabolic conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMN for age-related metabolic decline
NMN supplementation is being investigated as a potential intervention for age-related metabolic decline. Studies suggest that NMN may help mitigate the effects of aging on metabolism by improving mitochondrial function, enhancing cellular energy production, and reducing oxidative stress. This research has implications for age-related metabolic disorders and overall healthspan.Expand Specific Solutions05 Mechanisms of NMN in metabolic regulation
Ongoing research is elucidating the molecular mechanisms by which NMN influences metabolic regulation. This includes its effects on sirtuins, AMPK activation, and gene expression related to metabolism. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for optimizing NMN-based therapies and identifying potential targets for treating metabolic disorders.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in NMN Research and Development
The research on NMN's role in metabolic disorders is in a rapidly evolving phase, with a growing market size driven by increasing prevalence of metabolic diseases. The technology is at an intermediate maturity level, with companies like Life BioScience, Inc. and Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. leading the way in research and development. Academic institutions such as Zhejiang University and Vanderbilt University are also contributing significantly to the field. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms, indicating a high level of interest and potential for breakthrough discoveries in NMN's application to metabolic disorders.
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute
Breakthrough Studies on NMN's Metabolic Effects
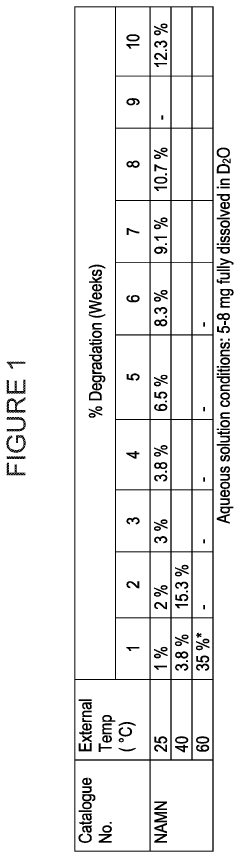
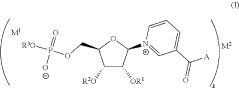
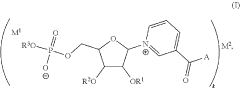
- Development of inorganic salts of nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN) that exhibit enhanced stability and increased NAD+ levels, formulated into pharmaceutical compositions for treating age-related disorders and infertility.
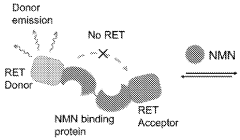
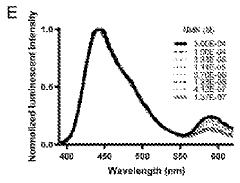
- A fully genetically encoded NMN protein probe based on resonance energy transfer is used to express it in living cells and perform quantitative detection of NMN through the dual-wavelength light intensity ratio. The phenomenon of resonance energy transfer between NMN response protein and luciferase or fluorescent protein is used to optimize Probe structure to maximize dynamic range.
Regulatory Landscape for NMN Supplements
The regulatory landscape for NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in this compound's potential health benefits, particularly in metabolic disorders. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not yet approved NMN as a dietary supplement, citing safety concerns and the need for further research.
This regulatory stance has created challenges for manufacturers and distributors of NMN products. In late 2022, the FDA issued a statement indicating that NMN does not meet the definition of a dietary ingredient under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. This decision was based on the agency's interpretation that NMN was first investigated as a new drug before being marketed as a dietary supplement.
Despite this, the market for NMN supplements continues to grow, with many products still available through various channels. This has led to a regulatory gray area, where enforcement actions are inconsistent, and consumer safety concerns persist. The situation highlights the need for clearer guidelines and more robust safety studies.
In other regions, the regulatory approach to NMN supplements varies. Japan, for instance, has approved NMN as a food ingredient, allowing its use in supplements and functional foods. This approval was based on safety data and the compound's history of use in traditional foods. The European Union, on the other hand, classifies NMN as a novel food, requiring extensive safety assessments before market authorization.
The global regulatory divergence presents challenges for international trade and harmonization efforts. Companies operating in multiple markets must navigate different regulatory frameworks, potentially leading to inconsistent product formulations and marketing claims across regions.
As research into NMN's role in metabolic disorders progresses, regulatory bodies are under pressure to develop more nuanced approaches. There is a growing call for a balanced regulatory framework that ensures consumer safety while allowing for innovation in the field of metabolic health supplements. This may involve the development of specific safety standards for NMN and similar compounds, as well as clearer guidelines for manufacturers on product development and marketing.
The evolving regulatory landscape also underscores the need for ongoing dialogue between researchers, industry stakeholders, and regulatory agencies. As new findings emerge on NMN's efficacy and safety profile in treating metabolic disorders, regulatory policies may need to be adjusted to reflect the latest scientific understanding.
Safety and Long-term Effects of NMN Supplementation
The safety and long-term effects of NMN supplementation are crucial considerations in the context of its potential role in treating metabolic disorders. Recent studies have shed light on both the short-term safety profile and potential long-term implications of NMN use.
Short-term safety studies have generally reported favorable outcomes. Clinical trials involving human subjects have shown that NMN supplementation is well-tolerated at doses up to 1000 mg per day for periods of 8-12 weeks. Common side effects, when reported, have been mild and transient, including gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, and fatigue. These effects typically subside as the body adjusts to the supplementation.
However, the long-term effects of NMN supplementation remain an area of ongoing research and debate. While animal studies have demonstrated promising results in terms of improved metabolic health and longevity, the translation of these findings to humans over extended periods is still under investigation. Some researchers have raised concerns about the potential for long-term NMN supplementation to interfere with natural NAD+ biosynthesis pathways, potentially leading to a dependency on exogenous sources.
One key area of focus in long-term safety assessments is the impact of NMN on cellular senescence and cancer risk. Theoretical concerns have been raised about the potential for increased NAD+ levels to promote the survival of senescent cells or accelerate the growth of existing tumors. However, current evidence does not support these concerns, with some studies even suggesting potential anti-cancer properties of NMN.
Metabolic adaptations to long-term NMN supplementation are another important consideration. While short-term studies have shown improvements in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, the sustainability of these effects over years of supplementation remains to be determined. Some researchers hypothesize that the body may develop compensatory mechanisms that could diminish the efficacy of NMN over time.
Cardiovascular safety is another critical aspect of long-term NMN use. Initial studies have shown potential benefits for heart health, including improved blood flow and reduced arterial stiffness. However, the long-term impact on blood pressure regulation and overall cardiovascular risk requires further investigation.
As research in this field progresses, ongoing clinical trials are focusing on longer intervention periods and more diverse population groups to better understand the safety profile and efficacy of NMN supplementation. These studies will be crucial in establishing guidelines for optimal dosing, duration of use, and identifying any potential contraindications or interactions with other medications or health conditions.