Effects of NMN on Inflammation: Research-Based Insights
NMN and Inflammation: Background and Objectives
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising compound in the field of anti-aging and metabolic health research. As a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), NMN plays a crucial role in cellular energy production and various metabolic processes. The exploration of NMN's effects on inflammation represents a significant area of interest, given the fundamental role inflammation plays in aging and numerous age-related diseases.
The study of NMN and inflammation is rooted in the broader context of NAD+ biology and its impact on cellular health. Over the past decade, researchers have increasingly focused on understanding how NAD+ levels decline with age and how this decline contributes to various aspects of aging, including increased inflammation. This has led to a surge in research investigating potential interventions to boost NAD+ levels, with NMN emerging as a key candidate.
The primary objective of investigating the effects of NMN on inflammation is to elucidate the potential therapeutic applications of NMN supplementation in managing inflammatory conditions and age-related diseases. This research aims to uncover the molecular mechanisms by which NMN may modulate inflammatory responses, potentially offering new strategies for intervention in chronic inflammatory disorders.
Recent studies have suggested that NMN supplementation may have anti-inflammatory effects through various pathways. These include the activation of sirtuins, particularly SIRT1, which are known to have anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, NMN's role in enhancing mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress may indirectly contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects.
The technological evolution in this field has been marked by advancements in analytical techniques for measuring NAD+ and its metabolites, as well as improved methods for synthesizing and delivering NMN. These developments have enabled more precise and comprehensive studies on the effects of NMN supplementation on various physiological parameters, including inflammatory markers.
As research progresses, the scientific community aims to establish a clear understanding of the dose-response relationship between NMN supplementation and inflammatory outcomes. This includes determining optimal dosing regimens, identifying potential synergistic effects with other compounds, and assessing long-term safety and efficacy.
The exploration of NMN's effects on inflammation also intersects with broader research into the aging process and the development of interventions to promote healthspan. By targeting inflammation, a key hallmark of aging, NMN research contributes to the larger goal of developing strategies to extend healthy lifespan and reduce the burden of age-related diseases.
Market Analysis for NMN-based Anti-inflammatory Products
The market for NMN-based anti-inflammatory products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the potential health benefits of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) in managing inflammation. This market segment is part of the broader nutraceutical and dietary supplement industry, which has been expanding rapidly in recent years.
Consumer demand for natural and preventive health solutions has been a key factor in the market's development. As more research emerges on the anti-inflammatory effects of NMN, health-conscious individuals are increasingly seeking out these products as part of their wellness routines. The aging population in many developed countries has also contributed to market growth, as older adults are more prone to chronic inflammation and are actively looking for ways to manage it.
The global NMN market, including its anti-inflammatory applications, has been growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% in recent years. This growth is expected to continue as more scientific evidence supports the efficacy of NMN in reducing inflammation. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly Japan and China, has been at the forefront of NMN research and product development, but North America and Europe are quickly catching up.
Market segmentation for NMN-based anti-inflammatory products includes various forms such as capsules, powders, and liquid supplements. Each segment caters to different consumer preferences and usage scenarios. The capsule form currently dominates the market due to its convenience and precise dosing, but powders are gaining popularity for their versatility in mixing with beverages or foods.
Distribution channels for these products are diverse, ranging from traditional brick-and-mortar health food stores to online retailers and direct-to-consumer platforms. The e-commerce sector has been particularly instrumental in driving sales, especially during the global pandemic when online shopping for health supplements surged.
Despite the promising growth, the market faces challenges such as regulatory hurdles in some countries and the need for more extensive clinical trials to substantiate health claims. Additionally, the high cost of NMN production currently limits widespread adoption, although economies of scale are expected to bring prices down as the market matures.
Looking ahead, the market for NMN-based anti-inflammatory products is poised for continued expansion. Factors such as ongoing research into NMN's mechanisms of action, potential new applications in managing specific inflammatory conditions, and increasing consumer education about the role of inflammation in overall health are likely to fuel this growth. As the market evolves, we can expect to see more innovative product formulations, targeted marketing strategies, and potentially, the integration of NMN into functional foods and beverages.
Current State and Challenges in NMN Research
The current state of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) research is characterized by a growing body of evidence supporting its potential anti-inflammatory effects. Numerous studies have demonstrated NMN's ability to modulate inflammatory responses in various cellular and animal models. However, the field faces several challenges that need to be addressed to fully understand and harness NMN's therapeutic potential.
One of the primary challenges in NMN research is the limited number of human clinical trials. While preclinical studies have shown promising results, there is a need for more extensive and well-designed human studies to validate these findings. The lack of long-term safety data in humans also presents a significant hurdle, as the effects of prolonged NMN supplementation remain unclear.
Another challenge lies in understanding the precise mechanisms by which NMN exerts its anti-inflammatory effects. While it is known that NMN acts as a precursor to NAD+, which plays a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism and signaling pathways, the specific molecular targets and pathways involved in its anti-inflammatory action are not fully elucidated. This gap in knowledge hinders the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
The bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of NMN pose additional challenges. Researchers are still working to optimize delivery methods and dosing regimens to ensure that NMN reaches its target tissues effectively. The stability of NMN in various formulations and its potential interactions with other compounds or medications also require further investigation.
Furthermore, the field faces challenges in standardizing NMN production and quality control. As interest in NMN supplementation grows, ensuring consistent purity and potency across different sources and formulations becomes crucial for reliable research outcomes and potential therapeutic applications.
Regulatory hurdles also present a significant challenge in NMN research. The classification of NMN as a dietary supplement in some countries, but not in others, creates a complex landscape for conducting clinical trials and bringing NMN-based products to market. Harmonizing regulatory approaches across different jurisdictions would greatly facilitate research progress and potential therapeutic development.
Lastly, the field must address the challenge of translating preclinical findings into clinically relevant outcomes. While animal studies have shown promising results in reducing inflammation and age-related diseases, bridging the gap between these models and human physiology remains a critical task. Developing appropriate biomarkers and outcome measures for assessing NMN's effects on inflammation in humans is essential for advancing the field.
Existing Approaches to NMN-mediated Inflammation Reduction
01 NMN's anti-inflammatory effects
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has been shown to have potent anti-inflammatory properties. It can reduce inflammation by modulating various inflammatory pathways and cytokine production. This effect is particularly beneficial in age-related inflammatory conditions and metabolic disorders.- NMN's anti-inflammatory effects: Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has been shown to have potent anti-inflammatory properties. It can reduce inflammation by modulating various inflammatory pathways and cytokine production. This effect is particularly beneficial in age-related inflammatory conditions and metabolic disorders.
- NMN in treating inflammatory diseases: Research indicates that NMN supplementation may be effective in treating various inflammatory diseases. It has shown promise in conditions such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and neurodegenerative disorders characterized by chronic inflammation. The compound's ability to regulate inflammatory responses makes it a potential therapeutic agent for these conditions.
- Mechanisms of NMN's anti-inflammatory action: NMN exerts its anti-inflammatory effects through multiple mechanisms. It enhances NAD+ levels, which in turn activates sirtuins, particularly SIRT1 and SIRT3. These sirtuins play crucial roles in regulating inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. Additionally, NMN can modulate NF-κB signaling, a key pathway in inflammation.
- NMN's role in reducing oxidative stress-induced inflammation: NMN has been found to mitigate inflammation caused by oxidative stress. By boosting NAD+ levels, it enhances cellular antioxidant defenses and promotes the activity of enzymes that neutralize reactive oxygen species. This reduction in oxidative stress leads to a decrease in inflammation, particularly in conditions where oxidative damage is a primary driver of inflammatory responses.
- Synergistic effects of NMN with other anti-inflammatory compounds: Studies have explored the potential synergistic effects of combining NMN with other anti-inflammatory agents. These combinations may enhance the overall anti-inflammatory efficacy and provide more comprehensive protection against various inflammatory conditions. Such synergistic approaches could lead to more effective treatments for chronic inflammatory diseases.
02 NMN in treating inflammatory diseases
Research indicates that NMN supplementation may be effective in treating various inflammatory diseases. It has shown promise in conditions such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and neurodegenerative disorders characterized by chronic inflammation. The compound's ability to regulate inflammatory responses makes it a potential therapeutic agent for these conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mechanisms of NMN's anti-inflammatory action
NMN exerts its anti-inflammatory effects through multiple mechanisms. It enhances NAD+ levels, which in turn activates SIRT1, a key regulator of inflammation. NMN also modulates NF-κB signaling, reduces oxidative stress, and improves mitochondrial function, all of which contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMN in combination with other anti-inflammatory agents
Combining NMN with other anti-inflammatory compounds or therapies may enhance its efficacy in reducing inflammation. Studies have explored synergistic effects when NMN is used alongside traditional anti-inflammatory drugs or natural compounds, potentially leading to more effective treatment strategies for inflammatory conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 NMN's role in age-related inflammation
NMN has shown particular promise in addressing age-related inflammation, often referred to as inflammaging. By boosting NAD+ levels, which decline with age, NMN can help mitigate chronic low-grade inflammation associated with aging. This effect may contribute to improved healthspan and reduced risk of age-related inflammatory diseases.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in NMN Research and Development
The research on NMN's effects on inflammation is in an emerging stage, with a growing market driven by increasing interest in anti-aging and metabolic health. The technology is still developing, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Key players like Metro International Biotech LLC, ChromaDex, Inc., and Massachusetts Institute of Technology are leading research efforts, while institutions such as Zhejiang University and University of Massachusetts contribute to the expanding knowledge base. The involvement of pharmaceutical companies like Bayer HealthCare and Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co., KG suggests potential for future clinical applications. As the field progresses, collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners are likely to accelerate technological advancements and market growth.
Metro International Biotech LLC
ChromaDex, Inc.
Core Findings on NMN's Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms
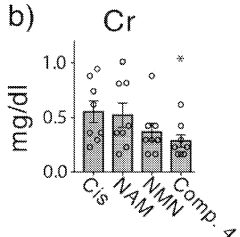
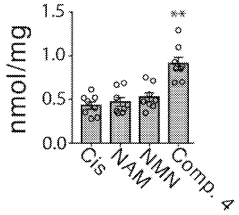
- A pharmaceutical composition containing nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is developed to activate the NAMPT-dependent NAD+ biosynthetic pathway, reducing the severity of inflammatory diseases by administering NMN to patients with NAMPT protein knock out.
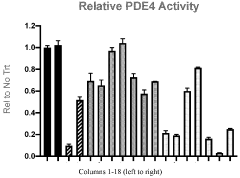
- Development of compounds with a xanthine moiety or its analogues, along with additional moieties, which are administered to treat inflammation and potentially increase NAD+ levels by inhibiting phosphodiesterase, thereby addressing inflammation-related conditions such as asthma, COPD, and acute kidney injury, and providing a pharmaceutical composition in various forms for oral administration.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations for NMN Supplements
As the use of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements continues to grow, it is crucial to address the safety and regulatory considerations surrounding these products. The safety profile of NMN is generally considered favorable, with several studies reporting no significant adverse effects in human trials. However, long-term safety data remains limited, necessitating ongoing research and vigilance.
Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States, have not yet fully evaluated NMN supplements. Currently, NMN is classified as a dietary supplement rather than a drug, which means it is not subject to the same rigorous approval process as pharmaceutical products. This classification places the responsibility on manufacturers to ensure product safety and accuracy in labeling.
Quality control is a critical concern in the production of NMN supplements. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistency, purity, and accurate dosing. Third-party testing and certification can provide additional assurance of product quality and safety.
Potential interactions between NMN and other medications or supplements remain an area of ongoing investigation. Healthcare providers should be aware of possible interactions, particularly in patients with pre-existing health conditions or those taking multiple medications.
Dosage recommendations for NMN supplements vary, and optimal dosages for different health outcomes have not been definitively established. This variability underscores the need for standardized dosing guidelines based on robust clinical evidence.
Labeling and marketing of NMN supplements must comply with regulatory guidelines to avoid misleading claims. Manufacturers should provide clear information on dosage, potential side effects, and any known contraindications.
As research on NMN continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt. Future regulations could potentially reclassify NMN or impose stricter controls on its production and distribution, depending on emerging safety data and efficacy studies.
Consumer education is essential to promote safe and informed use of NMN supplements. Clear communication of potential benefits, limitations, and safety considerations can help individuals make informed decisions about NMN supplementation.
Potential Applications in Age-related Inflammatory Conditions
The potential applications of NMN in age-related inflammatory conditions are vast and promising, given the compound's ability to modulate inflammation and its role in cellular energy production. As we age, chronic low-grade inflammation, often referred to as "inflammaging," becomes a significant factor in the development of various age-related diseases.
One of the most promising areas for NMN application is in cardiovascular health. Age-related inflammation is a key contributor to atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. NMN supplementation has shown potential in reducing vascular inflammation and improving endothelial function, which could lead to better cardiovascular outcomes in older adults.
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, are also closely linked to age-related inflammation. NMN's neuroprotective properties and its ability to reduce neuroinflammation make it a potential candidate for preventive or adjunct therapies in these conditions. By supporting mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress in neurons, NMN could help slow the progression of these debilitating diseases.
In the realm of metabolic disorders, NMN shows promise in addressing age-related insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Chronic inflammation plays a crucial role in the development of these conditions, and NMN's anti-inflammatory effects, coupled with its ability to improve insulin sensitivity, could offer new avenues for treatment or prevention.
Osteoarthritis, a common age-related inflammatory condition affecting joints, is another area where NMN could have significant impact. By reducing inflammation in cartilage and synovial tissue, NMN might help alleviate pain and slow the progression of joint degeneration.
Skin aging, characterized by chronic inflammation and reduced cellular energy production, is yet another potential application for NMN. Topical or oral NMN supplementation could potentially improve skin elasticity, reduce inflammation-induced damage, and slow the visible signs of aging.
Lastly, age-related decline in immune function, known as immunosenescence, is closely tied to chronic inflammation. NMN's ability to modulate inflammatory responses and support cellular energy production could help maintain a more balanced and effective immune system in older adults, potentially reducing the risk of age-related infections and autoimmune disorders.
As research progresses, these potential applications of NMN in age-related inflammatory conditions may lead to novel therapeutic strategies, offering hope for improved health and quality of life in aging populations. However, further clinical studies are needed to fully elucidate the efficacy and safety of NMN in these various applications.