Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) as a nutraceutical – Efficiency and Safety
NMN Background and Objectives
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising nutraceutical in recent years, garnering significant attention from researchers and the health-conscious public alike. This compound, a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), plays a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism and has been linked to various potential health benefits, particularly in the context of aging and age-related diseases.
The scientific interest in NMN can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began to unravel the intricate relationships between NAD+ levels, sirtuins, and cellular aging. As NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, the idea of supplementing with its precursor, NMN, to boost NAD+ levels and potentially slow down or reverse certain aspects of aging gained traction.
Over the past decade, numerous studies have been conducted to explore the effects of NMN supplementation on various physiological processes. Animal studies have shown promising results in areas such as improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced mitochondrial function, and increased lifespan in certain model organisms. These findings have fueled optimism about NMN's potential as a nutraceutical for human health and longevity.
The evolution of NMN research has been marked by several key milestones. Initial studies focused on establishing the safety and bioavailability of NMN in animal models. Subsequent research expanded to investigate its effects on specific health parameters, such as cardiovascular function, cognitive performance, and metabolic health. More recently, human clinical trials have begun to emerge, aiming to translate the promising results observed in animal studies to human subjects.
As the field progresses, the primary objectives of NMN research and development as a nutraceutical are multifaceted. First and foremost, there is a need to conclusively establish the efficacy of NMN supplementation in humans across various health outcomes. This involves conducting large-scale, long-term clinical trials to assess its effects on biomarkers of aging, metabolic health, and overall well-being.
Another critical objective is to optimize the delivery and bioavailability of NMN. Current research is exploring various formulations and delivery methods to enhance its absorption and utilization by the body. Additionally, determining the optimal dosage and timing of NMN supplementation for different age groups and health conditions remains an important goal.
Safety considerations are paramount in the development of NMN as a nutraceutical. While initial studies have shown promising safety profiles, ongoing research aims to identify any potential long-term side effects or interactions with other medications or supplements. Establishing robust safety data is crucial for regulatory approval and consumer confidence.
NMN Market Analysis
The global market for Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) as a nutraceutical has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of its potential health benefits and the growing demand for anti-aging supplements. The market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including capsules, powders, and beverages, catering to different consumer preferences and lifestyles.
Key factors contributing to the market expansion include the aging global population, rising disposable incomes, and a growing emphasis on preventive healthcare. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly Japan and China, has emerged as a major market for NMN supplements, with a strong cultural focus on longevity and wellness. North America and Europe also represent substantial market segments, driven by health-conscious consumers and a robust nutraceutical industry.
The NMN market is highly fragmented, with numerous small to medium-sized companies competing alongside a few larger pharmaceutical and nutraceutical firms. This competitive landscape has led to increased product innovation and diversification, as companies strive to differentiate their offerings and capture market share.
Despite the promising growth trajectory, the NMN market faces several challenges. Regulatory uncertainties in various countries regarding the classification and approval of NMN as a dietary supplement have impacted market expansion. Additionally, the high production costs of NMN have resulted in relatively expensive end products, potentially limiting widespread adoption among price-sensitive consumers.
Consumer education remains a critical factor in market development, as many potential users are still unfamiliar with NMN and its purported benefits. Marketing efforts have focused on highlighting scientific research supporting NMN's potential role in cellular health and longevity, although more long-term human studies are needed to solidify these claims.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the NMN market. While it has increased consumer interest in health supplements, supply chain disruptions and economic uncertainties have posed challenges for manufacturers and distributors. However, the pandemic has also accelerated the trend towards online sales channels, providing new opportunities for market growth and consumer engagement.
Looking ahead, the NMN market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with increasing research investments likely to yield new insights into NMN's efficacy and potential applications. As production technologies improve and economies of scale are achieved, there is potential for price reductions, which could further expand the consumer base for NMN products.
NMN Research Status
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising nutraceutical in recent years, with research focusing on its potential to combat aging and age-related diseases. The current research status of NMN is characterized by a growing body of scientific evidence, primarily from animal studies, with an increasing number of human trials being conducted.
Preclinical studies in mice have shown that NMN supplementation can improve various aspects of health, including metabolism, cardiovascular function, and cognitive performance. These studies have demonstrated that NMN can effectively raise NAD+ levels in multiple tissues, which is believed to be the primary mechanism behind its beneficial effects. The ability of NMN to cross cell membranes and rapidly convert to NAD+ has made it a subject of intense research interest.
Human clinical trials investigating NMN's effects are still in their early stages, but initial results are promising. A small-scale study published in 2019 showed that NMN was safe and well-tolerated in healthy men, with no significant adverse effects reported. This study also provided preliminary evidence of NMN's potential to improve insulin sensitivity and muscle function.
Recent research has also explored the optimal dosage and delivery methods for NMN supplementation. Studies have investigated various administration routes, including oral, sublingual, and intravenous, to determine the most effective way to increase NAD+ levels in humans. Additionally, researchers are working on developing novel formulations to enhance NMN's bioavailability and stability.
The safety profile of NMN is an ongoing area of investigation. While short-term studies have not revealed significant side effects, long-term safety data in humans is still limited. Researchers are actively monitoring for potential adverse effects and interactions with other medications or supplements.
One of the key challenges in NMN research is translating the promising results from animal studies to human applications. The differences in metabolism and physiology between species necessitate careful interpretation of preclinical data and rigorous human trials to establish efficacy and safety in humans.
Current research is also focusing on identifying specific populations that may benefit most from NMN supplementation. This includes studies on individuals with age-related conditions, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. The potential of NMN as a therapeutic agent for these conditions is an active area of investigation.
In conclusion, the research status of NMN as a nutraceutical is characterized by growing scientific interest and promising preclinical results. While human studies are still in their early stages, the initial findings suggest potential benefits in various aspects of health. Ongoing research aims to establish the long-term safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in humans, as well as to optimize its delivery and identify the most suitable applications for this promising compound.
Current NMN Formulations
01 Efficiency of NMN in NAD+ biosynthesis
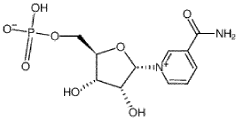
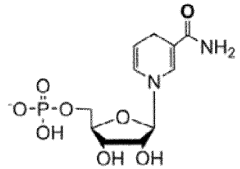
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has been shown to be an efficient precursor in the biosynthesis of NAD+, a crucial coenzyme involved in various cellular processes. Studies indicate that NMN supplementation can effectively increase NAD+ levels in cells and tissues, potentially offering benefits for cellular energy metabolism and overall health.- Efficacy of NMN in improving cellular health: Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has shown promising results in enhancing cellular health by boosting NAD+ levels. Studies indicate that NMN supplementation can improve mitochondrial function, energy metabolism, and DNA repair processes, potentially slowing down age-related cellular decline.
- Safety profile of NMN supplementation: Research suggests that NMN supplementation is generally well-tolerated in various dosages. Clinical trials have reported minimal side effects, with most being mild and transient. However, long-term safety data is still limited, and more extensive studies are needed to fully establish its safety profile across different populations.
- NMN's potential in age-related disease prevention: Emerging evidence suggests that NMN may have protective effects against various age-related diseases. Studies have shown promising results in areas such as cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and metabolic disorders. However, more clinical research is needed to confirm these potential benefits in humans.
- Bioavailability and delivery methods of NMN: Research is ongoing to improve the bioavailability and delivery methods of NMN. Various formulations and administration routes are being explored, including oral supplements, sublingual tablets, and transdermal applications. Enhancing absorption and cellular uptake of NMN is crucial for maximizing its potential benefits.
- Combination therapies involving NMN: Studies are investigating the potential synergistic effects of combining NMN with other compounds or interventions. These combinations aim to enhance the overall efficacy of NMN in promoting cellular health and longevity. Promising areas include combining NMN with exercise regimens, other NAD+ precursors, or complementary antioxidants.
02 Safety profile of NMN supplementation
Research on the safety of NMN supplementation has shown promising results. Clinical trials and animal studies have demonstrated that NMN is generally well-tolerated at various doses. However, long-term safety data in humans is still limited, and ongoing studies are evaluating potential side effects and optimal dosing regimens.Expand Specific Solutions03 NMN formulations and delivery methods
Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to enhance the efficiency and bioavailability of NMN. These include oral supplements, sublingual tablets, and topical applications. Some formulations incorporate additional compounds to improve stability and absorption of NMN in the body.Expand Specific Solutions04 Potential therapeutic applications of NMN
Research has explored the potential therapeutic applications of NMN in various health conditions. Studies have investigated its effects on age-related diseases, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. While results are promising, more clinical research is needed to establish the efficacy of NMN in specific therapeutic contexts.Expand Specific Solutions05 Production and quality control of NMN
Advancements in the production and quality control of NMN have been made to ensure its purity and efficacy. Novel synthesis methods and analytical techniques have been developed to produce high-quality NMN and verify its authenticity. These improvements aim to enhance the reliability and consistency of NMN products for research and consumer use.Expand Specific Solutions
Key NMN Industry Players
The market for Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) as a nutraceutical is in its growth phase, with increasing research and commercial interest. The global NMN market is expanding rapidly, driven by growing consumer awareness of anti-aging products. Technologically, NMN research is advancing, with companies like Mirailab Bioscience, Metro International Biotech, and Meiji Holdings leading innovation. Academic institutions such as Washington University in St. Louis and Kyoto University are contributing to the scientific understanding of NMN's efficacy and safety. While the technology is promising, further clinical studies are needed to fully establish NMN's long-term effects and optimal dosage, indicating a moderate level of technological maturity in this field.
Mirailab Bioscience, Inc.
Life BioScience, Inc.
NMN Efficacy Studies
- Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and its derivatives are used to prevent and treat pain, particularly nociceptive pain, by reducing pain intensity and tolerance threshold, administered in various forms and combinations with other therapeutic agents.
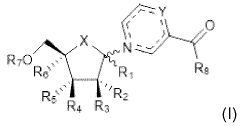
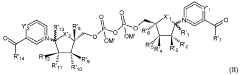
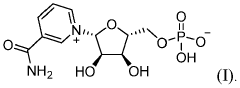
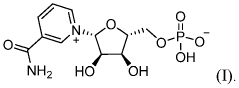
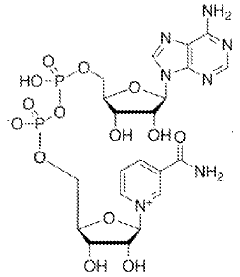
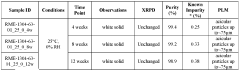
- The development of crystalline forms of NMN, specifically Forms I and II, which are anhydrous or DMSO solvates, characterized by unique XRD patterns, and methods for their preparation involving crystallization from solvents like methanol or DMSO, ensuring high purity and stability.
NMN Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework for Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) as a nutraceutical varies significantly across different regions and countries, reflecting the complex nature of its classification and the evolving understanding of its efficacy and safety.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not explicitly approved NMN as a dietary supplement. In 2022, the FDA issued a statement indicating that NMN may not qualify as a dietary ingredient under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This decision was based on the agency's interpretation that NMN was first investigated as a new drug before being marketed as a dietary supplement. However, this stance remains controversial and subject to ongoing discussions within the industry and regulatory bodies.
The European Union has taken a more cautious approach. NMN is currently classified as a novel food under EU regulations, requiring extensive safety assessments before it can be marketed as a food supplement. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of novel foods, including NMN, before they can be authorized for sale in the EU market.
In Japan, NMN has gained more regulatory acceptance. The Japanese government has approved NMN as a food ingredient, allowing its use in various products. This approval was based on safety data and the long history of consumption of foods containing NMN precursors, such as niacin.
China has also shown a more open stance towards NMN. In 2020, the Chinese government approved NMN as a new food raw material, permitting its use in food products. This decision was supported by safety evaluations conducted by Chinese regulatory authorities.
The regulatory landscape for NMN is further complicated by its dual nature as both a potential pharmaceutical and a nutraceutical. Many countries are grappling with how to classify and regulate substances that fall into this gray area between food and drug.
As research on NMN's efficacy and safety continues to evolve, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will adapt accordingly. This may lead to more harmonized approaches across different regions or to further divergence based on individual country assessments of the risks and benefits associated with NMN supplementation.
NMN Safety Profile
The safety profile of Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) as a nutraceutical is a critical aspect of its potential widespread use. Extensive research has been conducted to evaluate the safety and potential side effects of NMN supplementation in various populations.
Short-term studies have shown that NMN is generally well-tolerated in healthy adults when taken orally. Clinical trials have reported no significant adverse effects at doses ranging from 100 mg to 1200 mg per day for periods up to 12 weeks. Common minor side effects include mild gastrointestinal discomfort, headache, and fatigue, which typically subside with continued use.
Long-term safety data on NMN supplementation is still limited, as most studies have been conducted over relatively short durations. However, animal studies have provided insights into potential long-term effects. Rodent studies lasting up to 12 months have not revealed any significant toxicity or adverse effects on organ function, even at high doses.
One area of concern is the potential interaction of NMN with existing medications. As NMN influences cellular metabolism and energy production, it may interact with drugs that affect similar pathways. Particular attention should be given to potential interactions with diabetes medications, as NMN has been shown to influence glucose metabolism.
The safety of NMN in specific populations, such as pregnant women, children, and individuals with chronic diseases, requires further investigation. Current data is insufficient to make definitive recommendations for these groups, and caution is advised until more targeted studies are conducted.
Regulatory bodies have not yet established official safety guidelines or recommended daily intake levels for NMN. This lack of standardization highlights the need for continued research and regulatory oversight to ensure consumer safety as NMN gains popularity as a nutraceutical.
Quality control in NMN production and distribution is another crucial aspect of its safety profile. As with many supplements, the purity and consistency of commercially available NMN products can vary. Ensuring standardized manufacturing processes and third-party testing for contaminants is essential to maintain safety standards.
In conclusion, while current evidence suggests that NMN is generally safe for short-term use in healthy adults, more comprehensive long-term studies are needed to fully establish its safety profile. As research progresses, ongoing monitoring and reporting of potential adverse effects will be crucial in refining our understanding of NMN's safety as a nutraceutical.