The Science Behind NMN's Anti-Aging Facets
NMN Anti-Aging Background
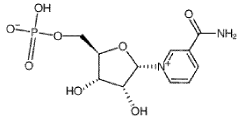
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising compound in the field of anti-aging research. This naturally occurring molecule is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a critical coenzyme involved in numerous cellular processes. The interest in NMN stems from its potential to boost NAD+ levels, which tend to decline with age, leading to various age-related health issues.
The scientific exploration of NMN's anti-aging properties began in the early 2000s, with groundbreaking studies demonstrating its ability to enhance NAD+ biosynthesis. Researchers discovered that NMN could be rapidly converted to NAD+ in tissues, potentially reversing age-related decline in NAD+ levels. This finding sparked a wave of investigations into NMN's effects on various aspects of aging.
Over the past two decades, numerous studies have highlighted the diverse anti-aging facets of NMN. These include improvements in metabolic health, enhanced DNA repair mechanisms, increased cellular energy production, and protection against oxidative stress. Animal studies have shown promising results, with NMN supplementation leading to increased lifespan and healthspan in various model organisms.
The mechanism of action for NMN's anti-aging effects primarily revolves around its role in NAD+ production. NAD+ is a crucial cofactor for sirtuins, a family of proteins known for their involvement in cellular stress responses, DNA repair, and metabolic regulation. By boosting NAD+ levels, NMN indirectly activates sirtuins, potentially mimicking the beneficial effects of calorie restriction, a well-established intervention for extending lifespan.
Recent research has also uncovered additional pathways through which NMN may exert its anti-aging effects. These include modulation of mitochondrial function, enhancement of stem cell activity, and regulation of inflammatory responses. The multifaceted nature of NMN's impact on cellular processes underscores its potential as a comprehensive anti-aging intervention.
As the scientific community continues to unravel the complexities of aging, NMN remains at the forefront of anti-aging research. Clinical trials in humans are ongoing, aiming to translate the promising results observed in animal studies to human applications. The growing body of evidence supporting NMN's anti-aging properties has led to increased interest from both the scientific community and the general public, driving further research and development in this field.
NMN Market Analysis
The NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer interest in anti-aging solutions and longevity-enhancing supplements. This market expansion is closely tied to the growing body of scientific research supporting NMN's potential benefits in cellular health and age-related decline mitigation.
The global NMN market size was valued at approximately $253 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $386 million by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising aging population, increasing health consciousness among consumers, and the expanding nutraceutical industry.
North America currently dominates the NMN market, accounting for the largest market share due to high consumer awareness and disposable income. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by the rapidly aging population in countries like Japan and China, coupled with increasing health expenditure and growing interest in preventive healthcare.
The market is segmented based on product type, including capsules, tablets, and powder forms. Capsules currently hold the largest market share due to their convenience and precise dosage control. However, the powder segment is anticipated to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period, as it offers flexibility in dosage and can be easily incorporated into various dietary regimens.
Key market players in the NMN industry include GeneHarbor Biotechnology, Shinkowa Pharmaceutical, Herbalmax, and Genex Formulas. These companies are focusing on product innovation, clinical trials, and strategic partnerships to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
Consumer demand for NMN supplements is primarily driven by the desire to combat age-related health issues, improve overall well-being, and potentially extend healthspan. The market is also benefiting from the increasing adoption of NMN in cosmetic and skincare products, as research suggests potential benefits for skin health and appearance.
However, the NMN market faces challenges such as high production costs, limited clinical evidence for long-term efficacy in humans, and regulatory uncertainties in some regions. Despite these obstacles, the market is expected to continue its growth trajectory as ongoing research provides more insights into NMN's mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications.
NMN Research Challenges
Research on NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) as a potential anti-aging compound has gained significant momentum in recent years. However, several challenges persist in fully understanding and harnessing its potential. One of the primary obstacles is the limited long-term human studies available. While animal models have shown promising results, translating these findings to human applications requires extensive clinical trials over extended periods.
Another challenge lies in the bioavailability and stability of NMN. The compound's molecular structure makes it susceptible to degradation, potentially reducing its efficacy when administered orally. Researchers are grappling with developing delivery methods that can ensure NMN reaches target tissues in its active form. This includes exploring novel formulations and delivery systems to enhance absorption and cellular uptake.
The mechanism of action of NMN in different tissues and cell types presents another area of complexity. While it's known that NMN serves as a precursor to NAD+, a critical coenzyme in cellular metabolism, the specific pathways and interactions in various physiological contexts are not fully elucidated. Understanding these nuanced effects is crucial for optimizing NMN's therapeutic potential and minimizing potential side effects.
Dosage optimization remains a significant challenge. The optimal dose for achieving anti-aging effects while maintaining safety is still under investigation. Factors such as age, health status, and genetic variations may influence individual responses to NMN supplementation, necessitating personalized approaches to dosing strategies.
The long-term safety profile of NMN supplementation is another area requiring extensive research. While short-term studies have not reported significant adverse effects, the implications of sustained, high-dose NMN intake over years or decades are yet to be fully understood. This is particularly important given that anti-aging interventions may require lifelong administration.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for NMN as a potential therapeutic or nutraceutical agent presents challenges. As it straddles the line between a dietary supplement and a pharmaceutical, establishing clear regulatory guidelines for its development, testing, and marketing is crucial. This regulatory ambiguity can impact research funding, clinical trial designs, and ultimately, the pathway to market for NMN-based products.
Current NMN Applications
01 NMN formulations for anti-aging
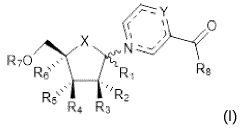
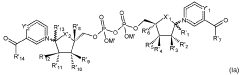
Various formulations of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) are developed for anti-aging purposes. These include oral supplements, topical applications, and injectable solutions. The formulations are designed to enhance bioavailability and efficacy of NMN in promoting cellular health and longevity.- NMN supplementation for anti-aging effects: Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is used as a dietary supplement to combat aging. It is a precursor to NAD+, a crucial molecule for cellular energy production and DNA repair. NMN supplementation has shown potential in improving various age-related conditions, including metabolic health, cognitive function, and overall longevity.
- NMN delivery methods and formulations: Various delivery methods and formulations have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of NMN. These include oral supplements, transdermal applications, and novel drug delivery systems. Some formulations combine NMN with other compounds to potentially synergize its anti-aging effects.
- NMN in cosmetic and skincare applications: NMN is being incorporated into cosmetic and skincare products for its potential anti-aging effects on the skin. These formulations aim to improve skin elasticity, reduce wrinkles, and enhance overall skin health by promoting cellular rejuvenation and protecting against oxidative stress.
- Combination therapies with NMN: Research is exploring the use of NMN in combination with other anti-aging compounds or therapies. These combinations aim to enhance the overall anti-aging effects by targeting multiple pathways involved in the aging process, potentially leading to more comprehensive age-reversal strategies.
- NMN production and quality control: Advancements in the production methods of NMN focus on improving purity, yield, and cost-effectiveness. Quality control measures are being developed to ensure the safety and efficacy of NMN supplements, including methods for detecting adulterants and assessing the stability of NMN in various formulations.
02 Combination therapies with NMN
NMN is combined with other anti-aging compounds or therapies to enhance its effects. These combinations may include antioxidants, other NAD+ precursors, or complementary lifestyle interventions. The synergistic effects of these combinations aim to provide more comprehensive anti-aging benefits.Expand Specific Solutions03 Delivery systems for NMN
Novel delivery systems are developed to improve the absorption and effectiveness of NMN. These may include nanoparticle-based delivery, liposomal encapsulation, or sustained-release formulations. The goal is to enhance the bioavailability and stability of NMN in the body.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMN for specific age-related conditions
Research focuses on the application of NMN for targeting specific age-related conditions or diseases. This includes studies on its effects on cardiovascular health, cognitive function, metabolic disorders, and skin aging. The aim is to develop targeted therapies for age-related health issues.Expand Specific Solutions05 Production and purification of NMN
Improved methods for the production and purification of NMN are developed to enhance its quality and reduce production costs. This includes novel synthesis pathways, enzymatic production methods, and advanced purification techniques to ensure high-quality NMN for anti-aging applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key NMN Industry Players
The research into NMN's anti-aging properties is in a rapidly evolving phase, with a growing market driven by increasing consumer interest in longevity solutions. The technology is still maturing, with various companies at different stages of development. Key players like Washington University in St. Louis, Nuvamid SA, and Teijin Ltd. are leading academic and industrial research efforts. Companies such as Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd. and Hongboyuan Life Technology are advancing commercial applications. The market is seeing a mix of established pharmaceutical firms and innovative biotechnology startups, indicating a competitive landscape with significant potential for growth and technological breakthroughs in the coming years.
Washington University in St. Louis
Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd.
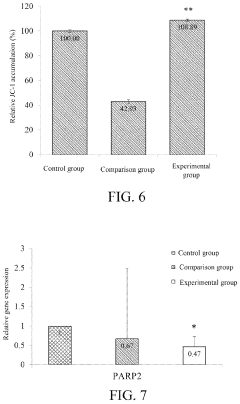
NMN Mechanism Insights
- Development of cosmetic compositions incorporating nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) or its derivatives, which are used to prevent and treat signs of aging like wrinkles, skin roughness, and loss of elasticity without causing allergic reactions, by improving skin hydration and firmness.
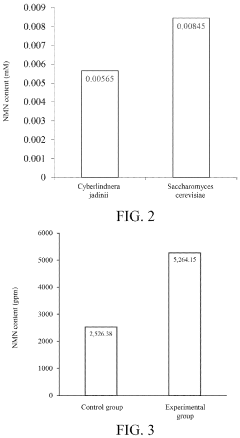
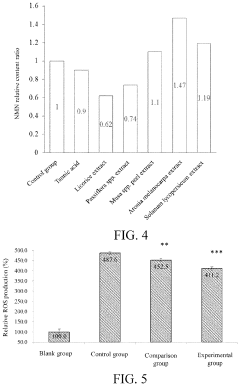
- A method for preparing yeast powder rich in nicotinamide mononucleotide through a multi-stage fermentation process using media with nicotinamide, tryptophan, and niacin, which increases the NMN content to at least 5000 ppm, and optionally includes plant extracts like Musa, Aronia, and Solanum extracts to enhance production.
NMN Regulatory Status
The regulatory status of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) varies significantly across different countries and regions, reflecting the complex landscape of dietary supplement regulation worldwide. In the United States, NMN currently exists in a regulatory gray area. While it has been marketed as a dietary supplement, the FDA issued a statement in November 2022 indicating that NMN is excluded from the definition of a dietary supplement under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
This decision was based on the fact that NMN was authorized for investigation as a new drug before it was marketed as a dietary supplement. As a result, many companies have had to reformulate their products or remove NMN from the U.S. market. However, the situation remains fluid, with ongoing discussions between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies.
In Japan, NMN has a more favorable regulatory status. It has been approved as a food ingredient and is widely available in various forms, including supplements and functional foods. The Japanese government has recognized NMN as a food with function claims, allowing manufacturers to make certain health-related statements about their products containing NMN.
The European Union has taken a cautious approach to NMN. As of now, it is not approved as a novel food ingredient, which is required for new substances to be used in food products within the EU. Manufacturers seeking to introduce NMN-containing products in the EU market must go through the novel food authorization process, which involves rigorous safety assessments.
In China, NMN is classified as a "blue hat" health food ingredient, allowing its use in dietary supplements. However, the regulatory framework for NMN is still evolving, with ongoing research and discussions about its safety and efficacy.
Australia and New Zealand have not yet established specific regulations for NMN. It is currently not included in the Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code, which means it cannot be added to foods. However, it may be available as a complementary medicine, subject to the regulations of the Therapeutic Goods Administration.
The global regulatory landscape for NMN is dynamic and subject to change as more research emerges and regulatory bodies refine their positions. Companies operating in the NMN market must navigate these complex and varying regulations, often adapting their strategies and product offerings to comply with different regional requirements. As the scientific understanding of NMN's potential health benefits continues to evolve, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will also develop to address the growing interest in this compound.
NMN Safety Profile
The safety profile of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) is a critical aspect to consider in its potential use as an anti-aging supplement. Extensive research has been conducted to evaluate the safety and tolerability of NMN in various animal models and human trials. Studies have shown that NMN is generally well-tolerated, with no significant adverse effects reported in short-term and medium-term studies.
In preclinical studies, NMN has demonstrated a favorable safety profile across different species, including mice, rats, and dogs. These studies have explored various dosage levels and administration routes, finding no evidence of toxicity or severe side effects. Long-term studies in mice have shown that NMN supplementation does not increase cancer incidence or mortality rates, addressing concerns about potential oncogenic effects.
Human clinical trials have further supported the safety of NMN supplementation. A phase I clinical study conducted in Japan reported no serious adverse events in healthy adults taking NMN orally for up to 12 weeks. The study found that NMN was well-tolerated at doses up to 500 mg per day, with only minor gastrointestinal discomfort reported in a small number of participants.
However, it is important to note that long-term safety data in humans is still limited. Most human studies have been relatively short in duration, typically lasting several weeks to a few months. As such, the long-term effects of NMN supplementation in humans remain an area of ongoing research and scrutiny.
One potential concern that has been raised is the impact of NMN on cellular senescence. While NMN is known to boost NAD+ levels and potentially reverse certain aspects of aging, some researchers have questioned whether long-term elevation of NAD+ could inadvertently promote the survival of senescent cells. This theoretical risk requires further investigation to fully understand its implications for long-term use.
Interactions with medications and existing health conditions are another important consideration in the safety profile of NMN. As NMN influences cellular metabolism and energy production, it may potentially interact with drugs that affect similar pathways. Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, particularly those related to metabolism or cellular energy production, should consult healthcare professionals before using NMN supplements.
In conclusion, while the current body of evidence suggests that NMN has a favorable safety profile, continued research is necessary to fully elucidate its long-term effects and potential interactions. As with any supplement, careful monitoring and further clinical studies are essential to ensure its safe use in diverse populations and over extended periods.