NMN Supplement: Enhancing Metabolic Health Naturally
NMN Background and Objectives
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising compound in the field of metabolic health and anti-aging research. This naturally occurring molecule, a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), has garnered significant attention due to its potential to enhance cellular energy production and promote overall metabolic wellness.
The exploration of NMN as a dietary supplement stems from decades of research into the fundamental processes of aging and cellular metabolism. Scientists have long recognized the crucial role of NAD+ in various biological functions, including DNA repair, energy metabolism, and cellular signaling. As NAD+ levels decline with age, researchers hypothesized that replenishing these levels could potentially mitigate age-related metabolic decline and associated health issues.
The primary objective of NMN research is to investigate its efficacy in boosting NAD+ levels and, consequently, improving metabolic health markers. This includes examining its effects on insulin sensitivity, glucose metabolism, mitochondrial function, and overall energy production at the cellular level. Additionally, researchers aim to elucidate the potential benefits of NMN supplementation in addressing age-related conditions such as cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndrome.
Another key goal is to establish the optimal dosage, delivery methods, and long-term safety profile of NMN supplementation in humans. While animal studies have shown promising results, translating these findings to human applications requires rigorous clinical trials and comprehensive safety assessments. Researchers are particularly interested in determining the most effective formulation of NMN for human consumption and identifying any potential side effects or interactions with other medications or supplements.
Furthermore, the research aims to uncover the molecular mechanisms through which NMN exerts its effects on metabolic health. This involves investigating its impact on various cellular pathways, gene expression patterns, and epigenetic modifications. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted interventions and potentially combining NMN with other compounds for synergistic effects.
As the field of NMN research evolves, there is also a growing interest in exploring its potential applications beyond metabolic health. This includes investigating its effects on cognitive function, muscle strength, and overall longevity. The ultimate goal is to determine whether NMN supplementation can effectively contribute to healthier aging and improved quality of life in the general population.
Market Analysis for NMN Supplements
The global market for NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the potential health benefits associated with NAD+ boosting compounds. This market segment is part of the broader nutraceutical and anti-aging industry, which has been expanding rapidly due to growing interest in preventive healthcare and longevity.
The demand for NMN supplements is primarily fueled by aging populations in developed countries, rising disposable incomes, and a shift towards proactive health management. Consumers are increasingly seeking natural solutions to support metabolic health, energy levels, and overall well-being as they age. This trend has been further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has heightened public awareness of the importance of maintaining robust health.
Market research indicates that the Asia-Pacific region, particularly Japan and China, currently leads in NMN supplement consumption. This is attributed to the strong cultural emphasis on longevity and the early adoption of NAD+ precursor supplements in these markets. However, North America and Europe are rapidly catching up, with growing consumer interest and increasing product availability through both online and brick-and-mortar retail channels.
The target demographic for NMN supplements primarily consists of middle-aged and older adults, typically aged 40 and above, who are proactively seeking to maintain their health and vitality. However, there is a growing trend of younger consumers, particularly in the 25-40 age range, showing interest in these products for their potential cognitive and athletic performance benefits.
Key market drivers include ongoing scientific research into the effects of NMN on aging and metabolic health, celebrity endorsements, and increased media coverage of longevity science. The market is also benefiting from the broader trend towards personalized nutrition and supplement regimens tailored to individual health goals.
Despite the positive growth trajectory, the NMN supplement market faces challenges such as high production costs, which translate to premium pricing for consumers. This factor may limit market penetration in price-sensitive segments. Additionally, regulatory uncertainties in some regions regarding the classification and marketing of NMN as a dietary supplement pose potential hurdles for market expansion.
Looking ahead, the NMN supplement market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with opportunities for product diversification, such as combination formulas with other longevity-associated compounds. The increasing focus on clinical research and potential therapeutic applications of NMN may also open new market segments in the future, bridging the gap between dietary supplements and pharmaceutical interventions for age-related conditions.
Current NMN Research Challenges
The current research situation regarding NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) as a supplement for enhancing metabolic health naturally is characterized by a rapidly expanding interest across both academic and commercial sectors. Current studies highlight NMN's potential in improving mitochondrial function, enhancing cellular energy production, and supporting metabolism. The primary driver for this interest is NMN's role as a precursor to NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), a critical coenzyme involved in numerous metabolic reactions and known for its declining levels with age.
NMN research primarily explores its efficacy in counteracting age-related metabolic decline, and expanding the understanding of its bioavailability and safety profiles. Recent research underscores NMN's impact on metabolic pathways, suggesting improvements in insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and cardiovascular function. These findings are significant given the rising prevalence of metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. However, translating these results into practical health benefits involves overcoming several challenges.
One of the major challenges in NMN research is understanding its precise mechanism of action in human physiology. Most studies to date have been conducted on animal models, with limited human clinical data available. This presents a significant barrier to fully validating its safety and efficacy in humans. Furthermore, the pharmacokinetics of NMN, including optimal dosing strategies and long-term effects, remain areas requiring further inquiry.
Another salient challenge is the regulatory environment. As NMN is increasingly perceived as a potential nutraceutical, understanding and navigating the regulatory frameworks across different regions poses substantial hurdles. Notably, the variability in standards for dietary supplements and pharmaceuticals complicates the path to market in different jurisdictions.
Moreover, the sourcing and stability of NMN as a raw material present logistical and technical hurdles. Development of cost-effective and efficient production methods to ensure consistent bioavailability and quality is essential to support large-scale applications and commercialization.
Given these challenges, future research directions may focus on developing standardized protocols for human clinical trials to validate the numerous health benefits attributed to NMN. Collaborations between academic researchers and industry players could help in addressing bioavailability and production issues, while comprehensive regulatory studies will be critical in streamlining its path to market.
Thus, while NMN holds substantial promise as a natural enhancer of metabolic health, achieving its full potential requires concerted efforts to address the current research gaps and challenges identified.
NMN Supplementation Strategies
01 NMN supplementation for metabolic health improvement
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplements are used to enhance metabolic health. NMN is a precursor to NAD+, a crucial molecule for cellular energy production and metabolism. Supplementation with NMN has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, and overall metabolic function, particularly in aging individuals.- NMN supplementation for metabolic health improvement: Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplements are used to enhance metabolic health. NMN is a precursor to NAD+, a crucial molecule for cellular energy production and metabolism. Supplementation with NMN has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, and overall metabolic function, particularly in aging individuals.
- Formulations and delivery methods for NMN supplements: Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of NMN supplements. These include oral capsules, sublingual tablets, and transdermal patches. Some formulations incorporate additional compounds to improve absorption or synergistic effects, such as resveratrol or other NAD+ precursors.
- NMN supplementation for age-related metabolic disorders: NMN supplements are being investigated for their potential to prevent or treat age-related metabolic disorders. Research suggests that NMN supplementation may help mitigate the decline in metabolic function associated with aging, including improvements in mitochondrial function, energy metabolism, and cellular repair mechanisms.
- Combination of NMN with other nutraceuticals for metabolic health: Combining NMN with other nutraceuticals or bioactive compounds has been explored to enhance its metabolic health benefits. These combinations may include antioxidants, flavonoids, or other metabolic regulators to create synergistic effects on energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, and overall metabolic health.
- NMN supplementation for specific metabolic conditions: Research has focused on the potential of NMN supplementation to address specific metabolic conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Studies have investigated the effects of NMN on glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in these conditions, showing promising results for metabolic health improvement.
02 Formulations and delivery methods for NMN supplements
Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of NMN supplements. These include oral capsules, sublingual tablets, transdermal patches, and liposomal formulations. Some formulations combine NMN with other compounds to improve absorption or synergistic effects on metabolic health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination of NMN with other metabolic health-promoting compounds
NMN supplements are often combined with other compounds known to support metabolic health. These may include resveratrol, quercetin, or other NAD+ precursors like nicotinamide riboside. Such combinations aim to provide comprehensive support for cellular energy production, mitochondrial function, and overall metabolic wellness.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMN supplementation for specific metabolic conditions
Research has explored the use of NMN supplements for specific metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Studies have investigated the potential of NMN to improve glucose metabolism, reduce inflammation, and enhance mitochondrial function in these conditions, showing promising results for metabolic health management.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and dosage considerations for NMN supplementation
As NMN supplementation gains popularity, research has focused on determining optimal dosages and assessing long-term safety. Studies have explored various dosage regimens and their effects on metabolic parameters, as well as potential side effects or interactions with other medications. Establishing safe and effective dosing guidelines is crucial for the widespread use of NMN supplements for metabolic health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key NMN Industry Players
The research on NMN supplements for enhancing metabolic health is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for NMN supplements is expanding rapidly, driven by growing consumer interest in anti-aging and health optimization. Technologically, the field is progressing from early-stage research to more advanced clinical applications. Companies like Metro International Biotech LLC, Life BioScience, Inc., and Société des Produits Nestlé SA are at the forefront, developing innovative NMN formulations and delivery methods. Academic institutions such as Washington University in St. Louis and Huazhong Agricultural University are contributing to the scientific understanding of NMN's effects on metabolism. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech startups vying for market share and scientific breakthroughs.
Metro International Biotech LLC
Life BioScience, Inc.
Breakthrough NMN Studies
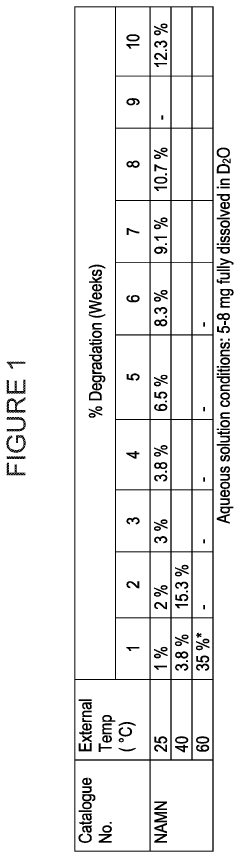
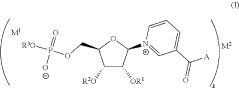
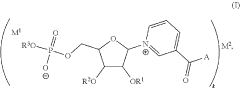
- Development of inorganic salts of nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN) that exhibit enhanced stability and increased NAD+ levels, formulated into pharmaceutical compositions for treating age-related disorders and infertility.
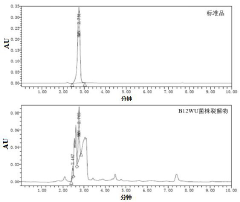
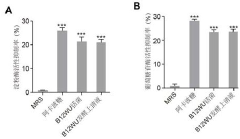
- Screening and isolation of Lactobacillus salivarius strain B12WU with high acid-base tolerance, which can synthesize NMN in the gastrointestinal environment, has high α-amylase or α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, reduces blood sugar levels, and provides a safe Reliable source of NMN.
Regulatory Framework for NMN
The regulatory framework for NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements is complex and varies across different regions, reflecting the evolving nature of this emerging health product. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not explicitly approved NMN as a dietary supplement. However, it falls under the broader category of dietary supplements regulated by the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. They must also ensure that any claims made about the supplement are not false or misleading. The FDA has the authority to take action against unsafe or misbranded supplements after they reach the market. This post-market approach means that NMN supplements can be sold without pre-market approval, but manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and other regulatory requirements.
In Japan, NMN has gained more regulatory acceptance. The Japanese government has approved NMN as a food additive, allowing its use in various products. This approval came after extensive safety studies and reflects Japan's more proactive approach to regulating novel food ingredients.
The European Union takes a more cautious approach. NMN is considered a novel food under EU regulations, which means it requires pre-market authorization. Manufacturers must submit a dossier demonstrating the safety and efficacy of NMN before it can be marketed as a food supplement in EU member states.
In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulates complementary medicines, including supplements. NMN would likely be classified as a complementary medicine and would need to be listed or registered with the TGA before being sold in Australia.
China has recently included NMN in its catalog of dietary supplements, signaling a more open regulatory stance towards this compound. This move is expected to boost the development of NMN-related products in the Chinese market.
The global regulatory landscape for NMN is still evolving. As more research emerges on its safety and efficacy, regulatory bodies may update their positions. This dynamic situation underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring of regulatory developments for companies involved in the NMN market. It also highlights the need for harmonization of regulations across different regions to facilitate global trade and ensure consistent safety standards for consumers.
NMN Safety and Efficacy Profile
The safety and efficacy profile of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation has been a subject of extensive research in recent years. Clinical studies have demonstrated that NMN is generally well-tolerated in humans, with no significant adverse effects reported in short-term trials. The most common side effects observed are mild gastrointestinal discomfort and headaches, which typically subside with continued use.
Long-term safety data is still limited, as most human trials have been conducted over periods of 8-12 weeks. However, animal studies have shown promising results, with no toxicity observed even at high doses over extended periods. These findings suggest a favorable safety profile, though more research is needed to confirm long-term effects in humans.
Regarding efficacy, NMN supplementation has shown potential in improving various aspects of metabolic health. Studies have reported improvements in insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, and lipid metabolism. Some research indicates that NMN may enhance mitochondrial function and energy production, potentially contributing to improved physical performance and endurance.
Cognitive function has also been a focus of NMN research, with some studies suggesting potential benefits in memory and learning. However, these cognitive effects require further investigation to establish their significance and reproducibility in human subjects.
It's important to note that the efficacy of NMN can vary depending on factors such as age, health status, and dosage. Some studies have found more pronounced effects in older individuals or those with pre-existing metabolic conditions, suggesting that NMN may be particularly beneficial for age-related metabolic decline.
The bioavailability of NMN has been a key consideration in efficacy studies. Recent research has focused on developing delivery methods to enhance absorption and cellular uptake of NMN, which could potentially improve its therapeutic effects.
While the current body of evidence is promising, larger, long-term clinical trials are still needed to fully establish the safety and efficacy profile of NMN supplementation. Ongoing research is exploring optimal dosing regimens, potential interactions with other supplements or medications, and the long-term impact on various health parameters.