NMN’s Role in Anti Aging: Scientific Insights
NMN and Aging: Background and Objectives
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising compound in the field of anti-aging research, garnering significant attention from scientists and the public alike. The exploration of NMN's potential role in combating aging processes stems from its fundamental involvement in cellular energy metabolism and its ability to boost levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a crucial coenzyme in various biological processes.
The journey of NMN in anti-aging research began with the discovery of its precursor role in NAD+ biosynthesis. As organisms age, NAD+ levels naturally decline, leading to a cascade of cellular dysfunctions associated with the aging process. This decline has been linked to various age-related conditions, including metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular issues. The primary objective of NMN research in the context of aging is to investigate whether supplementation can effectively restore NAD+ levels and, consequently, mitigate or reverse some of the deleterious effects of aging.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in scientific interest surrounding NMN, with numerous studies conducted on animal models demonstrating promising results. These studies have shown improvements in various markers of aging, including enhanced metabolic function, improved cardiovascular health, and increased lifespan in some organisms. The potential of NMN to cross the blood-brain barrier has also sparked interest in its possible neuroprotective effects, opening avenues for research into age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders.
As research progresses, the scientific community aims to elucidate the precise mechanisms through which NMN exerts its anti-aging effects. This includes understanding its interaction with sirtuins, a class of proteins known for their role in regulating cellular health and longevity. Additionally, researchers are investigating the optimal dosage, delivery methods, and potential long-term effects of NMN supplementation in humans.
The evolving landscape of NMN research also encompasses its potential synergistic effects with other compounds and lifestyle interventions in promoting healthy aging. This holistic approach aligns with the broader goal of not merely extending lifespan but enhancing the quality of life in later years, a concept known as "healthspan."
As we delve deeper into the role of NMN in anti-aging, the scientific community faces the challenge of translating promising animal studies into human clinical trials. The ultimate objective is to determine whether NMN can be safely and effectively used as a therapeutic intervention to combat age-related decline in humans, potentially revolutionizing our approach to healthy aging and age-related diseases.
Market Analysis for Anti-Aging Supplements
The anti-aging supplement market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness, as well as the aging global population. The market for NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements, in particular, has gained traction due to its potential role in cellular aging processes.
Market research indicates that the global anti-aging supplement market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $75 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of around 7% during the forecast period. NMN supplements, while still a niche segment, are expected to see rapid growth within this broader market.
The demand for anti-aging supplements is primarily driven by the aging baby boomer population in developed countries, increasing disposable income in emerging markets, and growing consumer interest in preventive healthcare. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years due to rising health consciousness and increasing purchasing power.
Key market players in the anti-aging supplement industry include established pharmaceutical companies, nutraceutical firms, and specialized supplement manufacturers. Some notable companies active in the NMN supplement space include Chromadex, Elysium Health, and Tru Niagen. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to substantiate the efficacy of NMN and other NAD+ precursors in anti-aging applications.
Consumer demographics for anti-aging supplements skew towards middle-aged and older adults, typically aged 40 and above. However, there is a growing trend of younger consumers adopting these products as part of their preventive health routines. High-income individuals and health-conscious consumers are the primary target markets for premium anti-aging supplements like NMN.
Market challenges include regulatory hurdles, as many countries have strict regulations governing the sale and marketing of dietary supplements. Additionally, the high cost of NMN supplements compared to traditional anti-aging products may limit market penetration in price-sensitive segments. Consumer skepticism regarding the efficacy of anti-aging supplements also remains a significant barrier to market growth.
Despite these challenges, the market outlook for NMN and other anti-aging supplements remains positive. Ongoing scientific research into the mechanisms of aging and the potential benefits of NAD+ precursors is likely to drive further market expansion. As more clinical studies validate the efficacy of NMN in human subjects, consumer confidence and market demand are expected to increase substantially in the coming years.
Current State of NMN Research and Challenges
The current state of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) research in anti-aging is characterized by significant progress and ongoing challenges. Globally, numerous studies have demonstrated NMN's potential to mitigate age-related decline in various physiological systems. Researchers have observed improvements in metabolic health, cardiovascular function, and cognitive performance in animal models treated with NMN supplementation.
One of the primary focuses of current research is understanding the mechanisms by which NMN exerts its anti-aging effects. Studies have shown that NMN acts as a precursor to NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), a crucial coenzyme involved in cellular energy production and DNA repair. The decline in NAD+ levels with age has been linked to various age-related disorders, making NMN supplementation a promising intervention strategy.
However, several challenges persist in translating these findings to human applications. The bioavailability and optimal dosage of NMN in humans remain subjects of ongoing investigation. While animal studies have shown promising results, human clinical trials are still in their early stages, with limited long-term data available on efficacy and safety.
Another significant challenge is the stability of NMN in various formulations and storage conditions. Researchers are working on developing stable forms of NMN that can maintain their potency over time and survive the digestive process to reach target tissues effectively.
The field also faces the challenge of standardization in NMN production and quality control. As interest in NMN grows, ensuring consistent purity and potency across different manufacturers and research labs is crucial for reliable and comparable results.
Geographically, NMN research is distributed across several countries, with significant contributions from the United States, Japan, and China. Each region brings unique perspectives and approaches to NMN research, fostering a diverse and collaborative international scientific community.
Looking ahead, key areas of focus include elucidating the long-term effects of NMN supplementation, optimizing delivery methods, and exploring potential synergies with other anti-aging interventions. Researchers are also investigating the role of NMN in specific age-related conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic disorders.
As the field progresses, addressing these challenges and expanding our understanding of NMN's mechanisms and effects will be crucial in realizing its potential as a therapeutic intervention in aging and age-related diseases.
Existing NMN Supplementation Strategies
01 NMN supplementation for cellular NAD+ levels
NMN acts as a precursor to NAD+, a crucial coenzyme involved in various cellular processes. Supplementation with NMN can increase NAD+ levels in cells, potentially reversing age-related decline in NAD+ and improving cellular function. This mechanism is believed to contribute to the anti-aging effects of NMN.- NMN supplementation for cellular NAD+ levels: NMN acts as a precursor to NAD+, a crucial molecule for cellular energy production and DNA repair. Supplementation with NMN can increase NAD+ levels in cells, potentially slowing down the aging process and improving overall cellular function. This approach may help combat age-related decline in various physiological processes.
- NMN for mitochondrial function and energy metabolism: NMN supplementation has been shown to enhance mitochondrial function and energy metabolism. By improving these cellular processes, NMN may help reduce oxidative stress, increase ATP production, and support overall cellular health. This can potentially lead to improved physical performance and longevity.
- NMN for cardiovascular health and protection: Research suggests that NMN supplementation may have beneficial effects on cardiovascular health. It may help improve blood flow, reduce inflammation in blood vessels, and protect against age-related cardiovascular diseases. These effects could contribute to overall heart health and longevity.
- NMN for cognitive function and neuroprotection: NMN has shown potential in improving cognitive function and providing neuroprotection. It may help maintain brain health by supporting neuronal function, reducing inflammation, and protecting against age-related cognitive decline. These effects could potentially aid in preventing or managing neurodegenerative diseases.
- NMN in combination with other anti-aging compounds: Combining NMN with other anti-aging compounds or interventions may enhance its overall effectiveness. This approach could include pairing NMN with antioxidants, other NAD+ precursors, or lifestyle interventions to create synergistic effects for combating aging and age-related diseases.
02 NMN for mitochondrial function and energy metabolism
NMN supplementation has been shown to enhance mitochondrial function and energy metabolism. By improving these cellular processes, NMN may help combat age-related decline in energy production and cellular efficiency, contributing to its anti-aging effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 NMN for DNA repair and genomic stability
Research suggests that NMN can support DNA repair mechanisms and promote genomic stability. These effects may help reduce age-related DNA damage and mutations, potentially slowing down the aging process at a cellular level.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMN in combination with other anti-aging compounds
Formulations combining NMN with other anti-aging compounds or natural extracts have been developed to potentially enhance its effects. These combinations may target multiple aspects of aging simultaneously, offering a more comprehensive approach to anti-aging.Expand Specific Solutions05 Topical application of NMN for skin anti-aging
Some research focuses on the topical application of NMN for skin anti-aging effects. These formulations aim to improve skin health, reduce wrinkles, and enhance skin elasticity by delivering NMN directly to the skin cells.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in NMN Production and Research
The NMN anti-aging market is in a growth phase, with increasing research and commercial interest. The global market size for NMN supplements is expanding rapidly, driven by growing consumer awareness of longevity and health benefits. Technologically, NMN research is advancing, with institutions like Washington University in St. Louis and companies such as Nuvamid SA and Mirailab Bioscience, Inc. leading scientific investigations. The field is seeing a mix of academic research and commercial product development, with companies like Teijin Ltd. and Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd. entering the market. While promising, NMN technology is still evolving, with ongoing studies to fully understand its efficacy and long-term effects in human anti-aging applications.
Mirailab Bioscience, Inc.
Chemiteras, Inc.
Breakthrough Studies on NMN's Anti-Aging Effects
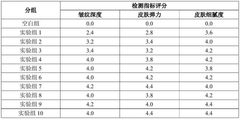
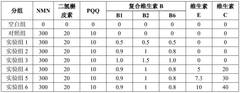
- Using a composition containing NAD or its precursor, flavonoids and coenzymes, the side effects are reduced and anti-aging effects are improved by optimizing the proportion of components such as NMN, quercetin, PQQ and vitamin B complex.
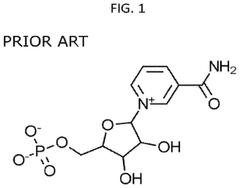
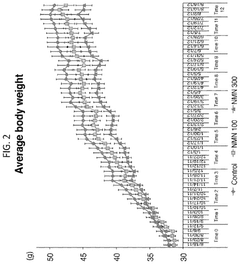
- Administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) to subjects, either through compositions that include NMN alone or in combination with excipients, to treat, ameliorate, or reverse age-associated degenerative changes. NMN can be formulated into various dosage forms, including pills, tablets, and solutions, for oral, parenteral, or topical administration.
Regulatory Framework for NMN Supplements
The regulatory framework for NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in this potential anti-aging compound. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing dietary supplements, including NMN products. Currently, NMN is classified as a dietary supplement, which means it is not subject to the same rigorous pre-market approval process as pharmaceutical drugs.
However, manufacturers are required to comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and ensure their products are safe for consumption. The FDA also mandates that supplement labels must not make false or misleading claims about the product's benefits. Specifically for NMN, companies cannot claim it treats, cures, or prevents any disease, including aging-related conditions.
In Japan, NMN has been approved as a food additive, allowing for its inclusion in various products. This regulatory approach has made Japan a leader in NMN research and product development. The Japanese government's proactive stance on NMN regulation has contributed to increased consumer confidence and market growth in the country.
The European Union (EU) takes a more cautious approach to novel food ingredients. NMN is currently under review by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as a novel food. Until approved, NMN supplements cannot be legally marketed within the EU. This process involves a thorough safety assessment and can take several years to complete.
In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulates complementary medicines, including supplements. NMN is not currently listed in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods, which means it cannot be legally sold as a therapeutic good in the country. However, it may be available as a food supplement, subject to food safety regulations.
China has recently implemented new regulations for health food products, which include dietary supplements. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) requires pre-market approval for health food products, including those containing NMN. This process involves submitting safety and efficacy data for review.
As research on NMN's potential health benefits continues to expand, regulatory bodies worldwide are likely to refine their approaches. This may lead to more specific guidelines for NMN supplements, potentially including standardized dosage recommendations and quality control measures. The evolving regulatory landscape will significantly impact the global market for NMN supplements and shape future research directions in the field of anti-aging science.
Ethical Considerations in Longevity Research
The pursuit of longevity through scientific research raises significant ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. As NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) emerges as a potential anti-aging compound, it becomes crucial to examine the ethical implications of its development and use.
One primary concern is the equitable access to longevity-enhancing treatments. If NMN or similar compounds prove effective in extending human lifespan, there is a risk of creating a societal divide between those who can afford such treatments and those who cannot. This could exacerbate existing health inequalities and raise questions about fairness and social justice in healthcare distribution.
The potential for unintended consequences in altering human biology must also be considered. While NMN aims to promote healthy aging, interfering with fundamental biological processes could have unforeseen long-term effects on individuals and populations. Researchers must carefully weigh the benefits against potential risks and ensure thorough long-term studies are conducted.
Privacy and data protection present another ethical challenge. As longevity research often involves extensive genetic and health data collection, safeguarding this sensitive information becomes paramount. Researchers must implement robust data protection measures and obtain informed consent from study participants, ensuring transparency about how their data will be used and stored.
The impact of extended lifespans on societal structures and resources is a critical ethical consideration. Increased longevity could strain pension systems, healthcare resources, and environmental sustainability. Policymakers and researchers must collaboratively address these potential challenges to ensure that longevity advancements benefit society as a whole.
Ethical concerns also arise regarding the potential for coercion or pressure to use life-extending treatments. As these technologies become available, individuals may feel compelled to use them to remain competitive in the workforce or maintain social relationships. This raises questions about personal autonomy and the right to age naturally.
Furthermore, the allocation of research funding and resources towards longevity studies must be ethically justified. With limited resources available for medical research, prioritizing anti-aging research over other pressing health issues could be seen as ethically questionable. A balanced approach that considers immediate health needs alongside long-term longevity goals is essential.
Lastly, the ethical implications of altering the natural human lifespan must be carefully examined. This includes philosophical and religious considerations about the meaning of life, death, and the human condition. Open dialogue involving diverse perspectives is crucial to navigate these complex ethical territories as longevity research progresses.