NMN Supplements: Exploring Anti-Aging Benefits
NMN Background and Goals
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising compound in the field of anti-aging research. This naturally occurring molecule is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a critical coenzyme involved in various cellular processes. The interest in NMN as a potential anti-aging supplement has grown significantly over the past decade, driven by the increasing understanding of NAD+ metabolism and its role in cellular health and longevity.
The primary goal of exploring NMN supplements is to investigate their potential to mitigate age-related decline and promote healthy aging. Researchers aim to determine whether NMN supplementation can effectively boost NAD+ levels in humans, thereby supporting cellular energy production, DNA repair, and other vital functions that tend to deteriorate with age. Additionally, studies seek to establish the optimal dosage, delivery methods, and long-term safety profile of NMN supplements.
The development of NMN as an anti-aging intervention is rooted in the broader context of longevity research. As global populations continue to age, there is an increasing demand for strategies to extend healthspan – the period of life free from age-related diseases. NMN represents a targeted approach to address one of the fundamental aspects of aging: the decline in NAD+ levels and subsequent cellular dysfunction.
Historical milestones in NMN research include the discovery of its role in NAD+ biosynthesis, early animal studies demonstrating its potential benefits, and the initiation of human clinical trials. The field has progressed from basic science investigations to translational research, with a growing focus on practical applications and commercialization of NMN-based products.
Current technological advancements in NMN research encompass improved synthesis methods, enhanced delivery systems, and more sophisticated analytical techniques for measuring NAD+ levels in various tissues. These developments aim to overcome challenges such as NMN's limited bioavailability and the need for more accurate assessment of its effects on human physiology.
Looking ahead, the goals for NMN research include conducting larger-scale, long-term human studies to validate its anti-aging effects, exploring potential synergies with other interventions, and developing personalized supplementation strategies based on individual genetic and metabolic profiles. Additionally, researchers are investigating the broader implications of NMN supplementation, including its potential impact on age-related diseases such as cardiovascular disorders, neurodegenerative conditions, and metabolic syndromes.
As the field evolves, there is also a growing emphasis on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying NMN's effects, identifying potential biomarkers of its efficacy, and elucidating any possible contraindications or interactions with other medications or supplements. These efforts aim to establish NMN as a scientifically validated anti-aging intervention and pave the way for its potential integration into mainstream healthcare practices.
Anti-Aging Market Analysis
The global anti-aging market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness, rising disposable incomes, and a growing aging population. The market encompasses a wide range of products and services, including skincare, supplements, cosmetic procedures, and wellness programs. Within this broader context, the NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplement segment has emerged as a promising niche with substantial growth potential.
The anti-aging supplement market, which includes NMN products, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is fueled by a shift towards preventive healthcare and a desire for longevity among consumers. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like Japan and China, is expected to witness the fastest growth due to their rapidly aging populations and increasing health consciousness.
Consumer demand for NMN supplements is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing body of scientific research supporting the potential anti-aging benefits of NMN, which has piqued consumer interest. Secondly, the increasing prevalence of age-related diseases and conditions has led many individuals to seek out preventive measures. Lastly, the trend towards natural and non-invasive anti-aging solutions has boosted the appeal of dietary supplements like NMN.
The target demographic for NMN supplements primarily consists of middle-aged and older adults, typically aged 40 and above. However, there is a growing interest among younger consumers who are taking a proactive approach to aging. High-income individuals and health-conscious consumers are also key market segments for premium NMN products.
Market challenges include regulatory hurdles, as the classification and approval processes for NMN supplements vary across different countries. Additionally, the high cost of NMN production and the resulting premium pricing of supplements may limit market penetration in some regions. Consumer education remains a crucial factor, as many potential customers are still unfamiliar with NMN and its purported benefits.
Looking ahead, the NMN supplement market is poised for continued growth. Factors such as ongoing research into the efficacy of NMN, potential breakthroughs in production methods that could lower costs, and increasing consumer awareness are expected to drive market expansion. As competition intensifies, product differentiation through quality, purity, and bioavailability will become increasingly important for manufacturers to gain market share.
NMN Research Challenges
Despite the promising potential of NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements in anti-aging research, several significant challenges persist in this field. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of NMN's long-term effects on human health. While animal studies have shown encouraging results, translating these findings to human subjects remains complex due to differences in metabolism and physiological processes between species.
Another major challenge lies in determining the optimal dosage and delivery method for NMN supplements. The bioavailability of NMN varies depending on the route of administration, and researchers are still working to identify the most effective way to ensure that the compound reaches target tissues in sufficient quantities. This is further complicated by individual variations in metabolism and genetic factors that may influence NMN's efficacy.
The stability of NMN in supplement form presents another hurdle. The compound is sensitive to environmental factors such as heat and light, which can degrade its potency. Developing stable formulations that maintain NMN's integrity from production to consumption is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable results in both research and practical applications.
Regulatory challenges also pose significant obstacles in NMN research. As a relatively new compound in the supplement market, NMN faces scrutiny from regulatory bodies regarding its safety and efficacy claims. Navigating the complex landscape of dietary supplement regulations while conducting rigorous scientific studies requires careful balance and coordination among researchers, manufacturers, and regulatory agencies.
Furthermore, the mechanism of action by which NMN exerts its anti-aging effects is not fully elucidated. While it is known to be a precursor to NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), a crucial molecule in cellular energy metabolism, the exact pathways and interactions involved in its anti-aging properties are still being investigated. This gap in knowledge hinders the development of targeted interventions and the ability to predict potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
Lastly, the field faces challenges in standardizing research protocols and outcome measures. The multifaceted nature of aging makes it difficult to establish universally accepted biomarkers or endpoints for anti-aging studies. This lack of standardization complicates the comparison of results across different studies and impedes the development of a cohesive body of evidence supporting NMN's anti-aging benefits.
Current NMN Formulations
01 NMN supplementation for cellular NAD+ levels
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements are used to boost cellular NAD+ levels, which decline with age. Increased NAD+ levels can potentially improve cellular energy production, DNA repair, and overall cellular health, contributing to anti-aging effects.- NMN supplementation for cellular NAD+ levels: NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements are used to boost cellular NAD+ levels, which decline with age. Increased NAD+ levels can potentially improve mitochondrial function, energy metabolism, and cellular repair processes, contributing to anti-aging effects.
- Combination of NMN with other anti-aging compounds: NMN supplements are often formulated in combination with other anti-aging compounds such as resveratrol, pterostilbene, or antioxidants. These combinations may have synergistic effects in promoting longevity and overall health.
- NMN delivery methods and bioavailability: Various delivery methods are explored to improve NMN bioavailability and efficacy. These include sublingual tablets, liposomal formulations, and sustained-release capsules, which aim to enhance absorption and prolong the supplement's effects in the body.
- NMN's effects on specific age-related conditions: Research focuses on NMN's potential benefits for specific age-related conditions, including cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and metabolic disorders. Studies investigate how NMN supplementation may help prevent or alleviate these conditions.
- Safety and optimal dosage of NMN supplements: Ongoing studies aim to determine the safety profile and optimal dosage of NMN supplements for anti-aging benefits. This includes investigating potential side effects, long-term usage implications, and identifying the most effective dosing regimens for different age groups.
02 NMN's role in mitochondrial function
NMN supplementation may enhance mitochondrial function, which is crucial for cellular energy production. Improved mitochondrial health can lead to better overall cellular performance and potentially slow down age-related decline in various tissues and organs.Expand Specific Solutions03 NMN and sirtuin activation
NMN, as a precursor to NAD+, can activate sirtuin enzymes, particularly SIRT1. Sirtuins are involved in various cellular processes related to aging, including DNA repair, stress resistance, and metabolic regulation. Activation of these enzymes may contribute to the anti-aging benefits of NMN supplements.Expand Specific Solutions04 NMN's potential effects on longevity and healthspan
Research suggests that NMN supplementation may extend lifespan and improve healthspan in animal models. While human studies are ongoing, preliminary results indicate potential benefits in areas such as cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and metabolic regulation, which are all important aspects of healthy aging.Expand Specific Solutions05 Formulations and delivery methods for NMN supplements
Various formulations and delivery methods are being developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of NMN supplements. These include sublingual tablets, liposomal formulations, and combination with other compounds that may synergize with NMN's effects or improve its absorption and utilization in the body.Expand Specific Solutions
Key NMN Industry Players
The anti-aging NMN supplement market is in a growth phase, with increasing research and commercial interest. The global market size for NMN supplements is expanding rapidly, driven by growing consumer awareness of longevity and health optimization. Technologically, NMN supplements are at a moderate maturity level, with ongoing research to enhance efficacy and bioavailability. Key players like Washington University in St. Louis, Metro International Biotech LLC, and Suntory Holdings Ltd. are advancing the field through clinical trials and product development. Companies such as Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd. and TCI Co., Ltd. are focusing on commercial production and distribution. Academic institutions like Keio University and the University of California are contributing to the fundamental research, while biotechnology firms like Mirailab Bioscience, Inc. are bridging the gap between research and commercialization.
Metro International Biotech LLC
Suntory Holdings Ltd.
NMN Mechanism of Action
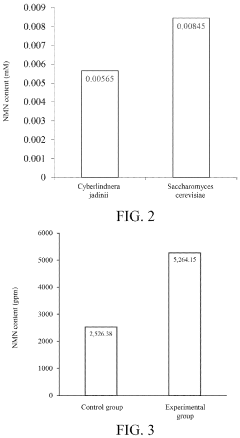
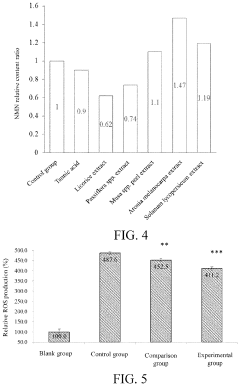
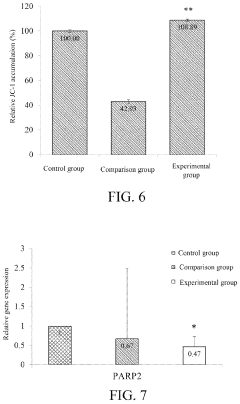
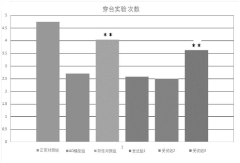
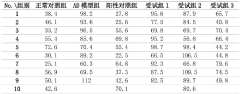
- A method for preparing yeast powder rich in nicotinamide mononucleotide through a multi-stage fermentation process using media with nicotinamide, tryptophan, and niacin, which increases the NMN content to at least 5000 ppm, and optionally includes plant extracts like Musa, Aronia, and Solanum extracts to enhance production.
- Development of a composition containing β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and L-α-glycerophosphocholine (α-GPC) in combination as a drug or functional agent for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease Foods, delivered via oral solid dosage forms or functional food forms.
NMN Safety and Efficacy
The safety and efficacy of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) supplements have been subjects of extensive research in recent years. Clinical studies have demonstrated promising results regarding the safety profile of NMN when administered orally. A 2019 study published in the journal "Endocrine" found that single oral doses of NMN up to 500 mg were well-tolerated in healthy men, with no significant adverse effects reported.
Regarding efficacy, several animal studies have shown positive outcomes in various aspects of aging. A landmark study in mice, published in "Cell Metabolism" in 2016, demonstrated that NMN supplementation could effectively mitigate age-associated physiological decline. The study reported improvements in energy metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and mitochondrial function.
Human trials, while more limited, have also yielded encouraging results. A 2021 study in the "Science" journal reported that NMN supplementation improved muscle insulin sensitivity and signaling in prediabetic women. Another study, published in "Nature Metabolism" in 2022, found that NMN supplementation enhanced aerobic capacity in amateur runners.
However, it's important to note that long-term safety data in humans is still limited. Most human trials have been relatively short-term, typically lasting a few months. The potential effects of prolonged NMN supplementation over years or decades remain to be fully elucidated.
Efficacy studies have primarily focused on biomarkers of aging and metabolic health. While these results are promising, more research is needed to definitively establish NMN's impact on lifespan and healthspan in humans. Additionally, optimal dosing regimens and potential interactions with other supplements or medications require further investigation.
Regulatory status is another crucial aspect of NMN safety and efficacy. In some countries, NMN is classified as a dietary supplement, while in others, it may be considered a novel food or drug. This classification impacts the level of scrutiny applied to safety and efficacy claims, as well as the availability of the supplement to consumers.
In conclusion, while initial studies on NMN safety and efficacy are promising, continued research is essential. Larger, long-term human trials are needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks associated with NMN supplementation as an anti-aging intervention.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplements is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in anti-aging products and the need for consumer protection. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies NMN as a dietary supplement, which falls under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This classification means that NMN supplements do not require pre-market approval, but manufacturers are responsible for ensuring their products are safe and that any claims made are not misleading.
However, the regulatory status of NMN has faced challenges. In November 2022, the FDA issued a statement indicating that NMN could not be marketed as a dietary supplement due to its investigation as a pharmaceutical drug. This decision was based on the "drug preclusion" provision of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The announcement created uncertainty in the market, leading to discussions between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies.
In other regions, the regulatory approach to NMN supplements varies. The European Union, for instance, classifies NMN as a novel food, requiring safety assessment and authorization before it can be marketed. This process involves submitting a comprehensive dossier to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) for evaluation. Japan, on the other hand, has approved NMN as a food ingredient, allowing its use in various products without specific health claims.
China has taken a proactive approach to NMN regulation. In 2020, the Chinese government approved NMN as a new food raw material, setting specific requirements for its production and use. This move has positioned China as a significant player in the global NMN market, potentially influencing regulatory decisions in other countries.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses labeling and marketing regulations. While manufacturers cannot make direct claims about NMN's ability to treat or prevent age-related diseases, they often use carefully worded statements about supporting cellular health or energy production. Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing these claims, emphasizing the need for scientific evidence to support any statements made about NMN's benefits.
As research into NMN's anti-aging properties continues, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve. Policymakers are faced with the challenge of balancing innovation in the anti-aging field with consumer safety concerns. This dynamic regulatory environment underscores the importance of ongoing dialogue between scientists, industry representatives, and regulatory agencies to establish clear guidelines for the development, marketing, and use of NMN supplements.