Advanced Techniques for Sodium Bisulfate Synthesis
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate Synthesis Background and Objectives
Sodium bisulfate, a versatile chemical compound with the formula NaHSO4, has been a subject of significant interest in various industrial applications for decades. The synthesis of this compound has evolved over time, driven by the need for more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly production methods. Historically, sodium bisulfate was primarily obtained as a byproduct of other chemical processes, but the growing demand for high-purity sodium bisulfate has led to the development of dedicated synthesis techniques.
The evolution of sodium bisulfate synthesis techniques can be traced back to the early 20th century, with initial methods relying on the reaction between sodium chloride and sulfuric acid. As industrial processes advanced, more sophisticated approaches emerged, including the use of sodium sulfate as a starting material and the implementation of continuous flow reactors. These advancements aimed to improve yield, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste generation.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing advanced techniques that address the challenges of traditional synthesis methods. These challenges include the corrosive nature of the reactants, the need for precise temperature and pH control, and the environmental impact of byproducts. Modern research efforts are exploring innovative approaches such as electrochemical synthesis, microwave-assisted reactions, and the use of novel catalysts to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of sodium bisulfate production.
The objectives of current research in advanced sodium bisulfate synthesis techniques are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a strong emphasis on improving the purity of the final product, as many applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food industries, require high-grade sodium bisulfate. Secondly, researchers are striving to develop more energy-efficient processes that can reduce the carbon footprint of production. Thirdly, there is a growing interest in creating closed-loop systems that minimize waste and maximize the recycling of reagents and byproducts.
Another key objective is the development of scalable processes that can meet the increasing global demand for sodium bisulfate while maintaining economic viability. This includes exploring continuous flow synthesis methods and investigating the potential of modular production units that can be easily scaled up or down based on market demands. Additionally, researchers are focusing on enhancing the safety aspects of sodium bisulfate synthesis, given the corrosive nature of the compounds involved.
As we look towards the future, the field of sodium bisulfate synthesis is poised for significant advancements. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in process optimization, the exploration of bio-inspired synthesis routes, and the development of novel reactor designs are all promising avenues for innovation. These advanced techniques aim not only to improve the efficiency and quality of sodium bisulfate production but also to align with global sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
The evolution of sodium bisulfate synthesis techniques can be traced back to the early 20th century, with initial methods relying on the reaction between sodium chloride and sulfuric acid. As industrial processes advanced, more sophisticated approaches emerged, including the use of sodium sulfate as a starting material and the implementation of continuous flow reactors. These advancements aimed to improve yield, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste generation.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing advanced techniques that address the challenges of traditional synthesis methods. These challenges include the corrosive nature of the reactants, the need for precise temperature and pH control, and the environmental impact of byproducts. Modern research efforts are exploring innovative approaches such as electrochemical synthesis, microwave-assisted reactions, and the use of novel catalysts to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of sodium bisulfate production.
The objectives of current research in advanced sodium bisulfate synthesis techniques are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a strong emphasis on improving the purity of the final product, as many applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food industries, require high-grade sodium bisulfate. Secondly, researchers are striving to develop more energy-efficient processes that can reduce the carbon footprint of production. Thirdly, there is a growing interest in creating closed-loop systems that minimize waste and maximize the recycling of reagents and byproducts.
Another key objective is the development of scalable processes that can meet the increasing global demand for sodium bisulfate while maintaining economic viability. This includes exploring continuous flow synthesis methods and investigating the potential of modular production units that can be easily scaled up or down based on market demands. Additionally, researchers are focusing on enhancing the safety aspects of sodium bisulfate synthesis, given the corrosive nature of the compounds involved.
As we look towards the future, the field of sodium bisulfate synthesis is poised for significant advancements. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in process optimization, the exploration of bio-inspired synthesis routes, and the development of novel reactor designs are all promising avenues for innovation. These advanced techniques aim not only to improve the efficiency and quality of sodium bisulfate production but also to align with global sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
Market Analysis for Sodium Bisulfate Applications
The sodium bisulfate market has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. As a key ingredient in numerous industrial processes and consumer products, sodium bisulfate has established itself as an essential chemical compound with a diverse range of uses.
In the water treatment sector, sodium bisulfate has gained prominence as an effective pH adjuster and dechlorinating agent. The increasing focus on water quality and environmental regulations has led to a surge in demand for sodium bisulfate in municipal water treatment plants, swimming pools, and industrial wastewater management systems. This application segment is expected to continue its growth trajectory due to the rising global concerns over water scarcity and the need for efficient water treatment solutions.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for sodium bisulfate. Its use as a preservative, acidulant, and cleaning agent in food processing has contributed to its increased adoption. The growing consumer preference for packaged and convenience foods, particularly in developing economies, is likely to fuel further demand in this sector.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, sodium bisulfate finds applications in various products such as hair dyes, bath salts, and exfoliating agents. The expanding beauty and personal care market, driven by rising disposable incomes and changing consumer lifestyles, is expected to create new opportunities for sodium bisulfate manufacturers.
The textile industry also utilizes sodium bisulfate in dyeing processes and as a neutralizing agent. With the global textile market experiencing steady growth, particularly in emerging economies, the demand for sodium bisulfate in this sector is projected to increase.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as a key market for sodium bisulfate, owing to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and population growth in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant consumers, primarily driven by stringent environmental regulations and the presence of established end-use industries.
Market challenges include fluctuations in raw material prices, particularly sulfuric acid, which can impact production costs and profit margins. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives may pose challenges to the sodium bisulfate market in certain applications.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for sodium bisulfate remains positive. The compound's multifunctional properties, coupled with ongoing research and development efforts to expand its applications, are expected to drive market growth in the coming years. As industries continue to seek efficient and cost-effective solutions, sodium bisulfate is well-positioned to maintain its importance in various industrial processes and consumer products.
In the water treatment sector, sodium bisulfate has gained prominence as an effective pH adjuster and dechlorinating agent. The increasing focus on water quality and environmental regulations has led to a surge in demand for sodium bisulfate in municipal water treatment plants, swimming pools, and industrial wastewater management systems. This application segment is expected to continue its growth trajectory due to the rising global concerns over water scarcity and the need for efficient water treatment solutions.
The food and beverage industry represents another significant market for sodium bisulfate. Its use as a preservative, acidulant, and cleaning agent in food processing has contributed to its increased adoption. The growing consumer preference for packaged and convenience foods, particularly in developing economies, is likely to fuel further demand in this sector.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, sodium bisulfate finds applications in various products such as hair dyes, bath salts, and exfoliating agents. The expanding beauty and personal care market, driven by rising disposable incomes and changing consumer lifestyles, is expected to create new opportunities for sodium bisulfate manufacturers.
The textile industry also utilizes sodium bisulfate in dyeing processes and as a neutralizing agent. With the global textile market experiencing steady growth, particularly in emerging economies, the demand for sodium bisulfate in this sector is projected to increase.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as a key market for sodium bisulfate, owing to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and population growth in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant consumers, primarily driven by stringent environmental regulations and the presence of established end-use industries.
Market challenges include fluctuations in raw material prices, particularly sulfuric acid, which can impact production costs and profit margins. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives may pose challenges to the sodium bisulfate market in certain applications.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for sodium bisulfate remains positive. The compound's multifunctional properties, coupled with ongoing research and development efforts to expand its applications, are expected to drive market growth in the coming years. As industries continue to seek efficient and cost-effective solutions, sodium bisulfate is well-positioned to maintain its importance in various industrial processes and consumer products.
Current Challenges in Sodium Bisulfate Production
The production of sodium bisulfate faces several significant challenges in the current industrial landscape. One of the primary issues is the control of reaction conditions during synthesis. The process requires precise temperature and pressure management to ensure optimal yield and product quality. Fluctuations in these parameters can lead to inconsistent product characteristics and reduced efficiency.
Another major challenge is the corrosive nature of the reactants and products involved in sodium bisulfate production. This necessitates the use of specialized equipment and materials that can withstand the harsh chemical environment. The selection and maintenance of such equipment add considerable costs to the production process and require ongoing attention to prevent equipment degradation and potential safety hazards.
The environmental impact of sodium bisulfate production is also a growing concern. The process generates acidic waste streams that require careful treatment and disposal. Regulatory pressures are increasing to minimize these environmental effects, pushing manufacturers to develop more sustainable production methods. This includes exploring ways to reduce emissions, improve waste management, and implement closed-loop systems for resource recovery.
Raw material sourcing presents another challenge, particularly in terms of sulfuric acid supply. The availability and cost of high-quality sulfuric acid can fluctuate, affecting production costs and consistency. Additionally, the transportation and storage of sulfuric acid pose logistical and safety challenges that must be carefully managed.
Energy efficiency is a critical issue in sodium bisulfate production. The process is energy-intensive, particularly in the drying and crystallization stages. Improving energy utilization without compromising product quality is a constant challenge for manufacturers, especially as energy costs continue to rise and environmental regulations become more stringent.
Product purity and consistency are ongoing concerns in sodium bisulfate synthesis. Impurities can significantly affect the performance of the final product in various applications. Achieving and maintaining high purity levels while operating at industrial scales requires sophisticated process control and quality assurance measures.
Lastly, the scaling of production to meet growing demand while maintaining product quality and cost-effectiveness is a complex challenge. As new applications for sodium bisulfate emerge, manufacturers must adapt their processes to handle larger volumes without sacrificing efficiency or quality. This often requires significant investment in research and development, as well as in new production facilities and technologies.
Another major challenge is the corrosive nature of the reactants and products involved in sodium bisulfate production. This necessitates the use of specialized equipment and materials that can withstand the harsh chemical environment. The selection and maintenance of such equipment add considerable costs to the production process and require ongoing attention to prevent equipment degradation and potential safety hazards.
The environmental impact of sodium bisulfate production is also a growing concern. The process generates acidic waste streams that require careful treatment and disposal. Regulatory pressures are increasing to minimize these environmental effects, pushing manufacturers to develop more sustainable production methods. This includes exploring ways to reduce emissions, improve waste management, and implement closed-loop systems for resource recovery.
Raw material sourcing presents another challenge, particularly in terms of sulfuric acid supply. The availability and cost of high-quality sulfuric acid can fluctuate, affecting production costs and consistency. Additionally, the transportation and storage of sulfuric acid pose logistical and safety challenges that must be carefully managed.
Energy efficiency is a critical issue in sodium bisulfate production. The process is energy-intensive, particularly in the drying and crystallization stages. Improving energy utilization without compromising product quality is a constant challenge for manufacturers, especially as energy costs continue to rise and environmental regulations become more stringent.
Product purity and consistency are ongoing concerns in sodium bisulfate synthesis. Impurities can significantly affect the performance of the final product in various applications. Achieving and maintaining high purity levels while operating at industrial scales requires sophisticated process control and quality assurance measures.
Lastly, the scaling of production to meet growing demand while maintaining product quality and cost-effectiveness is a complex challenge. As new applications for sodium bisulfate emerge, manufacturers must adapt their processes to handle larger volumes without sacrificing efficiency or quality. This often requires significant investment in research and development, as well as in new production facilities and technologies.
State-of-the-Art Synthesis Techniques
01 Use of sodium bisulfate in cleaning compositions
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various cleaning compositions due to its acidic properties. It can be incorporated into formulations for household and industrial cleaning products, providing effective cleaning and descaling capabilities. The compound's ability to lower pH and react with alkaline substances makes it useful for removing mineral deposits and tough stains.- Use of sodium bisulfate in cleaning compositions: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various cleaning compositions due to its acidic properties. It can be incorporated into formulations for household and industrial cleaning products, providing effective cleaning and descaling capabilities. The compound's ability to lower pH and react with mineral deposits makes it useful for removing limescale and other tough stains.
- Application in water treatment processes: Sodium bisulfate finds applications in water treatment processes, particularly for pH adjustment and disinfection. It can be used to lower the pH of water in swimming pools, spas, and industrial water systems. The compound's ability to neutralize alkalinity and control microbial growth makes it valuable in maintaining water quality and safety.
- Use as a food additive and preservative: Sodium bisulfate is employed as a food additive and preservative in various food products. It can be used to control acidity, prevent microbial growth, and extend shelf life. The compound's ability to inhibit enzymatic browning in fruits and vegetables makes it useful in food processing and preservation applications.
- Application in pharmaceutical formulations: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations for various purposes. It can be used as a pH adjuster, stabilizer, or solubilizing agent in drug preparations. The compound's ability to enhance the solubility and stability of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients makes it valuable in the development of oral and topical medications.
- Use in agricultural and horticultural applications: Sodium bisulfate finds applications in agriculture and horticulture. It can be used as a soil amendment to lower soil pH, making it suitable for acid-loving plants. The compound's ability to control algae growth in irrigation systems and its potential use as a fertilizer additive make it valuable in agricultural practices.
02 Application in water treatment processes
Sodium bisulfate finds applications in water treatment processes, particularly for pH adjustment and disinfection. It can be used to lower the pH of water in swimming pools, spas, and industrial water systems. The compound also aids in the removal of chloramines and helps maintain proper water chemistry in aquatic environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in food preservation and processing
Sodium bisulfate is employed in the food industry as a preservative and processing aid. It can be used to control microbial growth, prevent discoloration, and extend the shelf life of various food products. The compound's acidic nature also makes it useful in certain food processing applications, such as pH adjustment in beverages.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in personal care and cosmetic products
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in personal care and cosmetic formulations for its pH-adjusting properties. It can be incorporated into products such as hair dyes, skin exfoliants, and oral care items. The compound helps maintain the stability and effectiveness of active ingredients in these products by controlling acidity levels.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use in agricultural and horticultural applications
Sodium bisulfate finds applications in agriculture and horticulture as a soil amendment and fertilizer component. It can be used to lower soil pH, making it beneficial for acid-loving plants. The compound also aids in the solubilization of certain nutrients, improving their availability to plants. Additionally, it may be used in animal feed additives to control urinary pH in livestock.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The advanced techniques for sodium bisulfate synthesis market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The global market size is estimated to be in the range of $500 million to $1 billion, with steady annual growth projected. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations focused on improving efficiency and sustainability. Key players like Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and Sumitomo Metal Mining are investing in R&D to enhance production processes. Emerging companies such as Tessenderlo Kerley and Nanjing Gekof Institute are also contributing to technological advancements, particularly in environmental applications. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical giants and specialized manufacturers, with increasing focus on eco-friendly synthesis methods.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has pioneered a sodium bisulfate synthesis technique utilizing by-products from their petroleum refining processes. Their method involves the controlled oxidation of sodium sulfide waste streams, followed by precise pH adjustment using proprietary acid blends[2]. This approach not only produces high-quality sodium bisulfate but also addresses environmental concerns by reducing sulfur-containing waste. Sinopec's process achieves a conversion efficiency of over 95% and has been implemented in several of their refineries, reducing raw material costs by up to 40%[4].
Strengths: Cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and integrated with existing refinery operations. Weaknesses: Dependent on petroleum refining by-products, which may limit scalability for standalone production.
Sumitomo Metal Mining Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Metal Mining has developed an advanced hydrometallurgical process for sodium bisulfate synthesis as a by-product of their metal refining operations. Their technique involves the careful management of acid mine drainage, converting it into a valuable product through a series of precipitation and crystallization steps[10]. This process not only produces high-quality sodium bisulfate but also helps in environmental remediation. Sumitomo's method achieves a recovery rate of over 90% of sulfate ions from the mine drainage, significantly reducing the environmental impact of their mining operations while creating a marketable product[12].
Strengths: Environmentally beneficial, utilizes waste streams, and integrated with existing mining operations. Weaknesses: Production capacity limited by the availability of suitable mine drainage sources.
Innovative Approaches in Sodium Bisulfate Synthesis
Process for the synthesis of bisphosphonic acids and salts there of
PatentInactiveIN2076MUM2008A
Innovation
- A process involving a-substituted acetates combined with phosphorous acid and a halophosphorous compound in a hydrocarbon solvent, such as aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbons, to directly produce bisphosphonic acids and salts, reducing reaction time and improving yield and purity.
Method for production of sodium bicarbonate from sodium sulfate and apparatus for the same
PatentPendingKR1020230167643A
Innovation
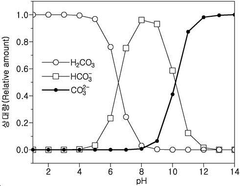
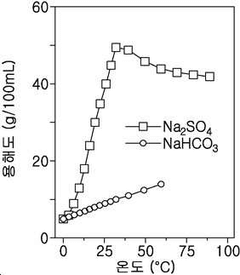
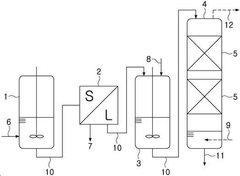
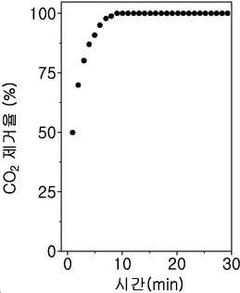
- A method involving the mixing of a sodium sulfate solution with an aqueous ammonia solution, followed by a countercurrent injection of carbon dioxide gas to enhance solubility and reaction efficiency, utilizing a reactor system with specific pH and temperature controls to produce high-purity sodium bicarbonate.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The synthesis of sodium bisulfate, while an important industrial process, carries significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered. The production process typically involves the reaction of sodium chloride with sulfuric acid, which can generate harmful byproducts and emissions if not properly managed. One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential release of sulfur dioxide, a major air pollutant that contributes to acid rain and respiratory issues. Advanced techniques for sodium bisulfate synthesis aim to mitigate these environmental impacts through improved process efficiency and emission control measures.
Sustainable production methods focus on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste generation. Closed-loop systems and heat recovery technologies are being implemented to capture and reuse thermal energy, significantly lowering the overall energy footprint of the synthesis process. Additionally, innovative catalysts and reaction conditions are being explored to enhance conversion rates and selectivity, thereby reducing the amount of raw materials required and minimizing unwanted side products.
Water usage and wastewater management are critical aspects of environmental sustainability in sodium bisulfate production. Advanced techniques incorporate water recycling systems and efficient purification methods to minimize freshwater consumption and reduce the discharge of contaminated effluents. Some facilities are implementing zero-liquid discharge technologies, aiming to eliminate wastewater release entirely and recover valuable byproducts from process streams.
The life cycle assessment of sodium bisulfate production is gaining importance in evaluating its overall environmental impact. This comprehensive approach considers not only the immediate production process but also the sourcing of raw materials, transportation, and end-of-life disposal or recycling. Advanced techniques are being developed to optimize each stage of the life cycle, from using renewable energy sources in production to designing products for easier recycling or biodegradation.
Regulatory compliance and voluntary environmental standards are driving innovation in sodium bisulfate synthesis. Stricter emissions regulations have led to the development of advanced scrubbing technologies and real-time monitoring systems to ensure that air and water quality standards are consistently met. Furthermore, industry leaders are adopting circular economy principles, exploring ways to repurpose byproducts and create closed-loop material flows within and between industries.
As sustainability becomes increasingly central to industrial operations, research into alternative synthesis routes for sodium bisulfate is intensifying. Biotechnological approaches, such as microbial synthesis or enzyme-catalyzed reactions, are being investigated as potentially more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional chemical processes. These bio-based methods could significantly reduce the carbon footprint and environmental impact of sodium bisulfate production in the future.
Sustainable production methods focus on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste generation. Closed-loop systems and heat recovery technologies are being implemented to capture and reuse thermal energy, significantly lowering the overall energy footprint of the synthesis process. Additionally, innovative catalysts and reaction conditions are being explored to enhance conversion rates and selectivity, thereby reducing the amount of raw materials required and minimizing unwanted side products.
Water usage and wastewater management are critical aspects of environmental sustainability in sodium bisulfate production. Advanced techniques incorporate water recycling systems and efficient purification methods to minimize freshwater consumption and reduce the discharge of contaminated effluents. Some facilities are implementing zero-liquid discharge technologies, aiming to eliminate wastewater release entirely and recover valuable byproducts from process streams.
The life cycle assessment of sodium bisulfate production is gaining importance in evaluating its overall environmental impact. This comprehensive approach considers not only the immediate production process but also the sourcing of raw materials, transportation, and end-of-life disposal or recycling. Advanced techniques are being developed to optimize each stage of the life cycle, from using renewable energy sources in production to designing products for easier recycling or biodegradation.
Regulatory compliance and voluntary environmental standards are driving innovation in sodium bisulfate synthesis. Stricter emissions regulations have led to the development of advanced scrubbing technologies and real-time monitoring systems to ensure that air and water quality standards are consistently met. Furthermore, industry leaders are adopting circular economy principles, exploring ways to repurpose byproducts and create closed-loop material flows within and between industries.
As sustainability becomes increasingly central to industrial operations, research into alternative synthesis routes for sodium bisulfate is intensifying. Biotechnological approaches, such as microbial synthesis or enzyme-catalyzed reactions, are being investigated as potentially more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional chemical processes. These bio-based methods could significantly reduce the carbon footprint and environmental impact of sodium bisulfate production in the future.
Quality Control and Regulatory Compliance
Quality control and regulatory compliance are critical aspects of advanced sodium bisulfate synthesis techniques. Manufacturers must adhere to stringent standards to ensure product safety, consistency, and efficacy. The quality control process begins with raw material inspection, where incoming chemicals are thoroughly tested for purity and composition. This step is crucial in preventing contamination and ensuring the final product meets specifications.
Throughout the synthesis process, in-line monitoring systems are employed to track key parameters such as temperature, pH, and reaction rates. Advanced spectroscopic techniques, including Near-Infrared (NIR) and Raman spectroscopy, allow for real-time analysis of the reaction progress and product quality. These methods enable rapid adjustments to process conditions, minimizing batch-to-batch variations and optimizing yield.
The final product undergoes rigorous testing to verify its chemical and physical properties. Analytical techniques such as titration, ion chromatography, and atomic absorption spectroscopy are used to determine the sodium bisulfate concentration and detect impurities. Particle size distribution, bulk density, and moisture content are also carefully controlled to meet customer specifications and ensure product stability during storage and transportation.
Regulatory compliance in sodium bisulfate production involves adherence to various national and international standards. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates sodium bisulfate as a food additive, requiring manufacturers to follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and maintain detailed documentation of production processes. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also oversees the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate production, mandating proper waste management and emissions control.
Globally, manufacturers must comply with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulations in the European Union and similar frameworks in other regions. These regulations require comprehensive safety assessments and registration of chemical substances, including sodium bisulfate, to ensure their safe use throughout the supply chain.
To maintain compliance and quality standards, advanced sodium bisulfate synthesis facilities implement robust quality management systems, often based on ISO 9001 standards. These systems encompass all aspects of production, from supplier qualification to customer feedback, ensuring continuous improvement and traceability. Regular internal and external audits are conducted to verify compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, manufacturers are also focusing on developing environmentally friendly production methods. This includes optimizing energy efficiency, reducing water consumption, and exploring greener synthesis routes. Such initiatives not only improve regulatory compliance but also enhance the overall sustainability profile of sodium bisulfate production.
Throughout the synthesis process, in-line monitoring systems are employed to track key parameters such as temperature, pH, and reaction rates. Advanced spectroscopic techniques, including Near-Infrared (NIR) and Raman spectroscopy, allow for real-time analysis of the reaction progress and product quality. These methods enable rapid adjustments to process conditions, minimizing batch-to-batch variations and optimizing yield.
The final product undergoes rigorous testing to verify its chemical and physical properties. Analytical techniques such as titration, ion chromatography, and atomic absorption spectroscopy are used to determine the sodium bisulfate concentration and detect impurities. Particle size distribution, bulk density, and moisture content are also carefully controlled to meet customer specifications and ensure product stability during storage and transportation.
Regulatory compliance in sodium bisulfate production involves adherence to various national and international standards. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates sodium bisulfate as a food additive, requiring manufacturers to follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and maintain detailed documentation of production processes. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also oversees the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate production, mandating proper waste management and emissions control.
Globally, manufacturers must comply with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulations in the European Union and similar frameworks in other regions. These regulations require comprehensive safety assessments and registration of chemical substances, including sodium bisulfate, to ensure their safe use throughout the supply chain.
To maintain compliance and quality standards, advanced sodium bisulfate synthesis facilities implement robust quality management systems, often based on ISO 9001 standards. These systems encompass all aspects of production, from supplier qualification to customer feedback, ensuring continuous improvement and traceability. Regular internal and external audits are conducted to verify compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, manufacturers are also focusing on developing environmentally friendly production methods. This includes optimizing energy efficiency, reducing water consumption, and exploring greener synthesis routes. Such initiatives not only improve regulatory compliance but also enhance the overall sustainability profile of sodium bisulfate production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!