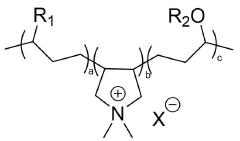
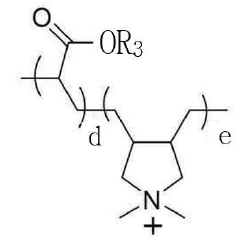
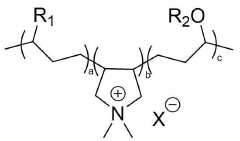
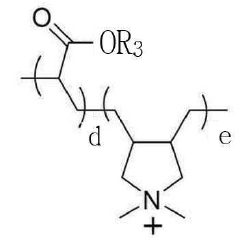
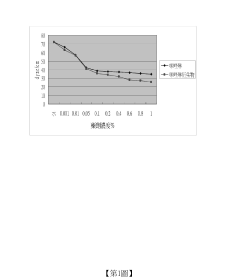
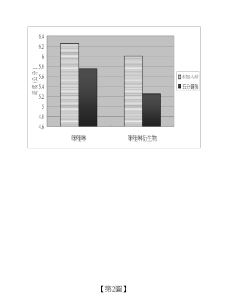
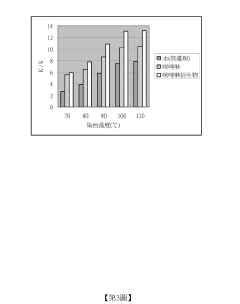
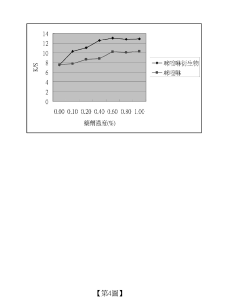
Sodium Bisulfate’s Influence on Textile Advancement and Dye Solutions
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate in Textiles: Background and Objectives
Sodium bisulfate has played a significant role in the textile industry for decades, contributing to various advancements in fabric processing and dyeing techniques. This compound, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate or sodium acid sulfate, is a versatile chemical with a wide range of applications in textile manufacturing. Its unique properties have made it an essential component in many textile processes, particularly in dyeing and finishing operations.
The evolution of sodium bisulfate's use in textiles can be traced back to the early 20th century when the chemical industry began to develop more sophisticated methods for fabric treatment. Initially, it was primarily used as a pH regulator in dyebaths, helping to maintain optimal acidity levels for effective dye absorption. Over time, researchers and textile engineers discovered additional benefits of sodium bisulfate, leading to its expanded use in various stages of textile production.
One of the key objectives in utilizing sodium bisulfate in textiles is to enhance the overall quality and performance of fabrics. This includes improving color fastness, increasing dye uptake, and enhancing the durability of finished products. By carefully controlling the pH levels during dyeing processes, sodium bisulfate helps to ensure more uniform and vibrant color results across different types of fibers and fabrics.
Another important goal in the application of sodium bisulfate is to optimize resource efficiency in textile manufacturing. The compound's ability to adjust pH levels quickly and effectively allows for more precise control over dyeing processes, potentially reducing water and energy consumption. This aligns with the industry's growing focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility.
In recent years, the textile industry has faced increasing pressure to develop more eco-friendly production methods. This has led to a renewed interest in exploring the potential of sodium bisulfate as a more sustainable alternative to some traditional chemicals used in textile processing. Researchers are investigating ways to maximize the efficiency of sodium bisulfate usage while minimizing its environmental impact.
The ongoing technological advancements in textile manufacturing have also influenced the application of sodium bisulfate. Modern dyeing equipment and automated process control systems have enabled more precise dosing and monitoring of chemical additives, including sodium bisulfate. This has opened up new possibilities for fine-tuning fabric treatments and achieving more consistent results across large-scale production runs.
As the textile industry continues to evolve, the role of sodium bisulfate is expected to expand further. Current research is focused on developing novel applications for this versatile compound, such as its potential use in smart textiles and advanced functional fabrics. These emerging areas present exciting opportunities for innovation and could lead to significant breakthroughs in textile technology.
The evolution of sodium bisulfate's use in textiles can be traced back to the early 20th century when the chemical industry began to develop more sophisticated methods for fabric treatment. Initially, it was primarily used as a pH regulator in dyebaths, helping to maintain optimal acidity levels for effective dye absorption. Over time, researchers and textile engineers discovered additional benefits of sodium bisulfate, leading to its expanded use in various stages of textile production.
One of the key objectives in utilizing sodium bisulfate in textiles is to enhance the overall quality and performance of fabrics. This includes improving color fastness, increasing dye uptake, and enhancing the durability of finished products. By carefully controlling the pH levels during dyeing processes, sodium bisulfate helps to ensure more uniform and vibrant color results across different types of fibers and fabrics.
Another important goal in the application of sodium bisulfate is to optimize resource efficiency in textile manufacturing. The compound's ability to adjust pH levels quickly and effectively allows for more precise control over dyeing processes, potentially reducing water and energy consumption. This aligns with the industry's growing focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility.
In recent years, the textile industry has faced increasing pressure to develop more eco-friendly production methods. This has led to a renewed interest in exploring the potential of sodium bisulfate as a more sustainable alternative to some traditional chemicals used in textile processing. Researchers are investigating ways to maximize the efficiency of sodium bisulfate usage while minimizing its environmental impact.
The ongoing technological advancements in textile manufacturing have also influenced the application of sodium bisulfate. Modern dyeing equipment and automated process control systems have enabled more precise dosing and monitoring of chemical additives, including sodium bisulfate. This has opened up new possibilities for fine-tuning fabric treatments and achieving more consistent results across large-scale production runs.
As the textile industry continues to evolve, the role of sodium bisulfate is expected to expand further. Current research is focused on developing novel applications for this versatile compound, such as its potential use in smart textiles and advanced functional fabrics. These emerging areas present exciting opportunities for innovation and could lead to significant breakthroughs in textile technology.
Market Analysis for Sodium Bisulfate in Textile Industry
The global market for sodium bisulfate in the textile industry has been experiencing steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality textiles and the need for efficient dyeing processes. Sodium bisulfate plays a crucial role in textile manufacturing, particularly in dyeing and finishing processes, due to its ability to control pH levels and enhance dye fixation.
The textile industry's expansion in developing countries, especially in Asia-Pacific regions such as China, India, and Bangladesh, has significantly contributed to the rising demand for sodium bisulfate. These countries have become major textile manufacturing hubs, catering to both domestic and international markets. The growing population, rising disposable incomes, and changing fashion trends in these regions have further fueled the demand for textiles, consequently boosting the sodium bisulfate market.
In developed economies, the focus on sustainable and eco-friendly textile production has led to increased adoption of sodium bisulfate as a more environmentally friendly alternative to other chemical agents. This shift towards greener practices has opened up new opportunities for sodium bisulfate suppliers in premium textile markets.
The denim industry, in particular, has been a significant consumer of sodium bisulfate. The popularity of denim products worldwide has sustained a consistent demand for sodium bisulfate in denim processing, where it is used for achieving desired wash effects and color fading.
Market analysts predict that the sodium bisulfate market in the textile industry will continue to grow at a moderate rate in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the ongoing technological advancements in textile manufacturing, which often require precise pH control and efficient dyeing processes where sodium bisulfate excels.
However, the market also faces challenges. Fluctuations in raw material prices, particularly sulfuric acid, can impact the production costs of sodium bisulfate. Additionally, stringent environmental regulations in some regions may require manufacturers to invest in advanced treatment systems for effluents containing sodium bisulfate, potentially affecting profit margins.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for sodium bisulfate in the textile industry remains positive. The compound's versatility, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with various textile processes continue to make it an essential chemical in the industry. As textile manufacturers strive for improved product quality and process efficiency, the demand for sodium bisulfate is expected to remain robust in the foreseeable future.
The textile industry's expansion in developing countries, especially in Asia-Pacific regions such as China, India, and Bangladesh, has significantly contributed to the rising demand for sodium bisulfate. These countries have become major textile manufacturing hubs, catering to both domestic and international markets. The growing population, rising disposable incomes, and changing fashion trends in these regions have further fueled the demand for textiles, consequently boosting the sodium bisulfate market.
In developed economies, the focus on sustainable and eco-friendly textile production has led to increased adoption of sodium bisulfate as a more environmentally friendly alternative to other chemical agents. This shift towards greener practices has opened up new opportunities for sodium bisulfate suppliers in premium textile markets.
The denim industry, in particular, has been a significant consumer of sodium bisulfate. The popularity of denim products worldwide has sustained a consistent demand for sodium bisulfate in denim processing, where it is used for achieving desired wash effects and color fading.
Market analysts predict that the sodium bisulfate market in the textile industry will continue to grow at a moderate rate in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the ongoing technological advancements in textile manufacturing, which often require precise pH control and efficient dyeing processes where sodium bisulfate excels.
However, the market also faces challenges. Fluctuations in raw material prices, particularly sulfuric acid, can impact the production costs of sodium bisulfate. Additionally, stringent environmental regulations in some regions may require manufacturers to invest in advanced treatment systems for effluents containing sodium bisulfate, potentially affecting profit margins.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for sodium bisulfate in the textile industry remains positive. The compound's versatility, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with various textile processes continue to make it an essential chemical in the industry. As textile manufacturers strive for improved product quality and process efficiency, the demand for sodium bisulfate is expected to remain robust in the foreseeable future.
Current Challenges in Sodium Bisulfate Application
Despite the widespread use of sodium bisulfate in textile processing and dyeing, several challenges persist in its application. One of the primary issues is the corrosive nature of sodium bisulfate, which can lead to equipment degradation over time. This necessitates the use of specialized, corrosion-resistant materials in manufacturing processes, increasing production costs and potentially limiting the scalability of operations.
Another significant challenge lies in maintaining precise pH control during textile treatment. Sodium bisulfate's effectiveness as a pH adjuster is well-established, but achieving and maintaining the optimal pH level for different textile processes can be complex. Variations in fabric composition, dye types, and desired outcomes require careful calibration of sodium bisulfate concentrations, which can be difficult to standardize across diverse production lines.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in sodium bisulfate application. The discharge of effluents containing residual sodium bisulfate can potentially impact aquatic ecosystems if not properly treated. This necessitates the implementation of robust wastewater treatment systems, which can be costly and technologically demanding, especially for smaller textile manufacturers.
The interaction between sodium bisulfate and various dyes presents another area of difficulty. While it enhances the fixation of certain dyes, it may adversely affect others, leading to color inconsistencies or reduced color fastness. This variability requires extensive testing and formulation adjustments, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Furthermore, worker safety remains a concern in the handling and application of sodium bisulfate. Its acidic nature poses risks of skin irritation and respiratory issues if proper safety protocols are not strictly adhered to. This necessitates ongoing training and the use of personal protective equipment, adding to operational complexities and costs.
The textile industry's push towards more sustainable practices also presents challenges in sodium bisulfate usage. There is growing pressure to find eco-friendly alternatives or to develop methods that reduce the overall chemical footprint of textile processing. This requires significant research and development efforts to innovate processes that maintain efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
Lastly, the global supply chain for sodium bisulfate can be subject to fluctuations, affecting its availability and pricing. These market dynamics can impact the consistency of textile production processes and potentially drive up costs, particularly for manufacturers in regions with limited access to reliable chemical suppliers.
Another significant challenge lies in maintaining precise pH control during textile treatment. Sodium bisulfate's effectiveness as a pH adjuster is well-established, but achieving and maintaining the optimal pH level for different textile processes can be complex. Variations in fabric composition, dye types, and desired outcomes require careful calibration of sodium bisulfate concentrations, which can be difficult to standardize across diverse production lines.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in sodium bisulfate application. The discharge of effluents containing residual sodium bisulfate can potentially impact aquatic ecosystems if not properly treated. This necessitates the implementation of robust wastewater treatment systems, which can be costly and technologically demanding, especially for smaller textile manufacturers.
The interaction between sodium bisulfate and various dyes presents another area of difficulty. While it enhances the fixation of certain dyes, it may adversely affect others, leading to color inconsistencies or reduced color fastness. This variability requires extensive testing and formulation adjustments, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Furthermore, worker safety remains a concern in the handling and application of sodium bisulfate. Its acidic nature poses risks of skin irritation and respiratory issues if proper safety protocols are not strictly adhered to. This necessitates ongoing training and the use of personal protective equipment, adding to operational complexities and costs.
The textile industry's push towards more sustainable practices also presents challenges in sodium bisulfate usage. There is growing pressure to find eco-friendly alternatives or to develop methods that reduce the overall chemical footprint of textile processing. This requires significant research and development efforts to innovate processes that maintain efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
Lastly, the global supply chain for sodium bisulfate can be subject to fluctuations, affecting its availability and pricing. These market dynamics can impact the consistency of textile production processes and potentially drive up costs, particularly for manufacturers in regions with limited access to reliable chemical suppliers.
Existing Sodium Bisulfate Solutions in Dyeing
01 pH adjustment in chemical processes
Sodium bisulfate is used as a pH adjuster in various chemical processes. It can effectively lower the pH of solutions, making it useful in applications where acidic conditions are required. This property is particularly valuable in water treatment, cleaning products, and industrial processes where pH control is crucial.- pH adjustment in chemical processes: Sodium bisulfate is used as a pH adjuster in various chemical processes. It can effectively lower the pH of solutions, making it useful in applications where acidic conditions are required. This property is particularly valuable in water treatment, cleaning products, and industrial processes where pH control is crucial.
- Food preservation and flavor enhancement: In the food industry, sodium bisulfate serves as a preservative and flavor enhancer. It can inhibit microbial growth, extend shelf life, and contribute to the tartness of certain foods. Its use in food products helps maintain quality and safety while improving taste profiles.
- Water treatment and disinfection: Sodium bisulfate plays a significant role in water treatment processes. It can be used to adjust pH levels in swimming pools and other water systems, helping to maintain proper chemical balance and enhance the effectiveness of disinfectants. Additionally, it can aid in the removal of chloramines and other contaminants.
- Industrial cleaning and descaling: The acidic properties of sodium bisulfate make it effective for industrial cleaning and descaling applications. It can remove mineral deposits, rust, and other stubborn contaminants from various surfaces and equipment. This is particularly useful in industries such as manufacturing, mining, and oil and gas.
- Environmental remediation: Sodium bisulfate has applications in environmental remediation processes. It can be used to treat contaminated soils and groundwater, helping to neutralize alkaline conditions and facilitate the removal of certain pollutants. Its effectiveness in pH adjustment makes it valuable in various environmental cleanup efforts.
02 Food preservation and flavor enhancement
In the food industry, sodium bisulfate serves as a preservative and flavor enhancer. It helps prevent microbial growth, extends shelf life, and can impart a tangy taste to certain food products. Its use is regulated in many countries due to its potential effects on food quality and safety.Expand Specific Solutions03 Water treatment and disinfection
Sodium bisulfate is employed in water treatment processes for its ability to adjust pH and act as a disinfectant. It can help control algae growth in swimming pools and other water systems. Additionally, it's used in the treatment of wastewater to neutralize alkaline effluents before discharge.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial cleaning and descaling
In industrial applications, sodium bisulfate is used as a cleaning agent and descaler. It can effectively remove mineral deposits, rust, and other contaminants from various surfaces and equipment. This makes it valuable in maintenance processes for industrial machinery and systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental remediation
Sodium bisulfate plays a role in environmental remediation efforts. It can be used to treat contaminated soils and groundwater, particularly in cases of heavy metal pollution. Its ability to adjust pH and form complexes with certain contaminants makes it useful in soil and water decontamination processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sodium Bisulfate and Textile Chemistry
The sodium bisulfate market in textile advancement and dye solutions is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for efficient dyeing processes and sustainable textile production. The market size is expanding, with key players like BASF, Henkel, and Procter & Gamble investing in research and development. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with established companies like Rohm & Haas and Hoechst AG having a strong foundation. However, there's room for innovation, particularly in eco-friendly applications. Universities such as Dalian University of Technology and University of Leeds are contributing to academic research, potentially leading to breakthroughs in sodium bisulfate utilization for textile advancements.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed innovative solutions using sodium bisulfate for textile advancement and dye solutions. Their approach involves utilizing sodium bisulfate as a pH regulator in dyeing processes, which enhances color fastness and improves dye penetration[1]. BASF has also created a sustainable dyeing method that incorporates sodium bisulfate to reduce water consumption by up to 50% compared to conventional processes[2]. Additionally, they have formulated a novel textile finishing treatment using sodium bisulfate to impart wrinkle-resistant properties while maintaining fabric softness[3].
Strengths: Improved color fastness, reduced water consumption, and enhanced fabric properties. Weaknesses: Potential for fabric degradation if not properly controlled, and the need for specialized equipment for some applications.
Archroma IP GmbH
Technical Solution: Archroma IP GmbH has pioneered the use of sodium bisulfate in eco-friendly textile processing and dyeing solutions. They have developed a low-impact dyeing system that utilizes sodium bisulfate to achieve optimal pH levels, resulting in up to 30% less water and energy consumption[7]. Archroma has also created a sodium bisulfate-based pre-treatment process for cotton fabrics, which improves dye uptake and reduces the need for harsh chemicals[8]. Additionally, they have formulated a sodium bisulfate-containing post-treatment solution that enhances color fastness and reduces effluent load[9].
Strengths: Reduced environmental impact, improved dye uptake, and enhanced color fastness. Weaknesses: Potential for increased production costs and the need for specialized training for proper implementation.
Innovative Sodium Bisulfate Formulations for Textiles
Cationizing agents for dyeing textiles with minimal amount of neutral salt, preparation method thereof, and method for dyeing textiles using same
PatentActiveKR1020210147766A
Innovation
- A novel polymeric cationizing agent, represented by Formulas 1 and 2, is used to modify fiber surfaces, reducing neutral salt usage by 50% or more, and enabling excellent dyeability without uneven dyeing through electrostatic bonding.
Dyeing auxiliary and manufacturing method and applied dyeing process thereof Capable of increasing the dyeing rate of the fabric and reduce the residual rate of the dyes in the subsequent wastewater during the dyeing process
PatentInactiveTW202206414A
Innovation
- Synthesis of imidazoline derivative surfactant using imidazoline, epichlorohydrin, and sodium bisulfite as raw materials.
- Utilization of the agglutination properties of the auxiliary to capture dyes from wastewater and bring them into the cellulose fabric.
- Simultaneous increase in fabric dyeing rate and reduction of dye residual rate in wastewater.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Bisulfate in Textiles
The environmental impact of sodium bisulfate in textiles is a critical consideration for the industry's sustainability efforts. This compound, widely used in textile processing, particularly in dyeing and finishing operations, has both direct and indirect effects on the environment.
Sodium bisulfate's primary environmental concern stems from its acidic nature. When released into water systems, it can significantly lower the pH, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems. This acidification can disrupt the delicate balance of freshwater habitats, affecting fish populations and other aquatic organisms. Moreover, the increased acidity can lead to the mobilization of heavy metals in sediments, exacerbating water pollution issues.
In textile manufacturing, the use of sodium bisulfate often results in wastewater with high salt content. This saline effluent, if not properly treated, can have detrimental effects on soil quality when discharged onto land. It may lead to soil salinization, reducing agricultural productivity in affected areas and altering local flora composition.
The production of sodium bisulfate itself contributes to environmental concerns. The manufacturing process typically involves the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium chloride or sodium hydroxide, both of which have their own environmental footprints. The energy-intensive nature of this production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, linking the compound to broader climate change issues.
However, it's important to note that sodium bisulfate also plays a role in environmental protection within the textile industry. Its use in pH adjustment of wastewater can help neutralize alkaline effluents, which is crucial for meeting environmental regulations. Additionally, its effectiveness in dye fixation can reduce the amount of unfixed dyes in wastewater, potentially decreasing the overall environmental impact of textile dyeing processes.
The textile industry has been exploring alternatives and optimizing processes to mitigate the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate. This includes developing closed-loop systems for water recycling, implementing advanced wastewater treatment technologies, and researching bio-based alternatives for pH adjustment and dye fixation. These efforts aim to reduce the reliance on sodium bisulfate and minimize its release into the environment.
In conclusion, while sodium bisulfate serves important functions in textile processing, its environmental impact necessitates careful management and ongoing research into more sustainable alternatives. The industry's challenge lies in balancing the compound's technical benefits with the imperative of environmental stewardship, driving innovation towards greener textile manufacturing practices.
Sodium bisulfate's primary environmental concern stems from its acidic nature. When released into water systems, it can significantly lower the pH, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems. This acidification can disrupt the delicate balance of freshwater habitats, affecting fish populations and other aquatic organisms. Moreover, the increased acidity can lead to the mobilization of heavy metals in sediments, exacerbating water pollution issues.
In textile manufacturing, the use of sodium bisulfate often results in wastewater with high salt content. This saline effluent, if not properly treated, can have detrimental effects on soil quality when discharged onto land. It may lead to soil salinization, reducing agricultural productivity in affected areas and altering local flora composition.
The production of sodium bisulfate itself contributes to environmental concerns. The manufacturing process typically involves the reaction of sulfuric acid with sodium chloride or sodium hydroxide, both of which have their own environmental footprints. The energy-intensive nature of this production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, linking the compound to broader climate change issues.
However, it's important to note that sodium bisulfate also plays a role in environmental protection within the textile industry. Its use in pH adjustment of wastewater can help neutralize alkaline effluents, which is crucial for meeting environmental regulations. Additionally, its effectiveness in dye fixation can reduce the amount of unfixed dyes in wastewater, potentially decreasing the overall environmental impact of textile dyeing processes.
The textile industry has been exploring alternatives and optimizing processes to mitigate the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate. This includes developing closed-loop systems for water recycling, implementing advanced wastewater treatment technologies, and researching bio-based alternatives for pH adjustment and dye fixation. These efforts aim to reduce the reliance on sodium bisulfate and minimize its release into the environment.
In conclusion, while sodium bisulfate serves important functions in textile processing, its environmental impact necessitates careful management and ongoing research into more sustainable alternatives. The industry's challenge lies in balancing the compound's technical benefits with the imperative of environmental stewardship, driving innovation towards greener textile manufacturing practices.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Sodium Bisulfate Usage
The cost-benefit analysis of sodium bisulfate usage in textile advancement and dye solutions reveals a complex interplay of economic, environmental, and technical factors. From an economic perspective, sodium bisulfate offers significant cost advantages compared to alternative chemicals. Its relatively low production cost and widespread availability contribute to reduced operational expenses for textile manufacturers.
In terms of process efficiency, sodium bisulfate's multifunctional properties streamline various textile treatment stages. It acts as an effective pH regulator, dye fixative, and cleaning agent, potentially reducing the need for multiple chemicals and simplifying production processes. This consolidation of functions can lead to decreased labor costs and improved production throughput.
However, the benefits of sodium bisulfate usage must be weighed against potential drawbacks. While generally considered safe, prolonged exposure or mishandling can pose health risks to workers, necessitating investment in proper safety equipment and training. Additionally, the corrosive nature of sodium bisulfate may accelerate wear on machinery and infrastructure, potentially increasing maintenance and replacement costs over time.
From an environmental standpoint, sodium bisulfate presents a mixed profile. Its biodegradability and low toxicity to aquatic life make it a more environmentally friendly option compared to some alternatives. However, improper disposal or accidental releases can still impact local ecosystems, particularly through pH alteration of water bodies. Compliance with environmental regulations may require investment in wastewater treatment systems, offsetting some of the initial cost savings.
The use of sodium bisulfate in dye solutions offers notable benefits in color fastness and dye penetration, potentially reducing the quantity of dye required and improving product quality. This can lead to decreased material costs and enhanced customer satisfaction, potentially commanding higher prices for finished textiles.
Long-term considerations include the potential for sodium bisulfate to contribute to sustainable textile production practices. Its role in water-saving processes and ability to facilitate recycling of process water align with growing industry trends towards sustainability. This alignment may offer competitive advantages and improved brand perception in environmentally conscious markets.
In conclusion, the cost-benefit analysis suggests that sodium bisulfate usage in textile advancement and dye solutions offers significant economic and technical advantages. However, these benefits must be carefully balanced against potential health, safety, and environmental considerations to ensure sustainable and responsible implementation in textile manufacturing processes.
In terms of process efficiency, sodium bisulfate's multifunctional properties streamline various textile treatment stages. It acts as an effective pH regulator, dye fixative, and cleaning agent, potentially reducing the need for multiple chemicals and simplifying production processes. This consolidation of functions can lead to decreased labor costs and improved production throughput.
However, the benefits of sodium bisulfate usage must be weighed against potential drawbacks. While generally considered safe, prolonged exposure or mishandling can pose health risks to workers, necessitating investment in proper safety equipment and training. Additionally, the corrosive nature of sodium bisulfate may accelerate wear on machinery and infrastructure, potentially increasing maintenance and replacement costs over time.
From an environmental standpoint, sodium bisulfate presents a mixed profile. Its biodegradability and low toxicity to aquatic life make it a more environmentally friendly option compared to some alternatives. However, improper disposal or accidental releases can still impact local ecosystems, particularly through pH alteration of water bodies. Compliance with environmental regulations may require investment in wastewater treatment systems, offsetting some of the initial cost savings.
The use of sodium bisulfate in dye solutions offers notable benefits in color fastness and dye penetration, potentially reducing the quantity of dye required and improving product quality. This can lead to decreased material costs and enhanced customer satisfaction, potentially commanding higher prices for finished textiles.
Long-term considerations include the potential for sodium bisulfate to contribute to sustainable textile production practices. Its role in water-saving processes and ability to facilitate recycling of process water align with growing industry trends towards sustainability. This alignment may offer competitive advantages and improved brand perception in environmentally conscious markets.
In conclusion, the cost-benefit analysis suggests that sodium bisulfate usage in textile advancement and dye solutions offers significant economic and technical advantages. However, these benefits must be carefully balanced against potential health, safety, and environmental considerations to ensure sustainable and responsible implementation in textile manufacturing processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!