How to Optimize Sodium Bisulfate Use in Enhanced Dairy Products?
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate in Dairy: Background and Objectives
Sodium bisulfate has emerged as a crucial ingredient in the dairy industry, particularly in the development of enhanced dairy products. This compound, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate, has a long history of use in food processing and preservation. Its application in dairy products has evolved significantly over the years, driven by the industry's need for improved product quality, extended shelf life, and enhanced functional properties.
The dairy industry has been continuously seeking ways to innovate and improve its products to meet changing consumer demands and regulatory requirements. Sodium bisulfate has played a pivotal role in this evolution, offering multiple benefits such as pH adjustment, microbial control, and flavor enhancement. Its ability to act as an acidulant and preservative has made it particularly valuable in the production of cultured dairy products, cheese, and other fermented milk products.
The primary objective of optimizing sodium bisulfate use in enhanced dairy products is to maximize its beneficial effects while minimizing any potential drawbacks. This involves finding the right balance between functionality and cost-effectiveness, as well as addressing any safety concerns associated with its use. The optimization process aims to improve product quality, extend shelf life, and enhance the overall consumer experience without compromising on taste or nutritional value.
Another key goal is to align the use of sodium bisulfate with current market trends and consumer preferences. As consumers increasingly demand clean label products with minimal additives, the dairy industry faces the challenge of utilizing sodium bisulfate in a way that meets these expectations while still maintaining product integrity and safety. This necessitates a thorough understanding of the compound's properties and its interactions with various dairy components.
Furthermore, the optimization of sodium bisulfate use is closely tied to regulatory compliance. Different regions and countries have varying regulations regarding the use of food additives, including sodium bisulfate. Therefore, a critical objective is to ensure that the optimization strategies developed are in line with these regulatory requirements, allowing for global market access and product consistency across different jurisdictions.
As the dairy industry continues to evolve, the role of sodium bisulfate in enhanced dairy products is expected to grow. This presents both opportunities and challenges for manufacturers, researchers, and food technologists. By focusing on optimizing its use, the industry can unlock new possibilities for product innovation, improved quality, and enhanced consumer satisfaction in the ever-competitive dairy market.
The dairy industry has been continuously seeking ways to innovate and improve its products to meet changing consumer demands and regulatory requirements. Sodium bisulfate has played a pivotal role in this evolution, offering multiple benefits such as pH adjustment, microbial control, and flavor enhancement. Its ability to act as an acidulant and preservative has made it particularly valuable in the production of cultured dairy products, cheese, and other fermented milk products.
The primary objective of optimizing sodium bisulfate use in enhanced dairy products is to maximize its beneficial effects while minimizing any potential drawbacks. This involves finding the right balance between functionality and cost-effectiveness, as well as addressing any safety concerns associated with its use. The optimization process aims to improve product quality, extend shelf life, and enhance the overall consumer experience without compromising on taste or nutritional value.
Another key goal is to align the use of sodium bisulfate with current market trends and consumer preferences. As consumers increasingly demand clean label products with minimal additives, the dairy industry faces the challenge of utilizing sodium bisulfate in a way that meets these expectations while still maintaining product integrity and safety. This necessitates a thorough understanding of the compound's properties and its interactions with various dairy components.
Furthermore, the optimization of sodium bisulfate use is closely tied to regulatory compliance. Different regions and countries have varying regulations regarding the use of food additives, including sodium bisulfate. Therefore, a critical objective is to ensure that the optimization strategies developed are in line with these regulatory requirements, allowing for global market access and product consistency across different jurisdictions.
As the dairy industry continues to evolve, the role of sodium bisulfate in enhanced dairy products is expected to grow. This presents both opportunities and challenges for manufacturers, researchers, and food technologists. By focusing on optimizing its use, the industry can unlock new possibilities for product innovation, improved quality, and enhanced consumer satisfaction in the ever-competitive dairy market.
Market Analysis for Enhanced Dairy Products
The enhanced dairy products market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for healthier and more functional food options. This segment encompasses a wide range of products, including fortified milk, probiotic yogurts, protein-enriched cheeses, and lactose-free alternatives. The global enhanced dairy market was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $24 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of around 8% during the forecast period.
Several factors contribute to the expanding market for enhanced dairy products. Health-conscious consumers are seeking products that offer additional nutritional benefits beyond traditional dairy. The rising prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases and growing awareness of the importance of gut health have fueled demand for probiotic and prebiotic-enriched dairy products. Additionally, the increasing popularity of high-protein diets and sports nutrition has boosted the market for protein-fortified dairy items.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the enhanced dairy products market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by changing dietary habits, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing middle-class population in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by intense competition among major dairy companies and innovative startups. Key players in the enhanced dairy sector include Danone, Nestlé, Arla Foods, and Fonterra. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to introduce new products and improve existing formulations. The use of sodium bisulfate in enhanced dairy products presents both opportunities and challenges for manufacturers.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards clean label products with minimal additives, which may impact the use of sodium bisulfate in certain applications. However, its potential benefits in extending shelf life, improving texture, and enhancing flavor profiles make it an attractive ingredient for dairy product innovation. Manufacturers must balance these factors while optimizing sodium bisulfate use to meet consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
The market for lactose-free and plant-based dairy alternatives is also experiencing rapid growth, presenting both competition and opportunities for enhanced dairy products. This trend is driven by increasing lactose intolerance awareness and the rising popularity of vegan diets. To remain competitive, traditional dairy manufacturers are exploring ways to incorporate sodium bisulfate and other functional ingredients into plant-based alternatives, further expanding the market potential.
Several factors contribute to the expanding market for enhanced dairy products. Health-conscious consumers are seeking products that offer additional nutritional benefits beyond traditional dairy. The rising prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases and growing awareness of the importance of gut health have fueled demand for probiotic and prebiotic-enriched dairy products. Additionally, the increasing popularity of high-protein diets and sports nutrition has boosted the market for protein-fortified dairy items.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the enhanced dairy products market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by changing dietary habits, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing middle-class population in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by intense competition among major dairy companies and innovative startups. Key players in the enhanced dairy sector include Danone, Nestlé, Arla Foods, and Fonterra. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to introduce new products and improve existing formulations. The use of sodium bisulfate in enhanced dairy products presents both opportunities and challenges for manufacturers.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards clean label products with minimal additives, which may impact the use of sodium bisulfate in certain applications. However, its potential benefits in extending shelf life, improving texture, and enhancing flavor profiles make it an attractive ingredient for dairy product innovation. Manufacturers must balance these factors while optimizing sodium bisulfate use to meet consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
The market for lactose-free and plant-based dairy alternatives is also experiencing rapid growth, presenting both competition and opportunities for enhanced dairy products. This trend is driven by increasing lactose intolerance awareness and the rising popularity of vegan diets. To remain competitive, traditional dairy manufacturers are exploring ways to incorporate sodium bisulfate and other functional ingredients into plant-based alternatives, further expanding the market potential.
Current Challenges in Sodium Bisulfate Application
The application of sodium bisulfate in enhanced dairy products faces several significant challenges that hinder its optimal utilization. One of the primary issues is the precise control of acidity levels in dairy products. Sodium bisulfate, being a strong acidulant, can easily lead to over-acidification if not carefully managed. This can result in undesirable changes in taste, texture, and overall product quality.
Another challenge lies in the potential interaction of sodium bisulfate with other ingredients in dairy formulations. These interactions may affect the stability of the product, leading to issues such as protein denaturation or unwanted precipitation. This is particularly problematic in complex dairy systems with multiple components, where the balance of ingredients is crucial for maintaining product integrity.
The impact of sodium bisulfate on the nutritional profile of dairy products is also a concern. While it can enhance certain functional properties, excessive use may lead to a reduction in the bioavailability of essential nutrients, particularly calcium and other minerals. This poses a challenge in maintaining the nutritional value that consumers expect from dairy products.
Furthermore, there are regulatory constraints to consider. Different countries and regions have varying regulations regarding the use of sodium bisulfate in food products, including maximum permissible levels. Navigating these regulatory landscapes while ensuring product consistency across different markets can be challenging for dairy manufacturers.
The sensory aspects of sodium bisulfate use also present difficulties. Balancing the functional benefits with consumer acceptance is crucial. Excessive use can impart an unpleasant acidic taste or affect the mouthfeel of the product, potentially leading to consumer rejection.
There are also processing challenges to address. The incorporation of sodium bisulfate into dairy products must be carefully controlled to ensure uniform distribution and prevent localized areas of high acidity. This requires sophisticated mixing and processing techniques, which may not be readily available in all production facilities.
Lastly, there are concerns regarding the long-term effects of sodium bisulfate on product shelf life and packaging materials. While it can act as a preservative, its acidic nature may interact with packaging over time, potentially affecting product safety and quality during storage and distribution.
Another challenge lies in the potential interaction of sodium bisulfate with other ingredients in dairy formulations. These interactions may affect the stability of the product, leading to issues such as protein denaturation or unwanted precipitation. This is particularly problematic in complex dairy systems with multiple components, where the balance of ingredients is crucial for maintaining product integrity.
The impact of sodium bisulfate on the nutritional profile of dairy products is also a concern. While it can enhance certain functional properties, excessive use may lead to a reduction in the bioavailability of essential nutrients, particularly calcium and other minerals. This poses a challenge in maintaining the nutritional value that consumers expect from dairy products.
Furthermore, there are regulatory constraints to consider. Different countries and regions have varying regulations regarding the use of sodium bisulfate in food products, including maximum permissible levels. Navigating these regulatory landscapes while ensuring product consistency across different markets can be challenging for dairy manufacturers.
The sensory aspects of sodium bisulfate use also present difficulties. Balancing the functional benefits with consumer acceptance is crucial. Excessive use can impart an unpleasant acidic taste or affect the mouthfeel of the product, potentially leading to consumer rejection.
There are also processing challenges to address. The incorporation of sodium bisulfate into dairy products must be carefully controlled to ensure uniform distribution and prevent localized areas of high acidity. This requires sophisticated mixing and processing techniques, which may not be readily available in all production facilities.
Lastly, there are concerns regarding the long-term effects of sodium bisulfate on product shelf life and packaging materials. While it can act as a preservative, its acidic nature may interact with packaging over time, potentially affecting product safety and quality during storage and distribution.
Existing Sodium Bisulfate Optimization Methods
01 Optimization of sodium bisulfate production process
Various methods are employed to optimize the production of sodium bisulfate, including improving reaction conditions, enhancing process efficiency, and reducing impurities. These optimizations aim to increase yield, reduce energy consumption, and improve product quality.- Optimization of sodium bisulfate in cleaning compositions: Sodium bisulfate is used in cleaning compositions to optimize pH levels and enhance cleaning effectiveness. The concentration of sodium bisulfate is carefully adjusted to achieve the desired acidity without causing damage to surfaces or equipment. This optimization improves the overall performance of cleaning products for various applications.
- Sodium bisulfate in water treatment processes: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in water treatment processes to adjust pH levels and control alkalinity. The optimization of sodium bisulfate dosage is crucial for maintaining water quality in various applications, including swimming pools, industrial water systems, and wastewater treatment. Proper dosing ensures effective disinfection and prevents scale formation.
- Use of sodium bisulfate in food preservation: Sodium bisulfate is employed as a food preservative and pH regulator in various food products. The optimization of sodium bisulfate concentration is essential to maintain food safety, extend shelf life, and prevent microbial growth without affecting taste or quality. Careful adjustment of sodium bisulfate levels ensures compliance with food safety regulations.
- Sodium bisulfate in pharmaceutical formulations: Sodium bisulfate is used in pharmaceutical formulations as a pH adjuster and stabilizer. The optimization of sodium bisulfate concentration is crucial for maintaining drug stability, enhancing bioavailability, and ensuring the effectiveness of active ingredients. Proper formulation with sodium bisulfate can improve the shelf life and performance of various medications.
- Optimization of sodium bisulfate in industrial processes: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various industrial processes, including metal treatment, textile manufacturing, and chemical synthesis. The optimization of sodium bisulfate concentration and application methods is essential for improving process efficiency, reducing waste, and enhancing product quality. Careful control of sodium bisulfate usage can lead to cost savings and improved environmental performance in industrial applications.
02 Application of sodium bisulfate in water treatment
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in water treatment processes for pH adjustment, disinfection, and removal of contaminants. Optimization techniques focus on improving dosage control, enhancing dissolution rates, and maximizing treatment efficacy while minimizing environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of sodium bisulfate in food preservation
Sodium bisulfate is employed as a food preservative and pH regulator. Optimization efforts concentrate on improving its effectiveness in extending shelf life, enhancing flavor preservation, and ensuring food safety while minimizing any potential negative effects on taste or texture.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium bisulfate in cleaning and disinfection products
The optimization of sodium bisulfate in cleaning and disinfection products focuses on improving its efficacy against various microorganisms, enhancing its compatibility with other ingredients, and developing formulations that are both effective and environmentally friendly.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sodium bisulfate in industrial applications
In industrial settings, sodium bisulfate optimization involves improving its performance in metal treatment, textile processing, and as a chemical intermediate. Efforts are made to enhance its reactivity, increase its purity, and develop more efficient handling and storage methods.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Dairy Additives Industry
The optimization of sodium bisulfate use in enhanced dairy products is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by the dairy industry's focus on product innovation and quality improvement. The global market for food additives, including sodium bisulfate, is expanding, with projections indicating continued growth. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with established players like Chr. Hansen A/S, Land O'Lakes, Inc., and Danone SA leading research and development efforts. However, there is still room for innovation, particularly in optimizing application methods and improving product efficacy. Emerging companies such as Ripple Foods PBC are also contributing to advancements in dairy alternatives, potentially influencing sodium bisulfate usage in this sector.
DSM IP Assets BV
Technical Solution: DSM has developed a proprietary technology for optimizing sodium bisulfate use in enhanced dairy products. Their approach involves a microencapsulation technique that allows for controlled release of sodium bisulfate in dairy matrices[1]. This method enhances the stability and shelf-life of dairy products while minimizing the impact on taste and texture. DSM's technology also incorporates a synergistic blend of sodium bisulfate with other functional ingredients, such as probiotics and vitamins, to create multi-functional dairy products with improved nutritional profiles[2]. The company has conducted extensive research on the interaction between sodium bisulfate and milk proteins, leading to optimized formulations for various dairy applications, including yogurt, cheese, and milk-based beverages[3].
Strengths: Controlled release technology, synergistic ingredient blending, extensive research on milk protein interactions. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for implementation, potential higher production costs.
Chr. Hansen A/S
Technical Solution: Chr. Hansen has developed an innovative approach to optimize sodium bisulfate use in enhanced dairy products through their advanced culture technology. Their method involves the use of specially selected lactic acid bacteria strains that work synergistically with sodium bisulfate to improve product quality and shelf-life[1]. The company's proprietary cultures are designed to produce specific metabolites that enhance the effectiveness of sodium bisulfate at lower concentrations, thereby reducing overall usage[2]. Chr. Hansen has also developed a predictive modeling tool that helps dairy manufacturers optimize the balance between sodium bisulfate and culture performance, ensuring consistent product quality across different dairy applications[3]. Their research has shown that this combined approach can lead to a reduction in sodium bisulfate use by up to 30% while maintaining or even improving product stability and sensory attributes[4].
Strengths: Synergistic use of cultures with sodium bisulfate, reduction in overall sodium bisulfate usage, predictive modeling tool for optimization. Weaknesses: Requires specific bacterial cultures, may need adjustments to existing production processes.
Innovative Approaches in Dairy Preservation
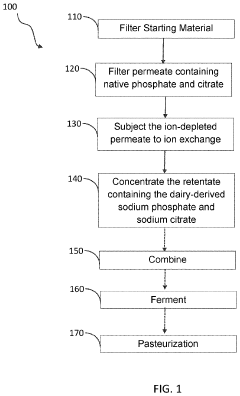
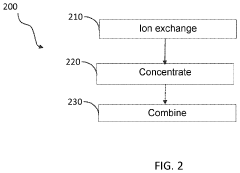
Product and method of producing dairy products comprising dairy-derived emulsifying salts
PatentActiveUS20220240530A1
Innovation
- The process involves demineralizing dairy materials to remove chloride or calcium, concentrating them, and combining with dairy components to produce dairy products containing native phosphate and citrate, which act as emulsifying agents, thereby disrupting calcium equilibrium and hydrating proteins without the need for external emulsifying salts.
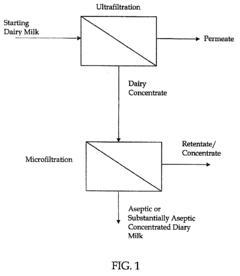
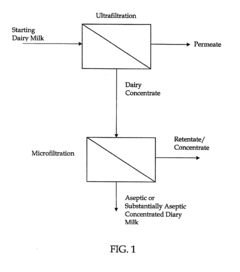
Method of producing concentrated liquid dairy products
PatentInactiveEP1938694A1
Innovation
- A method using ultrafiltration to concentrate dairy liquids followed by microfiltration to remove bacteria, achieving aseptic conditions without significant heat treatment, resulting in stable and non-gelling dairy products with a four-log reduction in bacteria and extended shelf life.
Regulatory Framework for Dairy Additives
The regulatory framework for dairy additives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of enhanced dairy products, including those utilizing sodium bisulfate. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of food additives, including those used in dairy products. The FDA's Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) designation is particularly relevant for sodium bisulfate, as it is considered safe for use in food products under specific conditions.
The European Union (EU) has its own regulatory body, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which evaluates the safety of food additives. In the EU, sodium bisulfate is listed as E514 and is approved for use in certain food categories, including dairy products, subject to specific limitations and conditions.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice. These standards often serve as a reference for national regulatory bodies when developing their own regulations.
Regulatory frameworks typically address several key aspects of additive use in dairy products. These include maximum permissible levels, labeling requirements, and specific applications within dairy products. For sodium bisulfate, regulations often specify the maximum quantities allowed in different dairy product categories, such as cheese, yogurt, or flavored milk.
Compliance with these regulations requires careful consideration of the intended use and dosage of sodium bisulfate in enhanced dairy products. Manufacturers must ensure that their products meet all applicable regulatory requirements, which may vary depending on the target market and distribution channels.
Regulatory bodies also mandate rigorous safety assessments and toxicological studies for food additives. These evaluations consider factors such as potential health risks, allergenicity, and long-term exposure effects. For sodium bisulfate, manufacturers must demonstrate that its use in dairy products does not pose any significant health risks to consumers when used as intended.
The regulatory landscape for food additives is dynamic, with ongoing research and new scientific findings potentially influencing regulations. Manufacturers and researchers working on optimizing sodium bisulfate use in enhanced dairy products must stay informed about regulatory changes and adapt their strategies accordingly. This may involve engaging with regulatory bodies, participating in public consultations, and contributing to the scientific discourse on food additive safety and efficacy.
The European Union (EU) has its own regulatory body, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which evaluates the safety of food additives. In the EU, sodium bisulfate is listed as E514 and is approved for use in certain food categories, including dairy products, subject to specific limitations and conditions.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice. These standards often serve as a reference for national regulatory bodies when developing their own regulations.
Regulatory frameworks typically address several key aspects of additive use in dairy products. These include maximum permissible levels, labeling requirements, and specific applications within dairy products. For sodium bisulfate, regulations often specify the maximum quantities allowed in different dairy product categories, such as cheese, yogurt, or flavored milk.
Compliance with these regulations requires careful consideration of the intended use and dosage of sodium bisulfate in enhanced dairy products. Manufacturers must ensure that their products meet all applicable regulatory requirements, which may vary depending on the target market and distribution channels.
Regulatory bodies also mandate rigorous safety assessments and toxicological studies for food additives. These evaluations consider factors such as potential health risks, allergenicity, and long-term exposure effects. For sodium bisulfate, manufacturers must demonstrate that its use in dairy products does not pose any significant health risks to consumers when used as intended.
The regulatory landscape for food additives is dynamic, with ongoing research and new scientific findings potentially influencing regulations. Manufacturers and researchers working on optimizing sodium bisulfate use in enhanced dairy products must stay informed about regulatory changes and adapt their strategies accordingly. This may involve engaging with regulatory bodies, participating in public consultations, and contributing to the scientific discourse on food additive safety and efficacy.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Bisulfate in Dairy
The use of sodium bisulfate in enhanced dairy products has raised concerns about its environmental impact. As a food additive and pH regulator, sodium bisulfate plays a crucial role in dairy processing, but its effects on the environment warrant careful consideration.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with sodium bisulfate is its potential to contribute to soil acidification. When sodium bisulfate-containing dairy products or their byproducts are disposed of or enter the environment, they can lower the pH of soil. This acidification can have detrimental effects on soil health, altering nutrient availability and potentially impacting plant growth in affected areas.
Water pollution is another significant environmental issue related to sodium bisulfate use in dairy. Runoff from dairy processing facilities or improper disposal of dairy products can introduce sodium bisulfate into aquatic ecosystems. This can lead to localized pH changes in water bodies, potentially disrupting aquatic life and altering ecosystem balance.
The production process of sodium bisulfate itself also carries environmental implications. Manufacturing this compound involves the use of sulfuric acid and sodium chloride, both of which have their own environmental footprints in terms of resource extraction and energy consumption. The industrial production of sodium bisulfate contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and may involve the generation of hazardous waste byproducts.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate extends beyond its immediate use in dairy products. The transportation and packaging of this additive contribute to carbon emissions and plastic waste, respectively. Additionally, the disposal of dairy products containing sodium bisulfate, particularly if not properly managed, can lead to increased waste in landfills or contamination of composting systems.
However, it's important to note that sodium bisulfate also plays a role in food safety and preservation, which indirectly benefits the environment by reducing food waste. By extending the shelf life of dairy products, it helps minimize the amount of spoiled food that ends up in landfills, thus mitigating some of its negative environmental impacts.
To address these environmental concerns, the dairy industry is exploring alternatives and optimizing the use of sodium bisulfate. This includes researching more environmentally friendly pH regulators, improving waste management practices in dairy processing, and developing more efficient production methods for sodium bisulfate itself. Additionally, there is a growing focus on circular economy principles within the dairy industry, aiming to reduce waste and maximize resource efficiency throughout the product lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with sodium bisulfate is its potential to contribute to soil acidification. When sodium bisulfate-containing dairy products or their byproducts are disposed of or enter the environment, they can lower the pH of soil. This acidification can have detrimental effects on soil health, altering nutrient availability and potentially impacting plant growth in affected areas.
Water pollution is another significant environmental issue related to sodium bisulfate use in dairy. Runoff from dairy processing facilities or improper disposal of dairy products can introduce sodium bisulfate into aquatic ecosystems. This can lead to localized pH changes in water bodies, potentially disrupting aquatic life and altering ecosystem balance.
The production process of sodium bisulfate itself also carries environmental implications. Manufacturing this compound involves the use of sulfuric acid and sodium chloride, both of which have their own environmental footprints in terms of resource extraction and energy consumption. The industrial production of sodium bisulfate contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and may involve the generation of hazardous waste byproducts.
From a lifecycle perspective, the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate extends beyond its immediate use in dairy products. The transportation and packaging of this additive contribute to carbon emissions and plastic waste, respectively. Additionally, the disposal of dairy products containing sodium bisulfate, particularly if not properly managed, can lead to increased waste in landfills or contamination of composting systems.
However, it's important to note that sodium bisulfate also plays a role in food safety and preservation, which indirectly benefits the environment by reducing food waste. By extending the shelf life of dairy products, it helps minimize the amount of spoiled food that ends up in landfills, thus mitigating some of its negative environmental impacts.
To address these environmental concerns, the dairy industry is exploring alternatives and optimizing the use of sodium bisulfate. This includes researching more environmentally friendly pH regulators, improving waste management practices in dairy processing, and developing more efficient production methods for sodium bisulfate itself. Additionally, there is a growing focus on circular economy principles within the dairy industry, aiming to reduce waste and maximize resource efficiency throughout the product lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!