Sodium Bisulfate’s Influence on Safer Waste Solutions
JUL 23, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate Overview
Sodium bisulfate, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate or sodium acid sulfate, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHSO4. It is a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water and exhibits strong acidic properties. This compound is formed by the partial neutralization of sulfuric acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium chloride, resulting in a product that retains some of the acidic characteristics of sulfuric acid while incorporating the properties of sodium.
In the context of waste management and safer waste solutions, sodium bisulfate plays a significant role due to its unique chemical properties. Its acidic nature makes it an effective pH adjuster, capable of lowering the pH of various solutions and materials. This property is particularly valuable in waste treatment processes where pH control is crucial for optimal chemical reactions and microbial activity.
One of the primary applications of sodium bisulfate in waste management is its use in wastewater treatment. It serves as a cost-effective alternative to other acidifying agents, helping to neutralize alkaline effluents and adjust pH levels to meet environmental regulations. Additionally, sodium bisulfate aids in the precipitation of heavy metals from wastewater, facilitating their removal and improving the overall quality of treated water.
In solid waste management, sodium bisulfate finds application in odor control. Its ability to lower pH inhibits the growth of odor-causing bacteria in organic waste, making it an effective additive in composting operations and landfill management. This not only improves the working conditions for waste management personnel but also reduces the environmental impact of waste facilities on surrounding communities.
Sodium bisulfate also contributes to safer waste solutions through its role in disinfection processes. When used in conjunction with chlorine-based disinfectants, it can enhance their effectiveness by lowering the pH, thereby increasing the proportion of active chlorine species. This synergistic effect allows for more efficient and thorough disinfection of water and surfaces, which is critical in maintaining hygienic conditions in waste treatment facilities.
Furthermore, the compound's influence extends to the realm of hazardous waste stabilization. By adjusting the pH of certain hazardous wastes, sodium bisulfate can alter their chemical properties, potentially reducing their toxicity or mobility. This process can facilitate safer handling, transportation, and disposal of hazardous materials, aligning with the principles of responsible waste management and environmental protection.
In summary, sodium bisulfate's influence on safer waste solutions is multifaceted, encompassing pH adjustment, odor control, disinfection enhancement, and hazardous waste stabilization. Its versatility and effectiveness in these applications make it a valuable tool in the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable and environmentally friendly waste management practices.
In the context of waste management and safer waste solutions, sodium bisulfate plays a significant role due to its unique chemical properties. Its acidic nature makes it an effective pH adjuster, capable of lowering the pH of various solutions and materials. This property is particularly valuable in waste treatment processes where pH control is crucial for optimal chemical reactions and microbial activity.
One of the primary applications of sodium bisulfate in waste management is its use in wastewater treatment. It serves as a cost-effective alternative to other acidifying agents, helping to neutralize alkaline effluents and adjust pH levels to meet environmental regulations. Additionally, sodium bisulfate aids in the precipitation of heavy metals from wastewater, facilitating their removal and improving the overall quality of treated water.
In solid waste management, sodium bisulfate finds application in odor control. Its ability to lower pH inhibits the growth of odor-causing bacteria in organic waste, making it an effective additive in composting operations and landfill management. This not only improves the working conditions for waste management personnel but also reduces the environmental impact of waste facilities on surrounding communities.
Sodium bisulfate also contributes to safer waste solutions through its role in disinfection processes. When used in conjunction with chlorine-based disinfectants, it can enhance their effectiveness by lowering the pH, thereby increasing the proportion of active chlorine species. This synergistic effect allows for more efficient and thorough disinfection of water and surfaces, which is critical in maintaining hygienic conditions in waste treatment facilities.
Furthermore, the compound's influence extends to the realm of hazardous waste stabilization. By adjusting the pH of certain hazardous wastes, sodium bisulfate can alter their chemical properties, potentially reducing their toxicity or mobility. This process can facilitate safer handling, transportation, and disposal of hazardous materials, aligning with the principles of responsible waste management and environmental protection.
In summary, sodium bisulfate's influence on safer waste solutions is multifaceted, encompassing pH adjustment, odor control, disinfection enhancement, and hazardous waste stabilization. Its versatility and effectiveness in these applications make it a valuable tool in the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable and environmentally friendly waste management practices.
Waste Management Market
The waste management market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns, stringent regulations, and the need for sustainable waste disposal solutions. This market encompasses various segments, including municipal solid waste, industrial waste, hazardous waste, and electronic waste. The global waste management market size was valued at approximately $400 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach over $600 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 5-6% during the forecast period.
The market demand for safer waste solutions has been on the rise, particularly in developed countries where environmental regulations are more stringent. This has led to increased interest in innovative technologies and processes that can effectively manage waste while minimizing environmental impact. Sodium bisulfate, a chemical compound with various industrial applications, has gained attention in the waste management sector due to its potential to enhance safety and efficiency in waste treatment processes.
In the context of waste management, sodium bisulfate offers several advantages. It can be used for pH adjustment in wastewater treatment, helping to neutralize alkaline waste streams and improve the overall treatment process. Additionally, sodium bisulfate has shown promise in odor control applications, particularly in landfills and composting facilities, where it can help mitigate unpleasant odors associated with decomposing organic matter.
The market for sodium bisulfate in waste management is expected to grow as more companies and municipalities seek cost-effective and environmentally friendly solutions for waste treatment. The compound's ability to address multiple challenges in waste management, such as pH control, odor reduction, and potentially pathogen inactivation, makes it an attractive option for industry players looking to improve their waste management practices.
However, the adoption of sodium bisulfate in waste management faces some challenges. These include the need for proper handling and storage due to its corrosive nature, potential environmental impacts if not used correctly, and competition from alternative chemicals and technologies. Despite these challenges, the growing emphasis on sustainable waste management practices and the search for safer waste solutions are likely to drive further research and development in this area, potentially expanding the applications of sodium bisulfate in the waste management market.
The market demand for safer waste solutions has been on the rise, particularly in developed countries where environmental regulations are more stringent. This has led to increased interest in innovative technologies and processes that can effectively manage waste while minimizing environmental impact. Sodium bisulfate, a chemical compound with various industrial applications, has gained attention in the waste management sector due to its potential to enhance safety and efficiency in waste treatment processes.
In the context of waste management, sodium bisulfate offers several advantages. It can be used for pH adjustment in wastewater treatment, helping to neutralize alkaline waste streams and improve the overall treatment process. Additionally, sodium bisulfate has shown promise in odor control applications, particularly in landfills and composting facilities, where it can help mitigate unpleasant odors associated with decomposing organic matter.
The market for sodium bisulfate in waste management is expected to grow as more companies and municipalities seek cost-effective and environmentally friendly solutions for waste treatment. The compound's ability to address multiple challenges in waste management, such as pH control, odor reduction, and potentially pathogen inactivation, makes it an attractive option for industry players looking to improve their waste management practices.
However, the adoption of sodium bisulfate in waste management faces some challenges. These include the need for proper handling and storage due to its corrosive nature, potential environmental impacts if not used correctly, and competition from alternative chemicals and technologies. Despite these challenges, the growing emphasis on sustainable waste management practices and the search for safer waste solutions are likely to drive further research and development in this area, potentially expanding the applications of sodium bisulfate in the waste management market.
Current Challenges
The use of sodium bisulfate in waste management solutions faces several significant challenges that require careful consideration and innovative approaches. One of the primary obstacles is the corrosive nature of sodium bisulfate, which can lead to accelerated degradation of waste containment systems and transportation equipment. This corrosivity not only poses risks to the structural integrity of waste management infrastructure but also raises concerns about potential environmental contamination if leaks occur.
Another challenge lies in the precise control of pH levels when using sodium bisulfate for waste treatment. While the compound is effective in lowering pH, achieving and maintaining the optimal acidity for various waste streams can be complex. Overuse may result in excessively acidic conditions, potentially harming beneficial microorganisms in biological treatment processes or causing downstream environmental issues.
The handling and storage of sodium bisulfate present additional hurdles. Workers involved in waste management operations must be adequately trained and equipped to safely handle this chemical, as exposure can cause skin irritation, respiratory problems, and other health issues. Proper storage facilities that protect against moisture and potential spills are essential, adding to the overall cost and complexity of waste management systems.
Environmental concerns also play a significant role in the challenges faced by sodium bisulfate usage. The potential for runoff or leaching of treated waste into soil and water systems raises questions about long-term ecological impacts. Regulatory compliance becomes increasingly stringent, requiring waste management facilities to implement robust monitoring and control measures to ensure that the use of sodium bisulfate does not lead to environmental degradation.
Furthermore, the scalability of sodium bisulfate-based solutions presents a challenge for large-scale waste management operations. As the volume of waste increases, so does the quantity of sodium bisulfate required, potentially leading to supply chain issues and increased operational costs. This scalability concern is particularly relevant for rapidly growing urban areas or industrial zones with high waste output.
Lastly, the integration of sodium bisulfate into existing waste management protocols and technologies poses a challenge. Many facilities may need to undergo significant retrofitting or process modifications to accommodate the use of this chemical effectively. This adaptation process can be time-consuming and costly, requiring careful planning and potentially disrupting ongoing waste management operations.
Another challenge lies in the precise control of pH levels when using sodium bisulfate for waste treatment. While the compound is effective in lowering pH, achieving and maintaining the optimal acidity for various waste streams can be complex. Overuse may result in excessively acidic conditions, potentially harming beneficial microorganisms in biological treatment processes or causing downstream environmental issues.
The handling and storage of sodium bisulfate present additional hurdles. Workers involved in waste management operations must be adequately trained and equipped to safely handle this chemical, as exposure can cause skin irritation, respiratory problems, and other health issues. Proper storage facilities that protect against moisture and potential spills are essential, adding to the overall cost and complexity of waste management systems.
Environmental concerns also play a significant role in the challenges faced by sodium bisulfate usage. The potential for runoff or leaching of treated waste into soil and water systems raises questions about long-term ecological impacts. Regulatory compliance becomes increasingly stringent, requiring waste management facilities to implement robust monitoring and control measures to ensure that the use of sodium bisulfate does not lead to environmental degradation.
Furthermore, the scalability of sodium bisulfate-based solutions presents a challenge for large-scale waste management operations. As the volume of waste increases, so does the quantity of sodium bisulfate required, potentially leading to supply chain issues and increased operational costs. This scalability concern is particularly relevant for rapidly growing urban areas or industrial zones with high waste output.
Lastly, the integration of sodium bisulfate into existing waste management protocols and technologies poses a challenge. Many facilities may need to undergo significant retrofitting or process modifications to accommodate the use of this chemical effectively. This adaptation process can be time-consuming and costly, requiring careful planning and potentially disrupting ongoing waste management operations.
Existing Applications
01 Safety considerations in industrial applications
Sodium bisulfate is widely used in industrial processes, but safety precautions are necessary. Proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures are essential to minimize risks associated with its corrosive nature. Personal protective equipment should be used when working with this chemical, and adequate ventilation is required in industrial settings.- Safety considerations in industrial applications: Sodium bisulfate is widely used in industrial processes, but safety precautions are necessary. Proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures are essential to prevent accidents and environmental contamination. Personal protective equipment should be used when working with this chemical, and adequate ventilation is required in industrial settings.
- Use in water treatment and pH adjustment: Sodium bisulfate is commonly used in water treatment processes for pH adjustment and as a disinfectant. While effective, proper dosing and monitoring are crucial to ensure safety for both humans and aquatic life. Regular testing and controlled application are necessary to maintain water quality standards.
- Food industry applications and safety measures: In the food industry, sodium bisulfate is used as a preservative and pH regulator. Strict adherence to food safety regulations is essential when using this compound. Proper labeling, controlled usage, and thorough rinsing procedures are necessary to ensure consumer safety and compliance with food safety standards.
- Environmental impact and waste management: The use and disposal of sodium bisulfate can have environmental implications. Proper waste management practices, including neutralization and controlled disposal, are crucial to minimize environmental impact. Recycling and recovery methods should be implemented where possible to reduce the overall environmental footprint.
- Safety in household and consumer products: Sodium bisulfate is found in various household and consumer products. While generally considered safe for intended use, proper handling and storage are important. Clear labeling, child-resistant packaging, and consumer education on proper usage and potential hazards are essential to ensure safety in domestic settings.
02 Use in water treatment and pH adjustment
Sodium bisulfate is commonly employed in water treatment processes for pH adjustment and as a disinfectant. Its effectiveness in controlling water quality parameters makes it valuable in various applications, including swimming pools and industrial water systems. However, proper dosing and monitoring are crucial to ensure safety and efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions03 Food industry applications and safety measures
In the food industry, sodium bisulfate is used as a food additive and preservative. Its application is regulated to ensure food safety. Proper handling and storage in food processing facilities are essential to prevent contamination and maintain product quality. Adherence to food safety guidelines and regulations is crucial when using this chemical in food-related applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental impact and waste management
The use and disposal of sodium bisulfate can have environmental implications. Proper waste management practices are necessary to minimize its impact on ecosystems. Treatment and neutralization of sodium bisulfate-containing waste before disposal are often required. Environmental regulations and guidelines should be followed to ensure responsible use and disposal of this chemical.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety in consumer products
Sodium bisulfate is used in various consumer products, including cleaning agents and personal care items. When formulating these products, manufacturers must consider safety aspects and adhere to regulatory guidelines. Proper labeling, packaging, and usage instructions are essential to ensure consumer safety. Risk assessments and safety testing are typically conducted for products containing this chemical.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for sodium bisulfate in waste solutions is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental regulations and the need for safer waste management practices. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations focused on improving efficiency and environmental impact. Key players like Ecolab USA, Inc., Kemira Oyj, and Earth Science Laboratories, Inc. are at the forefront, developing advanced applications for sodium bisulfate in waste treatment. These companies are investing in R&D to enhance product effectiveness and explore new applications, indicating a competitive and evolving landscape in this sector.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has developed innovative solutions utilizing sodium bisulfate for safer waste management. Their approach involves a proprietary blend of sodium bisulfate with other compounds to create a highly effective, yet environmentally friendly waste treatment system. This system is designed to neutralize alkaline waste streams, control odors, and reduce harmful emissions in various industrial applications[1][3]. The technology incorporates a controlled-release mechanism, allowing for gradual pH adjustment and prolonged effectiveness in waste treatment processes. Ecolab's solution also includes advanced monitoring systems that optimize the dosage of sodium bisulfate, ensuring maximum efficiency while minimizing chemical usage[2]. This integrated approach not only improves waste management safety but also contributes to overall operational sustainability.
Strengths: Comprehensive waste management solution, controlled-release technology, advanced monitoring systems. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for implementation, potentially higher initial costs compared to traditional methods.
Kemira Oyj
Technical Solution: Kemira has pioneered the use of sodium bisulfate in their KemConnect™ Optimization system for wastewater treatment. This innovative approach combines sodium bisulfate with advanced digital technology to create a more efficient and safer waste management solution. The system uses real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms to precisely control the dosing of sodium bisulfate, optimizing pH levels and reducing chemical consumption[1]. Kemira's technology also incorporates a unique formulation of sodium bisulfate that enhances its reactivity and effectiveness in neutralizing alkaline waste streams[2]. Additionally, they have developed a novel application method that minimizes dust formation during handling, significantly improving worker safety[3]. The KemConnect™ system also includes predictive maintenance features, reducing downtime and improving overall operational efficiency in waste treatment facilities.
Strengths: Integration of digital technology, optimized chemical usage, improved worker safety. Weaknesses: Requires significant initial investment in digital infrastructure, may need specialized training for operators.
Innovative Formulations
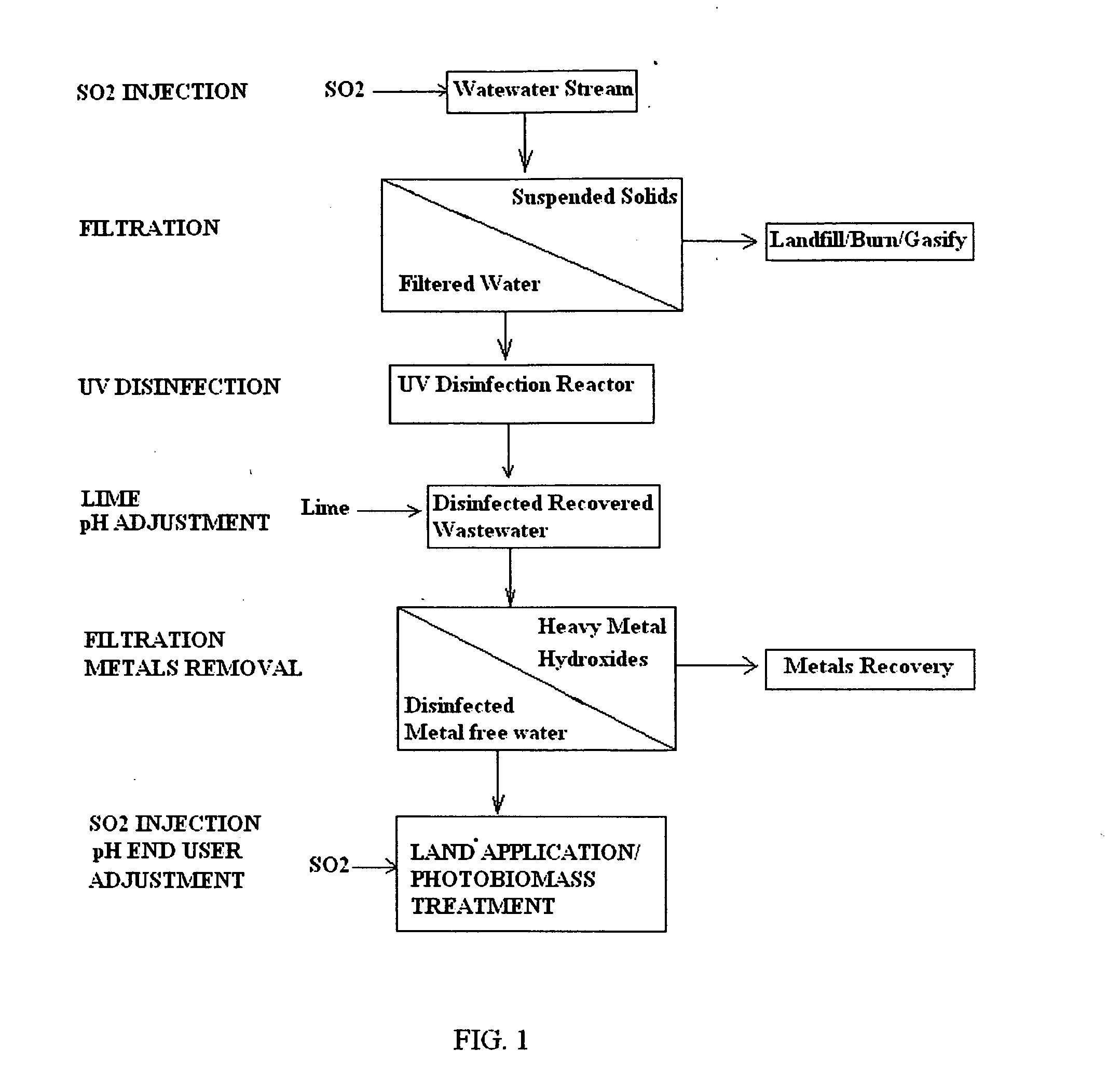
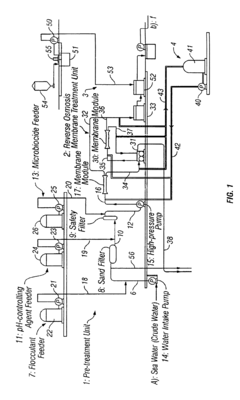
Acidification pre-treatment for UV water disinfection
PatentInactiveUS20110243665A1
Innovation
- A pre-treatment method using sulfurous acid to self-agglomerate suspended solids for easier filtration and reduce mineral scaling and microbial buildup on UV light tubes, achieved by injecting sulfur dioxide to generate sulfurous acid, which acts as a surfactant and biocide, preventing film formation and extending the time between cleanings.
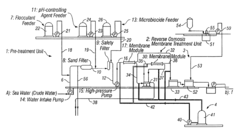
Method of bacteriostasis or disinfection for permselective membrane
PatentInactiveUS6743363B2
Innovation
- A method involving the treatment of crude water with an acid to a pH of at most 4, using sulfuric acid to effectively disinfect permselective membranes by creating an anaerobic environment that inhibits the growth and kills microorganisms, thereby improving membrane performance and water quality.
Environmental Regulations
The environmental regulations surrounding sodium bisulfate and its use in waste management solutions have become increasingly stringent in recent years. This shift reflects a growing global awareness of the potential environmental impacts associated with chemical waste and the need for safer, more sustainable practices in waste treatment and disposal.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established comprehensive guidelines for the handling and disposal of sodium bisulfate under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). These regulations classify sodium bisulfate as a hazardous substance due to its corrosive properties, requiring specific handling, storage, and disposal protocols. Facilities using sodium bisulfate in waste treatment must obtain proper permits and adhere to strict reporting requirements.
The European Union has implemented similar regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. Under REACH, sodium bisulfate is subject to rigorous safety assessments and usage restrictions. Companies operating within the EU must register their use of sodium bisulfate and demonstrate compliance with safety standards to continue its application in waste management processes.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS), which provides standardized hazard communication for chemicals like sodium bisulfate. This system ensures consistent labeling and safety data sheets across international borders, facilitating safer handling and transportation of the substance.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulations are evolving to promote the development and adoption of safer alternatives to traditional chemical waste solutions. This has led to increased research and investment in eco-friendly waste treatment technologies that minimize the use of potentially harmful substances like sodium bisulfate.
Local and regional governments are also implementing more stringent wastewater discharge regulations, often requiring advanced treatment processes to remove or neutralize sodium bisulfate before effluent release. These measures aim to protect aquatic ecosystems and ensure the safety of water resources for human consumption and agricultural use.
The regulatory landscape surrounding sodium bisulfate in waste management is dynamic, with ongoing revisions and updates to existing frameworks. Industry stakeholders must stay informed about these changes and adapt their practices accordingly to maintain compliance and minimize environmental risks associated with sodium bisulfate usage in waste treatment applications.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established comprehensive guidelines for the handling and disposal of sodium bisulfate under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). These regulations classify sodium bisulfate as a hazardous substance due to its corrosive properties, requiring specific handling, storage, and disposal protocols. Facilities using sodium bisulfate in waste treatment must obtain proper permits and adhere to strict reporting requirements.
The European Union has implemented similar regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. Under REACH, sodium bisulfate is subject to rigorous safety assessments and usage restrictions. Companies operating within the EU must register their use of sodium bisulfate and demonstrate compliance with safety standards to continue its application in waste management processes.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS), which provides standardized hazard communication for chemicals like sodium bisulfate. This system ensures consistent labeling and safety data sheets across international borders, facilitating safer handling and transportation of the substance.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, regulations are evolving to promote the development and adoption of safer alternatives to traditional chemical waste solutions. This has led to increased research and investment in eco-friendly waste treatment technologies that minimize the use of potentially harmful substances like sodium bisulfate.
Local and regional governments are also implementing more stringent wastewater discharge regulations, often requiring advanced treatment processes to remove or neutralize sodium bisulfate before effluent release. These measures aim to protect aquatic ecosystems and ensure the safety of water resources for human consumption and agricultural use.
The regulatory landscape surrounding sodium bisulfate in waste management is dynamic, with ongoing revisions and updates to existing frameworks. Industry stakeholders must stay informed about these changes and adapt their practices accordingly to maintain compliance and minimize environmental risks associated with sodium bisulfate usage in waste treatment applications.
Safety Considerations
When considering the use of sodium bisulfate in waste management solutions, safety is paramount. The chemical properties of sodium bisulfate, particularly its acidic nature, necessitate careful handling and implementation procedures. Workers involved in the application of sodium bisulfate must be equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory protection when dealing with dust or mist.
Proper storage of sodium bisulfate is crucial to prevent accidental exposure or reactions. It should be kept in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible materials such as strong bases, oxidizing agents, and metals. Containers must be tightly sealed to prevent moisture absorption, which can lead to caking and potential release of sulfur dioxide gas.
In waste treatment facilities, the introduction of sodium bisulfate requires precise dosing systems to ensure optimal pH control without over-acidification. Automated monitoring and control systems are recommended to maintain safe operating conditions and prevent potential hazards associated with pH fluctuations.
Emergency response protocols must be established and regularly reviewed. This includes having readily available neutralizing agents, such as sodium bicarbonate or lime, to address accidental spills or overexposure. Eyewash stations and safety showers should be installed in areas where sodium bisulfate is handled or stored.
Environmental considerations are also critical. The use of sodium bisulfate in waste solutions can potentially impact aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. Effluent monitoring and treatment before discharge are essential to comply with environmental regulations and protect local water bodies.
Training programs for personnel working with sodium bisulfate should be comprehensive and ongoing. These programs should cover proper handling techniques, understanding of safety data sheets (SDS), recognition of potential hazards, and appropriate emergency response procedures.
Risk assessments should be conducted regularly to identify potential safety issues and implement preventive measures. This includes evaluating the integrity of storage and application equipment, assessing ventilation systems, and reviewing operational procedures to minimize the risk of accidents or exposure.
Lastly, the integration of sodium bisulfate into waste management processes should be accompanied by a robust quality control system. This ensures the consistency and purity of the chemical used, reducing the risk of unexpected reactions or ineffective treatment due to contaminants or degraded product.
Proper storage of sodium bisulfate is crucial to prevent accidental exposure or reactions. It should be kept in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible materials such as strong bases, oxidizing agents, and metals. Containers must be tightly sealed to prevent moisture absorption, which can lead to caking and potential release of sulfur dioxide gas.
In waste treatment facilities, the introduction of sodium bisulfate requires precise dosing systems to ensure optimal pH control without over-acidification. Automated monitoring and control systems are recommended to maintain safe operating conditions and prevent potential hazards associated with pH fluctuations.
Emergency response protocols must be established and regularly reviewed. This includes having readily available neutralizing agents, such as sodium bicarbonate or lime, to address accidental spills or overexposure. Eyewash stations and safety showers should be installed in areas where sodium bisulfate is handled or stored.
Environmental considerations are also critical. The use of sodium bisulfate in waste solutions can potentially impact aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. Effluent monitoring and treatment before discharge are essential to comply with environmental regulations and protect local water bodies.
Training programs for personnel working with sodium bisulfate should be comprehensive and ongoing. These programs should cover proper handling techniques, understanding of safety data sheets (SDS), recognition of potential hazards, and appropriate emergency response procedures.
Risk assessments should be conducted regularly to identify potential safety issues and implement preventive measures. This includes evaluating the integrity of storage and application equipment, assessing ventilation systems, and reviewing operational procedures to minimize the risk of accidents or exposure.
Lastly, the integration of sodium bisulfate into waste management processes should be accompanied by a robust quality control system. This ensures the consistency and purity of the chemical used, reducing the risk of unexpected reactions or ineffective treatment due to contaminants or degraded product.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!