Sodium Bisulfate’s Role in Safer Agrochemical Solutions
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate in Agrochemicals: Background and Objectives
Sodium bisulfate has emerged as a significant player in the development of safer agrochemical solutions, marking a pivotal shift in agricultural practices. This compound, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate, has a long history of industrial and commercial applications, but its potential in agriculture has only recently gained substantial attention. The evolution of sodium bisulfate's role in agrochemicals is closely tied to the growing demand for environmentally friendly and sustainable farming practices.
The primary objective of incorporating sodium bisulfate into agrochemical formulations is to enhance the safety and efficacy of agricultural products while minimizing environmental impact. This aligns with the global trend towards sustainable agriculture and the increasing regulatory pressure to reduce the use of harmful chemicals in food production. Sodium bisulfate's unique properties make it an ideal candidate for addressing several challenges in modern agriculture.
One of the key technological goals in this field is to develop agrochemical solutions that can effectively control pests and diseases without compromising soil health or ecosystem balance. Sodium bisulfate contributes to this objective by acting as a pH adjuster and a synergist in various formulations. Its ability to lower pH can enhance the performance of certain pesticides and herbicides, potentially reducing the overall amount of active ingredients required.
Another critical aim is to improve the stability and shelf life of agrochemical products. Sodium bisulfate's preservative properties can help achieve this, potentially leading to reduced waste and more efficient use of resources in the agricultural supply chain. Furthermore, its role in water treatment applications opens up possibilities for developing integrated solutions that address both crop protection and water management challenges in agriculture.
The technological trajectory of sodium bisulfate in agrochemicals is closely linked to broader trends in precision agriculture and smart farming. As the industry moves towards more targeted and data-driven approaches, the versatility of sodium bisulfate positions it as a valuable component in developing tailored agrochemical solutions. This includes its potential use in controlled-release formulations and as part of multi-functional agrochemical systems.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of sodium bisulfate's role in safer agrochemical solutions reflect a convergence of technological innovation, environmental consciousness, and agricultural efficiency. As research and development in this area progress, sodium bisulfate is expected to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of sustainable and responsible agricultural practices.
The primary objective of incorporating sodium bisulfate into agrochemical formulations is to enhance the safety and efficacy of agricultural products while minimizing environmental impact. This aligns with the global trend towards sustainable agriculture and the increasing regulatory pressure to reduce the use of harmful chemicals in food production. Sodium bisulfate's unique properties make it an ideal candidate for addressing several challenges in modern agriculture.
One of the key technological goals in this field is to develop agrochemical solutions that can effectively control pests and diseases without compromising soil health or ecosystem balance. Sodium bisulfate contributes to this objective by acting as a pH adjuster and a synergist in various formulations. Its ability to lower pH can enhance the performance of certain pesticides and herbicides, potentially reducing the overall amount of active ingredients required.
Another critical aim is to improve the stability and shelf life of agrochemical products. Sodium bisulfate's preservative properties can help achieve this, potentially leading to reduced waste and more efficient use of resources in the agricultural supply chain. Furthermore, its role in water treatment applications opens up possibilities for developing integrated solutions that address both crop protection and water management challenges in agriculture.
The technological trajectory of sodium bisulfate in agrochemicals is closely linked to broader trends in precision agriculture and smart farming. As the industry moves towards more targeted and data-driven approaches, the versatility of sodium bisulfate positions it as a valuable component in developing tailored agrochemical solutions. This includes its potential use in controlled-release formulations and as part of multi-functional agrochemical systems.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of sodium bisulfate's role in safer agrochemical solutions reflect a convergence of technological innovation, environmental consciousness, and agricultural efficiency. As research and development in this area progress, sodium bisulfate is expected to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of sustainable and responsible agricultural practices.
Market Demand for Safer Agrochemical Solutions
The global market for safer agrochemical solutions has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of environmental and health concerns associated with traditional pesticides and fertilizers. Consumers, regulators, and agricultural stakeholders are demanding more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives to conventional agrochemicals, creating a robust market for innovative solutions.
The demand for safer agrochemical products is particularly strong in developed countries, where stringent regulations and consumer preferences are pushing farmers and agricultural businesses to adopt more environmentally responsible practices. In the United States and European Union, for instance, there has been a notable shift towards organic farming and integrated pest management systems, which rely on less harmful chemical inputs.
Emerging economies are also witnessing a growing interest in safer agrochemical solutions, as governments implement stricter environmental policies and farmers become more aware of the long-term benefits of sustainable agriculture. Countries like China and India, with their large agricultural sectors, represent significant market opportunities for safer agrochemical products.
The market demand is further fueled by the increasing focus on food safety and quality. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the potential health risks associated with pesticide residues in food, leading to a preference for products grown with safer agrochemical solutions. This trend is reflected in the rising sales of organic and pesticide-free produce in many markets worldwide.
In the context of sodium bisulfate's role in safer agrochemical solutions, there is a growing interest in its potential applications. Sodium bisulfate, known for its acidifying properties and ability to control pH levels, is being explored as a more environmentally friendly alternative to some traditional agrochemicals. Its use in soil treatment, pest control, and as a cleaning agent in agricultural settings aligns well with the market's demand for safer solutions.
The agriculture industry is also seeking innovative formulations that can reduce the overall chemical load on crops and soil while maintaining or improving crop yields. This has created opportunities for products that incorporate sodium bisulfate as part of multi-functional agrochemical solutions, addressing multiple agricultural needs with a single, safer product.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of precision agriculture techniques and smart farming practices is driving demand for agrochemical solutions that can be easily integrated into these systems. Sodium bisulfate-based products that offer precise pH control and can be applied through modern irrigation systems are likely to find a receptive market among tech-savvy farmers and large-scale agricultural operations.
The demand for safer agrochemical products is particularly strong in developed countries, where stringent regulations and consumer preferences are pushing farmers and agricultural businesses to adopt more environmentally responsible practices. In the United States and European Union, for instance, there has been a notable shift towards organic farming and integrated pest management systems, which rely on less harmful chemical inputs.
Emerging economies are also witnessing a growing interest in safer agrochemical solutions, as governments implement stricter environmental policies and farmers become more aware of the long-term benefits of sustainable agriculture. Countries like China and India, with their large agricultural sectors, represent significant market opportunities for safer agrochemical products.
The market demand is further fueled by the increasing focus on food safety and quality. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the potential health risks associated with pesticide residues in food, leading to a preference for products grown with safer agrochemical solutions. This trend is reflected in the rising sales of organic and pesticide-free produce in many markets worldwide.
In the context of sodium bisulfate's role in safer agrochemical solutions, there is a growing interest in its potential applications. Sodium bisulfate, known for its acidifying properties and ability to control pH levels, is being explored as a more environmentally friendly alternative to some traditional agrochemicals. Its use in soil treatment, pest control, and as a cleaning agent in agricultural settings aligns well with the market's demand for safer solutions.
The agriculture industry is also seeking innovative formulations that can reduce the overall chemical load on crops and soil while maintaining or improving crop yields. This has created opportunities for products that incorporate sodium bisulfate as part of multi-functional agrochemical solutions, addressing multiple agricultural needs with a single, safer product.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of precision agriculture techniques and smart farming practices is driving demand for agrochemical solutions that can be easily integrated into these systems. Sodium bisulfate-based products that offer precise pH control and can be applied through modern irrigation systems are likely to find a receptive market among tech-savvy farmers and large-scale agricultural operations.
Current State and Challenges in Sodium Bisulfate Application
Sodium bisulfate has gained significant attention in the agrochemical industry due to its potential to enhance the safety and efficacy of agricultural solutions. Currently, this compound is widely used as a pH adjuster, herbicide enhancer, and soil amendment. Its ability to lower pH levels in spray solutions has proven particularly valuable in improving the performance of certain pesticides and herbicides.
The application of sodium bisulfate in agrochemicals has shown promising results in reducing spray drift and increasing the effectiveness of active ingredients. By lowering the pH of spray solutions, it helps to stabilize sensitive compounds and prevent their degradation, thereby extending the shelf life of agrochemical products. This pH adjustment also aids in the penetration of pesticides through the waxy cuticles of plant leaves, enhancing their overall efficacy.
However, the widespread adoption of sodium bisulfate in agrochemical formulations faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the potential for soil acidification with prolonged use. While the compound's acidic nature is beneficial for certain applications, it may lead to long-term changes in soil pH, potentially affecting crop growth and soil microbial communities. This necessitates careful monitoring and management of soil conditions in areas where sodium bisulfate-based products are frequently applied.
Another challenge lies in the corrosive nature of sodium bisulfate, which can pose issues for storage, handling, and application equipment. Manufacturers and end-users must invest in corrosion-resistant materials and implement proper safety protocols to mitigate these risks. Additionally, the interaction of sodium bisulfate with other agrochemical ingredients can be complex, requiring extensive compatibility testing to ensure the stability and efficacy of final formulations.
The regulatory landscape surrounding sodium bisulfate in agrochemicals is evolving, with increasing scrutiny on its environmental impact and safety profile. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA for many applications, its use in agriculture is subject to ongoing evaluation. Manufacturers must navigate varying regulations across different regions, which can impact product development and market access.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of sodium bisulfate in creating safer and more effective agrochemical solutions continue to drive research and innovation in the field. Efforts are underway to develop improved formulations that maximize the advantages of sodium bisulfate while minimizing its drawbacks. These include exploring synergistic combinations with other compounds, developing controlled-release formulations, and investigating alternative delivery methods to optimize its application in agriculture.
The application of sodium bisulfate in agrochemicals has shown promising results in reducing spray drift and increasing the effectiveness of active ingredients. By lowering the pH of spray solutions, it helps to stabilize sensitive compounds and prevent their degradation, thereby extending the shelf life of agrochemical products. This pH adjustment also aids in the penetration of pesticides through the waxy cuticles of plant leaves, enhancing their overall efficacy.
However, the widespread adoption of sodium bisulfate in agrochemical formulations faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the potential for soil acidification with prolonged use. While the compound's acidic nature is beneficial for certain applications, it may lead to long-term changes in soil pH, potentially affecting crop growth and soil microbial communities. This necessitates careful monitoring and management of soil conditions in areas where sodium bisulfate-based products are frequently applied.
Another challenge lies in the corrosive nature of sodium bisulfate, which can pose issues for storage, handling, and application equipment. Manufacturers and end-users must invest in corrosion-resistant materials and implement proper safety protocols to mitigate these risks. Additionally, the interaction of sodium bisulfate with other agrochemical ingredients can be complex, requiring extensive compatibility testing to ensure the stability and efficacy of final formulations.
The regulatory landscape surrounding sodium bisulfate in agrochemicals is evolving, with increasing scrutiny on its environmental impact and safety profile. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA for many applications, its use in agriculture is subject to ongoing evaluation. Manufacturers must navigate varying regulations across different regions, which can impact product development and market access.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of sodium bisulfate in creating safer and more effective agrochemical solutions continue to drive research and innovation in the field. Efforts are underway to develop improved formulations that maximize the advantages of sodium bisulfate while minimizing its drawbacks. These include exploring synergistic combinations with other compounds, developing controlled-release formulations, and investigating alternative delivery methods to optimize its application in agriculture.
Existing Sodium Bisulfate-based Agrochemical Solutions
01 Use in water treatment and pH adjustment
Sodium bisulfate is commonly used in water treatment processes and for pH adjustment. It can effectively lower the pH of water, making it useful in swimming pools, spas, and industrial water treatment applications. The compound helps to maintain proper water chemistry and prevent scale formation.- Use in water treatment and pH adjustment: Sodium bisulfate is commonly used in water treatment processes and for pH adjustment. It can effectively lower the pH of water, making it useful in swimming pools, spas, and industrial water treatment applications. The compound helps to maintain proper water chemistry and prevent scale formation.
- Application in cleaning and disinfection: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various cleaning and disinfection products. Its acidic properties make it effective for removing mineral deposits, limescale, and other stubborn stains. It can be incorporated into cleaning formulations for bathrooms, kitchens, and industrial equipment.
- Use in food processing and preservation: In the food industry, sodium bisulfate is employed as a food additive and preservative. It acts as an acidulant and antimicrobial agent, helping to extend the shelf life of various food products. The compound can also be used to control microbial growth and maintain food quality during processing and storage.
- Application in agriculture and animal feed: Sodium bisulfate finds applications in agriculture and animal husbandry. It can be used as a soil amendment to lower soil pH and improve nutrient availability for certain crops. In animal feed, it serves as an acidifier and can help control bacterial growth in feed and water systems.
- Use in industrial processes and manufacturing: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various industrial processes and manufacturing applications. It can be used as a catalyst in chemical reactions, as a reducing agent in metal processing, and as a component in the production of certain chemicals and materials. The compound's acidic properties make it valuable in diverse industrial settings.
02 Application in cleaning and disinfection
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various cleaning and disinfection products. Its acidic properties make it effective for removing mineral deposits, lime scale, and other stubborn stains. It can be incorporated into cleaning formulations for bathrooms, kitchens, and industrial equipment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in food processing and preservation
Sodium bisulfate finds applications in food processing and preservation. It can be used as an acidulant, pH control agent, and preservative in various food products. The compound helps to extend shelf life, prevent microbial growth, and maintain food quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in agriculture and animal feed
Sodium bisulfate is used in agriculture and animal feed applications. It can be added to animal feed as an acidifying agent to improve digestion and nutrient absorption. In agriculture, it can be used for soil pH adjustment and as a component in fertilizer formulations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use in industrial processes and manufacturing
Sodium bisulfate has various industrial applications, including metal surface treatment, textile processing, and as a reagent in chemical manufacturing. It can be used for metal cleaning, pickling, and as a reducing agent in certain chemical reactions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sodium Bisulfate and Agrochemical Industry
The market for safer agrochemical solutions utilizing sodium bisulfate is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices. The global market size for eco-friendly agrochemicals is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Bayer CropScience, Tessenderlo Group, and Cargill leading innovation. These firms are developing more efficient and environmentally friendly formulations, leveraging sodium bisulfate's properties to enhance crop protection while minimizing environmental impact. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established agrochemical giants and specialized firms like Earth Science Laboratories contributing to technological advancements in this niche.
Bayer CropScience LP
Technical Solution: Bayer CropScience LP has developed innovative formulations incorporating sodium bisulfate for safer agrochemical solutions. Their approach focuses on using sodium bisulfate as a pH adjuster and stabilizer in pesticide formulations. This allows for improved efficacy and reduced environmental impact of active ingredients. The company has patented several formulations that utilize sodium bisulfate's acidifying properties to enhance the performance of herbicides and fungicides[1]. Additionally, Bayer has explored the use of sodium bisulfate in controlled-release fertilizer coatings, which helps regulate nutrient release and minimize leaching[2]. Their research also extends to using sodium bisulfate in seed treatment technologies, where it acts as a safener to protect crops from herbicide damage[3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global market presence, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges and public perception issues related to agrochemical safety.
Tessenderlo Group NV
Technical Solution: Tessenderlo Group NV, through its subsidiary Tessenderlo Kerley, has developed a range of sodium bisulfate-based products for agricultural applications. Their flagship product, Thio-Sul®, is a liquid ammonium thiosulfate fertilizer that incorporates sodium bisulfate to improve nutrient availability and soil health[4]. The company has also developed a line of soil amendments using sodium bisulfate to address alkaline soil conditions and improve nutrient uptake in crops. Tessenderlo's research focuses on the synergistic effects of sodium bisulfate with other nutrients, particularly sulfur-based compounds, to enhance crop yield and quality[5]. They have also explored the use of sodium bisulfate in irrigation systems to prevent clogging and improve water distribution efficiency[6].
Strengths: Specialized expertise in sulfur chemistry and established distribution networks. Weaknesses: Limited product diversification compared to larger agrochemical companies.
Core Innovations in Sodium Bisulfate Formulations
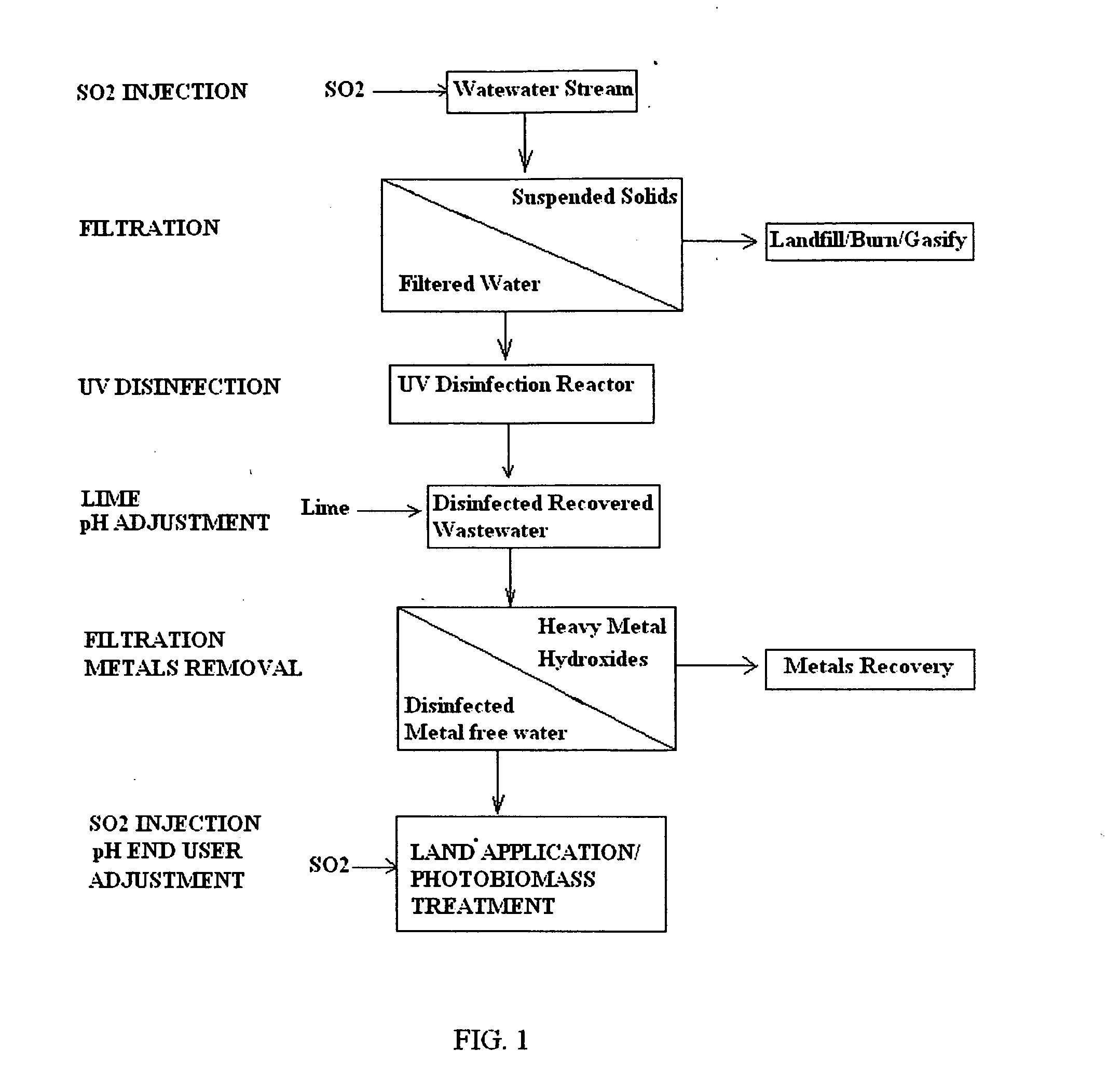
Acidification pre-treatment for UV water disinfection
PatentInactiveUS20110243665A1
Innovation
- A pre-treatment method using sulfurous acid to self-agglomerate suspended solids for easier filtration and reduce mineral scaling and microbial buildup on UV light tubes, achieved by injecting sulfur dioxide to generate sulfurous acid, which acts as a surfactant and biocide, preventing film formation and extending the time between cleanings.
Concentrated and fluid compositions containing biosynthetic pesticides, processes for their preparation and their use
PatentInactiveEP0390247A1
Innovation
- The compositions incorporate ammonium sulphate or sodium sulphate as stabilizing salts, allowing for stable suspensions with high active material concentrations, maintaining activity and fluidity over time, and are pH-adjustable between 3.5 and 8.5, preventing drum swelling/shrinking and odor release, while being non-toxic to animals.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Bisulfate in Agriculture
The environmental impact of sodium bisulfate in agriculture is a critical consideration for sustainable farming practices. This compound, widely used in agrochemical solutions, has both positive and negative effects on the ecosystem.
Sodium bisulfate's primary environmental benefit lies in its ability to reduce soil pH, which can be advantageous in areas with alkaline soils. By lowering soil pH, it enhances the availability of essential nutrients like phosphorus and micronutrients, potentially reducing the need for additional fertilizers. This can lead to more efficient nutrient uptake by plants and decreased runoff of excess nutrients into water bodies, mitigating eutrophication risks.
However, the use of sodium bisulfate also presents environmental challenges. Its application can lead to increased soil salinity, particularly in arid regions or areas with poor drainage. Elevated soil salinity can negatively impact soil structure, microbial activity, and plant growth, potentially leading to long-term soil degradation if not managed properly.
The compound's impact on water quality is another significant concern. When sodium bisulfate enters water systems through runoff or leaching, it can alter the pH of aquatic environments. This pH change may disrupt aquatic ecosystems, affecting the survival and reproduction of various organisms, including fish and aquatic plants.
Furthermore, the production and transportation of sodium bisulfate contribute to the overall carbon footprint of agricultural practices. The energy-intensive manufacturing process and the emissions associated with transportation add to the environmental cost of its use in agriculture.
On the positive side, sodium bisulfate's role in safer agrochemical solutions can indirectly benefit the environment. By enhancing the efficacy of certain pesticides and herbicides, it may allow for reduced application rates, potentially decreasing the overall chemical load on ecosystems.
To mitigate the negative environmental impacts, precision application techniques and proper soil management practices are crucial. Regular soil testing and careful monitoring of application rates can help prevent over-acidification and minimize the risk of soil and water contamination.
In conclusion, while sodium bisulfate offers benefits in agricultural applications, its environmental impact is complex and multifaceted. Balancing its advantages with potential risks requires careful management and consideration of local environmental conditions. Future research should focus on developing more environmentally friendly alternatives or improving application methods to minimize negative impacts while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Sodium bisulfate's primary environmental benefit lies in its ability to reduce soil pH, which can be advantageous in areas with alkaline soils. By lowering soil pH, it enhances the availability of essential nutrients like phosphorus and micronutrients, potentially reducing the need for additional fertilizers. This can lead to more efficient nutrient uptake by plants and decreased runoff of excess nutrients into water bodies, mitigating eutrophication risks.
However, the use of sodium bisulfate also presents environmental challenges. Its application can lead to increased soil salinity, particularly in arid regions or areas with poor drainage. Elevated soil salinity can negatively impact soil structure, microbial activity, and plant growth, potentially leading to long-term soil degradation if not managed properly.
The compound's impact on water quality is another significant concern. When sodium bisulfate enters water systems through runoff or leaching, it can alter the pH of aquatic environments. This pH change may disrupt aquatic ecosystems, affecting the survival and reproduction of various organisms, including fish and aquatic plants.
Furthermore, the production and transportation of sodium bisulfate contribute to the overall carbon footprint of agricultural practices. The energy-intensive manufacturing process and the emissions associated with transportation add to the environmental cost of its use in agriculture.
On the positive side, sodium bisulfate's role in safer agrochemical solutions can indirectly benefit the environment. By enhancing the efficacy of certain pesticides and herbicides, it may allow for reduced application rates, potentially decreasing the overall chemical load on ecosystems.
To mitigate the negative environmental impacts, precision application techniques and proper soil management practices are crucial. Regular soil testing and careful monitoring of application rates can help prevent over-acidification and minimize the risk of soil and water contamination.
In conclusion, while sodium bisulfate offers benefits in agricultural applications, its environmental impact is complex and multifaceted. Balancing its advantages with potential risks requires careful management and consideration of local environmental conditions. Future research should focus on developing more environmentally friendly alternatives or improving application methods to minimize negative impacts while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Regulatory Framework for Agrochemical Safety
The regulatory framework for agrochemical safety plays a crucial role in ensuring the responsible use of products like sodium bisulfate in agricultural applications. This framework encompasses a complex network of laws, regulations, and guidelines established by various governmental and international bodies to protect human health, environmental integrity, and food safety.
At the global level, organizations such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide overarching guidelines for the safe use of agrochemicals. These guidelines often serve as a foundation for national regulatory systems and help harmonize safety standards across borders.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing agrochemical safety. The EPA's Office of Pesticide Programs is responsible for registering pesticides and setting tolerance levels for residues on food crops. The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) provides the legal framework for pesticide regulation in the US, requiring extensive safety testing and risk assessment before a product can be approved for use.
The European Union has implemented a stringent regulatory system through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This comprehensive approach covers a wide range of chemicals, including those used in agriculture, and mandates thorough safety assessments and risk management measures.
Many countries have established their own regulatory bodies and frameworks. For instance, Health Canada's Pest Management Regulatory Agency (PMRA) oversees pesticide regulation in Canada, while the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA) performs a similar function in Australia.
These regulatory frameworks typically require manufacturers to provide extensive data on the safety and efficacy of their products. This includes information on toxicity, environmental impact, residue levels, and potential for bioaccumulation. The approval process often involves rigorous scientific review and public consultation periods.
For sodium bisulfate and similar compounds used in agrochemical solutions, regulatory compliance involves demonstrating their safety profile, efficacy in intended applications, and adherence to established maximum residue limits (MRLs). Manufacturers must also provide clear labeling and usage instructions to ensure proper handling and application by end-users.
As scientific understanding evolves and new safety concerns emerge, regulatory frameworks are continually updated. This dynamic nature of agrochemical regulation necessitates ongoing compliance efforts from manufacturers and regular reassessment of approved products. The trend towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural practices is also influencing regulatory approaches, with increasing emphasis on promoting alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides where possible.
At the global level, organizations such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide overarching guidelines for the safe use of agrochemicals. These guidelines often serve as a foundation for national regulatory systems and help harmonize safety standards across borders.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing agrochemical safety. The EPA's Office of Pesticide Programs is responsible for registering pesticides and setting tolerance levels for residues on food crops. The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) provides the legal framework for pesticide regulation in the US, requiring extensive safety testing and risk assessment before a product can be approved for use.
The European Union has implemented a stringent regulatory system through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This comprehensive approach covers a wide range of chemicals, including those used in agriculture, and mandates thorough safety assessments and risk management measures.
Many countries have established their own regulatory bodies and frameworks. For instance, Health Canada's Pest Management Regulatory Agency (PMRA) oversees pesticide regulation in Canada, while the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA) performs a similar function in Australia.
These regulatory frameworks typically require manufacturers to provide extensive data on the safety and efficacy of their products. This includes information on toxicity, environmental impact, residue levels, and potential for bioaccumulation. The approval process often involves rigorous scientific review and public consultation periods.
For sodium bisulfate and similar compounds used in agrochemical solutions, regulatory compliance involves demonstrating their safety profile, efficacy in intended applications, and adherence to established maximum residue limits (MRLs). Manufacturers must also provide clear labeling and usage instructions to ensure proper handling and application by end-users.
As scientific understanding evolves and new safety concerns emerge, regulatory frameworks are continually updated. This dynamic nature of agrochemical regulation necessitates ongoing compliance efforts from manufacturers and regular reassessment of approved products. The trend towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural practices is also influencing regulatory approaches, with increasing emphasis on promoting alternatives to traditional chemical pesticides where possible.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!