Sodium Bisulfate’s Role in Sustainable Waste Management
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate Overview
Sodium bisulfate, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate or sodium acid sulfate, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHSO4. It is a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water and exhibits acidic properties. This versatile compound plays a significant role in various industrial applications, particularly in sustainable waste management practices.
In the context of waste management, sodium bisulfate serves as a crucial pH adjuster and odor control agent. Its ability to lower pH levels makes it an effective tool for neutralizing alkaline waste streams, which is essential in maintaining environmental balance and preventing the release of harmful substances. The compound's acidic nature also inhibits the growth of odor-causing bacteria, making it valuable in controlling unpleasant smells associated with waste treatment processes.
One of the primary applications of sodium bisulfate in waste management is in the treatment of sewage and wastewater. By lowering the pH of these effluents, it helps to precipitate heavy metals and other contaminants, facilitating their removal from the water. This process is crucial in ensuring that treated water meets environmental standards before being discharged back into natural water bodies.
In solid waste management, sodium bisulfate finds use in landfill operations. It is applied to waste materials to control odors and reduce the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). By creating an acidic environment, it inhibits the microbial activity responsible for producing malodorous gases, thereby improving air quality around waste disposal sites.
The compound also plays a role in the treatment of industrial waste. Many industrial processes generate alkaline waste streams that require neutralization before disposal. Sodium bisulfate provides an efficient and cost-effective solution for this purpose, helping industries comply with environmental regulations while minimizing their ecological footprint.
In recent years, the use of sodium bisulfate has expanded to include innovative applications in sustainable waste management. For instance, it is being explored as a potential agent for the stabilization of contaminated soils, where its acidic properties can help immobilize certain pollutants, reducing their environmental impact.
The production of sodium bisulfate itself is relatively sustainable, as it can be manufactured from readily available raw materials. It is often produced as a byproduct of other industrial processes, making its use in waste management an example of circular economy principles in action.
As global focus on environmental sustainability intensifies, the role of sodium bisulfate in waste management is likely to grow. Its versatility, effectiveness, and relatively low environmental impact make it a valuable tool in the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable waste management practices. Research continues to explore new applications and optimize existing uses of this compound, ensuring its continued relevance in the field of environmental protection and sustainable resource management.
In the context of waste management, sodium bisulfate serves as a crucial pH adjuster and odor control agent. Its ability to lower pH levels makes it an effective tool for neutralizing alkaline waste streams, which is essential in maintaining environmental balance and preventing the release of harmful substances. The compound's acidic nature also inhibits the growth of odor-causing bacteria, making it valuable in controlling unpleasant smells associated with waste treatment processes.
One of the primary applications of sodium bisulfate in waste management is in the treatment of sewage and wastewater. By lowering the pH of these effluents, it helps to precipitate heavy metals and other contaminants, facilitating their removal from the water. This process is crucial in ensuring that treated water meets environmental standards before being discharged back into natural water bodies.
In solid waste management, sodium bisulfate finds use in landfill operations. It is applied to waste materials to control odors and reduce the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). By creating an acidic environment, it inhibits the microbial activity responsible for producing malodorous gases, thereby improving air quality around waste disposal sites.
The compound also plays a role in the treatment of industrial waste. Many industrial processes generate alkaline waste streams that require neutralization before disposal. Sodium bisulfate provides an efficient and cost-effective solution for this purpose, helping industries comply with environmental regulations while minimizing their ecological footprint.
In recent years, the use of sodium bisulfate has expanded to include innovative applications in sustainable waste management. For instance, it is being explored as a potential agent for the stabilization of contaminated soils, where its acidic properties can help immobilize certain pollutants, reducing their environmental impact.
The production of sodium bisulfate itself is relatively sustainable, as it can be manufactured from readily available raw materials. It is often produced as a byproduct of other industrial processes, making its use in waste management an example of circular economy principles in action.
As global focus on environmental sustainability intensifies, the role of sodium bisulfate in waste management is likely to grow. Its versatility, effectiveness, and relatively low environmental impact make it a valuable tool in the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable waste management practices. Research continues to explore new applications and optimize existing uses of this compound, ensuring its continued relevance in the field of environmental protection and sustainable resource management.
Waste Management Needs
The global waste management industry is facing unprecedented challenges due to rapid urbanization, population growth, and increasing consumption patterns. As cities expand and economies develop, the volume of waste generated continues to rise at an alarming rate. This surge in waste production has created a pressing need for sustainable and efficient waste management solutions.
One of the primary concerns in waste management is the environmental impact of traditional disposal methods. Landfills, which have long been the go-to solution for waste disposal, are reaching capacity in many regions. They also contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and pose risks of soil and water contamination. Incineration, another common waste treatment method, raises concerns about air pollution and the release of toxic substances.
The increasing complexity of waste streams further complicates management efforts. Modern consumer goods often contain a mix of materials, making recycling and proper disposal more challenging. Electronic waste, in particular, has become a major issue, with its hazardous components requiring specialized handling and treatment.
There is a growing demand for technologies and processes that can effectively manage organic waste, which constitutes a significant portion of municipal solid waste. Composting and anaerobic digestion have gained traction, but there is still a need for more efficient and scalable solutions to handle organic waste at a larger scale.
Water treatment is another critical area within waste management that requires attention. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, there is an increasing need for effective wastewater treatment technologies that can recycle and reuse water resources. This includes addressing challenges related to industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and municipal wastewater.
The waste management sector is also under pressure to adopt more circular economy principles. This shift requires innovative approaches to waste reduction, reuse, and recycling. There is a growing market demand for technologies that can transform waste into valuable resources, such as energy or raw materials for manufacturing.
In light of these challenges, there is a significant opportunity for chemical solutions like sodium bisulfate to play a role in addressing various waste management needs. From pH adjustment in water treatment to odor control in organic waste processing, chemical interventions can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of waste management processes.
One of the primary concerns in waste management is the environmental impact of traditional disposal methods. Landfills, which have long been the go-to solution for waste disposal, are reaching capacity in many regions. They also contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and pose risks of soil and water contamination. Incineration, another common waste treatment method, raises concerns about air pollution and the release of toxic substances.
The increasing complexity of waste streams further complicates management efforts. Modern consumer goods often contain a mix of materials, making recycling and proper disposal more challenging. Electronic waste, in particular, has become a major issue, with its hazardous components requiring specialized handling and treatment.
There is a growing demand for technologies and processes that can effectively manage organic waste, which constitutes a significant portion of municipal solid waste. Composting and anaerobic digestion have gained traction, but there is still a need for more efficient and scalable solutions to handle organic waste at a larger scale.
Water treatment is another critical area within waste management that requires attention. As water scarcity becomes a global concern, there is an increasing need for effective wastewater treatment technologies that can recycle and reuse water resources. This includes addressing challenges related to industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and municipal wastewater.
The waste management sector is also under pressure to adopt more circular economy principles. This shift requires innovative approaches to waste reduction, reuse, and recycling. There is a growing market demand for technologies that can transform waste into valuable resources, such as energy or raw materials for manufacturing.
In light of these challenges, there is a significant opportunity for chemical solutions like sodium bisulfate to play a role in addressing various waste management needs. From pH adjustment in water treatment to odor control in organic waste processing, chemical interventions can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of waste management processes.
Current Applications
Sodium bisulfate plays a crucial role in various aspects of sustainable waste management, offering innovative solutions to environmental challenges. One of its primary applications is in wastewater treatment, where it serves as an effective pH adjuster. By lowering the pH of wastewater, sodium bisulfate helps to neutralize alkaline effluents, ensuring compliance with discharge regulations and minimizing environmental impact.
In the realm of odor control, sodium bisulfate has proven to be a valuable tool for waste management facilities. It is particularly effective in mitigating hydrogen sulfide emissions from landfills and composting operations. By creating an acidic environment, sodium bisulfate inhibits the growth of odor-causing bacteria, significantly reducing unpleasant smells and improving air quality in surrounding areas.
The agriculture sector has also embraced sodium bisulfate as a sustainable solution for managing animal waste. When applied to poultry litter, it helps to reduce ammonia emissions, creating a healthier environment for both animals and workers. This application not only improves animal welfare but also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from livestock operations.
In the field of industrial waste management, sodium bisulfate is utilized for heavy metal precipitation. It effectively removes toxic metals from industrial effluents by converting them into insoluble compounds, which can then be easily separated and disposed of safely. This process is crucial for preventing the release of harmful substances into water bodies and ecosystems.
Sodium bisulfate also finds application in the treatment of biosolids, a byproduct of wastewater treatment. By lowering the pH of biosolids, it helps to control pathogens and reduce odors, making the material safer and more suitable for land application or further processing. This contributes to the circular economy by transforming waste into a valuable resource for agriculture and landscaping.
In the mining industry, sodium bisulfate is employed for acid mine drainage treatment. It neutralizes alkaline mine waters and helps precipitate dissolved metals, preventing environmental contamination and protecting aquatic ecosystems. This application is particularly important in areas with a history of mining activities, where long-term environmental management is crucial.
As sustainability concerns continue to grow, the versatility of sodium bisulfate in waste management applications is likely to expand. Research is ongoing to explore its potential in emerging areas such as e-waste recycling and advanced water purification technologies, further cementing its role in sustainable waste management practices.
In the realm of odor control, sodium bisulfate has proven to be a valuable tool for waste management facilities. It is particularly effective in mitigating hydrogen sulfide emissions from landfills and composting operations. By creating an acidic environment, sodium bisulfate inhibits the growth of odor-causing bacteria, significantly reducing unpleasant smells and improving air quality in surrounding areas.
The agriculture sector has also embraced sodium bisulfate as a sustainable solution for managing animal waste. When applied to poultry litter, it helps to reduce ammonia emissions, creating a healthier environment for both animals and workers. This application not only improves animal welfare but also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from livestock operations.
In the field of industrial waste management, sodium bisulfate is utilized for heavy metal precipitation. It effectively removes toxic metals from industrial effluents by converting them into insoluble compounds, which can then be easily separated and disposed of safely. This process is crucial for preventing the release of harmful substances into water bodies and ecosystems.
Sodium bisulfate also finds application in the treatment of biosolids, a byproduct of wastewater treatment. By lowering the pH of biosolids, it helps to control pathogens and reduce odors, making the material safer and more suitable for land application or further processing. This contributes to the circular economy by transforming waste into a valuable resource for agriculture and landscaping.
In the mining industry, sodium bisulfate is employed for acid mine drainage treatment. It neutralizes alkaline mine waters and helps precipitate dissolved metals, preventing environmental contamination and protecting aquatic ecosystems. This application is particularly important in areas with a history of mining activities, where long-term environmental management is crucial.
As sustainability concerns continue to grow, the versatility of sodium bisulfate in waste management applications is likely to expand. Research is ongoing to explore its potential in emerging areas such as e-waste recycling and advanced water purification technologies, further cementing its role in sustainable waste management practices.
Technical Solutions
01 Use of sodium bisulfate in cleaning compositions
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various cleaning compositions due to its acidic properties. It can be incorporated into formulations for household and industrial cleaning products, providing effective cleaning and descaling capabilities. The compound's ability to lower pH and react with mineral deposits makes it useful for removing limescale and other tough stains.- Use of sodium bisulfate in oral care products: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in oral care formulations such as toothpaste, mouthwash, and dental rinses. It acts as a pH adjuster and can help in reducing bacterial growth in the oral cavity. The compound's acidic nature contributes to its effectiveness in maintaining oral hygiene and freshness.
- Application in water treatment and purification: Sodium bisulfate finds extensive use in water treatment processes. It is employed as a pH reducer in swimming pools, spas, and industrial water systems. The compound helps in maintaining proper water chemistry, preventing scale formation, and controlling algae growth. It is also used in the treatment of wastewater and in the purification of drinking water.
- Use as a cleaning and descaling agent: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various cleaning and descaling applications. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, lime scale, and rust from surfaces and equipment. The compound is incorporated into cleaning products for household and industrial use, particularly for bathroom and kitchen cleaning, as well as in descaling solutions for appliances like coffee makers and dishwashers.
- Application in food processing and preservation: Sodium bisulfate is used in the food industry as a preservative and pH control agent. It helps in extending the shelf life of certain food products by inhibiting microbial growth. The compound is also employed in meat processing to control pathogens and improve food safety. Additionally, it finds application in the production of beverages and as a leavening agent in baked goods.
- Use in agricultural and horticultural applications: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in agriculture and horticulture for various purposes. It is used as a soil amendment to lower soil pH, making it suitable for acid-loving plants. The compound is also employed in the treatment of animal waste to reduce ammonia emissions and control odors in livestock facilities. Additionally, it finds application in the production of certain fertilizers and as a component in some pesticide formulations.
02 Application in water treatment
Sodium bisulfate finds applications in water treatment processes. It can be used to adjust pH levels in swimming pools, spas, and other water systems. The compound helps maintain proper water chemistry, preventing the growth of algae and bacteria, and ensuring safe and comfortable water conditions for users.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in food processing and preservation
Sodium bisulfate is employed in food processing and preservation techniques. It can be used as a food additive to control acidity, prevent microbial growth, and extend shelf life. The compound is particularly useful in meat processing, seafood preservation, and as a dough conditioner in baked goods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in agricultural products
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in various agricultural applications. It can be used as a soil amendment to lower soil pH, making it suitable for acid-loving plants. The compound is also employed in animal feed additives to improve digestion and nutrient absorption in livestock. Additionally, it can be used in fertilizer formulations to provide sulfur and adjust soil acidity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use in industrial processes and manufacturing
Sodium bisulfate finds applications in various industrial processes and manufacturing. It can be used in metal treatment for surface cleaning and etching, in textile processing for dyeing and bleaching, and in the production of certain chemicals. The compound's acidic properties make it useful for pH adjustment in industrial processes and as a catalyst in some chemical reactions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The sodium bisulfate market for sustainable waste management is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental regulations and the need for efficient waste treatment solutions. The market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 5-6% over the next five years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. and Yonker Environmental Protection Co., Ltd. leading innovation in waste treatment processes. Academic institutions such as Nanjing Tech University and Tongji University are contributing to research and development, enhancing the overall technological maturity of sodium bisulfate applications in waste management.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative approach to sustainable waste management using sodium bisulfate. Their process involves treating organic waste with sodium bisulfate to reduce pH levels, which inhibits microbial activity and odor production[1]. This treatment also helps in the stabilization of heavy metals in the waste. Sinopec has implemented this technology in their refinery waste treatment facilities, achieving a significant reduction in waste volume and environmental impact[2]. The company has also explored the use of sodium bisulfate in flue gas desulfurization, where it acts as a pH regulator and enhances sulfur dioxide removal efficiency[3].
Strengths: Extensive industrial application experience, integrated approach to waste management. Weaknesses: High energy consumption in some processes, potential for secondary pollution if not properly managed.
Yonker Environmental Protection Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Yonker Environmental Protection Co., Ltd. has developed a patented technology utilizing sodium bisulfate for wastewater treatment and sludge dewatering. Their process involves adding sodium bisulfate to wastewater to adjust pH and enhance coagulation-flocculation processes[4]. This results in improved removal of suspended solids and heavy metals. For sludge treatment, Yonker's method uses sodium bisulfate as a conditioning agent, which significantly improves sludge dewaterability and reduces the volume of sludge for disposal[5]. The company has successfully implemented this technology in several municipal wastewater treatment plants across China, demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing sludge volume by up to 30% and improving effluent quality[6].
Strengths: Proven technology with multiple successful implementations, effective in both wastewater and sludge treatment. Weaknesses: May require careful pH monitoring and control, potential for increased salt content in treated water.
Innovative Research
Utilization of the wastewater occurring during the production of lignocellulosic fibers, comprises combusting the parts of the substances contained in the wastewater or recovering the parts of the substances as usable substances
PatentInactiveDE102009037946A1
Innovation
- An electrochemical treatment combined with a separation process, including ion exchange using bipolar membranes and fractionation, to convert lignin sulfonic acid into usable thermal energy and recover valuable chemicals, while minimizing energy consumption and safety risks.
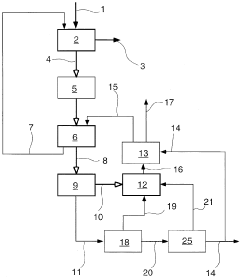
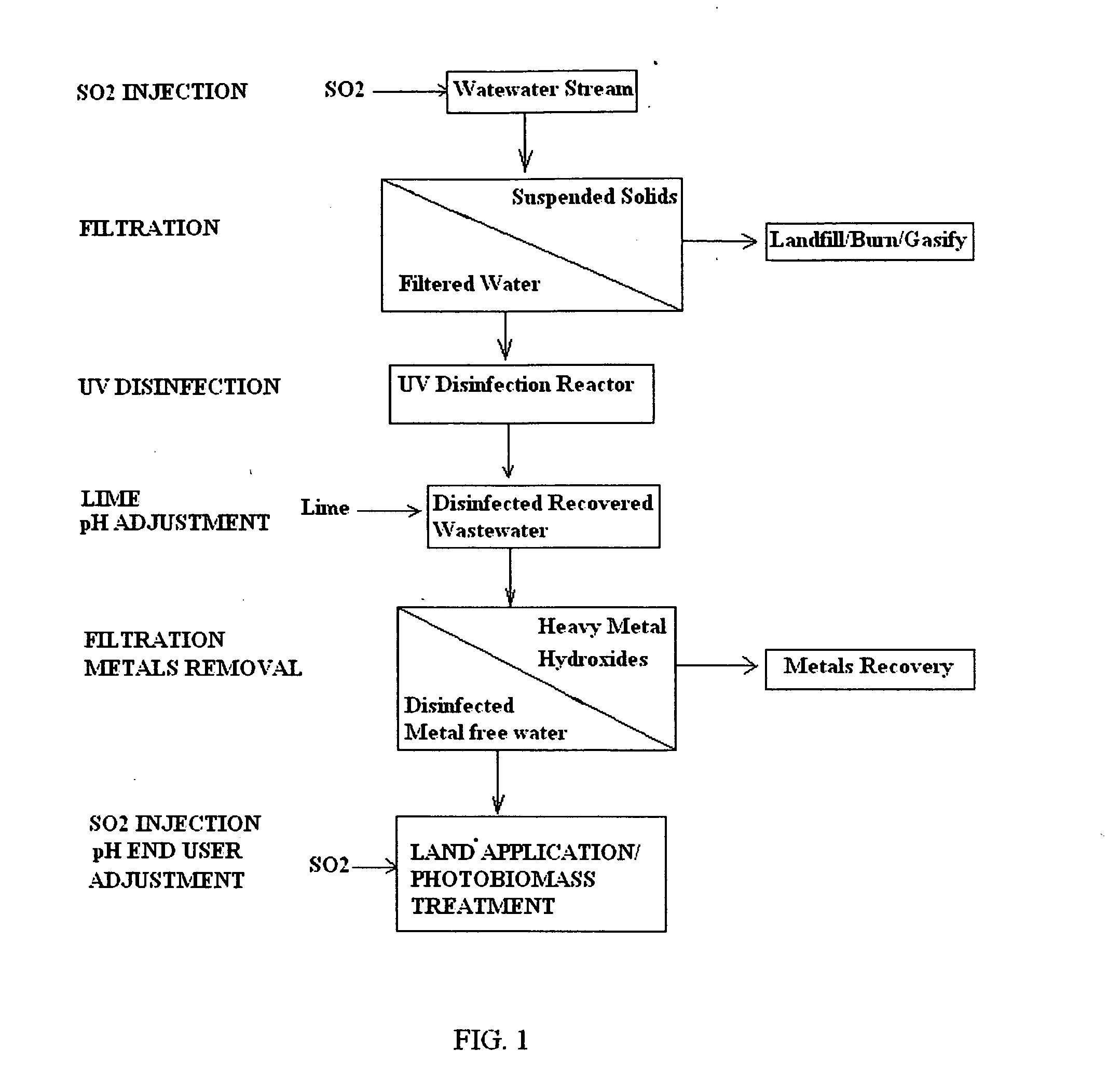
Acidification pre-treatment for UV water disinfection
PatentInactiveUS20110243665A1
Innovation
- A pre-treatment method using sulfurous acid to self-agglomerate suspended solids for easier filtration and reduce mineral scaling and microbial buildup on UV light tubes, achieved by injecting sulfur dioxide to generate sulfurous acid, which acts as a surfactant and biocide, preventing film formation and extending the time between cleanings.
Environmental Impact
Sodium bisulfate's application in sustainable waste management has significant environmental implications, both positive and negative. On the positive side, this compound plays a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of waste disposal processes. When used in wastewater treatment, sodium bisulfate helps to neutralize alkaline effluents, bringing pH levels to a more environmentally acceptable range. This pH adjustment is essential for protecting aquatic ecosystems from the harmful effects of highly alkaline discharges.
Furthermore, sodium bisulfate's ability to control odors in waste management facilities contributes to improved air quality in surrounding areas. By suppressing the formation of volatile organic compounds and hydrogen sulfide, it mitigates the release of noxious gases that can negatively impact local communities and wildlife. This odor control function is particularly valuable in densely populated areas where waste management facilities are in close proximity to residential zones.
In solid waste management, sodium bisulfate's application in landfills can help reduce the emission of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. By creating an acidic environment, it inhibits the growth of methane-producing bacteria, thereby contributing to the mitigation of climate change impacts associated with landfill operations. Additionally, its use in composting processes can accelerate the breakdown of organic matter, leading to more efficient resource recovery and reduced landfill volumes.
However, the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate is not without concerns. The production and transportation of this chemical compound involve energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. There are also potential risks related to its handling and storage, as accidental spills or improper disposal could lead to localized soil and water contamination. The increased acidity resulting from its use must be carefully managed to prevent adverse effects on soil and water ecosystems.
In the context of sustainable waste management, the long-term environmental effects of sodium bisulfate usage require ongoing monitoring and assessment. While it offers solutions to immediate waste management challenges, its cumulative impact on soil chemistry and microbial ecosystems in treatment areas needs further study. Balancing its benefits against potential environmental risks is crucial for developing truly sustainable waste management practices.
As waste management technologies evolve, the role of sodium bisulfate may shift. Research into alternative, more environmentally benign substances for pH control and odor management is ongoing. The future environmental impact of sodium bisulfate in waste management will likely depend on advancements in its production methods, application techniques, and the development of complementary or replacement technologies that can achieve similar results with a reduced ecological footprint.
Furthermore, sodium bisulfate's ability to control odors in waste management facilities contributes to improved air quality in surrounding areas. By suppressing the formation of volatile organic compounds and hydrogen sulfide, it mitigates the release of noxious gases that can negatively impact local communities and wildlife. This odor control function is particularly valuable in densely populated areas where waste management facilities are in close proximity to residential zones.
In solid waste management, sodium bisulfate's application in landfills can help reduce the emission of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. By creating an acidic environment, it inhibits the growth of methane-producing bacteria, thereby contributing to the mitigation of climate change impacts associated with landfill operations. Additionally, its use in composting processes can accelerate the breakdown of organic matter, leading to more efficient resource recovery and reduced landfill volumes.
However, the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate is not without concerns. The production and transportation of this chemical compound involve energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. There are also potential risks related to its handling and storage, as accidental spills or improper disposal could lead to localized soil and water contamination. The increased acidity resulting from its use must be carefully managed to prevent adverse effects on soil and water ecosystems.
In the context of sustainable waste management, the long-term environmental effects of sodium bisulfate usage require ongoing monitoring and assessment. While it offers solutions to immediate waste management challenges, its cumulative impact on soil chemistry and microbial ecosystems in treatment areas needs further study. Balancing its benefits against potential environmental risks is crucial for developing truly sustainable waste management practices.
As waste management technologies evolve, the role of sodium bisulfate may shift. Research into alternative, more environmentally benign substances for pH control and odor management is ongoing. The future environmental impact of sodium bisulfate in waste management will likely depend on advancements in its production methods, application techniques, and the development of complementary or replacement technologies that can achieve similar results with a reduced ecological footprint.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding sodium bisulfate's use in sustainable waste management is complex and multifaceted, encompassing various levels of governance and environmental protection standards. At the international level, the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal provides guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of hazardous materials, which may include certain applications of sodium bisulfate in waste treatment processes.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating the use of chemicals in waste management. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) establishes the framework for the proper management of hazardous and non-hazardous solid waste. Under this act, sodium bisulfate may be subject to specific handling and disposal requirements depending on its concentration and intended use in waste treatment applications.
The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) also comes into play, as it regulates the introduction of new or existing chemicals in the market. This act ensures that chemicals like sodium bisulfate are properly evaluated for their potential risks to human health and the environment before being approved for use in waste management processes.
At the state and local levels, additional regulations may apply to the use of sodium bisulfate in waste management facilities. These regulations often focus on air and water quality standards, as well as worker safety protocols. For instance, some states may require specific permits for facilities using sodium bisulfate in large quantities or for particular waste treatment processes.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for worker safety when handling chemicals like sodium bisulfate. These standards include requirements for personal protective equipment, proper storage and handling procedures, and emergency response protocols in case of accidental exposure or spills.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation governs the use of chemicals, including sodium bisulfate. This comprehensive regulatory framework requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with the substances they produce or import, ensuring their safe use throughout the supply chain.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important focus in waste management, regulatory bodies are also considering the life cycle impact of chemicals used in these processes. This has led to the development of green chemistry initiatives and eco-labeling programs that may influence the regulatory landscape for sodium bisulfate and similar substances in the future.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating the use of chemicals in waste management. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) establishes the framework for the proper management of hazardous and non-hazardous solid waste. Under this act, sodium bisulfate may be subject to specific handling and disposal requirements depending on its concentration and intended use in waste treatment applications.
The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) also comes into play, as it regulates the introduction of new or existing chemicals in the market. This act ensures that chemicals like sodium bisulfate are properly evaluated for their potential risks to human health and the environment before being approved for use in waste management processes.
At the state and local levels, additional regulations may apply to the use of sodium bisulfate in waste management facilities. These regulations often focus on air and water quality standards, as well as worker safety protocols. For instance, some states may require specific permits for facilities using sodium bisulfate in large quantities or for particular waste treatment processes.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for worker safety when handling chemicals like sodium bisulfate. These standards include requirements for personal protective equipment, proper storage and handling procedures, and emergency response protocols in case of accidental exposure or spills.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation governs the use of chemicals, including sodium bisulfate. This comprehensive regulatory framework requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with the substances they produce or import, ensuring their safe use throughout the supply chain.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important focus in waste management, regulatory bodies are also considering the life cycle impact of chemicals used in these processes. This has led to the development of green chemistry initiatives and eco-labeling programs that may influence the regulatory landscape for sodium bisulfate and similar substances in the future.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!