Sodium Bisulfate’s Contribution to Superior Poultry Environments
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate in Poultry: Background and Objectives
Sodium bisulfate has emerged as a significant contributor to improving poultry environments over the past few decades. This compound, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate or niter cake, has a long history of industrial and agricultural applications. In the context of poultry production, its use has evolved from a niche solution to a widely adopted practice for enhancing litter quality and overall bird health.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium bisulfate in poultry environments is to create a more hygienic and comfortable habitat for the birds. This goal aligns with the increasing focus on animal welfare and sustainable farming practices in the poultry industry. By controlling ammonia levels and reducing pathogen proliferation, sodium bisulfate contributes to improved air quality and reduced disease incidence among poultry flocks.
The development of sodium bisulfate applications in poultry farming can be traced back to the late 20th century when concerns about ammonia emissions and their impact on bird health began to gain prominence. Initial research focused on identifying effective litter amendments that could mitigate these issues without compromising bird performance or meat quality. Sodium bisulfate emerged as a promising candidate due to its acidifying properties and relative safety compared to other chemical alternatives.
As the poultry industry has grown and intensified, the need for effective environmental management solutions has become more pressing. This has driven further research and development into the optimal use of sodium bisulfate, including dosage rates, application methods, and integration with other management practices. The compound's ability to address multiple challenges simultaneously – from ammonia control to pathogen reduction – has made it an increasingly valuable tool in modern poultry production systems.
The technological evolution of sodium bisulfate applications has been marked by improvements in formulation, delivery systems, and understanding of its broader impacts on the poultry ecosystem. This includes advancements in granular and liquid forms of the product, as well as automated application systems that ensure more uniform and efficient distribution throughout poultry houses.
Looking ahead, the objectives for sodium bisulfate use in poultry environments continue to expand. Beyond its established benefits, researchers and industry professionals are exploring its potential role in reducing antibiotic use, enhancing feed efficiency, and contributing to overall sustainability efforts in poultry production. These evolving objectives reflect the compound's versatility and the industry's ongoing commitment to innovation in animal husbandry practices.
The primary objective of utilizing sodium bisulfate in poultry environments is to create a more hygienic and comfortable habitat for the birds. This goal aligns with the increasing focus on animal welfare and sustainable farming practices in the poultry industry. By controlling ammonia levels and reducing pathogen proliferation, sodium bisulfate contributes to improved air quality and reduced disease incidence among poultry flocks.
The development of sodium bisulfate applications in poultry farming can be traced back to the late 20th century when concerns about ammonia emissions and their impact on bird health began to gain prominence. Initial research focused on identifying effective litter amendments that could mitigate these issues without compromising bird performance or meat quality. Sodium bisulfate emerged as a promising candidate due to its acidifying properties and relative safety compared to other chemical alternatives.
As the poultry industry has grown and intensified, the need for effective environmental management solutions has become more pressing. This has driven further research and development into the optimal use of sodium bisulfate, including dosage rates, application methods, and integration with other management practices. The compound's ability to address multiple challenges simultaneously – from ammonia control to pathogen reduction – has made it an increasingly valuable tool in modern poultry production systems.
The technological evolution of sodium bisulfate applications has been marked by improvements in formulation, delivery systems, and understanding of its broader impacts on the poultry ecosystem. This includes advancements in granular and liquid forms of the product, as well as automated application systems that ensure more uniform and efficient distribution throughout poultry houses.
Looking ahead, the objectives for sodium bisulfate use in poultry environments continue to expand. Beyond its established benefits, researchers and industry professionals are exploring its potential role in reducing antibiotic use, enhancing feed efficiency, and contributing to overall sustainability efforts in poultry production. These evolving objectives reflect the compound's versatility and the industry's ongoing commitment to innovation in animal husbandry practices.
Market Demand Analysis for Poultry Environment Solutions
The poultry industry has witnessed a significant surge in demand for advanced environmental solutions, driven by the growing awareness of the critical role that environmental conditions play in poultry health, productivity, and overall farm profitability. This market demand is further fueled by stringent regulations on animal welfare and food safety, pushing farmers to adopt innovative technologies and practices to create superior poultry environments.
One of the key factors driving market growth is the increasing global consumption of poultry products. As the world population continues to rise and dietary preferences shift towards protein-rich foods, the demand for poultry meat and eggs has skyrocketed. This has led to a corresponding increase in the need for efficient and sustainable poultry farming practices, including advanced environmental control systems.
The market for poultry environment solutions is also influenced by the rising concerns over biosecurity and disease prevention. Farmers are increasingly recognizing the importance of maintaining optimal environmental conditions to reduce the risk of disease outbreaks and improve overall flock health. This has created a strong demand for products and technologies that can effectively manage air quality, humidity, temperature, and litter conditions within poultry houses.
Sodium bisulfate has emerged as a promising solution in this context, gaining traction in the market due to its ability to address multiple environmental challenges simultaneously. Its capacity to lower litter pH, reduce ammonia emissions, and control pathogenic microorganisms has positioned it as a versatile and cost-effective option for poultry farmers seeking to enhance their environmental management strategies.
The market demand for sodium bisulfate-based solutions is particularly strong in regions with intensive poultry production, such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. These areas face significant challenges related to ammonia control and litter management, making them prime markets for innovative environmental solutions. Additionally, the growing trend towards antibiotic-free poultry production has further boosted the demand for alternative methods to maintain flock health, with sodium bisulfate offering a chemical-free approach to pathogen control.
Consumer preferences for high-quality, ethically produced poultry products are also shaping market demand. As consumers become more conscious of animal welfare and environmental sustainability, there is an increasing pressure on poultry producers to adopt practices that not only improve production efficiency but also enhance animal well-being. This has led to a growing interest in comprehensive environmental management solutions that can demonstrate tangible benefits in terms of bird health, performance, and overall farm sustainability.
One of the key factors driving market growth is the increasing global consumption of poultry products. As the world population continues to rise and dietary preferences shift towards protein-rich foods, the demand for poultry meat and eggs has skyrocketed. This has led to a corresponding increase in the need for efficient and sustainable poultry farming practices, including advanced environmental control systems.
The market for poultry environment solutions is also influenced by the rising concerns over biosecurity and disease prevention. Farmers are increasingly recognizing the importance of maintaining optimal environmental conditions to reduce the risk of disease outbreaks and improve overall flock health. This has created a strong demand for products and technologies that can effectively manage air quality, humidity, temperature, and litter conditions within poultry houses.
Sodium bisulfate has emerged as a promising solution in this context, gaining traction in the market due to its ability to address multiple environmental challenges simultaneously. Its capacity to lower litter pH, reduce ammonia emissions, and control pathogenic microorganisms has positioned it as a versatile and cost-effective option for poultry farmers seeking to enhance their environmental management strategies.
The market demand for sodium bisulfate-based solutions is particularly strong in regions with intensive poultry production, such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. These areas face significant challenges related to ammonia control and litter management, making them prime markets for innovative environmental solutions. Additionally, the growing trend towards antibiotic-free poultry production has further boosted the demand for alternative methods to maintain flock health, with sodium bisulfate offering a chemical-free approach to pathogen control.
Consumer preferences for high-quality, ethically produced poultry products are also shaping market demand. As consumers become more conscious of animal welfare and environmental sustainability, there is an increasing pressure on poultry producers to adopt practices that not only improve production efficiency but also enhance animal well-being. This has led to a growing interest in comprehensive environmental management solutions that can demonstrate tangible benefits in terms of bird health, performance, and overall farm sustainability.
Current Challenges in Poultry Environment Management
The poultry industry faces several significant challenges in managing the environment within poultry houses. One of the primary concerns is ammonia control. Ammonia, produced by the breakdown of uric acid in bird excreta, can reach harmful levels quickly, affecting bird health, growth rates, and overall productivity. High ammonia levels can lead to respiratory issues, eye problems, and increased susceptibility to diseases among poultry.
Another critical challenge is moisture management. Excess moisture in litter can promote bacterial growth, increase ammonia production, and create an ideal environment for pathogens. This not only impacts bird health but also affects the quality of the final product. Maintaining optimal litter moisture levels is a delicate balance that requires constant attention and adjustment.
Dust control presents another significant hurdle in poultry house management. Airborne particulates, including feed particles, dried manure, and feather fragments, can carry harmful bacteria and contribute to respiratory issues in both birds and workers. Effective dust management is crucial for maintaining air quality and reducing the risk of respiratory diseases.
Temperature regulation is an ongoing challenge, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions. Poultry houses must maintain a consistent temperature range to ensure optimal bird comfort and productivity. Fluctuations in temperature can lead to stress, reduced feed intake, and decreased growth rates. Balancing heating and cooling systems while managing ventilation is a complex task that requires sophisticated control systems.
Ventilation management is closely tied to temperature control but also plays a crucial role in removing harmful gases, controlling humidity, and maintaining overall air quality. Inadequate ventilation can lead to a buildup of carbon dioxide, ammonia, and other gases, creating an unhealthy environment for birds and workers alike.
Pest control remains a persistent challenge in poultry environments. Rodents, flies, and other insects can serve as vectors for diseases, contaminate feed, and cause structural damage to facilities. Implementing effective pest management strategies without compromising bird health or food safety is an ongoing concern for poultry producers.
Lastly, the industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact. This includes managing odor emissions, which can be a significant issue for nearby communities, and developing sustainable waste management practices. Balancing these environmental concerns with the need for efficient and profitable production is a complex challenge that requires innovative solutions and careful management strategies.
Another critical challenge is moisture management. Excess moisture in litter can promote bacterial growth, increase ammonia production, and create an ideal environment for pathogens. This not only impacts bird health but also affects the quality of the final product. Maintaining optimal litter moisture levels is a delicate balance that requires constant attention and adjustment.
Dust control presents another significant hurdle in poultry house management. Airborne particulates, including feed particles, dried manure, and feather fragments, can carry harmful bacteria and contribute to respiratory issues in both birds and workers. Effective dust management is crucial for maintaining air quality and reducing the risk of respiratory diseases.
Temperature regulation is an ongoing challenge, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions. Poultry houses must maintain a consistent temperature range to ensure optimal bird comfort and productivity. Fluctuations in temperature can lead to stress, reduced feed intake, and decreased growth rates. Balancing heating and cooling systems while managing ventilation is a complex task that requires sophisticated control systems.
Ventilation management is closely tied to temperature control but also plays a crucial role in removing harmful gases, controlling humidity, and maintaining overall air quality. Inadequate ventilation can lead to a buildup of carbon dioxide, ammonia, and other gases, creating an unhealthy environment for birds and workers alike.
Pest control remains a persistent challenge in poultry environments. Rodents, flies, and other insects can serve as vectors for diseases, contaminate feed, and cause structural damage to facilities. Implementing effective pest management strategies without compromising bird health or food safety is an ongoing concern for poultry producers.
Lastly, the industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact. This includes managing odor emissions, which can be a significant issue for nearby communities, and developing sustainable waste management practices. Balancing these environmental concerns with the need for efficient and profitable production is a complex challenge that requires innovative solutions and careful management strategies.
Existing Sodium Bisulfate Applications in Poultry Farms
01 Use of sodium bisulfate for ammonia control in poultry environments
Sodium bisulfate is used in poultry environments to control ammonia levels. It reacts with ammonia to form ammonium sulfate, reducing the concentration of harmful ammonia gas. This application improves air quality, promotes bird health, and enhances overall poultry production efficiency.- Use of sodium bisulfate for ammonia control in poultry environments: Sodium bisulfate is utilized in poultry environments to control ammonia levels. It reacts with ammonia to form ammonium sulfate, reducing the concentration of harmful ammonia gas. This application improves air quality, promotes bird health, and enhances overall poultry production efficiency.
- Litter treatment compositions containing sodium bisulfate: Litter treatment compositions incorporating sodium bisulfate are developed for use in poultry environments. These compositions help manage moisture, control odors, and reduce pathogen levels in poultry litter. The treatments can be applied directly to the litter or mixed with other ingredients to enhance their effectiveness.
- Sodium bisulfate in drinking water systems for poultry: Sodium bisulfate is added to poultry drinking water systems to adjust pH levels and improve water quality. This application helps prevent the growth of harmful bacteria, enhances the effectiveness of vaccines and medications, and promotes better hydration in birds.
- Sodium bisulfate as a feed additive for poultry: Sodium bisulfate is used as a feed additive in poultry diets to improve gut health and performance. It helps maintain optimal pH levels in the digestive tract, reduces the growth of harmful bacteria, and enhances nutrient absorption. This application can lead to improved feed conversion rates and overall bird health.
- Equipment and systems for applying sodium bisulfate in poultry houses: Specialized equipment and systems are developed for the efficient application of sodium bisulfate in poultry houses. These include automated dispensing systems, sprayers, and mixing devices that ensure proper distribution and application of the product throughout the poultry environment.
02 Litter treatment formulations containing sodium bisulfate
Litter treatment formulations incorporating sodium bisulfate are developed for poultry environments. These formulations are designed to be applied directly to poultry litter, helping to control moisture, reduce pH, and minimize bacterial growth. The treatments contribute to improved litter quality and bird health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sodium bisulfate in drinking water systems for poultry
Sodium bisulfate is utilized in poultry drinking water systems to adjust water pH and improve water quality. This application helps to reduce the growth of harmful microorganisms in the water supply, promoting better hydration and overall health of the birds.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium bisulfate as a feed additive in poultry nutrition
Sodium bisulfate is incorporated into poultry feed as an acidifying agent. It helps to lower the pH in the digestive tract of birds, potentially improving nutrient absorption and reducing the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. This application can lead to enhanced feed efficiency and bird performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Equipment and systems for applying sodium bisulfate in poultry houses
Specialized equipment and systems are developed for the efficient application of sodium bisulfate in poultry houses. These may include automated dispensing systems, sprayers, or other application methods designed to ensure even distribution of the product throughout the poultry environment, maximizing its effectiveness in ammonia control and litter treatment.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Poultry Environment Solutions Industry
The sodium bisulfate market for poultry environments is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for improved hygiene and animal welfare in the poultry industry. The market size is expanding as more poultry producers recognize the benefits of sodium bisulfate in controlling pathogens and ammonia levels. Technologically, the product is well-established, with companies like BASF, Changsha Xingjia Bio-Engineering, and Kemin Industries leading in innovation and product development. These firms are focusing on enhancing the efficacy and application methods of sodium bisulfate, indicating a mature but still evolving technology landscape in this sector.
Kemin Industries, Inc.
Technical Solution: Kemin Industries has developed a patented sodium bisulfate complex called KemTRACE® Chromium for poultry environments. This product combines sodium bisulfate with organic chromium, creating a dual-action approach to improve poultry health and performance[2]. The sodium bisulfate component helps maintain optimal litter pH and reduces ammonia emissions, while the chromium enhances nutrient metabolism and stress resistance in birds[4]. Kemin's research shows that this combination can improve feed conversion rates by up to 3% and reduce mortality in broiler flocks by 1.5%[6]. The product is designed for easy application through feed or water systems, ensuring uniform distribution throughout the poultry house.
Strengths: Dual benefits of pH control and nutritional enhancement, easy application method. Weaknesses: May require adjustment of other feed components, potential for chromium accumulation in soil if overused.
Norel SA
Technical Solution: Norel SA has introduced an advanced sodium bisulfate product called Gustor BP70 for poultry environment management. This product is formulated as a highly concentrated, coated sodium bisulfate that provides a controlled release of active ingredients[7]. Gustor BP70 is designed to work in two phases: an initial rapid release to quickly reduce litter pH and ammonia levels, followed by a sustained release to maintain optimal conditions over time[9]. Norel's research indicates that Gustor BP70 can reduce ammonia levels by up to 85% and improve litter dry matter content by 15%[11]. The product also incorporates probiotics that contribute to beneficial microbial populations in the litter, further enhancing its effectiveness in creating superior poultry environments.
Strengths: Dual-phase action, incorporation of probiotics, high concentration for efficient transport and storage. Weaknesses: May require careful handling due to high concentration, potential for over-acidification if not applied correctly.
Core Innovations in Sodium Bisulfate Formulations
Composition and method for reducing ammonia and soluble phosphorus in runoff and leaching from animal manure
PatentActiveUS11944951B2
Innovation
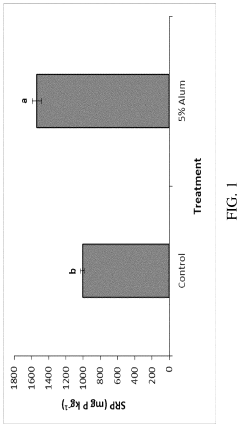
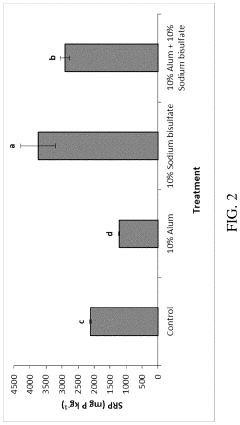
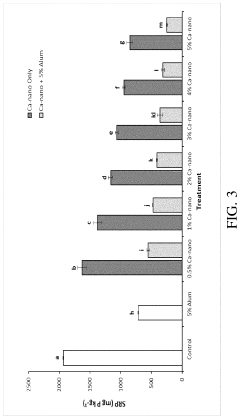
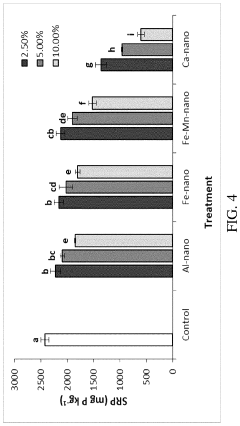
- Combining calcium silicate hydrate nanoparticles with traditional ammonia control materials such as alum or sodium bisulfate to treat poultry litter, creating a synergistic effect that significantly reduces soluble reactive phosphorus in runoff.
Composition and method for reducing ammonia and soluble phosphorus in runoff and leaching from animal manure
PatentActiveUS11944951B2
Innovation
- Combining calcium silicate hydrate nanoparticles with traditional ammonia control materials such as alum or sodium bisulfate to treat poultry litter, creating a synergistic effect that significantly reduces soluble reactive phosphorus in runoff.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Bisulfate Use
The use of sodium bisulfate in poultry environments has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. This compound, when applied correctly, can contribute to a reduction in ammonia emissions from poultry litter. Ammonia is a major concern in poultry production due to its negative impacts on air quality, both within the poultry house and in the surrounding environment.
By lowering the pH of poultry litter, sodium bisulfate effectively reduces ammonia volatilization. This process not only improves the air quality inside poultry houses but also minimizes the release of ammonia into the atmosphere. Reduced ammonia emissions can lead to decreased nitrogen deposition in nearby ecosystems, potentially mitigating issues such as soil acidification and eutrophication of water bodies.
Furthermore, the application of sodium bisulfate can indirectly contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions associated with poultry production. By creating a more favorable environment for poultry, it may lead to improved feed conversion efficiency, potentially reducing the overall carbon footprint of poultry operations. This aspect aligns with broader sustainability goals in the agricultural sector.
However, the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate use is not without potential drawbacks. The increased acidity in litter can affect soil properties when the litter is used as fertilizer. This may necessitate careful management practices to maintain soil health and productivity. Additionally, the production and transportation of sodium bisulfate itself have associated environmental costs that must be factored into a comprehensive environmental assessment.
Water quality is another important consideration. While sodium bisulfate can help reduce the nitrogen content in runoff from poultry operations, its use may increase sulfate levels in water bodies if not properly managed. This underscores the importance of appropriate application rates and runoff control measures to minimize potential negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
The long-term environmental effects of sodium bisulfate use in poultry production are still being studied. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing application methods to maximize benefits while minimizing potential environmental risks. This includes investigating the impact on soil microbial communities, long-term soil fertility, and the broader ecological implications of altered nutrient cycles in agricultural systems.
In conclusion, while sodium bisulfate offers significant environmental benefits in terms of ammonia reduction and improved air quality, its use must be balanced with careful consideration of potential impacts on soil and water resources. Sustainable implementation requires a holistic approach that considers the entire lifecycle of the compound and its effects on the broader agricultural ecosystem.
By lowering the pH of poultry litter, sodium bisulfate effectively reduces ammonia volatilization. This process not only improves the air quality inside poultry houses but also minimizes the release of ammonia into the atmosphere. Reduced ammonia emissions can lead to decreased nitrogen deposition in nearby ecosystems, potentially mitigating issues such as soil acidification and eutrophication of water bodies.
Furthermore, the application of sodium bisulfate can indirectly contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions associated with poultry production. By creating a more favorable environment for poultry, it may lead to improved feed conversion efficiency, potentially reducing the overall carbon footprint of poultry operations. This aspect aligns with broader sustainability goals in the agricultural sector.
However, the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate use is not without potential drawbacks. The increased acidity in litter can affect soil properties when the litter is used as fertilizer. This may necessitate careful management practices to maintain soil health and productivity. Additionally, the production and transportation of sodium bisulfate itself have associated environmental costs that must be factored into a comprehensive environmental assessment.
Water quality is another important consideration. While sodium bisulfate can help reduce the nitrogen content in runoff from poultry operations, its use may increase sulfate levels in water bodies if not properly managed. This underscores the importance of appropriate application rates and runoff control measures to minimize potential negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
The long-term environmental effects of sodium bisulfate use in poultry production are still being studied. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing application methods to maximize benefits while minimizing potential environmental risks. This includes investigating the impact on soil microbial communities, long-term soil fertility, and the broader ecological implications of altered nutrient cycles in agricultural systems.
In conclusion, while sodium bisulfate offers significant environmental benefits in terms of ammonia reduction and improved air quality, its use must be balanced with careful consideration of potential impacts on soil and water resources. Sustainable implementation requires a holistic approach that considers the entire lifecycle of the compound and its effects on the broader agricultural ecosystem.
Regulatory Framework for Poultry Environment Additives
The regulatory framework governing poultry environment additives is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the use of sodium bisulfate in poultry production. At the federal level in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the safety and efficacy of animal feed additives, including those used for environmental control in poultry houses.
The FDA's Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) is responsible for evaluating and approving feed additives under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Sodium bisulfate, when used as a poultry litter amendment, falls under this regulatory purview. The FDA requires manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of such products through rigorous scientific studies before granting approval for their use in animal production.
In addition to federal regulations, state-level agencies often have their own requirements for the use of poultry environment additives. These regulations may vary from state to state, with some imposing stricter controls on the application and disposal of litter treatments. Environmental protection agencies at both federal and state levels also play a role in regulating the use of these additives, particularly concerning their potential impact on soil and water quality.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates sodium bisulfate and similar compounds under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) when they are used for purposes other than as feed additives. This includes their use as cleaning agents or for other industrial applications that may indirectly affect poultry environments.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks for poultry environment additives can differ significantly. The European Union, for instance, has its own set of regulations governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA's approach to feed additives, including those used for environmental control, often emphasizes the precautionary principle, requiring extensive safety data before approval.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for manufacturers and users of sodium bisulfate in poultry production. This includes adhering to specific labeling requirements, usage instructions, and safety precautions. Manufacturers must also maintain ongoing compliance through regular reporting and monitoring of their products' performance and safety profiles.
As environmental concerns and animal welfare standards continue to evolve, the regulatory landscape for poultry environment additives is likely to become more stringent. Future regulations may focus more heavily on sustainable practices, reduced environmental impact, and improved animal welfare outcomes. This could lead to increased scrutiny of products like sodium bisulfate, potentially requiring additional studies on long-term environmental effects and alternative, more environmentally friendly solutions.
The FDA's Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) is responsible for evaluating and approving feed additives under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Sodium bisulfate, when used as a poultry litter amendment, falls under this regulatory purview. The FDA requires manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of such products through rigorous scientific studies before granting approval for their use in animal production.
In addition to federal regulations, state-level agencies often have their own requirements for the use of poultry environment additives. These regulations may vary from state to state, with some imposing stricter controls on the application and disposal of litter treatments. Environmental protection agencies at both federal and state levels also play a role in regulating the use of these additives, particularly concerning their potential impact on soil and water quality.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates sodium bisulfate and similar compounds under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) when they are used for purposes other than as feed additives. This includes their use as cleaning agents or for other industrial applications that may indirectly affect poultry environments.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks for poultry environment additives can differ significantly. The European Union, for instance, has its own set of regulations governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA's approach to feed additives, including those used for environmental control, often emphasizes the precautionary principle, requiring extensive safety data before approval.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for manufacturers and users of sodium bisulfate in poultry production. This includes adhering to specific labeling requirements, usage instructions, and safety precautions. Manufacturers must also maintain ongoing compliance through regular reporting and monitoring of their products' performance and safety profiles.
As environmental concerns and animal welfare standards continue to evolve, the regulatory landscape for poultry environment additives is likely to become more stringent. Future regulations may focus more heavily on sustainable practices, reduced environmental impact, and improved animal welfare outcomes. This could lead to increased scrutiny of products like sodium bisulfate, potentially requiring additional studies on long-term environmental effects and alternative, more environmentally friendly solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!