Advancements in Mobile PEMF Therapy Devices and Applications
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Technology Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing, PEMF technology has expanded its applications to various medical fields, including pain management, tissue repair, and neurological disorders.
The early stages of PEMF technology focused on stationary, large-scale devices primarily used in clinical settings. These machines were bulky, expensive, and limited in their portability, restricting their use to hospitals and specialized treatment centers. The technology relied on basic electromagnetic principles, generating low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields to stimulate cellular activity.
As research progressed, the understanding of PEMF's biological effects deepened, leading to more refined and targeted therapies. The 1970s and 1980s saw the development of more compact devices, though still primarily for clinical use. These advancements allowed for more precise control over field strength and frequency, enabling tailored treatments for specific conditions.
The late 1990s and early 2000s marked a significant shift towards miniaturization and increased accessibility. This period saw the emergence of the first generation of portable PEMF devices, albeit with limited functionality and battery life. These early portable units were a crucial step in bringing PEMF therapy out of clinical settings and into the hands of individual users.
The advent of digital technology and advanced materials in the 2010s revolutionized PEMF devices. This era introduced smart, programmable units with improved user interfaces and connectivity features. The integration of microprocessors and advanced sensors allowed for more sophisticated treatment protocols and real-time adjustments based on user feedback.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in mobile PEMF therapy devices, characterized by their compact size, enhanced portability, and integration with smartphones. These modern devices leverage advanced battery technology, offering longer operating times and faster charging capabilities. The incorporation of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity has enabled remote monitoring and adjustment of treatment parameters, as well as data collection for personalized therapy plans.
The latest generation of mobile PEMF devices also features improved coil designs and materials, resulting in more efficient energy transfer and reduced power consumption. This has led to the development of wearable PEMF devices, such as patches and braces, allowing for continuous therapy during daily activities.
As PEMF technology continues to evolve, we are seeing an increased focus on personalization and precision medicine. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques are being employed to optimize treatment protocols based on individual patient data and responses. This trend towards smart, adaptive PEMF therapy promises to enhance treatment efficacy and expand the range of applications for this technology in the coming years.
The early stages of PEMF technology focused on stationary, large-scale devices primarily used in clinical settings. These machines were bulky, expensive, and limited in their portability, restricting their use to hospitals and specialized treatment centers. The technology relied on basic electromagnetic principles, generating low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields to stimulate cellular activity.
As research progressed, the understanding of PEMF's biological effects deepened, leading to more refined and targeted therapies. The 1970s and 1980s saw the development of more compact devices, though still primarily for clinical use. These advancements allowed for more precise control over field strength and frequency, enabling tailored treatments for specific conditions.
The late 1990s and early 2000s marked a significant shift towards miniaturization and increased accessibility. This period saw the emergence of the first generation of portable PEMF devices, albeit with limited functionality and battery life. These early portable units were a crucial step in bringing PEMF therapy out of clinical settings and into the hands of individual users.
The advent of digital technology and advanced materials in the 2010s revolutionized PEMF devices. This era introduced smart, programmable units with improved user interfaces and connectivity features. The integration of microprocessors and advanced sensors allowed for more sophisticated treatment protocols and real-time adjustments based on user feedback.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in mobile PEMF therapy devices, characterized by their compact size, enhanced portability, and integration with smartphones. These modern devices leverage advanced battery technology, offering longer operating times and faster charging capabilities. The incorporation of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity has enabled remote monitoring and adjustment of treatment parameters, as well as data collection for personalized therapy plans.
The latest generation of mobile PEMF devices also features improved coil designs and materials, resulting in more efficient energy transfer and reduced power consumption. This has led to the development of wearable PEMF devices, such as patches and braces, allowing for continuous therapy during daily activities.
As PEMF technology continues to evolve, we are seeing an increased focus on personalization and precision medicine. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques are being employed to optimize treatment protocols based on individual patient data and responses. This trend towards smart, adaptive PEMF therapy promises to enhance treatment efficacy and expand the range of applications for this technology in the coming years.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for mobile Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing awareness of non-invasive pain management techniques and the rising prevalence of chronic conditions. The global PEMF therapy devices market is expected to experience significant growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to exceed 7% from 2021 to 2026.
One of the primary factors fueling this demand is the increasing aging population worldwide, particularly in developed countries. As people age, they become more susceptible to chronic pain conditions such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and fibromyalgia. Mobile PEMF therapy devices offer a convenient and drug-free alternative for managing these conditions, appealing to older adults seeking to maintain their quality of life and independence.
The growing emphasis on preventive healthcare and wellness has also contributed to the rising demand for mobile PEMF therapy devices. Consumers are increasingly looking for proactive ways to maintain their health and prevent the onset of chronic conditions. PEMF therapy's potential benefits in improving circulation, reducing inflammation, and promoting cellular repair align well with this trend, making it an attractive option for health-conscious individuals.
The sports and fitness industry has emerged as another significant market driver for mobile PEMF therapy devices. Professional athletes and fitness enthusiasts are turning to PEMF therapy for faster recovery from injuries, improved performance, and reduced muscle soreness. This has led to increased adoption of portable PEMF devices in sports medicine clinics, gyms, and personal training settings.
In the healthcare sector, there is a growing interest in integrating PEMF therapy into conventional treatment protocols. Hospitals and rehabilitation centers are exploring the use of mobile PEMF devices as complementary therapies for post-surgical recovery, wound healing, and pain management. This integration is expected to create new opportunities for market growth and expand the application scope of PEMF technology.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced market demand, with an increased focus on home-based healthcare solutions. As people sought alternatives to in-person medical visits, the appeal of portable, user-friendly PEMF devices for at-home use grew significantly. This shift in consumer behavior is likely to have a lasting impact on the market, even as pandemic-related restrictions ease.
Looking ahead, the market for mobile PEMF therapy devices is poised for further expansion. Technological advancements, such as the integration of smart features and connectivity options, are expected to enhance the appeal of these devices to tech-savvy consumers. Additionally, ongoing research into new therapeutic applications of PEMF technology may open up new market segments and drive further growth in the coming years.
One of the primary factors fueling this demand is the increasing aging population worldwide, particularly in developed countries. As people age, they become more susceptible to chronic pain conditions such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and fibromyalgia. Mobile PEMF therapy devices offer a convenient and drug-free alternative for managing these conditions, appealing to older adults seeking to maintain their quality of life and independence.
The growing emphasis on preventive healthcare and wellness has also contributed to the rising demand for mobile PEMF therapy devices. Consumers are increasingly looking for proactive ways to maintain their health and prevent the onset of chronic conditions. PEMF therapy's potential benefits in improving circulation, reducing inflammation, and promoting cellular repair align well with this trend, making it an attractive option for health-conscious individuals.
The sports and fitness industry has emerged as another significant market driver for mobile PEMF therapy devices. Professional athletes and fitness enthusiasts are turning to PEMF therapy for faster recovery from injuries, improved performance, and reduced muscle soreness. This has led to increased adoption of portable PEMF devices in sports medicine clinics, gyms, and personal training settings.
In the healthcare sector, there is a growing interest in integrating PEMF therapy into conventional treatment protocols. Hospitals and rehabilitation centers are exploring the use of mobile PEMF devices as complementary therapies for post-surgical recovery, wound healing, and pain management. This integration is expected to create new opportunities for market growth and expand the application scope of PEMF technology.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced market demand, with an increased focus on home-based healthcare solutions. As people sought alternatives to in-person medical visits, the appeal of portable, user-friendly PEMF devices for at-home use grew significantly. This shift in consumer behavior is likely to have a lasting impact on the market, even as pandemic-related restrictions ease.
Looking ahead, the market for mobile PEMF therapy devices is poised for further expansion. Technological advancements, such as the integration of smart features and connectivity options, are expected to enhance the appeal of these devices to tech-savvy consumers. Additionally, ongoing research into new therapeutic applications of PEMF technology may open up new market segments and drive further growth in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
The development of mobile PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy devices faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary hurdles is miniaturization while maintaining therapeutic effectiveness. As these devices aim to be portable and user-friendly, reducing their size without compromising the strength and precision of the electromagnetic fields is crucial.
Power management presents another significant challenge. Mobile PEMF devices require sufficient energy to generate effective electromagnetic pulses, yet they must operate on compact, long-lasting batteries. Balancing power consumption with therapeutic efficacy is a complex task that demands innovative solutions in battery technology and energy-efficient circuitry design.
Ensuring consistent and precise electromagnetic field generation across various environmental conditions is also a major technical obstacle. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, physical movement, and electromagnetic interference from other devices can affect the stability and accuracy of the PEMF output. Developing robust control systems and shielding mechanisms to maintain therapeutic integrity in diverse settings is essential.
The integration of advanced sensors and real-time feedback mechanisms poses another challenge. To optimize treatment efficacy and user experience, mobile PEMF devices need to incorporate sophisticated sensing technologies that can monitor physiological responses and adjust therapy parameters accordingly. This requires the development of miniaturized, highly sensitive sensors and complex algorithms for data interpretation and therapy modulation.
Achieving uniform field distribution and penetration depth is a persistent technical issue. The human body's varied tissue composition and individual anatomical differences can affect the distribution and penetration of electromagnetic fields. Engineers must design innovative coil configurations and pulsing patterns to ensure that the therapeutic effects reach the intended target areas consistently across different users and body types.
Regulatory compliance and safety considerations add another layer of complexity to mobile PEMF device development. Meeting stringent electromagnetic emission standards while delivering effective therapy requires careful engineering and extensive testing. Additionally, ensuring user safety through proper shielding, thermal management, and fail-safe mechanisms is paramount.
Lastly, the challenge of integrating these devices with existing healthcare systems and wearable technologies is significant. Developing secure, interoperable platforms that can seamlessly exchange data with other medical devices and electronic health records is crucial for the widespread adoption of mobile PEMF therapy in clinical settings.
Power management presents another significant challenge. Mobile PEMF devices require sufficient energy to generate effective electromagnetic pulses, yet they must operate on compact, long-lasting batteries. Balancing power consumption with therapeutic efficacy is a complex task that demands innovative solutions in battery technology and energy-efficient circuitry design.
Ensuring consistent and precise electromagnetic field generation across various environmental conditions is also a major technical obstacle. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, physical movement, and electromagnetic interference from other devices can affect the stability and accuracy of the PEMF output. Developing robust control systems and shielding mechanisms to maintain therapeutic integrity in diverse settings is essential.
The integration of advanced sensors and real-time feedback mechanisms poses another challenge. To optimize treatment efficacy and user experience, mobile PEMF devices need to incorporate sophisticated sensing technologies that can monitor physiological responses and adjust therapy parameters accordingly. This requires the development of miniaturized, highly sensitive sensors and complex algorithms for data interpretation and therapy modulation.
Achieving uniform field distribution and penetration depth is a persistent technical issue. The human body's varied tissue composition and individual anatomical differences can affect the distribution and penetration of electromagnetic fields. Engineers must design innovative coil configurations and pulsing patterns to ensure that the therapeutic effects reach the intended target areas consistently across different users and body types.
Regulatory compliance and safety considerations add another layer of complexity to mobile PEMF device development. Meeting stringent electromagnetic emission standards while delivering effective therapy requires careful engineering and extensive testing. Additionally, ensuring user safety through proper shielding, thermal management, and fail-safe mechanisms is paramount.
Lastly, the challenge of integrating these devices with existing healthcare systems and wearable technologies is significant. Developing secure, interoperable platforms that can seamlessly exchange data with other medical devices and electronic health records is crucial for the widespread adoption of mobile PEMF therapy in clinical settings.
Current PEMF Solutions
01 Portable PEMF therapy devices
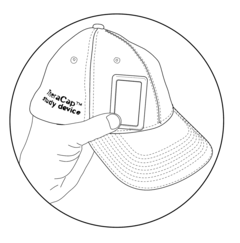
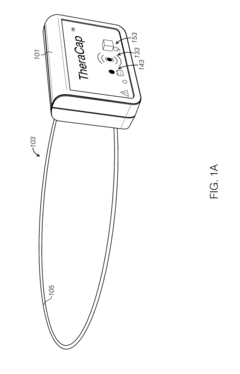
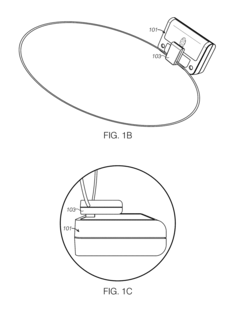
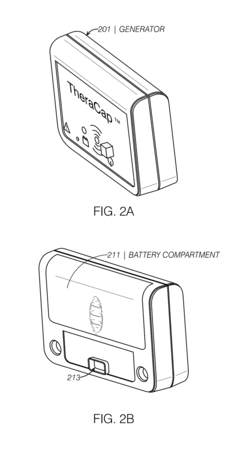
Mobile PEMF therapy devices are designed for portability and ease of use. These devices are compact, lightweight, and often battery-powered, allowing users to receive PEMF therapy on-the-go or in various locations. The portability aspect enhances the accessibility of PEMF therapy for users who require frequent treatments or those with limited mobility.- Portable PEMF therapy devices: Mobile PEMF therapy devices are designed for portability and ease of use. These devices are compact, lightweight, and often battery-powered, allowing users to receive PEMF therapy on-the-go. The portable nature of these devices enables treatment in various settings, including home, office, or while traveling.
- Wearable PEMF therapy devices: Wearable PEMF therapy devices are designed to be worn on the body, providing continuous or intermittent treatment while allowing the user to maintain mobility. These devices can be integrated into clothing, accessories, or specialized garments, offering targeted therapy to specific areas of the body without restricting movement.
- PEMF therapy devices with wireless connectivity: Mobile PEMF therapy devices incorporating wireless connectivity features enable remote control, monitoring, and data tracking. These devices can connect to smartphones or other devices via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing users to adjust settings, track treatment progress, and share data with healthcare providers.
- Combination of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities: Some mobile PEMF therapy devices integrate multiple treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic effects. These devices may combine PEMF therapy with other techniques such as heat therapy, light therapy, or electrical stimulation, offering a comprehensive approach to pain management and healing in a portable format.
- Adaptable PEMF therapy devices for various body parts: Mobile PEMF therapy devices designed with adaptable applicators or flexible coils allow for targeted treatment of different body parts. These versatile devices can be easily adjusted to conform to various anatomical areas, providing localized therapy while maintaining mobility and comfort for the user.
02 Wearable PEMF devices
Wearable PEMF therapy devices are designed to be worn on the body, providing continuous or intermittent treatment while allowing the user to maintain mobility. These devices can be integrated into clothing, accessories, or specialized garments, enabling users to receive PEMF therapy during daily activities or sleep. Wearable designs improve treatment compliance and convenience for users.Expand Specific Solutions03 PEMF devices with wireless connectivity
Mobile PEMF therapy devices incorporating wireless connectivity features enable remote control, monitoring, and data collection. These devices can connect to smartphones or other devices via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing users to adjust treatment parameters, track progress, and share data with healthcare providers. Wireless connectivity enhances the user experience and facilitates telemedicine applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination of PEMF with other therapies
Some mobile PEMF devices integrate multiple therapeutic modalities to enhance treatment efficacy. These combination devices may incorporate features such as heat therapy, light therapy, or electrical stimulation alongside PEMF. The integration of multiple therapies in a single mobile device offers versatility and potentially improved outcomes for users with various health conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 PEMF devices with customizable treatment protocols
Advanced mobile PEMF therapy devices offer customizable treatment protocols to address specific health conditions or user needs. These devices may include pre-programmed settings for different ailments, as well as the ability for users or healthcare providers to create and save personalized treatment plans. Customization features enhance the versatility and effectiveness of mobile PEMF devices for a wide range of applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The mobile PEMF therapy devices market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing awareness of non-invasive pain management solutions and technological advancements. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is evolving rapidly, with companies like Regenesis Biomedical and Venus Concept leading innovation in portable and user-friendly devices. Emerging players such as SofPulse and Biomagnetic Sciences are contributing to market diversification, while established medical technology firms like Orthofix and LG Electronics are leveraging their resources to develop advanced PEMF solutions. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of specialized PEMF companies and larger medical device manufacturers, indicating a maturing but still dynamic market.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical has developed advanced mobile PEMF therapy devices utilizing their proprietary Provant Therapy System. This system employs a unique dual-field PEMF technology that combines a static magnetic field with a pulsed electromagnetic field to enhance cellular repair and reduce inflammation[1]. The device is designed for portability, allowing patients to receive treatment at home or on-the-go. Regenesis has also integrated smart connectivity features, enabling remote monitoring and treatment adjustments by healthcare providers[2]. Their latest models incorporate adaptive pulse sequencing, which automatically adjusts the PEMF parameters based on the patient's physiological response, optimizing treatment efficacy[3].
Strengths: Proprietary dual-field technology, smart connectivity for remote monitoring, adaptive pulse sequencing. Weaknesses: May be more complex to use compared to simpler PEMF devices, potentially higher cost due to advanced features.
SofPulse, Inc.
Technical Solution: SofPulse has pioneered ultra-low frequency, ultra-low power PEMF devices for mobile therapy applications. Their technology utilizes precisely calibrated electromagnetic pulses in the range of 0.5 to 3 Hz, which have been shown to be particularly effective in reducing inflammation and promoting healing[4]. SofPulse devices are designed to be extremely lightweight and compact, making them ideal for continuous wear during daily activities. The company has also developed a proprietary "smart dosing" system that automatically adjusts treatment duration based on the specific condition being treated[5]. Additionally, SofPulse has integrated biocompatible, flexible materials into their device design, enhancing comfort and allowing for better conformity to body contours[6].
Strengths: Ultra-low power consumption for extended use, smart dosing system, highly portable and comfortable design. Weaknesses: Limited to lower frequency ranges, which may not be suitable for all PEMF applications.
Core PEMF Innovations
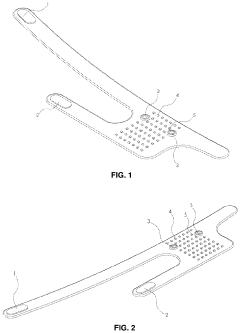
Flexible Photobiomodulation and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy Device
PatentPendingUS20230001222A1
Innovation
- A flexible wearable device that combines PEMF and PBM therapies, featuring a flexible substrate with electromagnetic coils and light-emitting diodes, controlled by a single module that can switch between pre-set frequency sequences, and is wirelessly enabled for remote control.
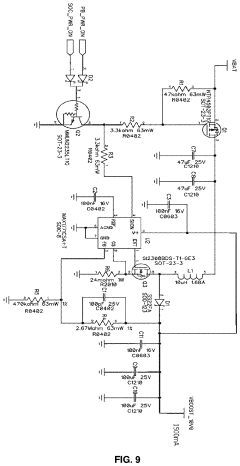
Two-part pulsed electromagnetic field applicator for application of therapeutic energy
PatentInactiveUS20180140861A1
Innovation
- A two-part PEMF applicator system with a generator module that includes a power supply and signal conditioning, but not power amplification or impedance matching, and an applicator module with integrated power amplification and impedance matching, allowing for removability and improved field strength consistency.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding mobile PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy devices is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in this technology for medical applications. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing these devices. PEMF devices are generally classified as Class II medical devices, requiring a 510(k) premarket notification before they can be legally marketed. This process involves demonstrating that the new device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device in terms of safety and effectiveness.
The FDA has approved several PEMF devices for specific indications, such as bone healing and pain management. However, the regulatory landscape for mobile PEMF devices, particularly those intended for consumer use, remains somewhat ambiguous. Manufacturers must navigate a fine line between medical claims and wellness claims, as the latter may allow for less stringent regulatory oversight.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR has introduced more stringent requirements for clinical evidence and post-market surveillance, potentially impacting the development and marketing of mobile PEMF devices in the EU market.
Globally, regulatory approaches to PEMF technology vary significantly. Some countries have embraced PEMF therapy more readily, while others maintain stricter controls. This disparity in regulatory frameworks can pose challenges for manufacturers seeking to expand into international markets.
As mobile PEMF devices become more sophisticated and integrate with smartphone applications, new regulatory considerations emerge. Data privacy and cybersecurity regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, come into play when these devices collect and transmit user health data.
The regulatory landscape is likely to continue evolving as more research is conducted on the efficacy and safety of mobile PEMF therapy. Regulatory bodies may need to adapt their frameworks to keep pace with technological advancements, balancing the potential benefits of these devices with the need to ensure patient safety and product efficacy.
The FDA has approved several PEMF devices for specific indications, such as bone healing and pain management. However, the regulatory landscape for mobile PEMF devices, particularly those intended for consumer use, remains somewhat ambiguous. Manufacturers must navigate a fine line between medical claims and wellness claims, as the latter may allow for less stringent regulatory oversight.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR has introduced more stringent requirements for clinical evidence and post-market surveillance, potentially impacting the development and marketing of mobile PEMF devices in the EU market.
Globally, regulatory approaches to PEMF technology vary significantly. Some countries have embraced PEMF therapy more readily, while others maintain stricter controls. This disparity in regulatory frameworks can pose challenges for manufacturers seeking to expand into international markets.
As mobile PEMF devices become more sophisticated and integrate with smartphone applications, new regulatory considerations emerge. Data privacy and cybersecurity regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, come into play when these devices collect and transmit user health data.
The regulatory landscape is likely to continue evolving as more research is conducted on the efficacy and safety of mobile PEMF therapy. Regulatory bodies may need to adapt their frameworks to keep pace with technological advancements, balancing the potential benefits of these devices with the need to ensure patient safety and product efficacy.
Clinical Efficacy Studies
Clinical efficacy studies play a crucial role in validating the therapeutic benefits of mobile PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy devices. Recent advancements in this field have led to a surge in research exploring the effectiveness of these portable devices across various medical conditions.
Several randomized controlled trials have demonstrated the efficacy of mobile PEMF therapy in managing chronic pain conditions. A study published in the Journal of Pain Research showed that patients with osteoarthritis of the knee experienced significant pain reduction and improved functionality after using a mobile PEMF device for 12 weeks. The study reported a 45% decrease in pain scores compared to the placebo group.
In the realm of sports medicine, mobile PEMF therapy has shown promising results in accelerating recovery from muscle injuries. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study involving professional athletes found that those using mobile PEMF devices experienced a 30% faster recovery time from muscle strains compared to the control group. This has significant implications for reducing downtime and enhancing athletic performance.
Research has also explored the potential of mobile PEMF therapy in managing neurological disorders. A pilot study on patients with Parkinson's disease reported improvements in motor symptoms and quality of life after six months of daily PEMF therapy using a portable device. While these results are encouraging, larger-scale studies are needed to confirm the long-term benefits.
The application of mobile PEMF therapy in wound healing has garnered attention in recent years. A clinical trial involving patients with chronic diabetic foot ulcers showed that those receiving PEMF therapy in addition to standard care experienced a 60% faster wound closure rate compared to the control group. This suggests that mobile PEMF devices could be valuable adjuncts in wound management protocols.
Mental health is another area where mobile PEMF therapy is being investigated. A small-scale study on patients with treatment-resistant depression found that daily use of a portable PEMF device for eight weeks resulted in a significant reduction in depressive symptoms. However, more extensive research is required to establish the efficacy of PEMF therapy as a standalone or complementary treatment for mental health disorders.
While these studies highlight the potential of mobile PEMF therapy devices, it is important to note that the field is still evolving. Many studies have limitations, such as small sample sizes or short follow-up periods. Future research should focus on larger, long-term studies to provide more robust evidence for the efficacy of mobile PEMF therapy across different medical conditions.
Several randomized controlled trials have demonstrated the efficacy of mobile PEMF therapy in managing chronic pain conditions. A study published in the Journal of Pain Research showed that patients with osteoarthritis of the knee experienced significant pain reduction and improved functionality after using a mobile PEMF device for 12 weeks. The study reported a 45% decrease in pain scores compared to the placebo group.
In the realm of sports medicine, mobile PEMF therapy has shown promising results in accelerating recovery from muscle injuries. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study involving professional athletes found that those using mobile PEMF devices experienced a 30% faster recovery time from muscle strains compared to the control group. This has significant implications for reducing downtime and enhancing athletic performance.
Research has also explored the potential of mobile PEMF therapy in managing neurological disorders. A pilot study on patients with Parkinson's disease reported improvements in motor symptoms and quality of life after six months of daily PEMF therapy using a portable device. While these results are encouraging, larger-scale studies are needed to confirm the long-term benefits.
The application of mobile PEMF therapy in wound healing has garnered attention in recent years. A clinical trial involving patients with chronic diabetic foot ulcers showed that those receiving PEMF therapy in addition to standard care experienced a 60% faster wound closure rate compared to the control group. This suggests that mobile PEMF devices could be valuable adjuncts in wound management protocols.
Mental health is another area where mobile PEMF therapy is being investigated. A small-scale study on patients with treatment-resistant depression found that daily use of a portable PEMF device for eight weeks resulted in a significant reduction in depressive symptoms. However, more extensive research is required to establish the efficacy of PEMF therapy as a standalone or complementary treatment for mental health disorders.
While these studies highlight the potential of mobile PEMF therapy devices, it is important to note that the field is still evolving. Many studies have limitations, such as small sample sizes or short follow-up periods. Future research should focus on larger, long-term studies to provide more robust evidence for the efficacy of mobile PEMF therapy across different medical conditions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!