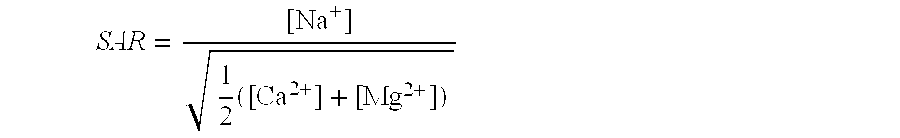Analyzing Sodium Bisulfate's Dechlorination Capabilities
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Bisulfate Dechlorination Background
Sodium bisulfate, a chemical compound with the formula NaHSO4, has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential dechlorination capabilities. This versatile substance, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate or sodium acid sulfate, is a byproduct of various industrial processes and has been widely used in water treatment, cleaning products, and food preservation.
The interest in sodium bisulfate's dechlorination properties stems from the growing need for efficient and cost-effective methods to remove chlorine and its compounds from water and other substances. Chlorine, while essential for disinfection in many applications, can form harmful byproducts and negatively impact the environment when present in excess.
The dechlorination process using sodium bisulfate involves a chemical reaction between the compound and chlorine molecules. When sodium bisulfate is added to chlorinated water, it reacts with free chlorine to form chloride ions and sulfate ions. This reaction effectively neutralizes the chlorine, reducing its concentration and potential harmful effects.
One of the key advantages of using sodium bisulfate for dechlorination is its relatively low cost and wide availability. As a byproduct of industrial processes, it is readily accessible and can be produced in large quantities. Additionally, sodium bisulfate is considered safer to handle compared to other dechlorination agents, making it an attractive option for various applications.
The effectiveness of sodium bisulfate in dechlorination has been demonstrated in several contexts, including swimming pool maintenance, wastewater treatment, and aquaculture. In swimming pools, it is used to lower chlorine levels after shock treatments or to prepare water for safe disposal. In wastewater treatment, sodium bisulfate helps neutralize residual chlorine before the treated water is released into the environment, protecting aquatic ecosystems.
Despite its promising capabilities, the use of sodium bisulfate for dechlorination is not without challenges. The effectiveness of the process can be influenced by factors such as pH levels, temperature, and the presence of other chemical compounds. Furthermore, the reaction between sodium bisulfate and chlorine can potentially lower the pH of the treated water, necessitating careful monitoring and adjustment in some applications.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent and the demand for efficient water treatment solutions grows, the role of sodium bisulfate in dechlorination processes is likely to expand. Ongoing research aims to optimize its use, explore new applications, and address any limitations or potential side effects associated with its implementation.
The interest in sodium bisulfate's dechlorination properties stems from the growing need for efficient and cost-effective methods to remove chlorine and its compounds from water and other substances. Chlorine, while essential for disinfection in many applications, can form harmful byproducts and negatively impact the environment when present in excess.
The dechlorination process using sodium bisulfate involves a chemical reaction between the compound and chlorine molecules. When sodium bisulfate is added to chlorinated water, it reacts with free chlorine to form chloride ions and sulfate ions. This reaction effectively neutralizes the chlorine, reducing its concentration and potential harmful effects.
One of the key advantages of using sodium bisulfate for dechlorination is its relatively low cost and wide availability. As a byproduct of industrial processes, it is readily accessible and can be produced in large quantities. Additionally, sodium bisulfate is considered safer to handle compared to other dechlorination agents, making it an attractive option for various applications.
The effectiveness of sodium bisulfate in dechlorination has been demonstrated in several contexts, including swimming pool maintenance, wastewater treatment, and aquaculture. In swimming pools, it is used to lower chlorine levels after shock treatments or to prepare water for safe disposal. In wastewater treatment, sodium bisulfate helps neutralize residual chlorine before the treated water is released into the environment, protecting aquatic ecosystems.
Despite its promising capabilities, the use of sodium bisulfate for dechlorination is not without challenges. The effectiveness of the process can be influenced by factors such as pH levels, temperature, and the presence of other chemical compounds. Furthermore, the reaction between sodium bisulfate and chlorine can potentially lower the pH of the treated water, necessitating careful monitoring and adjustment in some applications.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent and the demand for efficient water treatment solutions grows, the role of sodium bisulfate in dechlorination processes is likely to expand. Ongoing research aims to optimize its use, explore new applications, and address any limitations or potential side effects associated with its implementation.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for sodium bisulfate's dechlorination capabilities has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by increasing concerns over water quality and environmental regulations. The primary sectors fueling this demand include municipal water treatment, swimming pool maintenance, and industrial wastewater management.
In the municipal water treatment sector, there is a rising need for effective and cost-efficient dechlorination solutions. As cities and towns strive to meet stringent water quality standards, sodium bisulfate has emerged as a preferred choice due to its ability to rapidly neutralize residual chlorine in treated water before discharge into natural water bodies. This application is particularly crucial in areas where chlorinated effluents pose risks to aquatic ecosystems.
The swimming pool industry represents another significant market for sodium bisulfate's dechlorination capabilities. With millions of public and private pools worldwide requiring regular maintenance, the demand for safe and effective dechlorination agents is substantial. Pool owners and operators are increasingly turning to sodium bisulfate as a reliable solution for lowering chlorine levels, especially when preparing pools for closure or maintenance.
In the industrial sector, wastewater treatment facilities across various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing, are adopting sodium bisulfate for dechlorination purposes. The growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices and compliance with environmental regulations is driving the demand for efficient dechlorination solutions in industrial settings.
Market analysis indicates a positive growth trajectory for sodium bisulfate in dechlorination applications. The global water treatment chemicals market, which includes dechlorination agents, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include urbanization, industrialization, and the implementation of stricter environmental policies worldwide.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for dechlorination solutions, including sodium bisulfate, due to their well-established water treatment infrastructure and stringent environmental regulations. However, rapid industrialization and increasing water quality concerns in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to create substantial market opportunities in these regions.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly dechlorination methods. This trend is likely to influence the development of new formulations and applications of sodium bisulfate, potentially expanding its market reach. As research continues to unveil new capabilities and applications of sodium bisulfate in water treatment, the market demand is expected to diversify and grow across various sectors.
In the municipal water treatment sector, there is a rising need for effective and cost-efficient dechlorination solutions. As cities and towns strive to meet stringent water quality standards, sodium bisulfate has emerged as a preferred choice due to its ability to rapidly neutralize residual chlorine in treated water before discharge into natural water bodies. This application is particularly crucial in areas where chlorinated effluents pose risks to aquatic ecosystems.
The swimming pool industry represents another significant market for sodium bisulfate's dechlorination capabilities. With millions of public and private pools worldwide requiring regular maintenance, the demand for safe and effective dechlorination agents is substantial. Pool owners and operators are increasingly turning to sodium bisulfate as a reliable solution for lowering chlorine levels, especially when preparing pools for closure or maintenance.
In the industrial sector, wastewater treatment facilities across various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing, are adopting sodium bisulfate for dechlorination purposes. The growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices and compliance with environmental regulations is driving the demand for efficient dechlorination solutions in industrial settings.
Market analysis indicates a positive growth trajectory for sodium bisulfate in dechlorination applications. The global water treatment chemicals market, which includes dechlorination agents, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include urbanization, industrialization, and the implementation of stricter environmental policies worldwide.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for dechlorination solutions, including sodium bisulfate, due to their well-established water treatment infrastructure and stringent environmental regulations. However, rapid industrialization and increasing water quality concerns in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to create substantial market opportunities in these regions.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly dechlorination methods. This trend is likely to influence the development of new formulations and applications of sodium bisulfate, potentially expanding its market reach. As research continues to unveil new capabilities and applications of sodium bisulfate in water treatment, the market demand is expected to diversify and grow across various sectors.
Current Challenges
The dechlorination capabilities of sodium bisulfate face several significant challenges in current applications. One of the primary obstacles is the limited efficiency of the dechlorination process, particularly in large-scale water treatment systems. While sodium bisulfate has shown promise in laboratory settings, its performance in real-world scenarios often falls short of expectations, especially when dealing with high chlorine concentrations or complex water compositions.
Another challenge lies in the pH sensitivity of the dechlorination reaction. Sodium bisulfate's effectiveness is highly dependent on maintaining an optimal pH range, typically between 4.5 and 6.5. In practical applications, fluctuations in water chemistry can lead to pH variations, potentially compromising the dechlorination process. This necessitates constant monitoring and adjustment of pH levels, adding complexity and cost to treatment systems.
The formation of byproducts during the dechlorination process presents an additional hurdle. When sodium bisulfate reacts with chlorine, it can produce sulfate ions and other compounds that may affect water quality. In some cases, these byproducts can exceed regulatory limits or interfere with subsequent water treatment processes, requiring additional treatment steps or alternative dechlorination methods.
Scalability remains a significant challenge for sodium bisulfate-based dechlorination systems. As treatment capacities increase, ensuring uniform distribution and mixing of sodium bisulfate becomes more difficult. This can result in inconsistent dechlorination across large volumes of water, potentially leaving some areas undertreated while others may receive excess treatment.
The environmental impact of sodium bisulfate usage is also a growing concern. While it is generally considered less harmful than some alternative dechlorination agents, the long-term effects of increased sulfate levels in aquatic ecosystems are not fully understood. This has led to regulatory scrutiny and calls for more comprehensive environmental impact assessments.
Lastly, the economic viability of sodium bisulfate as a dechlorination agent faces challenges in comparison to other methods. While it is relatively inexpensive, the need for precise dosing, pH control, and potential additional treatment steps can increase operational costs. In some cases, alternative technologies such as activated carbon filtration or UV dechlorination may prove more cost-effective in the long run, despite higher initial investments.
Another challenge lies in the pH sensitivity of the dechlorination reaction. Sodium bisulfate's effectiveness is highly dependent on maintaining an optimal pH range, typically between 4.5 and 6.5. In practical applications, fluctuations in water chemistry can lead to pH variations, potentially compromising the dechlorination process. This necessitates constant monitoring and adjustment of pH levels, adding complexity and cost to treatment systems.
The formation of byproducts during the dechlorination process presents an additional hurdle. When sodium bisulfate reacts with chlorine, it can produce sulfate ions and other compounds that may affect water quality. In some cases, these byproducts can exceed regulatory limits or interfere with subsequent water treatment processes, requiring additional treatment steps or alternative dechlorination methods.
Scalability remains a significant challenge for sodium bisulfate-based dechlorination systems. As treatment capacities increase, ensuring uniform distribution and mixing of sodium bisulfate becomes more difficult. This can result in inconsistent dechlorination across large volumes of water, potentially leaving some areas undertreated while others may receive excess treatment.
The environmental impact of sodium bisulfate usage is also a growing concern. While it is generally considered less harmful than some alternative dechlorination agents, the long-term effects of increased sulfate levels in aquatic ecosystems are not fully understood. This has led to regulatory scrutiny and calls for more comprehensive environmental impact assessments.
Lastly, the economic viability of sodium bisulfate as a dechlorination agent faces challenges in comparison to other methods. While it is relatively inexpensive, the need for precise dosing, pH control, and potential additional treatment steps can increase operational costs. In some cases, alternative technologies such as activated carbon filtration or UV dechlorination may prove more cost-effective in the long run, despite higher initial investments.
Existing Dechlorination Solutions
01 Sodium bisulfate as a dechlorinating agent
Sodium bisulfate is used as an effective dechlorinating agent in water treatment processes. It reacts with chlorine to form chloride ions and sulfate ions, effectively removing free chlorine from water. This method is particularly useful in swimming pools, spas, and other water systems where chlorine levels need to be controlled.- Sodium bisulfate as a dechlorinating agent: Sodium bisulfate is used as an effective dechlorinating agent in water treatment processes. It reacts with chlorine to form chloride ions and sulfate ions, effectively removing free chlorine from water. This method is particularly useful in swimming pools, spas, and other water systems where chlorine levels need to be controlled.
- Dechlorination in industrial wastewater treatment: Sodium bisulfate is employed in industrial wastewater treatment for dechlorination purposes. It helps in neutralizing chlorine residuals before the treated water is discharged into the environment. This process is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and complying with environmental regulations.
- Combination with other chemicals for enhanced dechlorination: Sodium bisulfate is often combined with other chemicals to enhance its dechlorination efficiency. These combinations can include reducing agents or catalysts that improve the reaction rate or effectiveness of the dechlorination process. Such combinations are particularly useful in complex water treatment scenarios.
- Dechlorination systems and equipment: Various systems and equipment have been developed for sodium bisulfate dechlorination. These include automated dosing systems, mixing tanks, and specialized reactors designed to optimize the dechlorination process. Such equipment ensures precise control and efficient use of sodium bisulfate in water treatment applications.
- Applications in food and beverage industry: Sodium bisulfate dechlorination finds applications in the food and beverage industry. It is used to remove chlorine from process water, ensuring the quality and safety of food products. This application is particularly important in bottled water production and food processing facilities where chlorine-free water is essential.
02 Dechlorination in industrial wastewater treatment
Sodium bisulfate dechlorination is applied in industrial wastewater treatment processes. It helps neutralize chlorine-containing effluents before discharge, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. This method is particularly effective for treating cooling tower blowdown, textile industry wastewater, and other industrial processes that use chlorine-based disinfectants.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination with other dechlorinating agents
Sodium bisulfate is often used in combination with other dechlorinating agents to enhance the overall efficiency of the dechlorination process. These combinations can include activated carbon, vitamin C (ascorbic acid), or other reducing agents. The synergistic effects of these combinations can lead to more rapid and complete dechlorination in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Dechlorination systems and equipment
Specialized dechlorination systems and equipment have been developed to utilize sodium bisulfate effectively. These systems include automated dosing equipment, mixing chambers, and monitoring devices to ensure precise control of the dechlorination process. Such systems are used in municipal water treatment plants, aquaculture facilities, and large-scale industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The use of sodium bisulfate for dechlorination has environmental and safety implications. While it is generally considered safe and environmentally friendly, proper handling and dosing are crucial to prevent over-acidification of water bodies. Research has been conducted on optimizing dosage rates, assessing environmental impacts, and developing safer handling procedures for large-scale applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for analyzing sodium bisulfate's dechlorination capabilities is in a developing stage, with growing market potential as water treatment concerns increase globally. The technology's maturity varies among key players, with established chemical companies like ExxonMobil, Bayer, and Sumitomo Chemical leading in research and development. Specialized environmental firms such as Earth Renaissance Technologies and Advanced Environmental Technologies are also making strides. Academic institutions like Kunming University of Science & Technology and Anhui University of Science & Technology contribute to fundamental research. The market is characterized by a mix of large corporations and niche players, indicating opportunities for innovation and specialization in this field.
ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed an innovative approach to sodium bisulfate's dechlorination capabilities, particularly in the context of oil and gas production. Their method involves using sodium bisulfate as a key component in a multi-step process to remove chlorine compounds from produced water. The process includes injecting sodium bisulfate into the water stream, which reacts with chlorine to form less harmful compounds. This is followed by a separation step using advanced membrane technology to further purify the water[1][3]. The company has also integrated this technology with their existing water treatment systems, allowing for more efficient and cost-effective dechlorination in large-scale operations[5].
Strengths: Highly effective for large-scale operations, integrates well with existing systems, and reduces environmental impact. Weaknesses: May require significant initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Technical Solution: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries has developed a comprehensive dechlorination system utilizing sodium bisulfate's capabilities. Their approach involves a two-stage process: first, sodium bisulfate is used to neutralize chlorine in wastewater streams, and then a proprietary catalytic process further breaks down any remaining chlorinated compounds[2]. This system has been successfully implemented in various industrial applications, including power plants and chemical manufacturing facilities. Mitsubishi's technology also incorporates real-time monitoring and automated dosing systems to optimize the use of sodium bisulfate and ensure consistent dechlorination performance[4]. The company has reported achieving chlorine reduction rates of up to 99.9% in some applications[6].
Strengths: High efficiency in chlorine removal, versatile application across industries, and advanced monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: May require specialized training for operation and maintenance.
Core Innovations
Antimicrobial agent
PatentWO2011107753A1
Innovation
- A novel decontamination method using a composition comprising a modified acidified salt as an acidulant, which reduces the pH to at least 3, combined with an antioxidant like ascorbic acid, applied in a two-step process to effectively eliminate microorganisms from packaging and surfaces, including those for clean-in-place applications.
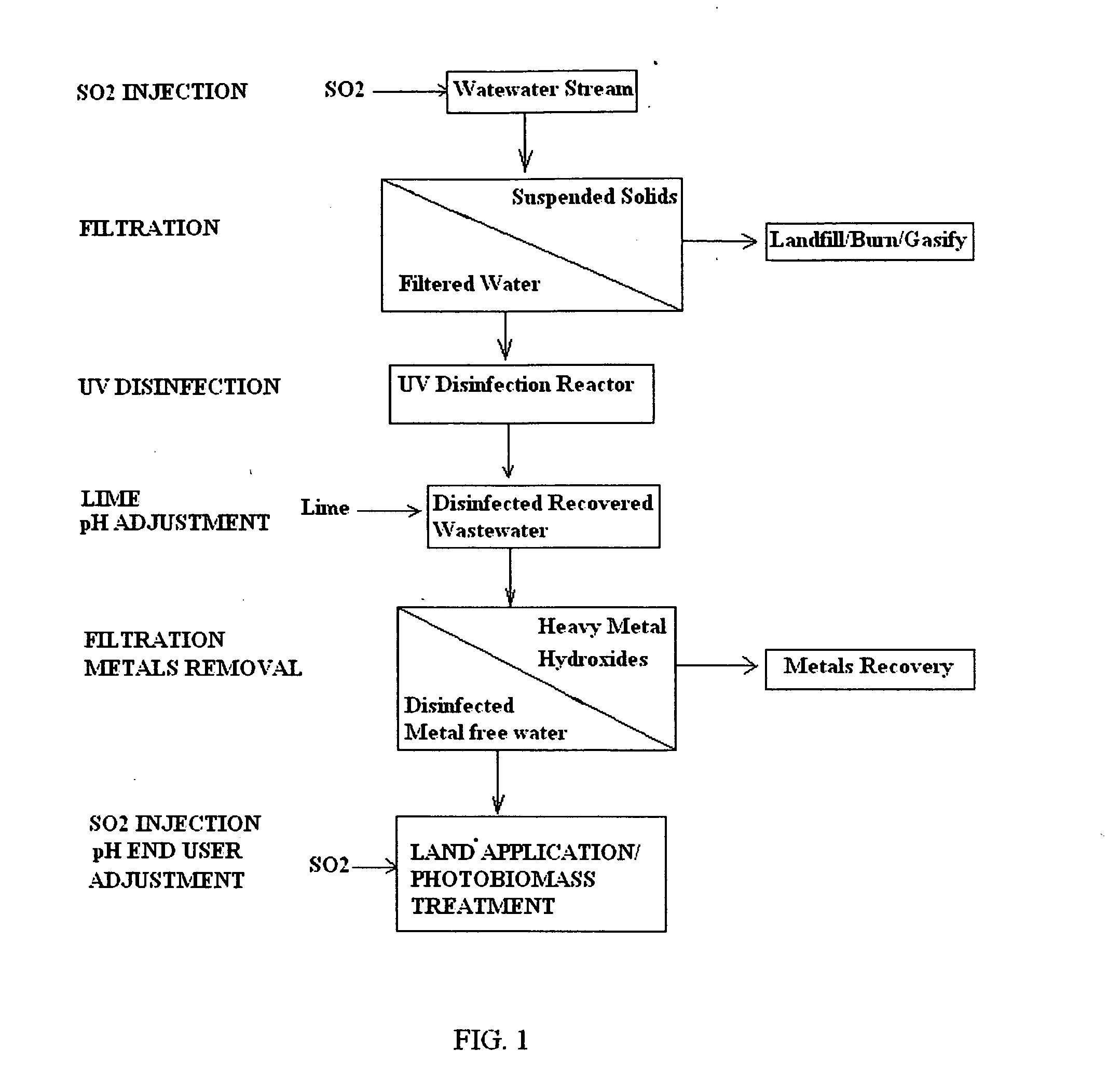
Acidification pre-treatment for UV water disinfection
PatentInactiveUS20110243665A1
Innovation
- A pre-treatment method using sulfurous acid to self-agglomerate suspended solids for easier filtration and reduce mineral scaling and microbial buildup on UV light tubes, achieved by injecting sulfur dioxide to generate sulfurous acid, which acts as a surfactant and biocide, preventing film formation and extending the time between cleanings.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of sodium bisulfate's dechlorination capabilities is a critical aspect of evaluating its potential use in water treatment processes. Sodium bisulfate, when used for dechlorination, primarily reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride and sodium sulfate. This reaction effectively removes free chlorine from water, which is beneficial for aquatic ecosystems and human health.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using sodium bisulfate for dechlorination is the reduction of chlorine-related toxicity in treated water discharged into natural water bodies. Chlorine, while effective for disinfection, can be harmful to aquatic life even at low concentrations. By neutralizing residual chlorine, sodium bisulfate helps prevent the formation of toxic chlorinated compounds in receiving waters, thus protecting fish, invertebrates, and other aquatic organisms.
However, the use of sodium bisulfate is not without potential environmental concerns. The addition of sodium bisulfate to water can lead to a temporary decrease in pH, which may impact sensitive aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. This pH reduction can be particularly problematic in areas with naturally low alkalinity or in waters that are already stressed by acidification. Careful monitoring and control of dosage are essential to minimize these pH-related impacts.
Another consideration is the increase in total dissolved solids (TDS) resulting from the dechlorination process. The formation of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate contributes to higher TDS levels in treated water. Elevated TDS can affect water quality and potentially impact aquatic life, especially in freshwater systems. Long-term accumulation of these salts in water bodies may lead to changes in osmotic pressure for aquatic organisms and alter the overall ecological balance.
The production and transportation of sodium bisulfate also have environmental implications. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Additionally, the transportation of the chemical to treatment facilities adds to the overall carbon footprint of the dechlorination process. These factors should be weighed against the environmental benefits of dechlorination when assessing the overall sustainability of using sodium bisulfate.
It is important to note that the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate dechlorination can vary depending on the specific application and local environmental conditions. Factors such as water chemistry, flow rates, and the presence of other pollutants can all influence the overall environmental outcome. Therefore, site-specific assessments and ongoing monitoring are crucial for ensuring that the use of sodium bisulfate for dechlorination remains environmentally sound and effective.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using sodium bisulfate for dechlorination is the reduction of chlorine-related toxicity in treated water discharged into natural water bodies. Chlorine, while effective for disinfection, can be harmful to aquatic life even at low concentrations. By neutralizing residual chlorine, sodium bisulfate helps prevent the formation of toxic chlorinated compounds in receiving waters, thus protecting fish, invertebrates, and other aquatic organisms.
However, the use of sodium bisulfate is not without potential environmental concerns. The addition of sodium bisulfate to water can lead to a temporary decrease in pH, which may impact sensitive aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. This pH reduction can be particularly problematic in areas with naturally low alkalinity or in waters that are already stressed by acidification. Careful monitoring and control of dosage are essential to minimize these pH-related impacts.
Another consideration is the increase in total dissolved solids (TDS) resulting from the dechlorination process. The formation of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate contributes to higher TDS levels in treated water. Elevated TDS can affect water quality and potentially impact aquatic life, especially in freshwater systems. Long-term accumulation of these salts in water bodies may lead to changes in osmotic pressure for aquatic organisms and alter the overall ecological balance.
The production and transportation of sodium bisulfate also have environmental implications. The manufacturing process requires energy and resources, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Additionally, the transportation of the chemical to treatment facilities adds to the overall carbon footprint of the dechlorination process. These factors should be weighed against the environmental benefits of dechlorination when assessing the overall sustainability of using sodium bisulfate.
It is important to note that the environmental impact of sodium bisulfate dechlorination can vary depending on the specific application and local environmental conditions. Factors such as water chemistry, flow rates, and the presence of other pollutants can all influence the overall environmental outcome. Therefore, site-specific assessments and ongoing monitoring are crucial for ensuring that the use of sodium bisulfate for dechlorination remains environmentally sound and effective.
Regulatory Compliance
The regulatory landscape surrounding sodium bisulfate's use in dechlorination processes is complex and multifaceted, requiring careful consideration of various national and international standards. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating the use of sodium bisulfate for water treatment purposes. The EPA's National Primary Drinking Water Regulations set strict limits on chlorine levels in drinking water, necessitating effective dechlorination methods.
Under the Safe Drinking Water Act, sodium bisulfate is classified as a secondary direct food additive permitted in food for human consumption when used for dechlorination purposes. This classification ensures its safety for use in water treatment processes that may impact potable water supplies. However, its application must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) as outlined in 21 CFR 173.310.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for the safe handling and storage of sodium bisulfate in industrial settings. These regulations include proper labeling, personal protective equipment requirements, and exposure limits to ensure worker safety during dechlorination operations.
On an international level, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines for drinking water quality that influence regulatory frameworks worldwide. While not directly regulating sodium bisulfate, these guidelines impact dechlorination practices and the acceptable methods for achieving safe chlorine levels in water supplies.
In the European Union, the use of sodium bisulfate for dechlorination must comply with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This comprehensive framework ensures that the chemical's use does not pose unacceptable risks to human health or the environment.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the environmental impact of dechlorination processes. The discharge of dechlorinated water into natural water bodies is subject to regulations such as the Clean Water Act in the United States. These regulations aim to protect aquatic ecosystems from potential harm caused by chemical treatments.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration, regulations are evolving to encourage the use of environmentally friendly dechlorination methods. This trend may influence future regulatory frameworks, potentially favoring sodium bisulfate due to its relatively low environmental impact compared to some alternative dechlorination agents.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements necessitates comprehensive quality control measures and documentation practices. Organizations utilizing sodium bisulfate for dechlorination must maintain detailed records of its use, storage, and disposal to demonstrate adherence to applicable regulations and standards.
Under the Safe Drinking Water Act, sodium bisulfate is classified as a secondary direct food additive permitted in food for human consumption when used for dechlorination purposes. This classification ensures its safety for use in water treatment processes that may impact potable water supplies. However, its application must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) as outlined in 21 CFR 173.310.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for the safe handling and storage of sodium bisulfate in industrial settings. These regulations include proper labeling, personal protective equipment requirements, and exposure limits to ensure worker safety during dechlorination operations.
On an international level, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines for drinking water quality that influence regulatory frameworks worldwide. While not directly regulating sodium bisulfate, these guidelines impact dechlorination practices and the acceptable methods for achieving safe chlorine levels in water supplies.
In the European Union, the use of sodium bisulfate for dechlorination must comply with the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This comprehensive framework ensures that the chemical's use does not pose unacceptable risks to human health or the environment.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the environmental impact of dechlorination processes. The discharge of dechlorinated water into natural water bodies is subject to regulations such as the Clean Water Act in the United States. These regulations aim to protect aquatic ecosystems from potential harm caused by chemical treatments.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important consideration, regulations are evolving to encourage the use of environmentally friendly dechlorination methods. This trend may influence future regulatory frameworks, potentially favoring sodium bisulfate due to its relatively low environmental impact compared to some alternative dechlorination agents.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements necessitates comprehensive quality control measures and documentation practices. Organizations utilizing sodium bisulfate for dechlorination must maintain detailed records of its use, storage, and disposal to demonstrate adherence to applicable regulations and standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!