Assessing the Impact of PEMF Therapy on Global Health Trends
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing applications, PEMF therapy has expanded its reach to address a wide range of health conditions. The therapy's evolution can be traced through several key phases, each marked by technological advancements and broadening applications.
In the 1950s and 1960s, researchers began exploring the effects of electromagnetic fields on biological systems. This early phase focused primarily on bone healing, with pioneering studies demonstrating the potential of PEMF to stimulate osteogenesis. The 1970s saw the first FDA-approved PEMF devices for bone healing, marking a significant milestone in the therapy's development.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed an expansion of PEMF applications beyond orthopedics. Researchers began investigating its potential in treating soft tissue injuries, pain management, and neurological disorders. This period also saw improvements in device design, with more portable and user-friendly PEMF systems becoming available.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era for PEMF therapy, characterized by miniaturization and increased accessibility. Advances in electronics and materials science led to the development of smaller, more powerful devices suitable for home use. This democratization of PEMF technology opened up new possibilities for chronic disease management and wellness applications.
In recent years, PEMF therapy has gained traction in the fields of sports medicine and anti-aging. Professional athletes and fitness enthusiasts have embraced PEMF for its potential to enhance recovery and performance. Simultaneously, researchers have been exploring its effects on cellular health and longevity, positioning PEMF as a potential tool in the quest for healthy aging.
The most recent phase of PEMF evolution has been marked by integration with other technologies. Wearable PEMF devices, smartphone-controlled systems, and combination therapies that pair PEMF with other modalities like light therapy or biofeedback are emerging. These developments are making PEMF more personalized and accessible to a broader audience.
Throughout its evolution, PEMF therapy has consistently expanded its evidence base. Clinical trials and meta-analyses have provided growing support for its efficacy in various applications, although some areas remain controversial and require further research. The therapy's non-invasive nature and relatively low risk profile have contributed to its increasing acceptance in both conventional and complementary medicine circles.
Looking ahead, the evolution of PEMF therapy is likely to continue along several trajectories. Advancements in precision medicine may lead to more targeted PEMF protocols tailored to individual genetic profiles. Integration with artificial intelligence could optimize treatment parameters in real-time based on physiological feedback. As global health trends increasingly focus on preventative and personalized care, PEMF therapy is poised to play a significant role in shaping future approaches to health and wellness.
In the 1950s and 1960s, researchers began exploring the effects of electromagnetic fields on biological systems. This early phase focused primarily on bone healing, with pioneering studies demonstrating the potential of PEMF to stimulate osteogenesis. The 1970s saw the first FDA-approved PEMF devices for bone healing, marking a significant milestone in the therapy's development.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed an expansion of PEMF applications beyond orthopedics. Researchers began investigating its potential in treating soft tissue injuries, pain management, and neurological disorders. This period also saw improvements in device design, with more portable and user-friendly PEMF systems becoming available.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era for PEMF therapy, characterized by miniaturization and increased accessibility. Advances in electronics and materials science led to the development of smaller, more powerful devices suitable for home use. This democratization of PEMF technology opened up new possibilities for chronic disease management and wellness applications.
In recent years, PEMF therapy has gained traction in the fields of sports medicine and anti-aging. Professional athletes and fitness enthusiasts have embraced PEMF for its potential to enhance recovery and performance. Simultaneously, researchers have been exploring its effects on cellular health and longevity, positioning PEMF as a potential tool in the quest for healthy aging.
The most recent phase of PEMF evolution has been marked by integration with other technologies. Wearable PEMF devices, smartphone-controlled systems, and combination therapies that pair PEMF with other modalities like light therapy or biofeedback are emerging. These developments are making PEMF more personalized and accessible to a broader audience.
Throughout its evolution, PEMF therapy has consistently expanded its evidence base. Clinical trials and meta-analyses have provided growing support for its efficacy in various applications, although some areas remain controversial and require further research. The therapy's non-invasive nature and relatively low risk profile have contributed to its increasing acceptance in both conventional and complementary medicine circles.
Looking ahead, the evolution of PEMF therapy is likely to continue along several trajectories. Advancements in precision medicine may lead to more targeted PEMF protocols tailored to individual genetic profiles. Integration with artificial intelligence could optimize treatment parameters in real-time based on physiological feedback. As global health trends increasingly focus on preventative and personalized care, PEMF therapy is poised to play a significant role in shaping future approaches to health and wellness.
Global Health Market Analysis
The global health market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by various factors including technological advancements, changing demographics, and increasing healthcare awareness. Within this context, the potential impact of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy on global health trends is a subject of growing interest and importance.
The global healthcare market size was valued at approximately $8.45 trillion in 2021 and is projected to continue its upward trajectory. This growth is fueled by an aging population, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and increased healthcare spending in both developed and developing countries. The market encompasses a wide range of sectors, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, healthcare services, and digital health solutions.
PEMF therapy, as an emerging non-invasive treatment modality, is positioned to potentially disrupt and reshape certain segments of the global health market. The therapy utilizes electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration, offering potential benefits for various health conditions. The global PEMF therapy devices market, while still relatively small compared to other medical device segments, is showing promising growth potential.
Market analysis indicates that the adoption of PEMF therapy is gaining traction across different regions. North America currently leads in terms of market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The increasing acceptance of alternative and complementary therapies in these regions is a key driver for PEMF therapy's growth. Additionally, the rising healthcare costs and the need for non-pharmacological treatment options are creating favorable conditions for PEMF therapy's expansion in the global health market.
The potential applications of PEMF therapy span across multiple health domains, including pain management, orthopedics, neurology, and wound healing. This versatility positions PEMF therapy to potentially impact various segments of the healthcare market. For instance, in the pain management sector, which is projected to reach $91.6 billion by 2025, PEMF therapy could emerge as a significant player, offering a non-opioid alternative for chronic pain treatment.
However, the integration of PEMF therapy into mainstream healthcare practices faces several challenges. These include the need for more robust clinical evidence, regulatory hurdles, and the conservative nature of traditional medical practices. Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for PEMF therapy to realize its full potential in the global health market.
As healthcare systems worldwide increasingly focus on preventive care and personalized medicine, PEMF therapy aligns well with these trends. Its non-invasive nature and potential for home-based use make it an attractive option in the growing market for remote patient monitoring and telemedicine solutions, which has seen accelerated growth in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The global healthcare market size was valued at approximately $8.45 trillion in 2021 and is projected to continue its upward trajectory. This growth is fueled by an aging population, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and increased healthcare spending in both developed and developing countries. The market encompasses a wide range of sectors, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, healthcare services, and digital health solutions.
PEMF therapy, as an emerging non-invasive treatment modality, is positioned to potentially disrupt and reshape certain segments of the global health market. The therapy utilizes electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration, offering potential benefits for various health conditions. The global PEMF therapy devices market, while still relatively small compared to other medical device segments, is showing promising growth potential.
Market analysis indicates that the adoption of PEMF therapy is gaining traction across different regions. North America currently leads in terms of market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The increasing acceptance of alternative and complementary therapies in these regions is a key driver for PEMF therapy's growth. Additionally, the rising healthcare costs and the need for non-pharmacological treatment options are creating favorable conditions for PEMF therapy's expansion in the global health market.
The potential applications of PEMF therapy span across multiple health domains, including pain management, orthopedics, neurology, and wound healing. This versatility positions PEMF therapy to potentially impact various segments of the healthcare market. For instance, in the pain management sector, which is projected to reach $91.6 billion by 2025, PEMF therapy could emerge as a significant player, offering a non-opioid alternative for chronic pain treatment.
However, the integration of PEMF therapy into mainstream healthcare practices faces several challenges. These include the need for more robust clinical evidence, regulatory hurdles, and the conservative nature of traditional medical practices. Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for PEMF therapy to realize its full potential in the global health market.
As healthcare systems worldwide increasingly focus on preventive care and personalized medicine, PEMF therapy aligns well with these trends. Its non-invasive nature and potential for home-based use make it an attractive option in the growing market for remote patient monitoring and telemedicine solutions, which has seen accelerated growth in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
PEMF Technology Status
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has gained significant traction in recent years as a non-invasive treatment modality for various health conditions. The current status of PEMF technology reflects a rapidly evolving field with promising applications across multiple medical domains.
PEMF devices have undergone substantial improvements in terms of portability, user-friendliness, and treatment customization. Modern PEMF systems range from small, wearable devices for localized therapy to larger, full-body mats for comprehensive treatment. These advancements have made PEMF therapy more accessible to both clinical settings and home users.
The technology behind PEMF therapy has also seen notable progress. Current devices utilize sophisticated waveform generators capable of producing a wide range of frequencies and intensities. This allows for more targeted and effective treatments tailored to specific health conditions. Additionally, the integration of smart technology and mobile applications has enhanced user experience and treatment monitoring capabilities.
Clinical research on PEMF therapy has expanded significantly, with numerous studies investigating its efficacy in various health conditions. Areas of focus include pain management, bone healing, wound care, and neurological disorders. While results have been promising in many cases, the scientific community continues to call for more rigorous, large-scale clinical trials to establish definitive evidence of PEMF's therapeutic benefits.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF devices varies globally. In some countries, certain PEMF devices have received approval from regulatory bodies for specific medical indications. However, the regulatory status remains complex, with many devices marketed as wellness products rather than medical devices, highlighting the need for clearer guidelines and standards in this emerging field.
Manufacturing and distribution of PEMF technology have seen notable growth, with both established medical device companies and innovative startups entering the market. This has led to increased competition and a wider range of product offerings, from high-end clinical systems to affordable consumer-grade devices.
Despite the progress, challenges remain in the PEMF technology sector. These include the need for standardization in treatment protocols, concerns about potential long-term effects of electromagnetic field exposure, and the ongoing debate about the optimal frequencies and intensities for different health conditions. Additionally, there is a growing focus on developing more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly PEMF devices.
As PEMF technology continues to evolve, its potential impact on global health trends is becoming increasingly apparent. The non-invasive nature and broad applicability of PEMF therapy position it as a promising complementary treatment option in various medical fields, potentially reducing reliance on pharmacological interventions for certain conditions.
PEMF devices have undergone substantial improvements in terms of portability, user-friendliness, and treatment customization. Modern PEMF systems range from small, wearable devices for localized therapy to larger, full-body mats for comprehensive treatment. These advancements have made PEMF therapy more accessible to both clinical settings and home users.
The technology behind PEMF therapy has also seen notable progress. Current devices utilize sophisticated waveform generators capable of producing a wide range of frequencies and intensities. This allows for more targeted and effective treatments tailored to specific health conditions. Additionally, the integration of smart technology and mobile applications has enhanced user experience and treatment monitoring capabilities.
Clinical research on PEMF therapy has expanded significantly, with numerous studies investigating its efficacy in various health conditions. Areas of focus include pain management, bone healing, wound care, and neurological disorders. While results have been promising in many cases, the scientific community continues to call for more rigorous, large-scale clinical trials to establish definitive evidence of PEMF's therapeutic benefits.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF devices varies globally. In some countries, certain PEMF devices have received approval from regulatory bodies for specific medical indications. However, the regulatory status remains complex, with many devices marketed as wellness products rather than medical devices, highlighting the need for clearer guidelines and standards in this emerging field.
Manufacturing and distribution of PEMF technology have seen notable growth, with both established medical device companies and innovative startups entering the market. This has led to increased competition and a wider range of product offerings, from high-end clinical systems to affordable consumer-grade devices.
Despite the progress, challenges remain in the PEMF technology sector. These include the need for standardization in treatment protocols, concerns about potential long-term effects of electromagnetic field exposure, and the ongoing debate about the optimal frequencies and intensities for different health conditions. Additionally, there is a growing focus on developing more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly PEMF devices.
As PEMF technology continues to evolve, its potential impact on global health trends is becoming increasingly apparent. The non-invasive nature and broad applicability of PEMF therapy position it as a promising complementary treatment option in various medical fields, potentially reducing reliance on pharmacological interventions for certain conditions.
Current PEMF Applications
01 Therapeutic applications of PEMF
PEMF therapy has various therapeutic applications, including pain management, tissue healing, and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. The pulsed electromagnetic fields stimulate cellular activity, promote blood circulation, and enhance the body's natural healing processes. This non-invasive treatment method can be used for conditions such as arthritis, fractures, and chronic pain.- Therapeutic applications of PEMF: Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has various therapeutic applications, including pain management, tissue healing, and improving overall health. It involves the use of electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular activity and promote healing processes in the body. PEMF devices can be designed for specific medical conditions or general wellness purposes.
- PEMF device design and configurations: PEMF devices come in various designs and configurations to suit different therapeutic needs. These can include wearable devices, portable units, or larger stationary systems. The design may incorporate features such as adjustable field strength, frequency settings, and treatment area coverage. Some devices are designed for specific body parts or conditions, while others offer full-body treatment options.
- PEMF in combination with other therapies: PEMF therapy can be combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This may include integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or other forms of electromagnetic stimulation. The synergistic effects of combined therapies can potentially improve treatment efficacy for various conditions.
- PEMF for specific medical conditions: Research and development in PEMF therapy focus on its application for specific medical conditions. These may include musculoskeletal disorders, neurological conditions, wound healing, and cardiovascular health. Studies aim to determine optimal treatment parameters and protocols for each condition to maximize therapeutic benefits.
- Technological advancements in PEMF systems: Ongoing technological advancements in PEMF systems aim to improve treatment efficacy, user experience, and device functionality. This includes the development of smart PEMF devices with features such as wireless connectivity, mobile app integration, and personalized treatment programs. Innovations also focus on enhancing the precision and control of electromagnetic field generation and delivery.
02 PEMF device design and configurations
PEMF devices come in various designs and configurations to suit different therapeutic needs. These may include wearable devices, portable units, or larger clinical systems. The devices typically consist of electromagnetic coils, control units, and power sources. Some designs incorporate flexible applicators for better conformity to body contours, while others feature multiple coils for targeted treatment of specific areas.Expand Specific Solutions03 PEMF frequency and intensity optimization
The effectiveness of PEMF therapy depends on optimizing the frequency and intensity of the electromagnetic fields. Research focuses on determining the most beneficial parameters for different conditions and treatment goals. This includes studying the effects of various frequencies, waveforms, and field strengths on cellular responses and therapeutic outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination of PEMF with other therapies
PEMF therapy can be combined with other treatment modalities to enhance overall therapeutic effects. This may include integration with physical therapy, acupuncture, or other forms of electromagnetic therapies. The synergistic approach aims to improve treatment outcomes and provide more comprehensive care for patients with various health conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 PEMF technology advancements
Ongoing advancements in PEMF technology focus on improving treatment efficacy, user experience, and device functionality. This includes the development of smart PEMF devices with programmable settings, integration with mobile applications for treatment monitoring, and the use of advanced materials for better energy transfer and comfort. These innovations aim to make PEMF therapy more accessible and effective for a wider range of applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Industry Players
The PEMF therapy market is in a growth phase, with increasing global health trends driving adoption. The market size is expanding, projected to reach several billion dollars by 2030. Technological maturity varies, with established players like Venus Concept and Regenesis Biomedical offering commercial products, while newer entrants like Galvanize Therapeutics and Shanghai Nuosheng Medical Technology are developing innovative applications. Research institutions such as Chongqing University and Zhejiang University are advancing the scientific understanding of PEMF. The competitive landscape is diverse, including medical device companies, biotech firms, and academic institutions, indicating a dynamic and evolving field with potential for significant advancements in healthcare applications.
Venus Concept Ltd.
Technical Solution: Venus Concept has developed advanced PEMF therapy devices for various medical applications. Their technology utilizes precise electromagnetic pulses to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration. The company's PEMF systems are designed to deliver targeted therapy for pain management, wound healing, and musculoskeletal disorders. Venus Concept's devices incorporate adjustable frequency and intensity settings, allowing for personalized treatment protocols. Their PEMF technology has shown promising results in clinical studies, demonstrating improved tissue oxygenation and enhanced cellular metabolism[1][3]. The company has also integrated PEMF therapy with other modalities like radiofrequency and magnetic pulse technology to create synergistic treatment options for aesthetic and therapeutic purposes.
Strengths: Versatile applications in both medical and aesthetic fields, clinically proven efficacy, and customizable treatment options. Weaknesses: Limited long-term data on certain applications, potential for high initial investment costs for healthcare providers.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical specializes in PEMF therapy devices for wound healing and pain management. Their flagship product, the Provant Therapy System, utilizes a proprietary PEMF technology that emits a specific electromagnetic field to promote cellular regeneration and reduce inflammation. The device operates at a carefully calibrated frequency of 27.12 MHz, which has been shown to effectively penetrate tissue and stimulate cellular activity[2]. Regenesis' PEMF technology has demonstrated significant results in accelerating wound healing, particularly in chronic wounds and post-operative recovery. The company's devices are designed for both clinical and home use, featuring portable and user-friendly designs. Regenesis has conducted extensive clinical research to validate the efficacy of their PEMF therapy in various medical conditions, including diabetic foot ulcers and post-operative pain[4].
Strengths: Focused expertise in wound healing and pain management, FDA-cleared devices, and strong clinical evidence base. Weaknesses: Narrower application range compared to some competitors, potential limitations in treating deep tissue conditions.
PEMF Research Innovations
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy Whole Body Wellness Device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveUS20190054308A1
Innovation
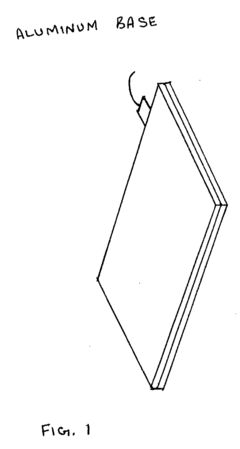
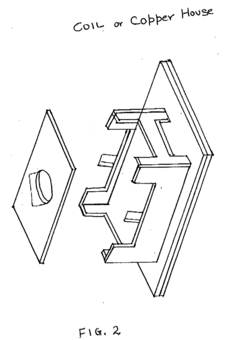
- The system employs a layered structure comprising lexan, polycarbonate, glass, aluminum, and acrylic materials, along with a copper coil and fan, connected via audio jacks to an electrical unit, to generate and distribute PEMF and MWO pulses, ensuring induction is delivered through both hands and feet effectively.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy is complex and varies significantly across different regions and countries. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved several PEMF devices for specific medical uses, such as bone healing and pain management. These devices are classified as Class III medical devices, requiring rigorous clinical trials and safety evaluations before approval.
In the European Union, PEMF devices are regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. The MDR has introduced more stringent requirements for clinical evidence and post-market surveillance, potentially impacting the approval process for new PEMF devices and the continued marketing of existing ones.
Many other countries, including Canada, Australia, and Japan, have their own regulatory bodies and approval processes for medical devices, including PEMF therapy equipment. These regulations often align with international standards, such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) for electromagnetic compatibility and safety.
Despite regulatory approvals in some areas, the use of PEMF therapy remains controversial in certain medical circles. This has led to varying levels of acceptance and integration into mainstream healthcare systems worldwide. Some countries have more permissive regulations, allowing PEMF devices to be marketed as wellness products rather than medical devices, which can lead to less stringent oversight.
The global regulatory landscape for PEMF therapy is evolving, with increasing attention being paid to the potential long-term effects of electromagnetic field exposure. This has prompted some regulatory bodies to call for more comprehensive studies on the safety and efficacy of PEMF therapy, particularly for extended use or in vulnerable populations.
As PEMF therapy gains more attention in the global health arena, there is a growing need for harmonized international standards and regulations. This would not only facilitate the development and approval of new PEMF technologies but also ensure consistent safety and efficacy standards across different markets. However, achieving such harmonization remains challenging due to differing healthcare priorities and regulatory philosophies among countries.
The regulatory framework also extends to the manufacturing and quality control processes of PEMF devices. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and quality management systems such as ISO 13485 are often required to ensure the consistency and reliability of these devices. This aspect of regulation is crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring the safe application of PEMF therapy in various healthcare settings.
In the European Union, PEMF devices are regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. The MDR has introduced more stringent requirements for clinical evidence and post-market surveillance, potentially impacting the approval process for new PEMF devices and the continued marketing of existing ones.
Many other countries, including Canada, Australia, and Japan, have their own regulatory bodies and approval processes for medical devices, including PEMF therapy equipment. These regulations often align with international standards, such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) for electromagnetic compatibility and safety.
Despite regulatory approvals in some areas, the use of PEMF therapy remains controversial in certain medical circles. This has led to varying levels of acceptance and integration into mainstream healthcare systems worldwide. Some countries have more permissive regulations, allowing PEMF devices to be marketed as wellness products rather than medical devices, which can lead to less stringent oversight.
The global regulatory landscape for PEMF therapy is evolving, with increasing attention being paid to the potential long-term effects of electromagnetic field exposure. This has prompted some regulatory bodies to call for more comprehensive studies on the safety and efficacy of PEMF therapy, particularly for extended use or in vulnerable populations.
As PEMF therapy gains more attention in the global health arena, there is a growing need for harmonized international standards and regulations. This would not only facilitate the development and approval of new PEMF technologies but also ensure consistent safety and efficacy standards across different markets. However, achieving such harmonization remains challenging due to differing healthcare priorities and regulatory philosophies among countries.
The regulatory framework also extends to the manufacturing and quality control processes of PEMF devices. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and quality management systems such as ISO 13485 are often required to ensure the consistency and reliability of these devices. This aspect of regulation is crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring the safe application of PEMF therapy in various healthcare settings.
PEMF Safety Considerations
As PEMF therapy gains prominence in global health trends, it is crucial to thoroughly examine the safety considerations associated with this technology. The non-invasive nature of PEMF therapy contributes to its overall safety profile, but potential risks and contraindications must be carefully evaluated.
One primary safety concern is the interaction between PEMF devices and implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers or defibrillators. The electromagnetic fields generated by PEMF therapy could potentially interfere with the functioning of these devices, necessitating caution and consultation with healthcare professionals before use.
Pregnant women and individuals with certain medical conditions, including epilepsy or active bleeding, are generally advised to avoid PEMF therapy due to potential risks. While research has not conclusively demonstrated adverse effects in these populations, a precautionary approach is recommended until more comprehensive studies are available.
The intensity and frequency of PEMF treatments also warrant consideration. Overexposure or improper use of PEMF devices may lead to temporary side effects, including dizziness, fatigue, or mild discomfort. Adhering to recommended treatment protocols and guidelines is essential to minimize these risks and optimize therapeutic benefits.
Quality control and regulatory compliance of PEMF devices are critical aspects of safety. As the market for PEMF therapy expands globally, ensuring that devices meet international safety standards and undergo rigorous testing becomes increasingly important. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe play crucial roles in overseeing the safety and efficacy of PEMF devices.
Long-term safety data on PEMF therapy is still limited, particularly regarding prolonged use or potential cumulative effects. Ongoing research and post-market surveillance are necessary to identify any rare or delayed adverse effects that may not be apparent in short-term studies.
Education and proper training for both healthcare providers and patients are essential components of PEMF safety. Clear instructions on device operation, treatment protocols, and potential contraindications can significantly reduce the risk of adverse events and enhance the overall safety profile of PEMF therapy.
As PEMF therapy continues to evolve and integrate into global health practices, maintaining a balanced approach to safety considerations is paramount. This involves ongoing research, vigilant monitoring, and adaptive regulatory frameworks to ensure that the potential benefits of PEMF therapy are realized while minimizing associated risks.
One primary safety concern is the interaction between PEMF devices and implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers or defibrillators. The electromagnetic fields generated by PEMF therapy could potentially interfere with the functioning of these devices, necessitating caution and consultation with healthcare professionals before use.
Pregnant women and individuals with certain medical conditions, including epilepsy or active bleeding, are generally advised to avoid PEMF therapy due to potential risks. While research has not conclusively demonstrated adverse effects in these populations, a precautionary approach is recommended until more comprehensive studies are available.
The intensity and frequency of PEMF treatments also warrant consideration. Overexposure or improper use of PEMF devices may lead to temporary side effects, including dizziness, fatigue, or mild discomfort. Adhering to recommended treatment protocols and guidelines is essential to minimize these risks and optimize therapeutic benefits.
Quality control and regulatory compliance of PEMF devices are critical aspects of safety. As the market for PEMF therapy expands globally, ensuring that devices meet international safety standards and undergo rigorous testing becomes increasingly important. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe play crucial roles in overseeing the safety and efficacy of PEMF devices.
Long-term safety data on PEMF therapy is still limited, particularly regarding prolonged use or potential cumulative effects. Ongoing research and post-market surveillance are necessary to identify any rare or delayed adverse effects that may not be apparent in short-term studies.
Education and proper training for both healthcare providers and patients are essential components of PEMF safety. Clear instructions on device operation, treatment protocols, and potential contraindications can significantly reduce the risk of adverse events and enhance the overall safety profile of PEMF therapy.
As PEMF therapy continues to evolve and integrate into global health practices, maintaining a balanced approach to safety considerations is paramount. This involves ongoing research, vigilant monitoring, and adaptive regulatory frameworks to ensure that the potential benefits of PEMF therapy are realized while minimizing associated risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!