Ball Mill Noise And Dust Mitigation For Plant Safety
AUG 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ball Mill Noise and Dust Control Background and Objectives
Ball mills have been a cornerstone technology in various industrial processes for over a century, primarily utilized in mining, cement production, power generation, and chemical manufacturing. These cylindrical devices, filled with grinding media such as steel balls, operate by rotating around a horizontal axis, effectively grinding materials into fine powder. However, this essential industrial equipment generates significant noise and dust emissions that pose serious occupational health and safety risks to plant workers and surrounding communities.
The evolution of ball mill technology has historically prioritized production efficiency and grinding performance, with environmental and safety considerations emerging as critical factors only in recent decades. Early ball mill designs from the early 20th century focused primarily on mechanical reliability and throughput capacity, with minimal attention to noise and dust control. The 1970s marked a turning point with the introduction of environmental regulations in industrialized nations, prompting initial efforts to address these issues.
Current industrial standards and regulations, including OSHA in the United States and similar bodies globally, have established strict limits on workplace noise exposure (typically 85-90 dBA over an 8-hour period) and airborne particulate concentrations. These regulations have accelerated technological innovation in noise and dust mitigation strategies for ball mill operations.
The primary sources of noise in ball mill operations include the impact of grinding media against the mill shell, material-to-material contact, drive systems, and auxiliary equipment. Dust generation occurs primarily during material feeding, discharge points, and through inadequate sealing systems. Both issues are exacerbated by operational factors such as mill speed, ball charge levels, and material characteristics.
The objectives of this technical research report are multifaceted. First, we aim to comprehensively evaluate existing noise and dust control technologies for ball mill operations, assessing their effectiveness, implementation requirements, and cost-benefit ratios. Second, we seek to identify emerging technologies and innovative approaches that show promise for superior mitigation performance. Third, we will analyze the regulatory landscape and industry best practices to establish benchmarks for optimal noise and dust control.
Additionally, this report intends to develop a technical roadmap for ball mill operators to systematically address these challenges, considering factors such as mill size, application type, and operational parameters. The ultimate goal is to support the development of integrated solutions that maintain operational efficiency while significantly reducing occupational hazards and environmental impact, thereby ensuring sustainable industrial practices in sectors reliant on ball mill technology.
The evolution of ball mill technology has historically prioritized production efficiency and grinding performance, with environmental and safety considerations emerging as critical factors only in recent decades. Early ball mill designs from the early 20th century focused primarily on mechanical reliability and throughput capacity, with minimal attention to noise and dust control. The 1970s marked a turning point with the introduction of environmental regulations in industrialized nations, prompting initial efforts to address these issues.
Current industrial standards and regulations, including OSHA in the United States and similar bodies globally, have established strict limits on workplace noise exposure (typically 85-90 dBA over an 8-hour period) and airborne particulate concentrations. These regulations have accelerated technological innovation in noise and dust mitigation strategies for ball mill operations.
The primary sources of noise in ball mill operations include the impact of grinding media against the mill shell, material-to-material contact, drive systems, and auxiliary equipment. Dust generation occurs primarily during material feeding, discharge points, and through inadequate sealing systems. Both issues are exacerbated by operational factors such as mill speed, ball charge levels, and material characteristics.
The objectives of this technical research report are multifaceted. First, we aim to comprehensively evaluate existing noise and dust control technologies for ball mill operations, assessing their effectiveness, implementation requirements, and cost-benefit ratios. Second, we seek to identify emerging technologies and innovative approaches that show promise for superior mitigation performance. Third, we will analyze the regulatory landscape and industry best practices to establish benchmarks for optimal noise and dust control.
Additionally, this report intends to develop a technical roadmap for ball mill operators to systematically address these challenges, considering factors such as mill size, application type, and operational parameters. The ultimate goal is to support the development of integrated solutions that maintain operational efficiency while significantly reducing occupational hazards and environmental impact, thereby ensuring sustainable industrial practices in sectors reliant on ball mill technology.
Market Demand for Plant Safety Solutions
The global market for ball mill noise and dust mitigation solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasingly stringent workplace safety regulations and heightened awareness of occupational health hazards. Current market analysis indicates that the industrial safety equipment sector, which includes noise and dust control systems, is projected to reach $70 billion by 2027, with dust and noise mitigation solutions accounting for approximately 15% of this market.
Mining and cement production industries represent the largest demand segments for ball mill safety solutions, collectively accounting for over 60% of the total market. These industries operate extensive ball mill operations that generate substantial noise pollution (often exceeding 95 dB) and hazardous dust particulates, creating urgent needs for effective mitigation technologies.
The regulatory landscape has become a primary market driver, with OSHA in the United States, the EU's Occupational Safety and Health Framework Directive, and similar bodies in Asia-Pacific regions implementing stricter exposure limits for both noise and airborne particulates. Companies failing to comply face penalties averaging $40,000 per serious violation, creating strong financial incentives for investment in mitigation technologies.
Worker compensation claims related to hearing loss and respiratory diseases have risen by 28% over the past five years, with average settlements reaching $175,000 per case. This liability exposure has prompted risk management departments to prioritize preventative safety measures, expanding the market for comprehensive ball mill safety solutions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated market growth by highlighting airborne contamination risks and workplace air quality concerns. This has resulted in a 34% increase in corporate spending on dust control systems between 2019 and 2022, with continued growth projected as health awareness remains elevated post-pandemic.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia and Africa, represent the fastest-growing market segments with annual growth rates exceeding 12%. This growth is driven by rapid industrialization, increasing regulatory oversight, and growing worker safety awareness in regions previously characterized by limited safety enforcement.
Customer demand is increasingly focused on integrated solutions that address both noise and dust simultaneously, rather than separate mitigation systems. Market research indicates that 76% of procurement managers prefer comprehensive safety packages that reduce implementation complexity and maintenance requirements while ensuring compliance across multiple safety parameters.
Return on investment considerations have become central to purchase decisions, with companies seeking solutions that demonstrate measurable improvements in worker productivity, reduced absenteeism, and decreased healthcare costs in addition to regulatory compliance benefits.
Mining and cement production industries represent the largest demand segments for ball mill safety solutions, collectively accounting for over 60% of the total market. These industries operate extensive ball mill operations that generate substantial noise pollution (often exceeding 95 dB) and hazardous dust particulates, creating urgent needs for effective mitigation technologies.
The regulatory landscape has become a primary market driver, with OSHA in the United States, the EU's Occupational Safety and Health Framework Directive, and similar bodies in Asia-Pacific regions implementing stricter exposure limits for both noise and airborne particulates. Companies failing to comply face penalties averaging $40,000 per serious violation, creating strong financial incentives for investment in mitigation technologies.
Worker compensation claims related to hearing loss and respiratory diseases have risen by 28% over the past five years, with average settlements reaching $175,000 per case. This liability exposure has prompted risk management departments to prioritize preventative safety measures, expanding the market for comprehensive ball mill safety solutions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated market growth by highlighting airborne contamination risks and workplace air quality concerns. This has resulted in a 34% increase in corporate spending on dust control systems between 2019 and 2022, with continued growth projected as health awareness remains elevated post-pandemic.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia and Africa, represent the fastest-growing market segments with annual growth rates exceeding 12%. This growth is driven by rapid industrialization, increasing regulatory oversight, and growing worker safety awareness in regions previously characterized by limited safety enforcement.
Customer demand is increasingly focused on integrated solutions that address both noise and dust simultaneously, rather than separate mitigation systems. Market research indicates that 76% of procurement managers prefer comprehensive safety packages that reduce implementation complexity and maintenance requirements while ensuring compliance across multiple safety parameters.
Return on investment considerations have become central to purchase decisions, with companies seeking solutions that demonstrate measurable improvements in worker productivity, reduced absenteeism, and decreased healthcare costs in addition to regulatory compliance benefits.
Current Challenges in Ball Mill Noise and Dust Control
Ball mill operations in industrial settings present significant challenges related to noise and dust control, which directly impact plant safety, worker health, and environmental compliance. Current noise levels in ball mill environments frequently exceed 85-90 dB, surpassing occupational safety thresholds established by regulatory bodies worldwide. This excessive noise exposure can lead to noise-induced hearing loss among workers, reduced communication effectiveness during operations, and increased accident risks due to impaired situational awareness.
Dust generation presents equally concerning challenges, with particulate matter concentrations often exceeding permissible exposure limits. Fine silica dust, metal particulates, and other airborne contaminants create respiratory hazards that can lead to chronic conditions including silicosis, pneumoconiosis, and other occupational lung diseases. The accumulation of combustible dust also introduces explosion and fire risks, particularly in enclosed processing areas with inadequate ventilation systems.
Existing control measures demonstrate varying degrees of effectiveness but face significant limitations. Conventional acoustic enclosures, while reducing ambient noise, often create accessibility issues for maintenance and inspection activities. These enclosures frequently lack proper integration with dust collection systems, creating competing operational priorities between noise reduction and dust management.
Current dust suppression technologies, including water spray systems and dry collection methods, present their own challenges. Water-based systems can interfere with material processing efficiency and create secondary issues such as slurry formation and increased equipment corrosion. Dry collection systems require substantial energy consumption and frequent maintenance, with filter clogging and pressure drop issues being common operational concerns.
The integration of monitoring systems presents additional challenges, as real-time noise and dust measurement technologies often lack durability in harsh mill environments. Sensor fouling, calibration drift, and connectivity issues undermine the reliability of monitoring networks, creating gaps in safety oversight and compliance documentation.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, with increasingly stringent standards for both noise and dust exposure. Many facilities struggle to meet these evolving requirements using existing control technologies, particularly in older plants where retrofitting presents significant engineering and economic challenges. The cost-benefit analysis of implementing comprehensive control measures remains problematic for many operations, especially smaller facilities with limited capital resources.
Cross-disciplinary challenges further complicate solutions, as effective mitigation requires expertise spanning mechanical engineering, industrial hygiene, materials science, and process control. The lack of standardized approaches across the industry has resulted in fragmented solutions that address symptoms rather than fundamental causes of noise and dust generation in ball mill operations.
Dust generation presents equally concerning challenges, with particulate matter concentrations often exceeding permissible exposure limits. Fine silica dust, metal particulates, and other airborne contaminants create respiratory hazards that can lead to chronic conditions including silicosis, pneumoconiosis, and other occupational lung diseases. The accumulation of combustible dust also introduces explosion and fire risks, particularly in enclosed processing areas with inadequate ventilation systems.
Existing control measures demonstrate varying degrees of effectiveness but face significant limitations. Conventional acoustic enclosures, while reducing ambient noise, often create accessibility issues for maintenance and inspection activities. These enclosures frequently lack proper integration with dust collection systems, creating competing operational priorities between noise reduction and dust management.
Current dust suppression technologies, including water spray systems and dry collection methods, present their own challenges. Water-based systems can interfere with material processing efficiency and create secondary issues such as slurry formation and increased equipment corrosion. Dry collection systems require substantial energy consumption and frequent maintenance, with filter clogging and pressure drop issues being common operational concerns.
The integration of monitoring systems presents additional challenges, as real-time noise and dust measurement technologies often lack durability in harsh mill environments. Sensor fouling, calibration drift, and connectivity issues undermine the reliability of monitoring networks, creating gaps in safety oversight and compliance documentation.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, with increasingly stringent standards for both noise and dust exposure. Many facilities struggle to meet these evolving requirements using existing control technologies, particularly in older plants where retrofitting presents significant engineering and economic challenges. The cost-benefit analysis of implementing comprehensive control measures remains problematic for many operations, especially smaller facilities with limited capital resources.
Cross-disciplinary challenges further complicate solutions, as effective mitigation requires expertise spanning mechanical engineering, industrial hygiene, materials science, and process control. The lack of standardized approaches across the industry has resulted in fragmented solutions that address symptoms rather than fundamental causes of noise and dust generation in ball mill operations.
Current Noise and Dust Suppression Techniques
01 Noise reduction enclosures and sound insulation systems
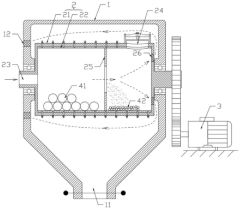
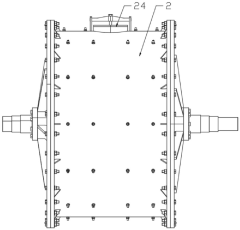
Various enclosure designs and sound insulation systems can be implemented to reduce the noise generated by ball mills during operation. These include soundproof cabins, acoustic enclosures with multilayer insulation materials, and noise-absorbing panels that can be installed around the mill. These systems effectively contain and absorb the sound waves produced during the grinding process, significantly reducing noise pollution in the working environment.- Noise reduction enclosures and sound insulation systems: Various enclosure designs and sound insulation systems can be implemented to reduce the noise generated by ball mills during operation. These include soundproof cabins, acoustic enclosures with noise-absorbing materials, and multi-layer insulation structures. These systems effectively contain and absorb the noise, preventing it from spreading to the surrounding environment while still allowing necessary access for operation and maintenance.
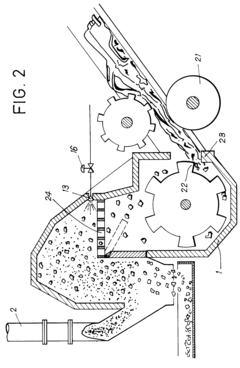
- Dust collection and suppression systems: Specialized dust collection systems can be integrated with ball mills to capture and filter dust particles generated during the grinding process. These systems typically include dust collectors, extraction hoods, filtration units, and sealed connections to prevent dust leakage. Some designs incorporate water spray or mist systems to suppress dust at the source, effectively reducing airborne particulates and improving air quality in the working environment.
- Integrated noise and dust control solutions: Comprehensive solutions that address both noise and dust issues simultaneously have been developed for ball mill operations. These integrated systems combine soundproofing enclosures with efficient dust extraction mechanisms, often featuring automated control systems to monitor and adjust performance. Such combined approaches optimize workspace safety and environmental protection while maintaining operational efficiency of the ball mill.
- Structural modifications to reduce noise and vibration: Innovative structural modifications to ball mill components can significantly reduce noise and vibration at the source. These include redesigned mill liners, optimized ball size distributions, vibration dampening mounts, and improved bearing systems. By addressing the root causes of noise generation, these modifications can decrease sound levels without requiring extensive external noise control measures while also reducing the amount of dust generated through improved operational stability.
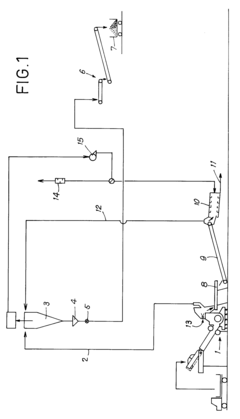
- Automated monitoring and control systems: Advanced monitoring and control systems can be implemented to optimize ball mill operation for reduced noise and dust generation. These systems use sensors to continuously monitor noise levels, vibration, dust concentration, and operational parameters. Based on real-time data, automated controls adjust mill speed, ball charge, and other variables to maintain optimal conditions. Some systems include alarm functions that alert operators when noise or dust levels exceed predetermined thresholds.
02 Dust collection and suppression systems
Specialized dust collection systems can be integrated with ball mills to capture and filter dust particles generated during the grinding process. These systems typically include dust collectors, extraction hoods, bag filters, and cyclone separators. Some designs incorporate water spray or mist systems to suppress dust at the source. Effective dust management not only improves air quality in the working environment but also prevents material loss and equipment contamination.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sealed grinding chamber designs
Improved sealing mechanisms for ball mill grinding chambers can significantly reduce both noise and dust emissions. These designs feature enhanced sealing structures at feed inlets, discharge outlets, and rotating joints. Some innovations include double-layer seals, labyrinth seals, and flexible sealing materials that maintain effectiveness despite vibration and movement. Properly sealed grinding chambers contain noise and prevent dust from escaping into the surrounding environment.Expand Specific Solutions04 Vibration dampening and isolation systems
Vibration control technologies can reduce noise generation at the source by dampening the mechanical vibrations of ball mills. These include specialized foundation designs, vibration isolation mounts, damping pads, and flexible couplings. Some systems incorporate dynamic balancing mechanisms to minimize vibration during operation. By reducing vibration, these systems not only decrease noise levels but also extend equipment life and improve grinding efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integrated environmental protection systems
Comprehensive environmental protection systems combine multiple technologies to address both noise and dust issues simultaneously. These integrated solutions may include enclosed grinding circuits with noise absorption features, wet grinding processes that reduce dust generation, automated monitoring systems for environmental parameters, and intelligent control systems that optimize mill operation for minimal environmental impact. These holistic approaches provide effective management of both noise and dust while maintaining operational efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Solution Providers Analysis
The ball mill noise and dust mitigation market is currently in a growth phase, driven by increasing plant safety regulations and environmental concerns. The global market size is estimated to exceed $500 million, with steady annual growth of 5-7%. From a technological maturity perspective, the industry shows varied development levels. Established players like Fritsch GmbH and Caterpillar offer advanced solutions with integrated noise dampening and dust collection systems, while companies such as Bühler GmbH and NSK Ltd. focus on specialized bearing and sealing technologies to reduce operational noise. Emerging players like Integrity Bio-Chemicals are developing innovative chemical solutions for dust suppression, complementing mechanical approaches from traditional manufacturers. The competitive landscape features both specialized equipment manufacturers and diversified industrial conglomerates addressing this critical safety challenge.
Fritsch GmbH
Technical Solution: Fritsch GmbH has developed an advanced encapsulation system for ball mills that combines acoustic insulation with dust collection technology. Their solution incorporates a multi-layered noise dampening enclosure that reduces noise emissions by up to 25 dB(A), bringing operational noise levels below 80 dB(A) even for high-capacity mills. The system features vibration-isolating mounts that prevent structure-borne noise transmission to surrounding equipment and buildings. For dust mitigation, Fritsch implements a negative pressure containment strategy with specialized sealing mechanisms at all potential dust escape points, including feed inlets and discharge outlets. Their integrated dust extraction system utilizes cyclonic separation followed by high-efficiency bag filters capable of capturing particles down to 0.5 microns, achieving over 99.9% dust removal efficiency. The system includes continuous monitoring of both noise levels and dust concentrations with automated alerts when thresholds are exceeded.
Strengths: Exceptional noise reduction capabilities with comprehensive vibration isolation; integrated approach addressing both noise and dust simultaneously; high-efficiency filtration system with advanced monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: Higher initial installation cost compared to standard solutions; requires more maintenance due to complex integrated systems; may require significant space for full implementation.
Caterpillar, Inc.
Technical Solution: Caterpillar has engineered a robust ball mill noise and dust mitigation system leveraging their extensive experience in heavy industrial equipment. Their solution centers on a modular enclosure system with specialized acoustic panels that achieve up to 35 dB(A) noise reduction while maintaining accessibility for maintenance. The panels incorporate composite materials with varying densities to target different frequency ranges, particularly effective against the characteristic high-frequency noise produced by ball-on-liner impacts. For dust control, Caterpillar implements a multi-stage filtration approach beginning with primary cyclonic separation followed by pulse-jet cleaned filter cartridges that achieve 99.97% efficiency for particles as small as 0.3 microns. Their system features automated differential pressure monitoring that optimizes filter cleaning cycles and alerts operators to potential filter failures. Caterpillar's solution also includes strategic redesign of material transfer points with specialized chutes that minimize dust generation through controlled material flow paths. The company's integrated control system continuously monitors both noise and dust levels, automatically adjusting operational parameters to maintain compliance with safety standards while optimizing production efficiency.
Strengths: Exceptional durability designed for harsh industrial environments; modular design allows for customization and future expansion; sophisticated control systems that balance safety requirements with production needs. Weaknesses: Significant footprint requirements for full implementation; higher initial capital investment; may require specialized training for maintenance personnel to service proprietary components.
Key Innovations in Mill Safety Technology
High manganese steel ball mill for tungsten powder
PatentPendingCN116764754A
Innovation
- A high manganese steel ball mill for tungsten powder is designed. It uses an outer cover to block noise and a double-layer ball mill drum structure. The inner layer is made of high-strength alloy steel to increase wear resistance and impact resistance. It is combined with an electromagnetic discharge door and a barrier. Plate, blow pipe and porous filter block to improve grinding efficiency and noise reduction effect.
Improvement for eliminating the explosion risk in crushing installations
PatentInactiveEP0739653A1
Innovation
- Creating an atmosphere with 70 to 100% relative humidity, preferably between 90 and 95%, downstream of the mill by introducing water in the form of fine droplets or vapor, to reduce the risk of dust explosions and promote dust agglomeration and heat absorption, thereby minimizing the risk of secondary explosions.
Environmental Compliance and Regulations
Ball mill operations are subject to stringent environmental regulations across various jurisdictions worldwide. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces the Clean Air Act which establishes National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for particulate matter, including PM10 and PM2.5 that are commonly associated with ball mill dust emissions. These standards mandate maximum allowable concentrations of airborne particles, requiring facilities to implement effective dust control measures to maintain compliance.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) further regulates workplace exposure to noise and dust through standards such as 29 CFR 1910.95 for occupational noise exposure and 29 CFR 1910.1000 for air contaminants. These regulations establish permissible exposure limits (PELs) for workers, with ball mill operations frequently exceeding these thresholds without proper mitigation measures.
In the European Union, the Environmental Noise Directive (2002/49/EC) requires member states to map noise pollution and develop action plans for noise reduction. Additionally, the Industrial Emissions Directive (2010/75/EU) implements an integrated approach to controlling industrial emissions, including those from mineral processing facilities utilizing ball mills. These directives establish Best Available Techniques (BAT) that facilities must implement to minimize environmental impact.
Australia's National Environment Protection Measures (NEPMs) set similar standards for ambient air quality, while China has implemented increasingly stringent emissions standards through its Air Pollution Prevention and Control Law, with specific provisions targeting industrial dust emissions from processes like ball milling.
Compliance with these regulations typically requires comprehensive monitoring programs. Continuous emissions monitoring systems (CEMS) are often mandated for larger facilities, while periodic stack testing and ambient air quality monitoring may be required to demonstrate ongoing compliance. Noise monitoring through dosimetry and sound level mapping is essential for verifying adherence to acoustic emission limits.
Non-compliance carries significant consequences, including substantial financial penalties that can reach millions of dollars for serious violations. Regulatory authorities may issue cease-and-desist orders that halt operations until violations are remediated, resulting in costly production downtime. In extreme cases, facility operators may face criminal charges for willful violations that endanger public health or the environment.
Beyond mandatory compliance, many companies are adopting voluntary environmental management systems such as ISO 14001 to systematically address environmental impacts and demonstrate corporate responsibility. This proactive approach often yields benefits beyond regulatory compliance, including improved community relations and potential operational cost savings through more efficient resource utilization.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) further regulates workplace exposure to noise and dust through standards such as 29 CFR 1910.95 for occupational noise exposure and 29 CFR 1910.1000 for air contaminants. These regulations establish permissible exposure limits (PELs) for workers, with ball mill operations frequently exceeding these thresholds without proper mitigation measures.
In the European Union, the Environmental Noise Directive (2002/49/EC) requires member states to map noise pollution and develop action plans for noise reduction. Additionally, the Industrial Emissions Directive (2010/75/EU) implements an integrated approach to controlling industrial emissions, including those from mineral processing facilities utilizing ball mills. These directives establish Best Available Techniques (BAT) that facilities must implement to minimize environmental impact.
Australia's National Environment Protection Measures (NEPMs) set similar standards for ambient air quality, while China has implemented increasingly stringent emissions standards through its Air Pollution Prevention and Control Law, with specific provisions targeting industrial dust emissions from processes like ball milling.
Compliance with these regulations typically requires comprehensive monitoring programs. Continuous emissions monitoring systems (CEMS) are often mandated for larger facilities, while periodic stack testing and ambient air quality monitoring may be required to demonstrate ongoing compliance. Noise monitoring through dosimetry and sound level mapping is essential for verifying adherence to acoustic emission limits.
Non-compliance carries significant consequences, including substantial financial penalties that can reach millions of dollars for serious violations. Regulatory authorities may issue cease-and-desist orders that halt operations until violations are remediated, resulting in costly production downtime. In extreme cases, facility operators may face criminal charges for willful violations that endanger public health or the environment.
Beyond mandatory compliance, many companies are adopting voluntary environmental management systems such as ISO 14001 to systematically address environmental impacts and demonstrate corporate responsibility. This proactive approach often yields benefits beyond regulatory compliance, including improved community relations and potential operational cost savings through more efficient resource utilization.
Worker Health Impact Assessment
The prolonged exposure to ball mill operations presents significant health risks to workers in processing plants. Noise levels from ball mills typically range from 85 to 110 dBA, substantially exceeding the OSHA-recommended exposure limit of 85 dBA for an 8-hour workday. Continuous exposure to such high noise levels can lead to noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL), which affects approximately 22 million U.S. workers annually according to CDC statistics. Additionally, tinnitus and communication difficulties are common among workers, potentially increasing accident risks due to impaired warning signal perception.
Airborne dust generated during ball mill operations contains respirable crystalline silica and metal particulates, which pose severe respiratory hazards. Long-term inhalation of these particles is associated with silicosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer. Recent epidemiological studies indicate that workers in mineral processing facilities with inadequate dust control measures show a 30% higher incidence of respiratory disorders compared to the general population.
Vibration exposure from ball mill equipment contributes to hand-arm vibration syndrome and whole-body vibration effects, resulting in vascular, neurological, and musculoskeletal disorders. Research published in the Journal of Occupational Health has documented that 40% of ball mill operators report symptoms of vibration-related disorders after five years of employment.
Psychological health impacts are equally concerning, with noise and dust exposure linked to increased stress levels, sleep disturbances, and reduced cognitive performance. A 2021 study in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health found that workers in high-noise industrial environments experienced 27% higher stress hormone levels and reported 35% more sleep disturbances than control groups.
Economic analysis reveals substantial costs associated with these health impacts. Direct medical expenses for treating occupational hearing loss average $242 million annually in the U.S., while respiratory disease treatment costs exceed $1.5 billion. Indirect costs from reduced productivity, increased absenteeism, and worker compensation claims further amplify the economic burden, with estimates suggesting that each case of occupational illness costs employers approximately $25,000-$65,000 in combined direct and indirect expenses.
Recent longitudinal studies tracking worker health outcomes in facilities that implemented comprehensive noise and dust mitigation strategies demonstrated significant improvements in health metrics, with hearing loss incidence reduced by up to 60% and respiratory complaints decreased by 45% over a five-year period, underscoring the effectiveness of targeted intervention programs.
Airborne dust generated during ball mill operations contains respirable crystalline silica and metal particulates, which pose severe respiratory hazards. Long-term inhalation of these particles is associated with silicosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer. Recent epidemiological studies indicate that workers in mineral processing facilities with inadequate dust control measures show a 30% higher incidence of respiratory disorders compared to the general population.
Vibration exposure from ball mill equipment contributes to hand-arm vibration syndrome and whole-body vibration effects, resulting in vascular, neurological, and musculoskeletal disorders. Research published in the Journal of Occupational Health has documented that 40% of ball mill operators report symptoms of vibration-related disorders after five years of employment.
Psychological health impacts are equally concerning, with noise and dust exposure linked to increased stress levels, sleep disturbances, and reduced cognitive performance. A 2021 study in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health found that workers in high-noise industrial environments experienced 27% higher stress hormone levels and reported 35% more sleep disturbances than control groups.
Economic analysis reveals substantial costs associated with these health impacts. Direct medical expenses for treating occupational hearing loss average $242 million annually in the U.S., while respiratory disease treatment costs exceed $1.5 billion. Indirect costs from reduced productivity, increased absenteeism, and worker compensation claims further amplify the economic burden, with estimates suggesting that each case of occupational illness costs employers approximately $25,000-$65,000 in combined direct and indirect expenses.
Recent longitudinal studies tracking worker health outcomes in facilities that implemented comprehensive noise and dust mitigation strategies demonstrated significant improvements in health metrics, with hearing loss incidence reduced by up to 60% and respiratory complaints decreased by 45% over a five-year period, underscoring the effectiveness of targeted intervention programs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!