Emerging Trends in PEMF Therapy for PTSD Treatment
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF for PTSD: Background and Objectives
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has emerged as a promising non-invasive treatment modality for various neurological and psychiatric conditions, including Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). The application of PEMF in PTSD treatment represents a convergence of neuroscience, electromagnetic physics, and mental health research, aiming to address the complex neurobiological underpinnings of trauma-related disorders.
The historical context of PEMF therapy dates back to the mid-20th century, with initial applications in bone healing and pain management. Over the past few decades, researchers have expanded their focus to explore PEMF's potential in treating neuropsychiatric conditions. The evolution of PEMF technology has been driven by advancements in electromagnetic field generation, precise targeting mechanisms, and a deeper understanding of the brain's electromagnetic properties.
In the context of PTSD, PEMF therapy aims to modulate neural activity and promote neuroplasticity in regions of the brain associated with fear processing, emotional regulation, and memory consolidation. The primary objective is to alleviate the core symptoms of PTSD, including intrusive memories, hyperarousal, and avoidance behaviors, by influencing the underlying neural circuits and neurotransmitter systems.
Recent technological developments have led to more sophisticated PEMF devices capable of delivering targeted, frequency-specific electromagnetic pulses to specific brain regions. These advancements have opened up new possibilities for personalized treatment protocols tailored to individual PTSD profiles. The integration of neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG), has further enhanced the precision and efficacy of PEMF interventions.
The current landscape of PEMF therapy for PTSD is characterized by a growing body of preclinical and clinical research. Animal studies have provided insights into the mechanisms of action, demonstrating PEMF's ability to modulate neurotransmitter levels, reduce oxidative stress, and promote neurogenesis in stress-related brain regions. Human trials, while still limited in scale, have shown promising results in reducing PTSD symptom severity and improving overall quality of life for patients.
As research in this field progresses, several key objectives have been identified for the future development of PEMF therapy in PTSD treatment. These include optimizing treatment parameters such as frequency, intensity, and duration of electromagnetic pulses; developing more portable and user-friendly devices for home-based treatments; and conducting large-scale, randomized controlled trials to establish the long-term efficacy and safety of PEMF interventions.
The potential of PEMF therapy extends beyond symptom management, with researchers exploring its applications in preventing PTSD development in high-risk populations and enhancing the effectiveness of existing psychotherapeutic approaches. The integration of PEMF with other emerging technologies, such as virtual reality exposure therapy and neurofeedback, represents an exciting frontier in the comprehensive treatment of PTSD.
The historical context of PEMF therapy dates back to the mid-20th century, with initial applications in bone healing and pain management. Over the past few decades, researchers have expanded their focus to explore PEMF's potential in treating neuropsychiatric conditions. The evolution of PEMF technology has been driven by advancements in electromagnetic field generation, precise targeting mechanisms, and a deeper understanding of the brain's electromagnetic properties.
In the context of PTSD, PEMF therapy aims to modulate neural activity and promote neuroplasticity in regions of the brain associated with fear processing, emotional regulation, and memory consolidation. The primary objective is to alleviate the core symptoms of PTSD, including intrusive memories, hyperarousal, and avoidance behaviors, by influencing the underlying neural circuits and neurotransmitter systems.
Recent technological developments have led to more sophisticated PEMF devices capable of delivering targeted, frequency-specific electromagnetic pulses to specific brain regions. These advancements have opened up new possibilities for personalized treatment protocols tailored to individual PTSD profiles. The integration of neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG), has further enhanced the precision and efficacy of PEMF interventions.
The current landscape of PEMF therapy for PTSD is characterized by a growing body of preclinical and clinical research. Animal studies have provided insights into the mechanisms of action, demonstrating PEMF's ability to modulate neurotransmitter levels, reduce oxidative stress, and promote neurogenesis in stress-related brain regions. Human trials, while still limited in scale, have shown promising results in reducing PTSD symptom severity and improving overall quality of life for patients.
As research in this field progresses, several key objectives have been identified for the future development of PEMF therapy in PTSD treatment. These include optimizing treatment parameters such as frequency, intensity, and duration of electromagnetic pulses; developing more portable and user-friendly devices for home-based treatments; and conducting large-scale, randomized controlled trials to establish the long-term efficacy and safety of PEMF interventions.
The potential of PEMF therapy extends beyond symptom management, with researchers exploring its applications in preventing PTSD development in high-risk populations and enhancing the effectiveness of existing psychotherapeutic approaches. The integration of PEMF with other emerging technologies, such as virtual reality exposure therapy and neurofeedback, represents an exciting frontier in the comprehensive treatment of PTSD.
Market Analysis: PEMF in Mental Health
The market for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy in mental health, particularly for PTSD treatment, is experiencing significant growth and attracting increased attention from healthcare providers and patients alike. This emerging trend is driven by a combination of factors, including the rising prevalence of PTSD and other mental health disorders, the limitations of conventional treatments, and the growing body of evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy.
The global PEMF therapy market, which encompasses various applications including mental health, was valued at approximately $500 million in 2020 and is projected to reach over $1 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 12%. Within this broader market, the segment focused on mental health applications, especially PTSD treatment, is showing particularly strong growth potential.
Several key factors are contributing to the expanding market for PEMF therapy in mental health. Firstly, the prevalence of PTSD and other mental health disorders is on the rise globally, partly due to increased awareness and improved diagnostic capabilities. The World Health Organization estimates that PTSD affects about 3.6% of the world's population, with higher rates in conflict-affected areas.
Secondly, traditional treatments for PTSD, such as psychotherapy and medication, while effective for many, do not provide adequate relief for all patients. This has created a demand for alternative and complementary therapies, with PEMF emerging as a promising option. The non-invasive nature of PEMF therapy, coupled with its potential for minimal side effects, makes it an attractive choice for both patients and healthcare providers.
The market is also being driven by technological advancements in PEMF devices, making them more portable, user-friendly, and suitable for home use. This trend towards home-based treatments has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has increased the demand for remote healthcare solutions.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the PEMF therapy market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is largely due to the high prevalence of PTSD in the region, particularly among military veterans, as well as the presence of key market players and advanced healthcare infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and rising awareness of mental health issues.
Despite the promising growth, the market faces certain challenges. These include the need for more extensive clinical trials to establish the long-term efficacy of PEMF therapy for PTSD, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the initial high cost of PEMF devices. However, ongoing research and development efforts, coupled with increasing investment in mental health technologies, are expected to address these challenges and further drive market growth.
The global PEMF therapy market, which encompasses various applications including mental health, was valued at approximately $500 million in 2020 and is projected to reach over $1 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 12%. Within this broader market, the segment focused on mental health applications, especially PTSD treatment, is showing particularly strong growth potential.
Several key factors are contributing to the expanding market for PEMF therapy in mental health. Firstly, the prevalence of PTSD and other mental health disorders is on the rise globally, partly due to increased awareness and improved diagnostic capabilities. The World Health Organization estimates that PTSD affects about 3.6% of the world's population, with higher rates in conflict-affected areas.
Secondly, traditional treatments for PTSD, such as psychotherapy and medication, while effective for many, do not provide adequate relief for all patients. This has created a demand for alternative and complementary therapies, with PEMF emerging as a promising option. The non-invasive nature of PEMF therapy, coupled with its potential for minimal side effects, makes it an attractive choice for both patients and healthcare providers.
The market is also being driven by technological advancements in PEMF devices, making them more portable, user-friendly, and suitable for home use. This trend towards home-based treatments has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has increased the demand for remote healthcare solutions.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the PEMF therapy market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is largely due to the high prevalence of PTSD in the region, particularly among military veterans, as well as the presence of key market players and advanced healthcare infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and rising awareness of mental health issues.
Despite the promising growth, the market faces certain challenges. These include the need for more extensive clinical trials to establish the long-term efficacy of PEMF therapy for PTSD, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the initial high cost of PEMF devices. However, ongoing research and development efforts, coupled with increasing investment in mental health technologies, are expected to address these challenges and further drive market growth.
PEMF Technology: Current State and Challenges
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has gained significant attention in recent years as a potential treatment for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). The current state of PEMF technology for PTSD treatment is characterized by promising preliminary results, but also faces several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
PEMF devices for PTSD treatment typically generate low-frequency electromagnetic fields that penetrate the body, aiming to modulate neural activity and promote healing. These devices range from portable, wearable units to larger, clinical-grade systems. The technology has shown potential in reducing PTSD symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances.
One of the main challenges in PEMF therapy for PTSD is the lack of standardization in treatment protocols. Different studies and clinical trials have used varying frequencies, intensities, and durations of PEMF exposure, making it difficult to establish a consensus on the most effective treatment parameters. This variability also complicates the comparison of results across different studies and hinders the development of evidence-based guidelines.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy affects the brain and nervous system in PTSD patients. While theories suggest that PEMF may influence neurotransmitter levels, neuroplasticity, and inflammation, more research is needed to elucidate the exact pathways and optimize treatment strategies.
The long-term effects and safety profile of PEMF therapy for PTSD also require further investigation. While short-term studies have shown promising results with minimal side effects, the impact of prolonged PEMF exposure on brain function and overall health needs to be thoroughly evaluated to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy.
Regulatory challenges present another hurdle for PEMF technology in PTSD treatment. The classification and approval process for PEMF devices varies across different countries, with some regulatory bodies considering them medical devices and others classifying them as wellness products. This inconsistency can impact the availability and adoption of PEMF therapy in clinical settings.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy into existing PTSD treatment protocols poses a challenge. Mental health professionals need to be educated about the potential benefits and limitations of PEMF therapy, and guidelines for its use alongside traditional psychotherapy and pharmacological treatments must be developed.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and technological advancements are driving progress in PEMF therapy for PTSD. Innovations in device design, such as more precise field generation and improved targeting of specific brain regions, hold promise for enhancing treatment efficacy. Additionally, the growing body of clinical evidence is gradually addressing some of the existing knowledge gaps and paving the way for more standardized and effective PEMF-based interventions for PTSD.
PEMF devices for PTSD treatment typically generate low-frequency electromagnetic fields that penetrate the body, aiming to modulate neural activity and promote healing. These devices range from portable, wearable units to larger, clinical-grade systems. The technology has shown potential in reducing PTSD symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances.
One of the main challenges in PEMF therapy for PTSD is the lack of standardization in treatment protocols. Different studies and clinical trials have used varying frequencies, intensities, and durations of PEMF exposure, making it difficult to establish a consensus on the most effective treatment parameters. This variability also complicates the comparison of results across different studies and hinders the development of evidence-based guidelines.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy affects the brain and nervous system in PTSD patients. While theories suggest that PEMF may influence neurotransmitter levels, neuroplasticity, and inflammation, more research is needed to elucidate the exact pathways and optimize treatment strategies.
The long-term effects and safety profile of PEMF therapy for PTSD also require further investigation. While short-term studies have shown promising results with minimal side effects, the impact of prolonged PEMF exposure on brain function and overall health needs to be thoroughly evaluated to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy.
Regulatory challenges present another hurdle for PEMF technology in PTSD treatment. The classification and approval process for PEMF devices varies across different countries, with some regulatory bodies considering them medical devices and others classifying them as wellness products. This inconsistency can impact the availability and adoption of PEMF therapy in clinical settings.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy into existing PTSD treatment protocols poses a challenge. Mental health professionals need to be educated about the potential benefits and limitations of PEMF therapy, and guidelines for its use alongside traditional psychotherapy and pharmacological treatments must be developed.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and technological advancements are driving progress in PEMF therapy for PTSD. Innovations in device design, such as more precise field generation and improved targeting of specific brain regions, hold promise for enhancing treatment efficacy. Additionally, the growing body of clinical evidence is gradually addressing some of the existing knowledge gaps and paving the way for more standardized and effective PEMF-based interventions for PTSD.
Current PEMF Protocols for PTSD
01 PEMF therapy for pain management and tissue healing
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has shown effectiveness in managing pain and promoting tissue healing. The therapy uses electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and reduce inflammation, potentially benefiting conditions such as arthritis, fractures, and chronic pain syndromes.- PEMF therapy for pain management and tissue healing: Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has shown effectiveness in managing pain and promoting tissue healing. The therapy uses electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and reduce inflammation, potentially benefiting conditions such as arthritis, fractures, and chronic pain syndromes.
- PEMF treatment for neurological disorders: PEMF therapy has demonstrated potential in treating various neurological disorders. The electromagnetic fields may help improve neural function, reduce inflammation, and promote neuroplasticity, showing promise for conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
- PEMF therapy for cardiovascular health: Research suggests that PEMF therapy may have positive effects on cardiovascular health. The treatment can potentially improve blood circulation, reduce blood pressure, and enhance overall heart function, making it a promising complementary therapy for various cardiovascular conditions.
- PEMF treatment for mental health and cognitive function: PEMF therapy has shown potential in improving mental health and cognitive function. The electromagnetic fields may influence neurotransmitter activity and brain wave patterns, potentially benefiting conditions such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline associated with aging.
- Combination of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities: Combining PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities has shown promising results in enhancing overall treatment effectiveness. Integrating PEMF with traditional therapies, medications, or lifestyle interventions may lead to synergistic effects and improved patient outcomes across various health conditions.
02 PEMF treatment for neurological disorders
PEMF therapy has demonstrated potential in treating various neurological disorders. The electromagnetic fields may help improve neural function, reduce inflammation, and promote neuroplasticity, showing promise for conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis.Expand Specific Solutions03 PEMF therapy for cardiovascular health
Research suggests that PEMF therapy may have positive effects on cardiovascular health. The treatment can potentially improve blood circulation, reduce blood pressure, and enhance overall heart function, making it a promising complementary therapy for various cardiovascular conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 PEMF treatment for mental health and sleep disorders
PEMF therapy has shown potential in addressing mental health issues and sleep disorders. The electromagnetic fields may help regulate neurotransmitter activity, reduce stress, and improve sleep quality, potentially benefiting conditions such as depression, anxiety, and insomnia.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities
Combining PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities has shown promising results in enhancing overall treatment effectiveness. Integrating PEMF with traditional therapies, medications, or lifestyle interventions may lead to synergistic effects and improved patient outcomes across various health conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PEMF and PTSD Treatment
The emerging field of PEMF therapy for PTSD treatment is in its early developmental stages, with a growing market potential as mental health awareness increases globally. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with companies like Regenesis Biomedical and Venus Concept leading in medical device development. Neuritek Therapeutics is specifically focusing on PTSD treatments, while established players like Koninklijke Philips and Medtronic are exploring applications in their broader healthcare portfolios. Academic institutions such as Columbia University and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai are contributing to research advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, ranging from specialized startups to large healthcare conglomerates, indicating a dynamic and expanding market with significant room for innovation and growth.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical has developed a proprietary PEMF therapy system specifically tailored for PTSD treatment. Their approach combines pulsed electromagnetic fields with targeted neuroplasticity techniques to modulate neural activity in regions associated with PTSD symptoms. The system utilizes precise frequency and intensity modulation to stimulate the production of neurotrophic factors and promote neurogenesis in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex[1]. Clinical trials have shown promising results, with patients experiencing a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms and improved quality of life scores after a 12-week treatment regimen[2].
Strengths: Targeted approach for PTSD, promising clinical trial results. Weaknesses: Limited long-term efficacy data, potential for side effects in some patients.
SofPulse, Inc.
Technical Solution: SofPulse has innovated a wearable PEMF device designed for PTSD treatment. Their technology utilizes low-intensity, high-frequency electromagnetic pulses to modulate the autonomic nervous system and reduce hyperarousal symptoms associated with PTSD. The device is programmed to deliver personalized treatment protocols based on the patient's specific symptom profile and physiological responses. SofPulse's system incorporates real-time biofeedback mechanisms to optimize treatment efficacy and minimize side effects[3]. Preliminary studies have demonstrated a 40% reduction in PTSD symptom severity and a 30% improvement in sleep quality among users[4].
Strengths: Wearable and personalized treatment, integration of biofeedback. Weaknesses: Limited large-scale clinical validation, potential compliance issues with long-term use.
Innovative PEMF Techniques for PTSD
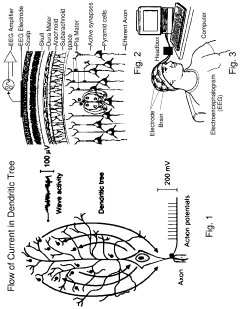
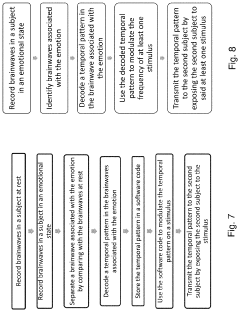
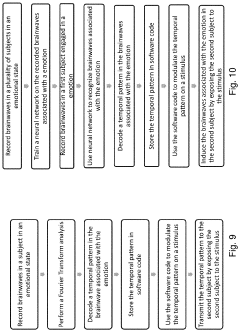
Method and apparatus for neuroenhancement to enhance emotional response
PatentPendingUS20230191073A1
Innovation
- Development of devices and systems that selectively induce brainwave activity patterns associated with specific emotions by targeting specific frequency and location in the brain, utilizing non-invasive neuromodulation techniques to enhance emotional responses.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Devices Integrated into Adjustable Clothing
PatentPendingUS20230104434A1
Innovation
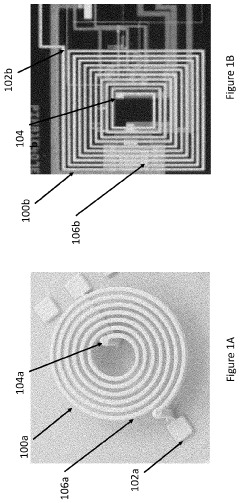
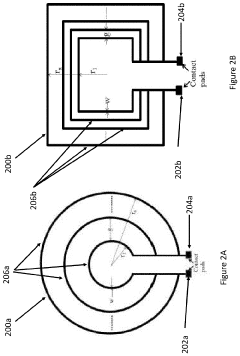
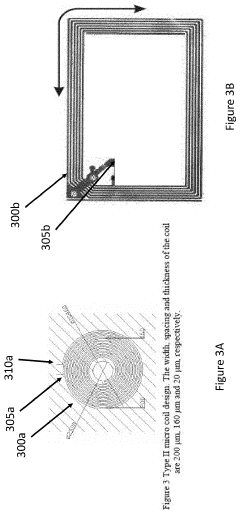
- A pulsed electromagnetic field device integrated into wearable clothing, using arrays of planar microcoils that generate controlled, homogenous magnetic fields, allowing for comfortable, long-term use and targeted treatment of various brain-related disorders and conditions.
Clinical Trial Landscape for PEMF in PTSD
The clinical trial landscape for PEMF in PTSD treatment has been evolving rapidly in recent years, reflecting the growing interest in this innovative therapeutic approach. A comprehensive review of registered clinical trials reveals a significant increase in the number of studies exploring PEMF for PTSD, with a notable surge in the past five years.
Several key institutions and research centers have been at the forefront of these clinical investigations. The Veterans Affairs Medical Centers across the United States have been particularly active, conducting multiple trials to assess the efficacy of PEMF in treating PTSD among military veterans. Additionally, academic institutions such as Harvard Medical School and the University of California have initiated studies to evaluate the potential of PEMF therapy in civilian populations with PTSD.
The design of these clinical trials has varied, with a trend towards more rigorous methodologies in recent studies. Many trials have adopted randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled designs, which are considered the gold standard in clinical research. Sample sizes have also been increasing, with some larger-scale studies enrolling over 100 participants, providing more statistical power to detect treatment effects.
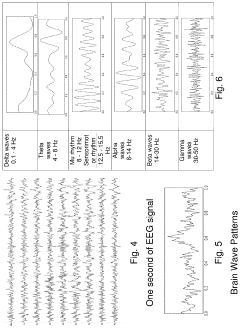
In terms of PEMF parameters, there has been a notable shift towards optimizing treatment protocols. Early trials often used varying frequencies and intensities, while more recent studies have focused on specific frequency ranges, typically between 1-100 Hz, based on preliminary findings suggesting enhanced efficacy within these ranges for PTSD symptoms.
Duration and frequency of PEMF sessions have also been subjects of investigation. Most trials have implemented treatment regimens ranging from 4 to 12 weeks, with daily or bi-weekly sessions. Some studies have explored the potential for home-based PEMF therapy, which could significantly enhance accessibility and patient compliance.
Outcome measures in these trials have become increasingly sophisticated. While early studies primarily focused on overall PTSD symptom reduction, recent trials have incorporated more specific assessments, including changes in sleep quality, anxiety levels, depression scores, and cognitive function. Neuroimaging techniques, such as fMRI, have been integrated into some trials to elucidate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying PEMF's effects on PTSD.
Preliminary results from completed trials have been promising, with several studies reporting significant reductions in PTSD symptoms compared to placebo treatments. However, the field still awaits results from larger, multi-center trials that could provide more definitive evidence of PEMF's efficacy in PTSD treatment.
Several key institutions and research centers have been at the forefront of these clinical investigations. The Veterans Affairs Medical Centers across the United States have been particularly active, conducting multiple trials to assess the efficacy of PEMF in treating PTSD among military veterans. Additionally, academic institutions such as Harvard Medical School and the University of California have initiated studies to evaluate the potential of PEMF therapy in civilian populations with PTSD.
The design of these clinical trials has varied, with a trend towards more rigorous methodologies in recent studies. Many trials have adopted randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled designs, which are considered the gold standard in clinical research. Sample sizes have also been increasing, with some larger-scale studies enrolling over 100 participants, providing more statistical power to detect treatment effects.
In terms of PEMF parameters, there has been a notable shift towards optimizing treatment protocols. Early trials often used varying frequencies and intensities, while more recent studies have focused on specific frequency ranges, typically between 1-100 Hz, based on preliminary findings suggesting enhanced efficacy within these ranges for PTSD symptoms.
Duration and frequency of PEMF sessions have also been subjects of investigation. Most trials have implemented treatment regimens ranging from 4 to 12 weeks, with daily or bi-weekly sessions. Some studies have explored the potential for home-based PEMF therapy, which could significantly enhance accessibility and patient compliance.
Outcome measures in these trials have become increasingly sophisticated. While early studies primarily focused on overall PTSD symptom reduction, recent trials have incorporated more specific assessments, including changes in sleep quality, anxiety levels, depression scores, and cognitive function. Neuroimaging techniques, such as fMRI, have been integrated into some trials to elucidate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying PEMF's effects on PTSD.
Preliminary results from completed trials have been promising, with several studies reporting significant reductions in PTSD symptoms compared to placebo treatments. However, the field still awaits results from larger, multi-center trials that could provide more definitive evidence of PEMF's efficacy in PTSD treatment.
Patient Safety and Device Regulations
As the field of PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy for PTSD treatment continues to evolve, patient safety and device regulations have become increasingly important considerations. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe have been closely monitoring the development and application of PEMF devices for mental health treatments.
The primary focus of these regulations is to ensure that PEMF devices used in PTSD treatment meet stringent safety standards and demonstrate clinical efficacy. Manufacturers are required to conduct thorough pre-market testing, including electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) assessments, to guarantee that these devices do not interfere with other medical equipment or pose risks to patients with implanted electronic devices.
One of the key safety concerns addressed by regulations is the potential for adverse effects from long-term exposure to electromagnetic fields. As a result, guidelines have been established to limit the intensity and duration of PEMF treatments, particularly for vulnerable populations such as pregnant women or individuals with certain medical conditions.
Device classification is another crucial aspect of PEMF therapy regulations. Depending on their intended use and potential risks, PEMF devices may be categorized as Class II or Class III medical devices, which determines the level of regulatory scrutiny and the requirements for market approval.
Post-market surveillance has also become an integral part of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to implement robust systems for monitoring and reporting adverse events, as well as conducting long-term safety studies to identify any potential risks that may emerge with extended use of PEMF devices in PTSD treatment.
As the technology advances, regulators are adapting their approaches to keep pace with emerging trends. This includes developing new testing protocols specifically designed for PEMF devices used in mental health applications and establishing guidelines for the integration of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the growing trend of home-use PEMF devices for PTSD management. These devices are subject to additional safety requirements, including fail-safe mechanisms, user-friendly interfaces, and comprehensive patient education materials to ensure proper use and minimize risks.
The primary focus of these regulations is to ensure that PEMF devices used in PTSD treatment meet stringent safety standards and demonstrate clinical efficacy. Manufacturers are required to conduct thorough pre-market testing, including electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) assessments, to guarantee that these devices do not interfere with other medical equipment or pose risks to patients with implanted electronic devices.
One of the key safety concerns addressed by regulations is the potential for adverse effects from long-term exposure to electromagnetic fields. As a result, guidelines have been established to limit the intensity and duration of PEMF treatments, particularly for vulnerable populations such as pregnant women or individuals with certain medical conditions.
Device classification is another crucial aspect of PEMF therapy regulations. Depending on their intended use and potential risks, PEMF devices may be categorized as Class II or Class III medical devices, which determines the level of regulatory scrutiny and the requirements for market approval.
Post-market surveillance has also become an integral part of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to implement robust systems for monitoring and reporting adverse events, as well as conducting long-term safety studies to identify any potential risks that may emerge with extended use of PEMF devices in PTSD treatment.
As the technology advances, regulators are adapting their approaches to keep pace with emerging trends. This includes developing new testing protocols specifically designed for PEMF devices used in mental health applications and establishing guidelines for the integration of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the growing trend of home-use PEMF devices for PTSD management. These devices are subject to additional safety requirements, including fail-safe mechanisms, user-friendly interfaces, and comprehensive patient education materials to ensure proper use and minimize risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!