Evaluating the Safety Protocols for PEMF Therapy Use
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Background and Objectives
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has emerged as a promising non-invasive treatment modality in recent years. This technology harnesses the power of electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and promote overall health. The evolution of PEMF therapy can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the past few decades.
The fundamental principle behind PEMF therapy lies in its ability to influence cellular behavior through the application of pulsed electromagnetic fields. These fields are designed to mimic the natural electromagnetic frequencies found in the human body, thereby enhancing cellular function and promoting healing processes. As research in this field has progressed, the potential applications of PEMF therapy have expanded considerably.
Initially, PEMF therapy was primarily used for bone healing and pain management. However, ongoing studies have revealed its potential in treating a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders, neurological issues, and even certain mental health conditions. This broadening scope of applications has led to increased interest from both the medical community and the general public.
The technological evolution of PEMF devices has been marked by improvements in precision, portability, and user-friendliness. Early PEMF machines were large, stationary units primarily found in clinical settings. Today, compact and portable PEMF devices are available for home use, making the therapy more accessible to a broader population.
As the adoption of PEMF therapy continues to grow, so does the need for comprehensive safety protocols. The primary objective in evaluating these safety protocols is to ensure that PEMF therapy can be administered effectively while minimizing any potential risks to users. This involves a thorough examination of various factors, including optimal frequency ranges, intensity levels, duration of exposure, and potential contraindications.
Another critical aspect of PEMF therapy development is the standardization of treatment protocols. As the technology advances, there is a growing need to establish consistent guidelines for its application across different medical conditions. This standardization aims to optimize treatment outcomes and facilitate more reliable research in the field.
Looking ahead, the future of PEMF therapy is likely to involve further refinement of the technology, with a focus on personalized treatment protocols. This may include the development of smart PEMF devices capable of adapting to individual user needs and real-time physiological feedback. Additionally, ongoing research is expected to uncover new potential applications for PEMF therapy, potentially expanding its role in preventive healthcare and wellness.
The fundamental principle behind PEMF therapy lies in its ability to influence cellular behavior through the application of pulsed electromagnetic fields. These fields are designed to mimic the natural electromagnetic frequencies found in the human body, thereby enhancing cellular function and promoting healing processes. As research in this field has progressed, the potential applications of PEMF therapy have expanded considerably.
Initially, PEMF therapy was primarily used for bone healing and pain management. However, ongoing studies have revealed its potential in treating a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal disorders, neurological issues, and even certain mental health conditions. This broadening scope of applications has led to increased interest from both the medical community and the general public.
The technological evolution of PEMF devices has been marked by improvements in precision, portability, and user-friendliness. Early PEMF machines were large, stationary units primarily found in clinical settings. Today, compact and portable PEMF devices are available for home use, making the therapy more accessible to a broader population.
As the adoption of PEMF therapy continues to grow, so does the need for comprehensive safety protocols. The primary objective in evaluating these safety protocols is to ensure that PEMF therapy can be administered effectively while minimizing any potential risks to users. This involves a thorough examination of various factors, including optimal frequency ranges, intensity levels, duration of exposure, and potential contraindications.
Another critical aspect of PEMF therapy development is the standardization of treatment protocols. As the technology advances, there is a growing need to establish consistent guidelines for its application across different medical conditions. This standardization aims to optimize treatment outcomes and facilitate more reliable research in the field.
Looking ahead, the future of PEMF therapy is likely to involve further refinement of the technology, with a focus on personalized treatment protocols. This may include the development of smart PEMF devices capable of adapting to individual user needs and real-time physiological feedback. Additionally, ongoing research is expected to uncover new potential applications for PEMF therapy, potentially expanding its role in preventive healthcare and wellness.
Market Analysis for PEMF Devices
The PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy device market has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of non-invasive treatment options and the rising prevalence of chronic conditions. The global PEMF device market was valued at approximately $500 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 12% during the forecast period.
The market demand for PEMF devices is primarily fueled by the growing aging population, rising incidence of musculoskeletal disorders, and increasing adoption of alternative therapies. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure.
Key market segments for PEMF devices include hospitals, clinics, and home healthcare settings. The home healthcare segment is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by the increasing trend of self-care and the convenience of portable PEMF devices. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of home-based therapies, further boosting this segment.
The market is characterized by the presence of both established players and new entrants. Major companies in the PEMF device market include OMI, Bemer Group, Earthpulse, and Swiss Bionic Solutions. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to gain a competitive edge.
Technological advancements in PEMF devices, such as improved portability, user-friendly interfaces, and integration with mobile applications, are driving market growth. There is also a growing trend towards personalized treatment protocols and the development of multi-functional devices that combine PEMF therapy with other modalities like heat therapy or light therapy.
Regulatory approvals and clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy are crucial factors influencing market growth. The FDA has cleared several PEMF devices for various indications, including pain management and bone healing. However, there is still a need for more comprehensive clinical studies to validate the long-term safety and effectiveness of PEMF therapy across different applications.
Challenges in the PEMF device market include the high cost of advanced devices, lack of awareness among healthcare professionals and patients, and varying regulatory standards across different regions. Despite these challenges, the market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by increasing research and development activities and the expanding applications of PEMF therapy in various medical fields.
The market demand for PEMF devices is primarily fueled by the growing aging population, rising incidence of musculoskeletal disorders, and increasing adoption of alternative therapies. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure.
Key market segments for PEMF devices include hospitals, clinics, and home healthcare settings. The home healthcare segment is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by the increasing trend of self-care and the convenience of portable PEMF devices. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of home-based therapies, further boosting this segment.
The market is characterized by the presence of both established players and new entrants. Major companies in the PEMF device market include OMI, Bemer Group, Earthpulse, and Swiss Bionic Solutions. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to gain a competitive edge.
Technological advancements in PEMF devices, such as improved portability, user-friendly interfaces, and integration with mobile applications, are driving market growth. There is also a growing trend towards personalized treatment protocols and the development of multi-functional devices that combine PEMF therapy with other modalities like heat therapy or light therapy.
Regulatory approvals and clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy are crucial factors influencing market growth. The FDA has cleared several PEMF devices for various indications, including pain management and bone healing. However, there is still a need for more comprehensive clinical studies to validate the long-term safety and effectiveness of PEMF therapy across different applications.
Challenges in the PEMF device market include the high cost of advanced devices, lack of awareness among healthcare professionals and patients, and varying regulatory standards across different regions. Despite these challenges, the market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by increasing research and development activities and the expanding applications of PEMF therapy in various medical fields.
Current Safety Challenges in PEMF Therapy
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic benefits. However, as with any medical treatment, safety remains a paramount concern. The current safety challenges in PEMF therapy stem from various factors, including the lack of standardized protocols, potential interactions with other medical devices, and the need for more comprehensive long-term studies.
One of the primary safety challenges is the absence of universally accepted guidelines for PEMF therapy application. Different devices operate at varying frequencies and intensities, making it difficult to establish a one-size-fits-all safety protocol. This variability can lead to inconsistent treatment outcomes and potential safety risks if not properly managed. Additionally, the optimal dosage and duration of PEMF therapy sessions remain subjects of ongoing research, further complicating the development of standardized safety measures.
Another significant challenge is the potential interference of PEMF devices with other medical implants or electronic devices. Patients with pacemakers, defibrillators, or other implanted electronic devices may be at risk of electromagnetic interference, which could compromise the functionality of these life-saving devices. This necessitates careful screening and monitoring of patients undergoing PEMF therapy, as well as the development of PEMF devices with built-in safety features to minimize such risks.
The long-term effects of PEMF therapy on human health are not yet fully understood, presenting another safety challenge. While short-term studies have shown promising results with minimal side effects, the potential cumulative impact of prolonged exposure to pulsed electromagnetic fields requires further investigation. This gap in knowledge underscores the need for extensive longitudinal studies to assess the long-term safety profile of PEMF therapy across various patient populations and treatment regimens.
Regulatory oversight and quality control of PEMF devices also pose significant challenges. The rapid proliferation of PEMF devices in the market, including those intended for home use, has outpaced the development of comprehensive regulatory frameworks. This situation raises concerns about the safety and efficacy of some commercially available devices, particularly those that may not have undergone rigorous testing or received proper certification.
Furthermore, the diverse range of PEMF applications, from pain management to bone healing and beyond, complicates the establishment of unified safety standards. Each application may require specific safety considerations, taking into account factors such as the target tissue, treatment duration, and patient characteristics. This complexity necessitates a multifaceted approach to safety protocol development, involving collaboration between medical professionals, researchers, and regulatory bodies.
Addressing these safety challenges requires a concerted effort from the scientific community, healthcare providers, and regulatory agencies. Ongoing research, improved standardization of PEMF devices and protocols, and enhanced patient education are crucial steps toward ensuring the safe and effective use of PEMF therapy. As the field continues to evolve, maintaining a balance between innovation and safety will be essential in realizing the full potential of this promising therapeutic modality.
One of the primary safety challenges is the absence of universally accepted guidelines for PEMF therapy application. Different devices operate at varying frequencies and intensities, making it difficult to establish a one-size-fits-all safety protocol. This variability can lead to inconsistent treatment outcomes and potential safety risks if not properly managed. Additionally, the optimal dosage and duration of PEMF therapy sessions remain subjects of ongoing research, further complicating the development of standardized safety measures.
Another significant challenge is the potential interference of PEMF devices with other medical implants or electronic devices. Patients with pacemakers, defibrillators, or other implanted electronic devices may be at risk of electromagnetic interference, which could compromise the functionality of these life-saving devices. This necessitates careful screening and monitoring of patients undergoing PEMF therapy, as well as the development of PEMF devices with built-in safety features to minimize such risks.
The long-term effects of PEMF therapy on human health are not yet fully understood, presenting another safety challenge. While short-term studies have shown promising results with minimal side effects, the potential cumulative impact of prolonged exposure to pulsed electromagnetic fields requires further investigation. This gap in knowledge underscores the need for extensive longitudinal studies to assess the long-term safety profile of PEMF therapy across various patient populations and treatment regimens.
Regulatory oversight and quality control of PEMF devices also pose significant challenges. The rapid proliferation of PEMF devices in the market, including those intended for home use, has outpaced the development of comprehensive regulatory frameworks. This situation raises concerns about the safety and efficacy of some commercially available devices, particularly those that may not have undergone rigorous testing or received proper certification.
Furthermore, the diverse range of PEMF applications, from pain management to bone healing and beyond, complicates the establishment of unified safety standards. Each application may require specific safety considerations, taking into account factors such as the target tissue, treatment duration, and patient characteristics. This complexity necessitates a multifaceted approach to safety protocol development, involving collaboration between medical professionals, researchers, and regulatory bodies.
Addressing these safety challenges requires a concerted effort from the scientific community, healthcare providers, and regulatory agencies. Ongoing research, improved standardization of PEMF devices and protocols, and enhanced patient education are crucial steps toward ensuring the safe and effective use of PEMF therapy. As the field continues to evolve, maintaining a balance between innovation and safety will be essential in realizing the full potential of this promising therapeutic modality.
Existing PEMF Safety Protocols
01 Electromagnetic field intensity control
Safety protocols for PEMF therapy involve controlling the intensity of electromagnetic fields. This includes adjusting the field strength, frequency, and duration of exposure to ensure therapeutic effects while minimizing potential risks. Devices may incorporate automatic intensity regulation mechanisms to maintain safe levels throughout treatment sessions.- Electromagnetic field intensity control: Safety protocols for PEMF therapy involve controlling the intensity of electromagnetic fields. This includes adjusting the field strength, frequency, and duration of exposure to ensure therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential risks. Devices may incorporate automatic intensity regulation mechanisms or allow manual adjustments based on individual patient needs and treatment protocols.
- Treatment duration and frequency management: PEMF therapy safety protocols include guidelines for managing treatment duration and frequency. This involves setting appropriate session lengths and intervals between treatments to prevent overexposure. Automated timers and treatment scheduling features may be incorporated into devices to ensure adherence to safe usage parameters.
- Patient-specific customization and monitoring: Safety protocols emphasize the importance of customizing PEMF therapy based on individual patient characteristics and medical conditions. This includes initial assessments, ongoing monitoring of patient responses, and adjusting treatment parameters accordingly. Advanced systems may incorporate real-time monitoring and feedback mechanisms to ensure patient safety throughout the therapy.
- Device design and shielding: PEMF therapy safety protocols extend to the design of treatment devices, including proper shielding to contain electromagnetic fields and prevent unintended exposure. This involves using appropriate materials and construction techniques to ensure that the electromagnetic fields are directed only to the intended treatment areas, minimizing potential risks to non-target tissues or nearby individuals.
- Contraindications and precautions: Safety protocols for PEMF therapy include clear guidelines on contraindications and precautions. This involves identifying conditions or situations where PEMF therapy may be unsuitable or require special considerations, such as for patients with implanted electronic devices, pregnancy, or certain medical conditions. Protocols may include screening procedures and safety checklists to ensure appropriate patient selection and risk mitigation.
02 Treatment duration and frequency management
PEMF therapy safety protocols include guidelines for managing treatment duration and frequency. This involves setting appropriate session lengths and intervals between treatments to prevent overexposure. Automated timers and treatment scheduling features may be incorporated into devices to ensure adherence to safe usage parameters.Expand Specific Solutions03 Patient-specific customization and monitoring
Safety protocols emphasize the importance of customizing PEMF therapy based on individual patient characteristics and conditions. This includes assessing medical history, contraindications, and real-time monitoring of patient responses during treatment. Advanced systems may incorporate biofeedback mechanisms to adjust therapy parameters dynamically for optimal safety and efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Device design and shielding
PEMF therapy safety protocols extend to the design of treatment devices, incorporating proper shielding and containment of electromagnetic fields. This includes using materials and configurations that minimize unintended exposure to non-target areas and reduce electromagnetic interference with other medical devices or electronic equipment in the vicinity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Compliance with regulatory standards
Safety protocols for PEMF therapy devices and treatments must adhere to regulatory standards and guidelines set by health authorities. This involves rigorous testing, documentation of safety measures, and ongoing compliance monitoring. Protocols may include regular device calibration, maintenance procedures, and software updates to ensure continued safety and effectiveness in clinical use.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Device Manufacturers
The competitive landscape for evaluating safety protocols in PEMF therapy is evolving rapidly, reflecting the technology's growing adoption and market potential. The industry is in a transitional phase, moving from early adoption to mainstream acceptance, with a projected market size reaching several billion dollars by 2025. Technological maturity varies among key players, with companies like Regenesis Biomedical and Venus Concept leading in innovation and product development. Established tech giants such as Huawei and Samsung are also entering the space, leveraging their R&D capabilities to enhance safety standards. Academic institutions like Xidian University and Southeast University contribute significantly to research, while emerging players like SofPulse and Galvanize Therapeutics focus on niche applications, driving competition and safety advancements in specific therapeutic areas.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical has developed advanced PEMF therapy devices with integrated safety protocols. Their technology utilizes precise electromagnetic field generation and control systems to ensure optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing potential risks. The company's devices incorporate real-time monitoring of field strength and exposure duration, automatically adjusting parameters to stay within established safety limits[1]. Additionally, they have implemented a multi-layered safety approach, including hardware failsafes, software controls, and user-friendly interfaces that guide proper device usage[3]. Regenesis has also conducted extensive clinical trials to validate the safety and efficacy of their PEMF protocols across various medical applications[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive safety features, clinically validated protocols, and user-friendly design. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to advanced technology, may require more frequent calibration and maintenance.
Venus Concept Ltd.
Technical Solution: Venus Concept has developed a proprietary PEMF technology platform with integrated safety measures. Their devices utilize a pulsed electromagnetic field with specific frequencies and intensities tailored for different therapeutic applications. The company's safety protocols include automatic shut-off mechanisms if the device detects any abnormalities in field generation or patient response[2]. Venus Concept has also implemented a smart sensor system that continuously monitors tissue temperature and impedance during treatment, adjusting the PEMF output in real-time to prevent overexposure[4]. Furthermore, they have developed a comprehensive training program for clinicians to ensure proper device usage and patient safety[6].
Strengths: Advanced real-time monitoring and adjustment capabilities, extensive clinician training program. Weaknesses: May be limited to specific therapeutic applications, potential for higher initial investment for healthcare providers.
Critical PEMF Safety Innovations
Treatment of conditions susceptible to pulsed electromagnetic field therapy
PatentActiveUS20170354830A1
Innovation
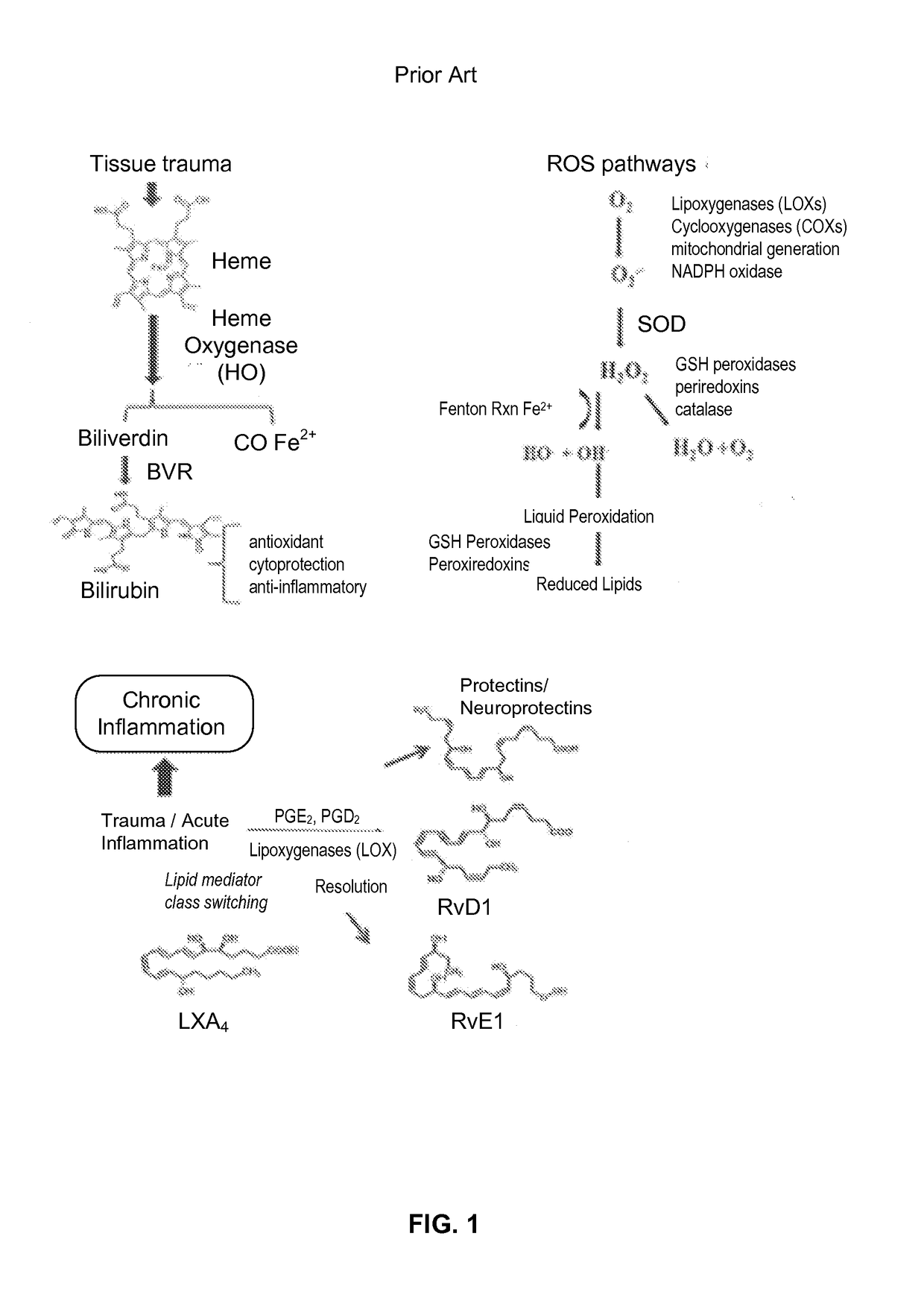
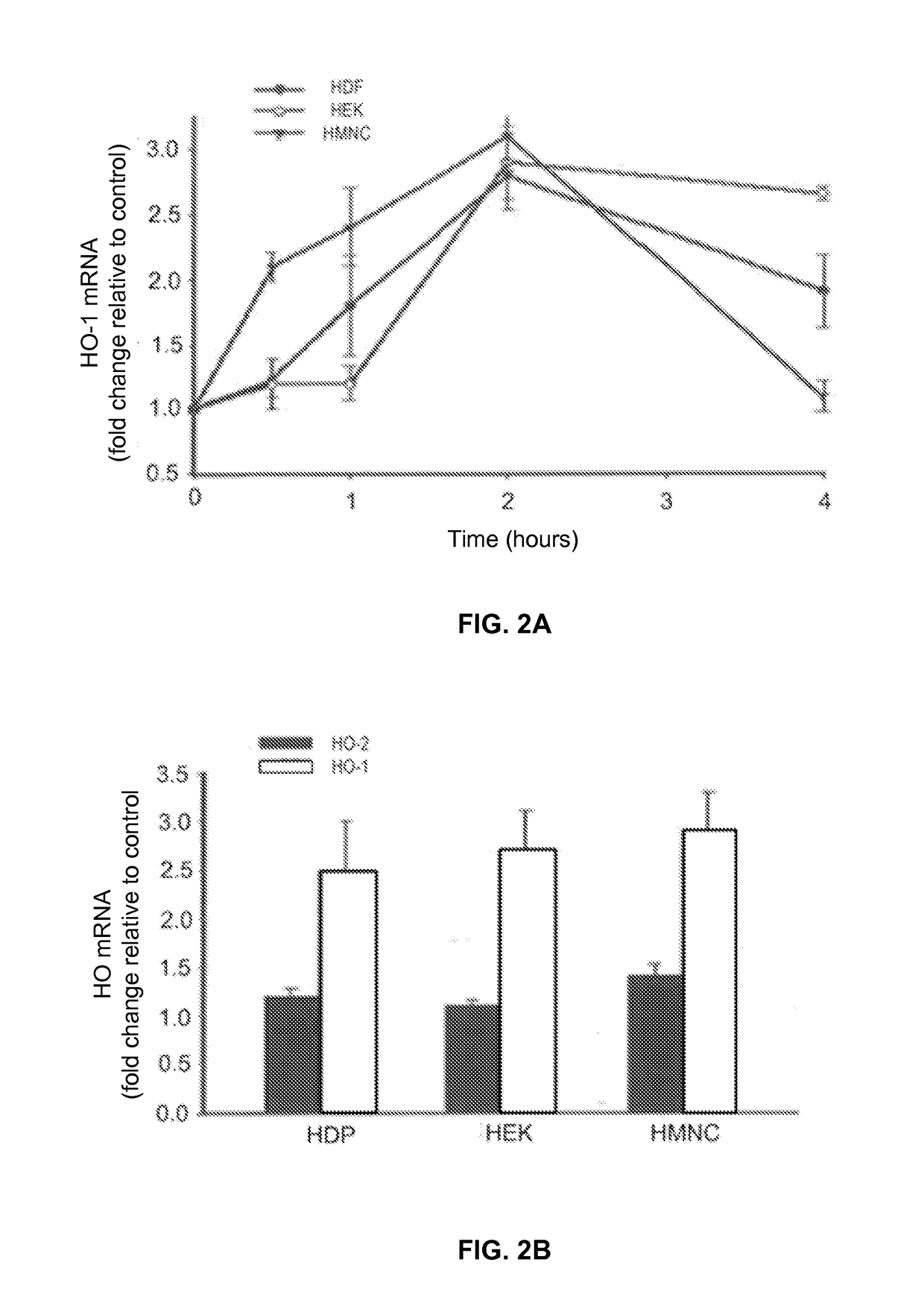
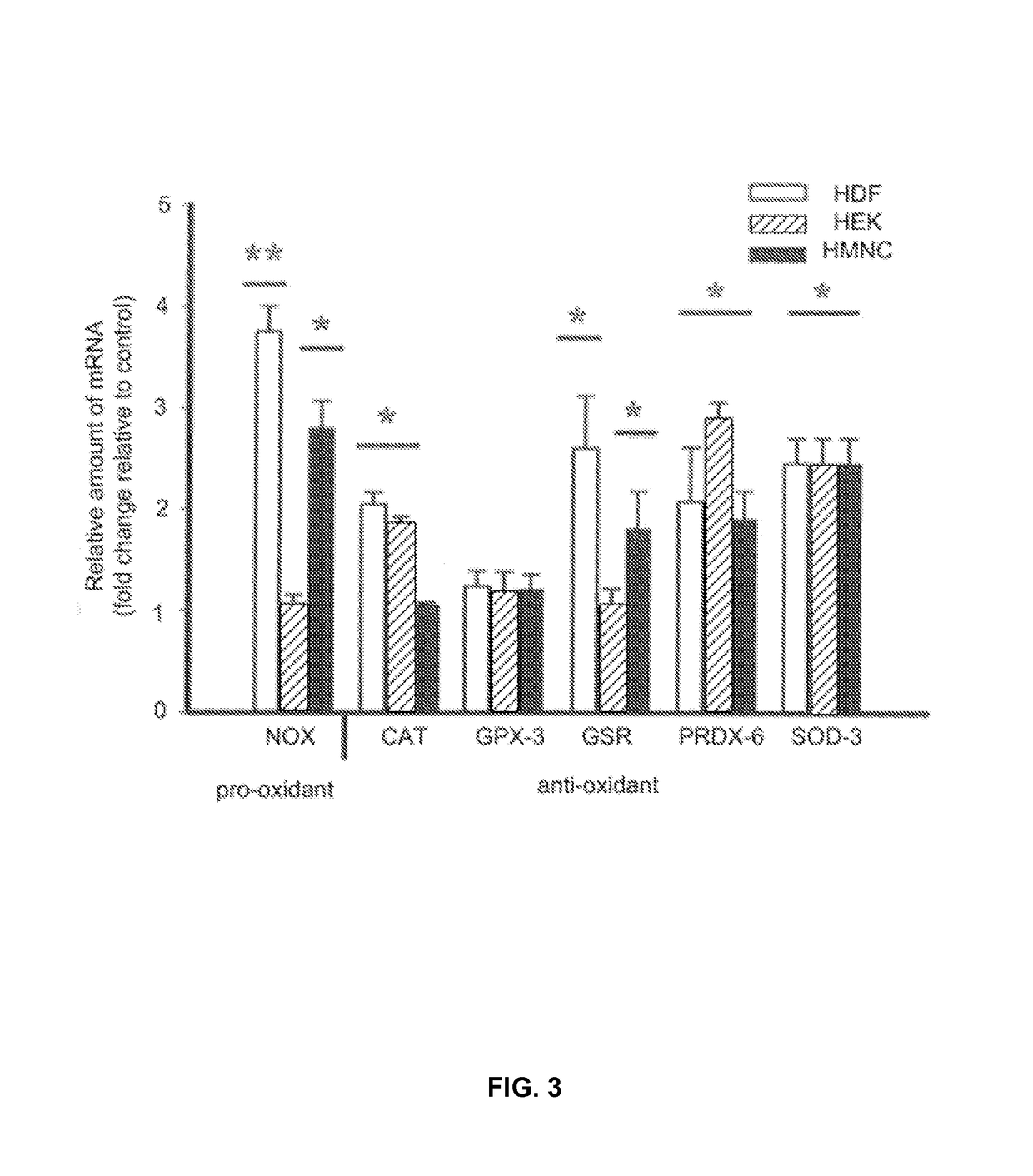
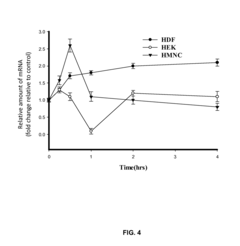
- PEMF therapy is administered to modulate gene expression associated with inflammation pathways, including heme oxygenase, antioxidant enzymes, lipid mediator biosynthesis, and cytokines, using specific parameters such as electric field strength, pulse rate, and duration to produce measurable clinical effects on pain, nerve function, and wound healing.
Pulsed electromagnetic field method of treating soft tissue wounds
PatentActiveUS7520849B1
Innovation
- The use of a pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) with specific signal characteristics, including repetitive pulse bursts and unipolar magnetic field pulses, is applied externally to the wound area without direct contact, using a treatment coil and signal generator to promote wound healing.
Regulatory Framework for PEMF Devices
The regulatory framework for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) devices is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety and efficacy of PEMF therapy. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in overseeing the regulation of PEMF devices. These devices are typically classified as Class II medical devices, which require a 510(k) premarket notification submission to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device.
The FDA's regulatory approach for PEMF devices focuses on several key areas. First, manufacturers must provide evidence of the device's safety and effectiveness through clinical studies or substantial equivalence to an already approved device. This includes demonstrating that the electromagnetic fields generated by the device fall within acceptable safety limits and do not pose undue risks to users.
Additionally, the FDA requires PEMF device manufacturers to implement and maintain quality management systems that comply with the Quality System Regulation (QSR). This ensures that devices are consistently manufactured to meet the required specifications and quality standards. Manufacturers must also adhere to labeling requirements, providing clear instructions for use, contraindications, and potential side effects.
In the European Union, PEMF devices are regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR requires manufacturers to obtain CE marking for their devices, which involves a conformity assessment process to demonstrate compliance with safety and performance requirements. This process often includes clinical evaluation and risk management procedures.
Internationally, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established standards for electromagnetic compatibility and safety of medical electrical equipment, which are often adopted or referenced by national regulatory bodies. These standards, such as IEC 60601-1 for general safety requirements and IEC 60601-1-2 for electromagnetic compatibility, provide a framework for ensuring the safety of PEMF devices across different jurisdictions.
Regulatory bodies also emphasize post-market surveillance as a crucial component of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to monitor the performance and safety of their devices after they have been placed on the market, reporting any adverse events or malfunctions to the appropriate authorities. This ongoing vigilance helps identify and address any unforeseen safety issues that may arise during real-world use of PEMF devices.
As the field of PEMF therapy continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt to address new technologies and applications. This may include more specific guidelines for different types of PEMF devices or updated safety protocols based on emerging scientific evidence. Staying informed about these regulatory developments is essential for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and researchers working in the field of PEMF therapy.
The FDA's regulatory approach for PEMF devices focuses on several key areas. First, manufacturers must provide evidence of the device's safety and effectiveness through clinical studies or substantial equivalence to an already approved device. This includes demonstrating that the electromagnetic fields generated by the device fall within acceptable safety limits and do not pose undue risks to users.
Additionally, the FDA requires PEMF device manufacturers to implement and maintain quality management systems that comply with the Quality System Regulation (QSR). This ensures that devices are consistently manufactured to meet the required specifications and quality standards. Manufacturers must also adhere to labeling requirements, providing clear instructions for use, contraindications, and potential side effects.
In the European Union, PEMF devices are regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR requires manufacturers to obtain CE marking for their devices, which involves a conformity assessment process to demonstrate compliance with safety and performance requirements. This process often includes clinical evaluation and risk management procedures.
Internationally, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has established standards for electromagnetic compatibility and safety of medical electrical equipment, which are often adopted or referenced by national regulatory bodies. These standards, such as IEC 60601-1 for general safety requirements and IEC 60601-1-2 for electromagnetic compatibility, provide a framework for ensuring the safety of PEMF devices across different jurisdictions.
Regulatory bodies also emphasize post-market surveillance as a crucial component of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to monitor the performance and safety of their devices after they have been placed on the market, reporting any adverse events or malfunctions to the appropriate authorities. This ongoing vigilance helps identify and address any unforeseen safety issues that may arise during real-world use of PEMF devices.
As the field of PEMF therapy continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt to address new technologies and applications. This may include more specific guidelines for different types of PEMF devices or updated safety protocols based on emerging scientific evidence. Staying informed about these regulatory developments is essential for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and researchers working in the field of PEMF therapy.
Long-term Health Effects of PEMF Exposure
The long-term health effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy exposure remain a subject of ongoing research and debate within the scientific community. While short-term studies have shown promising results for various medical conditions, the extended impact of regular PEMF exposure requires further investigation.
One primary concern is the potential for cellular changes over time. Some studies suggest that prolonged exposure to electromagnetic fields may alter cell membrane permeability and affect ion channels. These changes could potentially lead to modifications in cellular function and communication. However, the extent and significance of these alterations in the context of long-term health outcomes are not yet fully understood.
Another area of focus is the impact on the immune system. Some research indicates that PEMF therapy may modulate immune responses, potentially enhancing the body's ability to fight infections and reduce inflammation. However, the long-term consequences of this immune modulation, particularly in individuals with autoimmune disorders or compromised immune systems, require more extensive longitudinal studies.
Cardiovascular effects are also under scrutiny. While short-term PEMF exposure has shown benefits in improving circulation and reducing blood pressure, the long-term impact on heart health and vascular function needs further exploration. Researchers are particularly interested in understanding whether prolonged PEMF use could lead to any adverse effects on cardiac rhythms or blood vessel integrity.
Neurological implications are another critical aspect of long-term PEMF exposure. Some studies suggest potential neuroprotective effects, while others raise questions about the impact on neurotransmitter balance and cognitive function over extended periods. The interaction between PEMF and the central nervous system, especially in terms of sleep patterns and mood regulation, requires more comprehensive research.
Bone and joint health is an area where PEMF therapy has shown significant short-term benefits, particularly in fracture healing and osteoporosis management. However, the long-term effects on bone density, cartilage integrity, and overall skeletal health need further investigation to ensure that prolonged use does not lead to unintended consequences.
Hormonal balance is another concern in long-term PEMF exposure. Some studies have indicated potential effects on endocrine function, particularly on the production and regulation of melatonin and cortisol. The implications of these hormonal changes over extended periods, especially on sleep-wake cycles and stress responses, warrant careful examination.
In conclusion, while PEMF therapy shows promise in various short-term applications, the long-term health effects of sustained exposure remain an area requiring extensive research. Comprehensive longitudinal studies are necessary to fully understand the potential risks and benefits associated with prolonged PEMF use, ensuring its safe and effective application in medical treatments.
One primary concern is the potential for cellular changes over time. Some studies suggest that prolonged exposure to electromagnetic fields may alter cell membrane permeability and affect ion channels. These changes could potentially lead to modifications in cellular function and communication. However, the extent and significance of these alterations in the context of long-term health outcomes are not yet fully understood.
Another area of focus is the impact on the immune system. Some research indicates that PEMF therapy may modulate immune responses, potentially enhancing the body's ability to fight infections and reduce inflammation. However, the long-term consequences of this immune modulation, particularly in individuals with autoimmune disorders or compromised immune systems, require more extensive longitudinal studies.
Cardiovascular effects are also under scrutiny. While short-term PEMF exposure has shown benefits in improving circulation and reducing blood pressure, the long-term impact on heart health and vascular function needs further exploration. Researchers are particularly interested in understanding whether prolonged PEMF use could lead to any adverse effects on cardiac rhythms or blood vessel integrity.
Neurological implications are another critical aspect of long-term PEMF exposure. Some studies suggest potential neuroprotective effects, while others raise questions about the impact on neurotransmitter balance and cognitive function over extended periods. The interaction between PEMF and the central nervous system, especially in terms of sleep patterns and mood regulation, requires more comprehensive research.
Bone and joint health is an area where PEMF therapy has shown significant short-term benefits, particularly in fracture healing and osteoporosis management. However, the long-term effects on bone density, cartilage integrity, and overall skeletal health need further investigation to ensure that prolonged use does not lead to unintended consequences.
Hormonal balance is another concern in long-term PEMF exposure. Some studies have indicated potential effects on endocrine function, particularly on the production and regulation of melatonin and cortisol. The implications of these hormonal changes over extended periods, especially on sleep-wake cycles and stress responses, warrant careful examination.
In conclusion, while PEMF therapy shows promise in various short-term applications, the long-term health effects of sustained exposure remain an area requiring extensive research. Comprehensive longitudinal studies are necessary to fully understand the potential risks and benefits associated with prolonged PEMF use, ensuring its safe and effective application in medical treatments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!