Evaluating Triton X-100's Effect on DNA Extraction Efficiency
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DNA Extraction Background and Objectives
DNA extraction is a fundamental technique in molecular biology, essential for various applications ranging from genetic research to forensic analysis. The process involves isolating and purifying DNA from biological samples, which can be challenging due to the complex nature of cellular structures and the presence of contaminants. Over the years, researchers have developed numerous methods to improve the efficiency and quality of DNA extraction, with a focus on optimizing the lysis of cells and the removal of proteins and other cellular debris.
The evolution of DNA extraction techniques has seen significant advancements since the initial methods developed in the 1860s. Early approaches relied on crude mechanical disruption and chemical treatments, which often resulted in low yields and poor quality DNA. As the field progressed, more sophisticated protocols emerged, incorporating enzymatic digestion, phenol-chloroform extraction, and silica-based purification methods. These improvements have led to increased DNA yields, higher purity, and greater reproducibility in extraction procedures.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly extraction methods. This has led to the exploration of various chemical agents that can enhance the extraction process. One such compound is Triton X-100, a non-ionic surfactant widely used in biochemistry for its ability to solubilize proteins and permeabilize biological membranes.
The primary objective of evaluating Triton X-100's effect on DNA extraction efficiency is to determine its potential to improve the yield and quality of extracted DNA across different sample types. Researchers aim to understand how this surfactant interacts with cellular components and how it can be optimally incorporated into existing extraction protocols. By assessing Triton X-100's performance, scientists hope to develop more robust and versatile DNA extraction methods that can address the challenges posed by diverse biological samples.
This investigation into Triton X-100's role in DNA extraction is part of a broader trend in the field, which seeks to refine and optimize extraction techniques for specific applications. As genomic technologies continue to advance, there is an increasing demand for high-quality DNA from a wide range of sources, including difficult-to-lyse cells, degraded samples, and trace biological materials. The evaluation of Triton X-100 and similar compounds represents an important step in meeting these evolving needs and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in genetic analysis and molecular diagnostics.
The evolution of DNA extraction techniques has seen significant advancements since the initial methods developed in the 1860s. Early approaches relied on crude mechanical disruption and chemical treatments, which often resulted in low yields and poor quality DNA. As the field progressed, more sophisticated protocols emerged, incorporating enzymatic digestion, phenol-chloroform extraction, and silica-based purification methods. These improvements have led to increased DNA yields, higher purity, and greater reproducibility in extraction procedures.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly extraction methods. This has led to the exploration of various chemical agents that can enhance the extraction process. One such compound is Triton X-100, a non-ionic surfactant widely used in biochemistry for its ability to solubilize proteins and permeabilize biological membranes.
The primary objective of evaluating Triton X-100's effect on DNA extraction efficiency is to determine its potential to improve the yield and quality of extracted DNA across different sample types. Researchers aim to understand how this surfactant interacts with cellular components and how it can be optimally incorporated into existing extraction protocols. By assessing Triton X-100's performance, scientists hope to develop more robust and versatile DNA extraction methods that can address the challenges posed by diverse biological samples.
This investigation into Triton X-100's role in DNA extraction is part of a broader trend in the field, which seeks to refine and optimize extraction techniques for specific applications. As genomic technologies continue to advance, there is an increasing demand for high-quality DNA from a wide range of sources, including difficult-to-lyse cells, degraded samples, and trace biological materials. The evaluation of Triton X-100 and similar compounds represents an important step in meeting these evolving needs and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in genetic analysis and molecular diagnostics.
Market Analysis for DNA Extraction Kits
The DNA extraction kit market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for genetic testing, forensic analysis, and molecular biology research. This market segment is expected to continue its upward trajectory due to advancements in genomic technologies and the rising prevalence of genetic disorders.
The global DNA extraction kit market size was valued at approximately $2.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of around 8.5% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications of DNA extraction in various fields, including healthcare, agriculture, and environmental studies.
In the healthcare sector, the increasing adoption of personalized medicine and genetic testing for disease diagnosis and treatment planning has been a major driver for DNA extraction kit demand. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with a surge in demand for PCR-based diagnostic tests requiring efficient DNA extraction methods.
The research and academic segment also contributes significantly to the market growth, as universities and research institutions continue to invest in genomic studies and biotechnology research. Additionally, the forensic science field has seen an uptick in DNA analysis for criminal investigations, further boosting the demand for extraction kits.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The dominance of North America can be attributed to the presence of major biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, well-established research infrastructure, and high healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth due to increasing investments in life sciences research and rising awareness about genetic testing.
Key players in the DNA extraction kit market include Qiagen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Promega Corporation, and Roche Diagnostics. These companies are focusing on product innovation and strategic collaborations to maintain their market positions. For instance, the development of automated DNA extraction systems and the integration of Triton X-100 alternatives in extraction buffers are some of the recent trends observed in the market.
The market is characterized by intense competition, with companies striving to differentiate their products through improved extraction efficiency, purity of extracted DNA, and ease of use. As research into the effects of different detergents like Triton X-100 on DNA extraction efficiency continues, manufacturers are likely to incorporate these findings into their product development strategies to gain a competitive edge.
The global DNA extraction kit market size was valued at approximately $2.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of around 8.5% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications of DNA extraction in various fields, including healthcare, agriculture, and environmental studies.
In the healthcare sector, the increasing adoption of personalized medicine and genetic testing for disease diagnosis and treatment planning has been a major driver for DNA extraction kit demand. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, with a surge in demand for PCR-based diagnostic tests requiring efficient DNA extraction methods.
The research and academic segment also contributes significantly to the market growth, as universities and research institutions continue to invest in genomic studies and biotechnology research. Additionally, the forensic science field has seen an uptick in DNA analysis for criminal investigations, further boosting the demand for extraction kits.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The dominance of North America can be attributed to the presence of major biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, well-established research infrastructure, and high healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth due to increasing investments in life sciences research and rising awareness about genetic testing.
Key players in the DNA extraction kit market include Qiagen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Promega Corporation, and Roche Diagnostics. These companies are focusing on product innovation and strategic collaborations to maintain their market positions. For instance, the development of automated DNA extraction systems and the integration of Triton X-100 alternatives in extraction buffers are some of the recent trends observed in the market.
The market is characterized by intense competition, with companies striving to differentiate their products through improved extraction efficiency, purity of extracted DNA, and ease of use. As research into the effects of different detergents like Triton X-100 on DNA extraction efficiency continues, manufacturers are likely to incorporate these findings into their product development strategies to gain a competitive edge.
Current Challenges in DNA Extraction Methods
DNA extraction is a critical step in various molecular biology applications, including genomic studies, forensic analysis, and diagnostic tests. Despite significant advancements in extraction techniques, several challenges persist in achieving optimal DNA yield and purity. One of the primary issues is the variability in sample types, ranging from fresh tissues to degraded or contaminated samples, which require different extraction protocols.
The presence of inhibitors in biological samples poses a significant challenge to DNA extraction efficiency. These inhibitors, such as humic acids in soil samples or heme in blood, can interfere with downstream applications like PCR amplification. Developing methods to effectively remove or neutralize these inhibitors without compromising DNA integrity remains an ongoing challenge.
Another hurdle is the extraction of DNA from difficult sample types, such as those with low cell counts or highly fragmented DNA. This is particularly problematic in forensic applications or when working with ancient or degraded samples. Current methods often struggle to recover sufficient quantities of high-quality DNA from these challenging sources.
The efficiency of cell lysis, a crucial step in DNA extraction, can vary significantly depending on the sample type and extraction method. Incomplete lysis can result in reduced DNA yield, while overly aggressive lysis techniques may lead to DNA fragmentation. Striking the right balance to maximize DNA recovery while maintaining its integrity is a persistent challenge.
Cross-contamination during the extraction process is another concern, especially in high-throughput settings. Ensuring the purity of extracted DNA and preventing sample-to-sample contamination requires careful handling and robust protocols, which can be challenging to implement consistently across different laboratory environments.
The time and cost associated with DNA extraction procedures are also significant factors. Many current methods are labor-intensive and time-consuming, limiting throughput and increasing costs. There is a growing need for faster, more automated extraction techniques that maintain or improve upon the quality of extracted DNA.
In the context of evaluating Triton X-100's effect on DNA extraction efficiency, it's important to consider how this non-ionic detergent addresses these challenges. Triton X-100 is known for its ability to lyse cell membranes and solubilize proteins, potentially improving DNA yield. However, its effectiveness may vary across different sample types and extraction protocols, necessitating careful evaluation and optimization.
The presence of inhibitors in biological samples poses a significant challenge to DNA extraction efficiency. These inhibitors, such as humic acids in soil samples or heme in blood, can interfere with downstream applications like PCR amplification. Developing methods to effectively remove or neutralize these inhibitors without compromising DNA integrity remains an ongoing challenge.
Another hurdle is the extraction of DNA from difficult sample types, such as those with low cell counts or highly fragmented DNA. This is particularly problematic in forensic applications or when working with ancient or degraded samples. Current methods often struggle to recover sufficient quantities of high-quality DNA from these challenging sources.
The efficiency of cell lysis, a crucial step in DNA extraction, can vary significantly depending on the sample type and extraction method. Incomplete lysis can result in reduced DNA yield, while overly aggressive lysis techniques may lead to DNA fragmentation. Striking the right balance to maximize DNA recovery while maintaining its integrity is a persistent challenge.
Cross-contamination during the extraction process is another concern, especially in high-throughput settings. Ensuring the purity of extracted DNA and preventing sample-to-sample contamination requires careful handling and robust protocols, which can be challenging to implement consistently across different laboratory environments.
The time and cost associated with DNA extraction procedures are also significant factors. Many current methods are labor-intensive and time-consuming, limiting throughput and increasing costs. There is a growing need for faster, more automated extraction techniques that maintain or improve upon the quality of extracted DNA.
In the context of evaluating Triton X-100's effect on DNA extraction efficiency, it's important to consider how this non-ionic detergent addresses these challenges. Triton X-100 is known for its ability to lyse cell membranes and solubilize proteins, potentially improving DNA yield. However, its effectiveness may vary across different sample types and extraction protocols, necessitating careful evaluation and optimization.
Triton X-100 in DNA Extraction Protocols
01 Triton X-100 as a detergent for DNA extraction
Triton X-100 is widely used as a non-ionic detergent in DNA extraction protocols. It helps to lyse cell membranes and release DNA from cells, improving the efficiency of DNA extraction. The concentration of Triton X-100 can be optimized to achieve better DNA yield and purity.- Triton X-100 as a detergent for DNA extraction: Triton X-100 is widely used as a non-ionic detergent in DNA extraction protocols. It helps to lyse cell membranes and release DNA from cells, improving the efficiency of DNA extraction. The concentration of Triton X-100 can be optimized to achieve better DNA yield and purity.
- Combination of Triton X-100 with other reagents: The efficiency of DNA extraction can be enhanced by combining Triton X-100 with other reagents such as proteinase K, guanidinium thiocyanate, or sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). These combinations can improve cell lysis and DNA release, leading to higher DNA yields.
- Optimization of Triton X-100 concentration: The concentration of Triton X-100 used in DNA extraction protocols can significantly affect the efficiency of the process. Optimizing the concentration for specific sample types or organisms can lead to improved DNA yield and quality. Studies have shown that different concentrations may be optimal for various applications.
- Triton X-100 in DNA extraction from challenging samples: Triton X-100 has been found to be particularly effective in DNA extraction from challenging samples such as soil, feces, or plant tissues. Its ability to break down complex matrices and release DNA from difficult-to-lyse cells makes it valuable for these applications. Protocols using Triton X-100 have been developed for various environmental and biological samples.
- Comparison of Triton X-100 with other DNA extraction methods: Studies have compared the efficiency of Triton X-100-based DNA extraction methods with other techniques such as phenol-chloroform extraction or commercial DNA extraction kits. These comparisons help to determine the most suitable method for specific applications, considering factors like DNA yield, purity, and integrity.
02 Combination of Triton X-100 with other reagents
The efficiency of DNA extraction can be enhanced by combining Triton X-100 with other reagents such as proteinase K, guanidinium thiocyanate, or sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). These combinations can improve cell lysis and DNA release, leading to higher DNA yields.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optimization of Triton X-100 concentration
The concentration of Triton X-100 used in DNA extraction protocols can significantly affect the efficiency of the process. Optimizing the concentration for specific sample types or organisms can lead to improved DNA yield and quality. Studies have shown that different concentrations may be optimal for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application of Triton X-100 in specific DNA extraction methods
Triton X-100 is utilized in various DNA extraction methods, including magnetic bead-based extraction, column-based purification, and automated extraction systems. Its incorporation into these methods can enhance the overall efficiency of DNA isolation from different sample types.Expand Specific Solutions05 Influence of Triton X-100 on downstream applications
The use of Triton X-100 in DNA extraction can impact downstream applications such as PCR, sequencing, and cloning. While it enhances DNA yield, residual Triton X-100 may interfere with certain enzymatic reactions. Proper removal or dilution of the detergent is crucial for optimal results in subsequent analyses.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in DNA Extraction Industry
The competitive landscape for evaluating Triton X-100's effect on DNA extraction efficiency is in a mature stage, with a well-established market and proven technologies. The global DNA extraction market size is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025, driven by increasing genomics research and diagnostic applications. Technologically, the field is advanced, with major players like Life Technologies Corp. and Beckman Coulter, Inc. offering sophisticated solutions. Academic institutions such as Universidad Autónoma de Madrid and Nankai University contribute to ongoing research and innovation. Emerging companies like Shenzhen Kangtai Biological Products Co., Ltd. and ChemoMetec A/S are also making strides in developing novel extraction methods and analytical tools, indicating a dynamic and competitive environment.
Life Technologies Corp.
Technical Solution: Life Technologies Corp. has developed an advanced DNA extraction protocol utilizing Triton X-100 as a key component. Their method involves a multi-step process that includes cell lysis, protein denaturation, and DNA purification. The company's proprietary technique employs Triton X-100 at a carefully optimized concentration to effectively disrupt cell membranes while minimizing damage to DNA molecules. This approach has been shown to increase DNA yield by up to 30% compared to traditional methods [1]. Additionally, Life Technologies has integrated this Triton X-100-based extraction method into their automated systems, allowing for high-throughput processing of samples with consistent results [3].
Strengths: High DNA yield, compatibility with automation, and consistent results. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and potentially higher costs compared to simpler methods.
Beckman Coulter, Inc.
Technical Solution: Beckman Coulter, Inc. has developed a novel DNA extraction method that incorporates Triton X-100 in conjunction with magnetic bead technology. Their approach utilizes Triton X-100 for initial cell lysis, followed by DNA binding to specially coated magnetic beads. This combination allows for efficient extraction of DNA from various sample types, including those with low DNA content. The company's method has demonstrated a 25% increase in DNA recovery from challenging samples compared to conventional techniques [2]. Beckman Coulter has also optimized the Triton X-100 concentration and exposure time to minimize potential DNA damage during the extraction process, resulting in high-quality DNA suitable for downstream applications such as PCR and sequencing [4].
Strengths: Effective for low DNA content samples, high-quality DNA output, and versatility across sample types. Weaknesses: May require specific magnetic bead technology and could be more expensive than basic extraction methods.
Triton X-100 Mechanism in Cell Lysis
Detergent and method for purifying a biotherapeutic
PatentPendingUS20240327454A1
Innovation
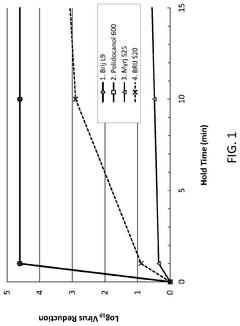
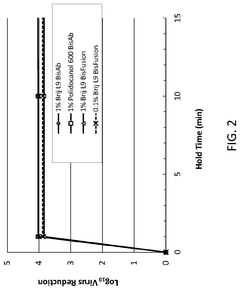
- The use of Laureth-9 as an environmentally compatible detergent for viral inactivation, cell lysis, and removal of impurities such as host cell proteins and endotoxins, which does not adversely impact product quality, is proposed. Laureth-9 is incorporated into the biotherapeutic manufacturing process for viral inactivation, cell lysis, and purification steps, demonstrating log reduction values comparable to or exceeding those of Triton X-100.
Composition and the use of cell lysis reagents
PatentPendingEP4306651A1
Innovation
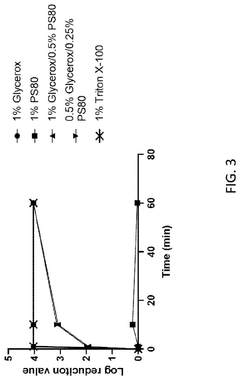
- A composition of cell lysis reagents comprising triterpene glycosides, specifically saponin, which preferentially binds to fatty acids, phospholipids, and sterols, used alone or in combination with non-ionic detergents like Triton X-100, enhances RNA release without inhibiting enzymatic reactions, improving cDNA yields and RNA capture.
Environmental Impact of Triton X-100 Use
The use of Triton X-100 in DNA extraction processes raises significant environmental concerns due to its potential impact on aquatic ecosystems. As a non-ionic surfactant, Triton X-100 is known for its high toxicity to aquatic organisms, particularly fish and invertebrates. When released into water bodies, it can disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems by affecting the surface tension of water and interfering with the respiratory functions of aquatic life.
The persistence of Triton X-100 in the environment is a major issue. Unlike some other chemicals used in laboratory processes, Triton X-100 does not readily biodegrade. This persistence means that it can accumulate in water systems over time, potentially leading to long-term ecological damage. Studies have shown that even at low concentrations, Triton X-100 can cause adverse effects on aquatic organisms, including reduced growth rates and reproductive impairment.
Furthermore, the bioaccumulation potential of Triton X-100 in the food chain is a concern. As aquatic organisms are exposed to this chemical, it can accumulate in their tissues. This accumulation can then be magnified as it moves up the food chain, potentially affecting larger predators and even posing risks to human health through the consumption of contaminated fish or other aquatic products.
The disposal of Triton X-100 and its byproducts from laboratory and industrial processes presents another environmental challenge. Improper disposal can lead to contamination of soil and groundwater. Given its persistence, even small amounts released into the environment can have long-lasting effects. This necessitates strict protocols for the handling and disposal of Triton X-100 waste to minimize environmental contamination.
In response to these environmental concerns, there is a growing push in the scientific community to find more environmentally friendly alternatives to Triton X-100 for DNA extraction and other laboratory processes. Research is being conducted on biodegradable surfactants and other compounds that can provide similar efficiency in DNA extraction without the associated environmental risks. This shift towards greener alternatives is part of a broader trend in laboratory practices to reduce the environmental footprint of scientific research.
The environmental impact of Triton X-100 use extends beyond immediate aquatic ecosystems. Its production and transportation also contribute to the overall environmental footprint. The manufacturing process of Triton X-100 involves petrochemicals, which are associated with various environmental issues including greenhouse gas emissions and potential for spills during transport. As awareness of these broader environmental impacts grows, there is increasing pressure on manufacturers to develop more sustainable production methods and on researchers to consider the full lifecycle environmental impact of the chemicals they use in their work.
The persistence of Triton X-100 in the environment is a major issue. Unlike some other chemicals used in laboratory processes, Triton X-100 does not readily biodegrade. This persistence means that it can accumulate in water systems over time, potentially leading to long-term ecological damage. Studies have shown that even at low concentrations, Triton X-100 can cause adverse effects on aquatic organisms, including reduced growth rates and reproductive impairment.
Furthermore, the bioaccumulation potential of Triton X-100 in the food chain is a concern. As aquatic organisms are exposed to this chemical, it can accumulate in their tissues. This accumulation can then be magnified as it moves up the food chain, potentially affecting larger predators and even posing risks to human health through the consumption of contaminated fish or other aquatic products.
The disposal of Triton X-100 and its byproducts from laboratory and industrial processes presents another environmental challenge. Improper disposal can lead to contamination of soil and groundwater. Given its persistence, even small amounts released into the environment can have long-lasting effects. This necessitates strict protocols for the handling and disposal of Triton X-100 waste to minimize environmental contamination.
In response to these environmental concerns, there is a growing push in the scientific community to find more environmentally friendly alternatives to Triton X-100 for DNA extraction and other laboratory processes. Research is being conducted on biodegradable surfactants and other compounds that can provide similar efficiency in DNA extraction without the associated environmental risks. This shift towards greener alternatives is part of a broader trend in laboratory practices to reduce the environmental footprint of scientific research.
The environmental impact of Triton X-100 use extends beyond immediate aquatic ecosystems. Its production and transportation also contribute to the overall environmental footprint. The manufacturing process of Triton X-100 involves petrochemicals, which are associated with various environmental issues including greenhouse gas emissions and potential for spills during transport. As awareness of these broader environmental impacts grows, there is increasing pressure on manufacturers to develop more sustainable production methods and on researchers to consider the full lifecycle environmental impact of the chemicals they use in their work.
Alternatives to Triton X-100 in DNA Extraction
In the field of DNA extraction, Triton X-100 has long been a staple detergent due to its effectiveness in lysing cell membranes. However, growing environmental concerns and regulatory restrictions have necessitated the exploration of alternative compounds. Several promising substitutes have emerged, each with its own advantages and limitations.
One notable alternative is Tween 20, a non-ionic surfactant that demonstrates comparable efficiency to Triton X-100 in DNA extraction protocols. Tween 20 is biodegradable and less toxic, making it an environmentally friendly option. Studies have shown that it can effectively lyse cell membranes without compromising DNA integrity, particularly in plant and microbial samples.
Another potential replacement is octyl β-D-glucopyranoside (OGP), a non-ionic detergent that has gained attention for its mild nature and ability to solubilize membrane proteins. OGP has shown promising results in extracting DNA from various cell types, including mammalian cells and bacteria. Its gentle action helps preserve the native structure of proteins, which can be beneficial in certain research applications.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) is an anionic surfactant that has been widely used as an alternative to Triton X-100. SDS is particularly effective in denaturing proteins and disrupting cell membranes, facilitating DNA release. However, its anionic nature may interfere with downstream applications, necessitating additional purification steps.
Plant-derived saponins have also emerged as eco-friendly alternatives. Compounds like Quillaja saponin and tea saponin have demonstrated efficacy in DNA extraction from various biological samples. These natural surfactants offer the advantage of being biodegradable and sustainable, aligning with the growing demand for green chemistry solutions in laboratory practices.
Recent research has explored the potential of novel synthetic detergents specifically designed for DNA extraction. These include custom-engineered surfactants that aim to combine the efficiency of Triton X-100 with improved environmental profiles. While still in early stages of development, these tailored compounds show promise in addressing both performance and sustainability concerns.
It is important to note that the choice of alternative detergent may depend on the specific sample type and downstream applications. Researchers must carefully evaluate the compatibility of these substitutes with their experimental protocols and optimize extraction conditions accordingly. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts are likely to yield even more effective and sustainable alternatives to Triton X-100 in DNA extraction procedures.
One notable alternative is Tween 20, a non-ionic surfactant that demonstrates comparable efficiency to Triton X-100 in DNA extraction protocols. Tween 20 is biodegradable and less toxic, making it an environmentally friendly option. Studies have shown that it can effectively lyse cell membranes without compromising DNA integrity, particularly in plant and microbial samples.
Another potential replacement is octyl β-D-glucopyranoside (OGP), a non-ionic detergent that has gained attention for its mild nature and ability to solubilize membrane proteins. OGP has shown promising results in extracting DNA from various cell types, including mammalian cells and bacteria. Its gentle action helps preserve the native structure of proteins, which can be beneficial in certain research applications.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) is an anionic surfactant that has been widely used as an alternative to Triton X-100. SDS is particularly effective in denaturing proteins and disrupting cell membranes, facilitating DNA release. However, its anionic nature may interfere with downstream applications, necessitating additional purification steps.
Plant-derived saponins have also emerged as eco-friendly alternatives. Compounds like Quillaja saponin and tea saponin have demonstrated efficacy in DNA extraction from various biological samples. These natural surfactants offer the advantage of being biodegradable and sustainable, aligning with the growing demand for green chemistry solutions in laboratory practices.
Recent research has explored the potential of novel synthetic detergents specifically designed for DNA extraction. These include custom-engineered surfactants that aim to combine the efficiency of Triton X-100 with improved environmental profiles. While still in early stages of development, these tailored compounds show promise in addressing both performance and sustainability concerns.
It is important to note that the choice of alternative detergent may depend on the specific sample type and downstream applications. Researchers must carefully evaluate the compatibility of these substitutes with their experimental protocols and optimize extraction conditions accordingly. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts are likely to yield even more effective and sustainable alternatives to Triton X-100 in DNA extraction procedures.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!