Exploring Future Trends in PEMF Therapy Technology
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing, PEMF therapy has expanded its applications to various medical fields, including pain management, tissue repair, and neurological disorders. The technology's progression can be traced through several key phases, each marked by advancements in device design, treatment protocols, and scientific understanding.
In the 1970s, PEMF therapy gained FDA approval for treating non-union fractures, marking its entry into mainstream medical practice. This period saw the development of large, stationary devices primarily used in clinical settings. The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a shift towards more portable PEMF devices, enabling home-based treatments and expanding the therapy's accessibility.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era in PEMF technology, characterized by miniaturization and increased precision. Advances in electronics and materials science allowed for the creation of smaller, more powerful devices capable of delivering targeted electromagnetic pulses. This period also saw the integration of digital controls and programmable settings, enabling more personalized treatment protocols.
Recent years have seen a surge in research exploring the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying PEMF therapy's effects. Studies have revealed its impact on ion channels, cell signaling pathways, and gene expression, providing a scientific basis for its therapeutic benefits. This deeper understanding has led to the development of more sophisticated PEMF devices tailored to specific physiological targets.
The current landscape of PEMF therapy is marked by a diverse range of devices, from full-body mats to localized applicators. Advanced features such as multiple frequency settings, variable intensities, and pre-programmed treatment cycles have become standard. Additionally, the integration of PEMF technology with other therapeutic modalities, such as infrared therapy and biofeedback systems, has opened new avenues for comprehensive health management.
Looking towards the future, PEMF therapy is poised for further innovation. Emerging trends include the development of smart, AI-driven devices capable of adapting treatment parameters in real-time based on physiological feedback. Wearable PEMF technology is also gaining traction, promising continuous, low-intensity treatments for chronic conditions. Furthermore, research into novel applications, such as cognitive enhancement and cellular regeneration, suggests an expanding role for PEMF therapy in preventive and regenerative medicine.
In the 1970s, PEMF therapy gained FDA approval for treating non-union fractures, marking its entry into mainstream medical practice. This period saw the development of large, stationary devices primarily used in clinical settings. The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a shift towards more portable PEMF devices, enabling home-based treatments and expanding the therapy's accessibility.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era in PEMF technology, characterized by miniaturization and increased precision. Advances in electronics and materials science allowed for the creation of smaller, more powerful devices capable of delivering targeted electromagnetic pulses. This period also saw the integration of digital controls and programmable settings, enabling more personalized treatment protocols.
Recent years have seen a surge in research exploring the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying PEMF therapy's effects. Studies have revealed its impact on ion channels, cell signaling pathways, and gene expression, providing a scientific basis for its therapeutic benefits. This deeper understanding has led to the development of more sophisticated PEMF devices tailored to specific physiological targets.
The current landscape of PEMF therapy is marked by a diverse range of devices, from full-body mats to localized applicators. Advanced features such as multiple frequency settings, variable intensities, and pre-programmed treatment cycles have become standard. Additionally, the integration of PEMF technology with other therapeutic modalities, such as infrared therapy and biofeedback systems, has opened new avenues for comprehensive health management.
Looking towards the future, PEMF therapy is poised for further innovation. Emerging trends include the development of smart, AI-driven devices capable of adapting treatment parameters in real-time based on physiological feedback. Wearable PEMF technology is also gaining traction, promising continuous, low-intensity treatments for chronic conditions. Furthermore, research into novel applications, such as cognitive enhancement and cellular regeneration, suggests an expanding role for PEMF therapy in preventive and regenerative medicine.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy technology has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of its potential health benefits and a growing emphasis on non-invasive treatment options. The global PEMF therapy devices market is expected to experience significant expansion, with projections indicating substantial growth over the next decade.
One of the primary factors fueling market demand is the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and musculoskeletal disorders. As populations age and lifestyles become increasingly sedentary, conditions such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and chronic pain are becoming more common. PEMF therapy offers a promising alternative or complementary treatment for these conditions, attracting both patients and healthcare providers seeking effective, non-pharmacological interventions.
The sports medicine and rehabilitation sectors have also shown considerable interest in PEMF technology. Professional athletes and sports teams are adopting PEMF devices for faster recovery and improved performance, while physiotherapists and rehabilitation centers are incorporating the technology into their treatment protocols. This trend is expected to continue, further driving market growth.
Another significant factor contributing to market demand is the increasing preference for home-based healthcare solutions. Portable PEMF devices allow patients to receive treatment in the comfort of their homes, aligning with the broader trend of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. This aspect has become particularly relevant in the wake of the global pandemic, which has accelerated the adoption of home-based medical technologies.
The wellness and preventive healthcare markets are also emerging as key drivers of PEMF therapy demand. Consumers are becoming more proactive about their health, seeking technologies that can enhance overall well-being and potentially prevent future health issues. PEMF therapy's purported benefits in improving sleep quality, reducing stress, and enhancing cellular function appeal to this growing segment of health-conscious individuals.
Geographically, North America currently leads the PEMF therapy market, followed by Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years. This is attributed to increasing healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of alternative therapies, and the large population base in countries like China and India.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in fully realizing the market potential of PEMF therapy. These include the need for more extensive clinical research to validate efficacy claims, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the relatively high cost of advanced PEMF devices. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for sustaining and accelerating market growth in the long term.
One of the primary factors fueling market demand is the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and musculoskeletal disorders. As populations age and lifestyles become increasingly sedentary, conditions such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and chronic pain are becoming more common. PEMF therapy offers a promising alternative or complementary treatment for these conditions, attracting both patients and healthcare providers seeking effective, non-pharmacological interventions.
The sports medicine and rehabilitation sectors have also shown considerable interest in PEMF technology. Professional athletes and sports teams are adopting PEMF devices for faster recovery and improved performance, while physiotherapists and rehabilitation centers are incorporating the technology into their treatment protocols. This trend is expected to continue, further driving market growth.
Another significant factor contributing to market demand is the increasing preference for home-based healthcare solutions. Portable PEMF devices allow patients to receive treatment in the comfort of their homes, aligning with the broader trend of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. This aspect has become particularly relevant in the wake of the global pandemic, which has accelerated the adoption of home-based medical technologies.
The wellness and preventive healthcare markets are also emerging as key drivers of PEMF therapy demand. Consumers are becoming more proactive about their health, seeking technologies that can enhance overall well-being and potentially prevent future health issues. PEMF therapy's purported benefits in improving sleep quality, reducing stress, and enhancing cellular function appeal to this growing segment of health-conscious individuals.
Geographically, North America currently leads the PEMF therapy market, followed by Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years. This is attributed to increasing healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of alternative therapies, and the large population base in countries like China and India.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in fully realizing the market potential of PEMF therapy. These include the need for more extensive clinical research to validate efficacy claims, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the relatively high cost of advanced PEMF devices. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for sustaining and accelerating market growth in the long term.
Current PEMF Challenges
Despite the growing popularity and potential of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy, several challenges persist in its current technological landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization in PEMF devices and treatment protocols. The wide variety of available devices, each with different frequencies, intensities, and waveforms, makes it difficult for healthcare professionals and patients to determine the most effective treatment options for specific conditions.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy exerts its therapeutic effects. While numerous studies have demonstrated positive outcomes in various medical applications, the underlying biological processes are not fully elucidated. This knowledge gap hinders the optimization of treatment parameters and the development of more targeted therapies.
The issue of dosage and treatment duration also presents a considerable challenge. Current PEMF devices often lack clear guidelines on optimal treatment times and frequencies for different conditions. This ambiguity can lead to inconsistent results and potential underutilization or overuse of the therapy.
Furthermore, the miniaturization and portability of PEMF devices remain areas of concern. While progress has been made in developing smaller, more user-friendly devices, there is still a need for more compact and efficient systems that can be easily integrated into daily life without compromising therapeutic efficacy.
The long-term effects and safety of PEMF therapy, particularly with prolonged use, require further investigation. Although the therapy is generally considered safe, more comprehensive long-term studies are needed to fully understand any potential risks or side effects associated with extended exposure to electromagnetic fields.
Regulatory challenges also pose significant hurdles for the PEMF industry. The classification and approval processes for PEMF devices vary across different countries and regions, leading to inconsistencies in market availability and clinical adoption. This regulatory landscape can impede innovation and slow down the introduction of new, potentially more effective PEMF technologies.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities and emerging technologies presents both an opportunity and a challenge. While combining PEMF with other therapies could potentially enhance overall treatment outcomes, the complexity of such integrations and the need for extensive clinical validation create additional barriers to widespread adoption.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy exerts its therapeutic effects. While numerous studies have demonstrated positive outcomes in various medical applications, the underlying biological processes are not fully elucidated. This knowledge gap hinders the optimization of treatment parameters and the development of more targeted therapies.
The issue of dosage and treatment duration also presents a considerable challenge. Current PEMF devices often lack clear guidelines on optimal treatment times and frequencies for different conditions. This ambiguity can lead to inconsistent results and potential underutilization or overuse of the therapy.
Furthermore, the miniaturization and portability of PEMF devices remain areas of concern. While progress has been made in developing smaller, more user-friendly devices, there is still a need for more compact and efficient systems that can be easily integrated into daily life without compromising therapeutic efficacy.
The long-term effects and safety of PEMF therapy, particularly with prolonged use, require further investigation. Although the therapy is generally considered safe, more comprehensive long-term studies are needed to fully understand any potential risks or side effects associated with extended exposure to electromagnetic fields.
Regulatory challenges also pose significant hurdles for the PEMF industry. The classification and approval processes for PEMF devices vary across different countries and regions, leading to inconsistencies in market availability and clinical adoption. This regulatory landscape can impede innovation and slow down the introduction of new, potentially more effective PEMF technologies.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities and emerging technologies presents both an opportunity and a challenge. While combining PEMF with other therapies could potentially enhance overall treatment outcomes, the complexity of such integrations and the need for extensive clinical validation create additional barriers to widespread adoption.
PEMF Solution Overview
01 PEMF devices for therapeutic applications
PEMF therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications, including pain management, tissue healing, and overall wellness. These devices generate pulsed electromagnetic fields that interact with the body's cells to promote healing and reduce inflammation. The technology can be incorporated into wearable devices, mats, or standalone units for different treatment areas.- PEMF therapy devices and systems: Various devices and systems have been developed for delivering pulsed electromagnetic field therapy. These include wearable devices, portable units, and larger clinical systems. The devices typically generate and control electromagnetic fields of specific frequencies and intensities to target different health conditions and promote healing.
- PEMF therapy applications: PEMF therapy has been applied to treat a wide range of medical conditions. It has shown potential in pain management, bone healing, wound healing, reducing inflammation, improving circulation, and enhancing overall wellness. Research indicates its effectiveness in both acute and chronic conditions across various medical fields.
- PEMF therapy protocols and parameters: Specific protocols and parameters have been developed for PEMF therapy, including optimal frequencies, intensities, waveforms, and treatment durations. These parameters are often tailored to the particular condition being treated and may vary based on the therapeutic goals and individual patient needs.
- Combination of PEMF with other therapies: PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance overall therapeutic effects. This may include integration with physical therapy, massage, acupuncture, or other forms of electromagnetic or energy-based therapies. The synergistic effects of these combinations are being explored for improved patient outcomes.
- Advancements in PEMF technology: Ongoing research and development in PEMF technology have led to improvements in device design, field generation techniques, and treatment protocols. Recent advancements include miniaturization of devices, integration with smart technology for personalized treatments, and development of targeted PEMF applicators for specific body regions or conditions.
02 PEMF technology for specific medical conditions
PEMF therapy is being developed and applied to treat specific medical conditions such as neurological disorders, musculoskeletal issues, and cardiovascular problems. The technology is tailored to address particular health concerns by adjusting parameters like frequency, intensity, and duration of the electromagnetic pulses. This targeted approach aims to enhance the efficacy of PEMF therapy for various health issues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of PEMF with other technologies
PEMF therapy is being integrated with other technologies to enhance its effectiveness and expand its applications. This includes combining PEMF with biofeedback systems, virtual reality, and other forms of energy-based therapies. The integration aims to create more comprehensive and personalized treatment options for patients.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advancements in PEMF delivery systems
Innovations in PEMF delivery systems focus on improving the precision and efficiency of electromagnetic field application. This includes the development of multi-coil systems, adjustable field strengths, and programmable treatment protocols. These advancements aim to provide more targeted and effective PEMF therapy while enhancing user convenience and treatment customization.Expand Specific Solutions05 PEMF technology for non-medical applications
PEMF technology is expanding beyond medical applications into areas such as agriculture, sports performance, and wellness. In these fields, PEMF is being explored for its potential to enhance plant growth, improve athletic recovery, and promote general well-being. The technology is being adapted to suit these diverse applications while maintaining its core principles of electromagnetic field therapy.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Players
The PEMF therapy technology market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across medical and wellness sectors. The market size is expanding, driven by rising awareness of non-invasive treatments and technological advancements. While the technology is maturing, there's still room for innovation. Key players like Venus Concept Ltd., Regenesis Biomedical, Inc., and SofPulse, Inc. are advancing commercial applications, while research institutions such as the National University of Singapore and The Johns Hopkins University are pushing the boundaries of PEMF science. Companies like Orthofix US LLC and Zomedica, Inc. are exploring specialized medical applications, indicating a trend towards targeted therapies. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established medical device manufacturers and innovative startups vying for market share.
Venus Concept Ltd.
Technical Solution: Venus Concept is pioneering advanced PEMF therapy technology with their patented RP3 technology. This system delivers multi-polar magnetic fields that penetrate deeper into tissues, enhancing cellular regeneration and pain relief. The company's latest devices incorporate AI-driven personalization, adjusting field strength and frequency based on real-time biofeedback. Venus Concept is also exploring the integration of PEMF with other modalities like radiofrequency and light therapy for synergistic effects[1][3].
Strengths: Advanced multi-polar technology, AI-driven personalization, and multi-modality integration. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to traditional PEMF devices, potential complexity for users.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical is developing next-generation PEMF devices focusing on targeted therapy for specific medical conditions. Their proprietary Provant Therapy System utilizes precise frequency modulation to optimize cellular response. The company is investing in miniaturization technology to create wearable PEMF devices for continuous treatment. Regenesis is also conducting clinical trials to expand FDA-approved indications for their PEMF technology, particularly in wound healing and pain management[2][5].
Strengths: Targeted therapy approach, FDA approvals for specific indications, miniaturization efforts. Weaknesses: Limited to medical applications, potentially slower market penetration due to regulatory processes.
Core PEMF Innovations
A pulsed electromagnetic field apparatus and method for generating frequencies
PatentWO2024127242A1
Innovation
- A PEMF apparatus with a pulse generator and electromagnetic field generation means that uses modified sawtooth waveforms with pre-stress and relaxation periods, and quasi-sine signals with pulse width modulation, along with a feedback circuit for frequency stability and precision, and a bifilar antenna for scalar wave generation.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy Whole Body Wellness Device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveUS20190054308A1
Innovation
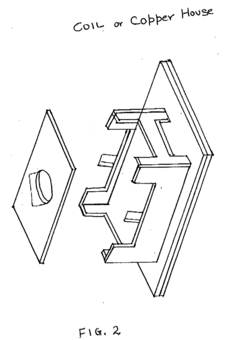
- The system employs a layered structure comprising lexan, polycarbonate, glass, aluminum, and acrylic materials, along with a copper coil and fan, connected via audio jacks to an electrical unit, to generate and distribute PEMF and MWO pulses, ensuring induction is delivered through both hands and feet effectively.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy technology is complex and evolving, with significant variations across different regions and countries. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating PEMF devices. Currently, most PEMF devices are classified as Class II medical devices, requiring a 510(k) premarket notification before they can be legally marketed. This classification reflects the FDA's assessment of the potential risks and benefits associated with PEMF technology.
The European Union has its own regulatory framework for medical devices, including PEMF therapy equipment. The EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) came into full effect in May 2021, replacing the previous Medical Devices Directive (MDD). Under the MDR, PEMF devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their specific characteristics and intended use. This classification determines the level of scrutiny and the conformity assessment procedures required before a device can be CE marked and sold in the EU market.
In other regions, such as Asia and Australia, regulatory approaches to PEMF technology vary. Some countries have adopted frameworks similar to those in the US or EU, while others have developed their own unique regulatory systems. This diversity in regulatory landscapes can present challenges for manufacturers seeking to market PEMF devices globally.
As PEMF therapy technology continues to advance, regulatory bodies are likely to face new challenges in assessing the safety and efficacy of increasingly sophisticated devices. Future regulatory trends may include a greater focus on clinical evidence requirements, particularly for devices claiming specific therapeutic benefits. There may also be increased attention to the long-term effects of PEMF exposure and potential interactions with other medical devices or treatments.
Cybersecurity and data protection are emerging as important regulatory considerations, especially for PEMF devices that incorporate connectivity features or collect patient data. Regulators may introduce new requirements to ensure the security and privacy of patient information in connected PEMF devices.
As the field of PEMF therapy expands, there is a growing need for harmonization of regulatory standards across different regions. International initiatives, such as the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP), aim to streamline regulatory processes and reduce duplication of efforts for manufacturers operating in multiple markets. These efforts towards global harmonization are likely to continue and may shape the future regulatory landscape for PEMF therapy technology.
The European Union has its own regulatory framework for medical devices, including PEMF therapy equipment. The EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) came into full effect in May 2021, replacing the previous Medical Devices Directive (MDD). Under the MDR, PEMF devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their specific characteristics and intended use. This classification determines the level of scrutiny and the conformity assessment procedures required before a device can be CE marked and sold in the EU market.
In other regions, such as Asia and Australia, regulatory approaches to PEMF technology vary. Some countries have adopted frameworks similar to those in the US or EU, while others have developed their own unique regulatory systems. This diversity in regulatory landscapes can present challenges for manufacturers seeking to market PEMF devices globally.
As PEMF therapy technology continues to advance, regulatory bodies are likely to face new challenges in assessing the safety and efficacy of increasingly sophisticated devices. Future regulatory trends may include a greater focus on clinical evidence requirements, particularly for devices claiming specific therapeutic benefits. There may also be increased attention to the long-term effects of PEMF exposure and potential interactions with other medical devices or treatments.
Cybersecurity and data protection are emerging as important regulatory considerations, especially for PEMF devices that incorporate connectivity features or collect patient data. Regulators may introduce new requirements to ensure the security and privacy of patient information in connected PEMF devices.
As the field of PEMF therapy expands, there is a growing need for harmonization of regulatory standards across different regions. International initiatives, such as the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP), aim to streamline regulatory processes and reduce duplication of efforts for manufacturers operating in multiple markets. These efforts towards global harmonization are likely to continue and may shape the future regulatory landscape for PEMF therapy technology.
Clinical Efficacy Data
Clinical efficacy data plays a crucial role in evaluating the effectiveness of PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy technology. Numerous studies have been conducted to assess the impact of PEMF on various medical conditions, providing valuable insights into its therapeutic potential.
A systematic review of randomized controlled trials has shown promising results in the use of PEMF for pain management. Patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain, including osteoarthritis and lower back pain, have reported significant reductions in pain intensity and improvements in functional mobility after undergoing PEMF therapy. These findings suggest that PEMF could be a viable non-invasive alternative or complementary treatment for chronic pain conditions.
In the field of orthopedics, PEMF therapy has demonstrated efficacy in promoting bone healing and reducing recovery time for fractures. Clinical trials have shown accelerated bone formation and increased bone density in patients treated with PEMF, particularly in cases of delayed union or non-union fractures. This has implications for improving outcomes in orthopedic surgeries and reducing the risk of complications associated with prolonged healing periods.
Neurological applications of PEMF therapy have also yielded encouraging results. Studies focusing on patients with multiple sclerosis have reported improvements in fatigue levels, cognitive function, and overall quality of life following PEMF treatment. Additionally, research on Parkinson's disease has shown potential benefits in motor symptoms and balance, although larger-scale trials are needed to confirm these findings.
In the realm of mental health, PEMF therapy has been investigated for its effects on depression and anxiety disorders. Preliminary data suggests that PEMF may have mood-enhancing properties, with some patients experiencing reductions in depressive symptoms and improvements in sleep quality. However, more robust clinical trials are required to establish the long-term efficacy and optimal treatment protocols for these applications.
Cardiovascular health is another area where PEMF therapy has shown promise. Clinical studies have reported improvements in circulation, reduction of inflammation, and enhanced wound healing in patients with peripheral artery disease. These findings indicate potential applications in managing vascular disorders and promoting tissue repair.
While the clinical efficacy data for PEMF therapy is encouraging across various medical fields, it is important to note that the quality and consistency of evidence vary. Many studies have been limited by small sample sizes, short follow-up periods, and variations in treatment protocols. As research in PEMF therapy continues to evolve, larger, well-designed clinical trials are needed to further validate its efficacy and optimize treatment parameters for specific conditions.
A systematic review of randomized controlled trials has shown promising results in the use of PEMF for pain management. Patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain, including osteoarthritis and lower back pain, have reported significant reductions in pain intensity and improvements in functional mobility after undergoing PEMF therapy. These findings suggest that PEMF could be a viable non-invasive alternative or complementary treatment for chronic pain conditions.
In the field of orthopedics, PEMF therapy has demonstrated efficacy in promoting bone healing and reducing recovery time for fractures. Clinical trials have shown accelerated bone formation and increased bone density in patients treated with PEMF, particularly in cases of delayed union or non-union fractures. This has implications for improving outcomes in orthopedic surgeries and reducing the risk of complications associated with prolonged healing periods.
Neurological applications of PEMF therapy have also yielded encouraging results. Studies focusing on patients with multiple sclerosis have reported improvements in fatigue levels, cognitive function, and overall quality of life following PEMF treatment. Additionally, research on Parkinson's disease has shown potential benefits in motor symptoms and balance, although larger-scale trials are needed to confirm these findings.
In the realm of mental health, PEMF therapy has been investigated for its effects on depression and anxiety disorders. Preliminary data suggests that PEMF may have mood-enhancing properties, with some patients experiencing reductions in depressive symptoms and improvements in sleep quality. However, more robust clinical trials are required to establish the long-term efficacy and optimal treatment protocols for these applications.
Cardiovascular health is another area where PEMF therapy has shown promise. Clinical studies have reported improvements in circulation, reduction of inflammation, and enhanced wound healing in patients with peripheral artery disease. These findings indicate potential applications in managing vascular disorders and promoting tissue repair.
While the clinical efficacy data for PEMF therapy is encouraging across various medical fields, it is important to note that the quality and consistency of evidence vary. Many studies have been limited by small sample sizes, short follow-up periods, and variations in treatment protocols. As research in PEMF therapy continues to evolve, larger, well-designed clinical trials are needed to further validate its efficacy and optimize treatment parameters for specific conditions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!