How Silicone Rubber Drives Revolution in Human-Centric Design?
JUL 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Silicone Rubber Evolution
Silicone rubber has undergone a remarkable evolution since its inception in the 1940s, transforming from a niche material to a versatile component in human-centric design. Initially developed as an insulator for electrical applications, silicone rubber quickly found its way into various industries due to its unique properties.
The early stages of silicone rubber development focused primarily on improving its thermal stability and electrical insulation capabilities. As research progressed, scientists discovered its exceptional biocompatibility, leading to groundbreaking applications in medical devices and prosthetics. This marked a significant shift towards human-centric design, as silicone rubber enabled the creation of more comfortable and safer medical implants.
In the 1960s and 1970s, advancements in polymer chemistry led to the development of liquid silicone rubber (LSR), which revolutionized manufacturing processes. LSR allowed for more intricate and precise molding techniques, opening up new possibilities in product design across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a surge in silicone rubber applications in the field of ergonomics. Its soft, pliable nature made it an ideal material for creating ergonomic keyboards, mouse pads, and other computer peripherals, significantly enhancing user comfort and reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
As environmental concerns gained prominence in the 21st century, silicone rubber's durability and resistance to degradation became both an advantage and a challenge. Researchers began focusing on developing more sustainable silicone rubber formulations and recycling methods to address these concerns while maintaining its beneficial properties.
Recent years have witnessed a convergence of silicone rubber technology with smart materials and nanotechnology. This integration has led to the development of self-healing silicone rubbers, conductive silicone composites, and shape-memory silicone materials. These innovations have further expanded the role of silicone rubber in human-centric design, enabling the creation of responsive and adaptive products that can better serve human needs.
The ongoing evolution of silicone rubber continues to push the boundaries of human-centric design. Current research focuses on enhancing its biocompatibility for advanced medical applications, improving its thermal management properties for electronics, and developing more sustainable production methods. As we look to the future, silicone rubber is poised to play an even more crucial role in creating products that seamlessly integrate with human physiology and environmental needs.
The early stages of silicone rubber development focused primarily on improving its thermal stability and electrical insulation capabilities. As research progressed, scientists discovered its exceptional biocompatibility, leading to groundbreaking applications in medical devices and prosthetics. This marked a significant shift towards human-centric design, as silicone rubber enabled the creation of more comfortable and safer medical implants.
In the 1960s and 1970s, advancements in polymer chemistry led to the development of liquid silicone rubber (LSR), which revolutionized manufacturing processes. LSR allowed for more intricate and precise molding techniques, opening up new possibilities in product design across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a surge in silicone rubber applications in the field of ergonomics. Its soft, pliable nature made it an ideal material for creating ergonomic keyboards, mouse pads, and other computer peripherals, significantly enhancing user comfort and reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
As environmental concerns gained prominence in the 21st century, silicone rubber's durability and resistance to degradation became both an advantage and a challenge. Researchers began focusing on developing more sustainable silicone rubber formulations and recycling methods to address these concerns while maintaining its beneficial properties.
Recent years have witnessed a convergence of silicone rubber technology with smart materials and nanotechnology. This integration has led to the development of self-healing silicone rubbers, conductive silicone composites, and shape-memory silicone materials. These innovations have further expanded the role of silicone rubber in human-centric design, enabling the creation of responsive and adaptive products that can better serve human needs.
The ongoing evolution of silicone rubber continues to push the boundaries of human-centric design. Current research focuses on enhancing its biocompatibility for advanced medical applications, improving its thermal management properties for electronics, and developing more sustainable production methods. As we look to the future, silicone rubber is poised to play an even more crucial role in creating products that seamlessly integrate with human physiology and environmental needs.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for silicone rubber in human-centric design has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is driven by the increasing focus on user comfort, safety, and personalization across various industries. Silicone rubber's unique properties, including flexibility, durability, and biocompatibility, make it an ideal material for applications that prioritize human interaction and experience.
In the healthcare sector, silicone rubber is witnessing a substantial increase in demand for medical devices, prosthetics, and wearable health monitors. The global medical silicone market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is fueled by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the need for more comfortable and adaptable medical solutions.
The consumer electronics industry is another major driver of silicone rubber demand in human-centric design. With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, manufacturers are increasingly turning to silicone rubber for protective cases, keypads, and touchscreens. The material's tactile properties and resistance to wear and tear make it ideal for enhancing user experience and product longevity.
In the automotive sector, silicone rubber is gaining traction in interior design, particularly for dashboard components, steering wheel covers, and seating materials. The global automotive silicone market is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing focus on passenger comfort and the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles.
The sports and fitness industry is also contributing to the growing demand for silicone rubber. From athletic footwear to fitness trackers, silicone rubber is being used to create more comfortable, durable, and performance-enhancing products. The global sports equipment market, which heavily utilizes silicone rubber, is projected to reach a value of over $100 billion by 2025.
The trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly materials is further boosting the demand for silicone rubber. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the recyclability and long lifespan of silicone rubber products are becoming increasingly attractive. This aligns with the growing market for sustainable consumer goods and packaging solutions.
In the realm of assistive technologies and accessibility devices, silicone rubber is playing a crucial role in creating more inclusive designs. From ergonomic grips to customizable interfaces, the material's versatility is enabling designers to address a wide range of user needs and abilities.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart home technologies continue to evolve, silicone rubber is finding new applications in human-machine interfaces. Its ability to withstand various environmental conditions while maintaining user-friendly properties makes it an excellent choice for smart home devices and controls.
Human-Centric Design:
In the healthcare sector, silicone rubber is witnessing a substantial increase in demand for medical devices, prosthetics, and wearable health monitors. The global medical silicone market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is fueled by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the need for more comfortable and adaptable medical solutions.
The consumer electronics industry is another major driver of silicone rubber demand in human-centric design. With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, manufacturers are increasingly turning to silicone rubber for protective cases, keypads, and touchscreens. The material's tactile properties and resistance to wear and tear make it ideal for enhancing user experience and product longevity.
In the automotive sector, silicone rubber is gaining traction in interior design, particularly for dashboard components, steering wheel covers, and seating materials. The global automotive silicone market is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing focus on passenger comfort and the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles.
The sports and fitness industry is also contributing to the growing demand for silicone rubber. From athletic footwear to fitness trackers, silicone rubber is being used to create more comfortable, durable, and performance-enhancing products. The global sports equipment market, which heavily utilizes silicone rubber, is projected to reach a value of over $100 billion by 2025.
The trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly materials is further boosting the demand for silicone rubber. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the recyclability and long lifespan of silicone rubber products are becoming increasingly attractive. This aligns with the growing market for sustainable consumer goods and packaging solutions.
In the realm of assistive technologies and accessibility devices, silicone rubber is playing a crucial role in creating more inclusive designs. From ergonomic grips to customizable interfaces, the material's versatility is enabling designers to address a wide range of user needs and abilities.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart home technologies continue to evolve, silicone rubber is finding new applications in human-machine interfaces. Its ability to withstand various environmental conditions while maintaining user-friendly properties makes it an excellent choice for smart home devices and controls.
Human-Centric Design:
Technical Challenges
Despite the numerous advantages of silicone rubber in human-centric design, several technical challenges persist in its widespread adoption and optimal utilization. One of the primary obstacles is achieving consistent material properties across different production batches. The complex chemical composition of silicone rubber makes it susceptible to variations in curing conditions, which can lead to inconsistencies in mechanical properties, durability, and performance.
Another significant challenge lies in enhancing the adhesion properties of silicone rubber. While its inert nature is beneficial in many applications, it also makes bonding silicone to other materials difficult. This limitation restricts its use in multi-material designs and can compromise the integrity of products where strong adhesion is crucial.
The development of silicone rubber with improved thermal conductivity presents another technical hurdle. Although silicone rubber is an excellent electrical insulator, its poor thermal conductivity can be a drawback in applications where heat dissipation is essential. Researchers are exploring various methods to incorporate thermally conductive fillers without compromising the material's desirable properties.
Balancing the trade-off between softness and durability remains a persistent challenge. While softer silicone rubbers offer enhanced comfort and flexibility, they often lack the necessary strength and wear resistance for long-term use. Conversely, harder formulations may provide better durability but sacrifice the tactile qualities that make silicone rubber attractive for human-centric design.
The environmental impact of silicone rubber production and disposal also poses technical challenges. Developing more sustainable manufacturing processes and improving the recyclability of silicone rubber products are areas that require significant research and innovation. This includes finding ways to efficiently separate silicone from other materials in composite products and developing effective methods for breaking down and repurposing used silicone rubber.
Lastly, the integration of smart functionalities into silicone rubber components presents complex technical challenges. As the demand for responsive and interactive materials grows, researchers are working on incorporating sensors, actuators, and other electronic components into silicone rubber matrices. This integration requires overcoming issues related to material compatibility, maintaining flexibility, and ensuring the longevity of embedded electronics in various environmental conditions.
Another significant challenge lies in enhancing the adhesion properties of silicone rubber. While its inert nature is beneficial in many applications, it also makes bonding silicone to other materials difficult. This limitation restricts its use in multi-material designs and can compromise the integrity of products where strong adhesion is crucial.
The development of silicone rubber with improved thermal conductivity presents another technical hurdle. Although silicone rubber is an excellent electrical insulator, its poor thermal conductivity can be a drawback in applications where heat dissipation is essential. Researchers are exploring various methods to incorporate thermally conductive fillers without compromising the material's desirable properties.
Balancing the trade-off between softness and durability remains a persistent challenge. While softer silicone rubbers offer enhanced comfort and flexibility, they often lack the necessary strength and wear resistance for long-term use. Conversely, harder formulations may provide better durability but sacrifice the tactile qualities that make silicone rubber attractive for human-centric design.
The environmental impact of silicone rubber production and disposal also poses technical challenges. Developing more sustainable manufacturing processes and improving the recyclability of silicone rubber products are areas that require significant research and innovation. This includes finding ways to efficiently separate silicone from other materials in composite products and developing effective methods for breaking down and repurposing used silicone rubber.
Lastly, the integration of smart functionalities into silicone rubber components presents complex technical challenges. As the demand for responsive and interactive materials grows, researchers are working on incorporating sensors, actuators, and other electronic components into silicone rubber matrices. This integration requires overcoming issues related to material compatibility, maintaining flexibility, and ensuring the longevity of embedded electronics in various environmental conditions.
Current Design Solutions
01 Ergonomic design for comfort and usability
Silicone rubber is used in human-centric designs to create ergonomic products that enhance comfort and usability. This includes designing grips, handles, and interfaces that conform to the natural contours of the human body, reducing strain and improving user experience.- Ergonomic design for comfort and usability: Silicone rubber is used in human-centric designs to create ergonomic products that enhance comfort and usability. This includes designing grips, handles, and interfaces that conform to the natural contours of the human body, reducing strain and improving user experience. The material's flexibility and softness make it ideal for creating products that adapt to individual users' needs.
- Biocompatible silicone rubber for medical applications: Human-centric design in medical devices often incorporates biocompatible silicone rubber. This material is used for implants, prosthetics, and wearable medical devices due to its non-toxicity, durability, and ability to mimic human tissue properties. The focus is on creating medical solutions that integrate seamlessly with the human body, minimizing rejection and improving patient comfort.
- Customizable silicone rubber formulations: Developing customizable silicone rubber formulations allows for tailored properties to meet specific human-centric design requirements. This includes adjusting hardness, elasticity, and thermal properties to create products that better serve human needs. The ability to fine-tune these characteristics enables designers to create more effective and comfortable solutions for various applications.
- Sensory-enhanced silicone rubber products: Human-centric design incorporates sensory elements into silicone rubber products to enhance user interaction and feedback. This includes developing textures, colors, and even scents that improve the overall user experience. The focus is on creating products that not only function well but also engage users on a sensory level, making interactions more intuitive and enjoyable.
- Sustainable and eco-friendly silicone rubber solutions: Human-centric design in silicone rubber products increasingly focuses on sustainability and eco-friendliness. This involves developing biodegradable silicone rubber formulations, improving recycling processes, and reducing the environmental impact of production. The aim is to create products that meet human needs while also considering long-term environmental and health impacts.
02 Biocompatible silicone rubber formulations
Development of silicone rubber formulations that are biocompatible and safe for prolonged contact with human skin or internal use. These materials are designed to minimize allergic reactions and irritation, making them suitable for medical devices and wearable technology.Expand Specific Solutions03 Customizable properties for specific applications
Silicone rubber compositions are tailored to achieve specific properties such as durability, flexibility, or thermal resistance. This allows for the creation of products that meet the diverse needs of users in various applications, from consumer goods to specialized industrial uses.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of smart features in silicone products
Incorporation of smart features into silicone rubber products, such as sensors or conductive elements. This enables the creation of interactive and responsive designs that can enhance user experience and provide valuable feedback or functionality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sustainable and eco-friendly silicone rubber solutions
Development of environmentally friendly silicone rubber formulations and manufacturing processes. This includes the use of renewable resources, biodegradable additives, or recycling methods to create more sustainable products that align with human-centric values of environmental consciousness.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The silicone rubber industry is in a mature growth phase, with a global market size expected to reach $9.34 billion by 2027. The technology's maturity is evident in its widespread adoption across various sectors, including automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics. Key players like Shin-Etsu Chemical, Momentive Performance Materials, and Wacker Chemie are driving innovation in human-centric design applications. These companies are focusing on developing advanced silicone rubber formulations with enhanced properties such as improved durability, flexibility, and biocompatibility. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing R&D efforts to create specialized silicone rubber products that cater to evolving consumer needs and emerging technologies in wearables, prosthetics, and soft robotics.
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. is a global leader in silicone products, offering a wide range of silicone rubber materials for human-centric design applications. Their LIMS (Liquid Injection Molding System) silicone rubbers are particularly notable for their ability to create complex, precise shapes with excellent durability and biocompatibility. Shin-Etsu's KE-2090 series, for example, is a high-transparency silicone rubber used in optical applications, enabling the development of advanced wearable displays and augmented reality devices[4]. The company has also developed silicone rubber compounds with enhanced thermal conductivity, crucial for heat management in wearable electronics and medical devices[5]. Their focus on developing materials with low volatility and minimal odor contributes to improved user comfort in close-contact applications.
Strengths: Comprehensive product range, strong R&D capabilities, global presence. Weaknesses: Potential supply chain vulnerabilities, competition from emerging markets.
Momentive Performance Materials, Inc.
Technical Solution: Momentive Performance Materials, Inc. has developed a range of silicone rubber solutions tailored for human-centric design applications. Their Silopren™ liquid silicone rubber (LSR) product line offers materials with varying degrees of softness and elasticity, allowing designers to create products with optimal tactile properties and comfort. Momentive's UV-curable silicone technology enables rapid prototyping and production of complex 3D-printed silicone parts, accelerating the development of customized wearable devices and medical products[9]. The company has also introduced self-lubricating silicone rubbers that reduce friction and improve the performance of moving parts in prosthetics and robotic interfaces. Momentive's focus on developing low-volatile silicone materials addresses concerns about long-term exposure in close-contact applications, enhancing the safety profile of their products for human-centric designs[10].
Strengths: Specialized product offerings, advanced manufacturing technologies, strong focus on customization. Weaknesses: Limited market share compared to larger competitors, potential challenges in scaling production for high-volume applications.
Innovative Applications
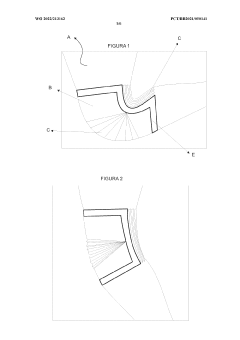
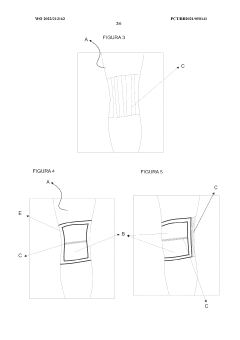
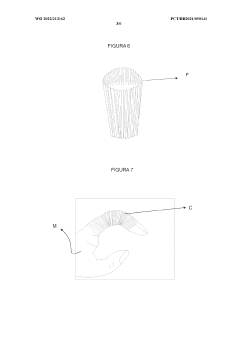
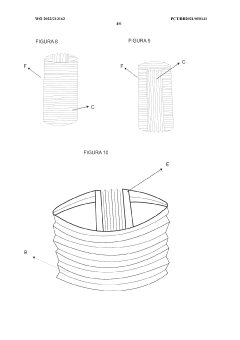
Configuration for product made of liquid silicone rubber (LSR) for providing comfort, protection, rehabilitation and bodily care
PatentWO2022213162A1
Innovation
- The use of Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) with pleated designs and gel inserts in products like gloves, socks, sleeves, and pads, which can be heated or cooled, providing a flexible, adherent, and protective layer that prevents friction and allows full mobility, while incorporating therapeutic benefits.
Silicone mixture and cured product thereof
PatentActiveEP3744757A1
Innovation
- A silicone admixture comprising millable silicone rubber, a silicone high polymer with no cross-linking sites, a peroxide-based vulcanizing agent, and rubber reinforcing silica, which adjusts the proportions of hard and soft segments to achieve a cured product with a Tan δ of 0.3 to 0.6, providing compatibility and comfort when in contact with human skin.
Sustainability Aspects
Silicone rubber's sustainability aspects play a crucial role in driving the revolution of human-centric design. This material offers significant environmental benefits compared to traditional alternatives, making it an attractive choice for eco-conscious designers and manufacturers.
One of the key sustainability advantages of silicone rubber is its durability and longevity. Products made from silicone rubber typically have a longer lifespan than those made from other materials, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This durability contributes to a reduction in waste generation and resource consumption over time, aligning with circular economy principles.
Furthermore, silicone rubber is highly resistant to extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. This resistance allows products to maintain their integrity and performance even in harsh environments, extending their useful life and reducing the environmental impact associated with premature product failure or degradation.
The production process of silicone rubber also offers sustainability benefits. It requires less energy compared to the production of many other synthetic materials, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. Additionally, silicone rubber production generates fewer harmful byproducts and emissions, contributing to cleaner manufacturing practices.
Silicone rubber's recyclability is another important sustainability aspect. While not as easily recyclable as some thermoplastics, silicone rubber can be recycled through specialized processes. These processes allow for the recovery and reuse of the material, reducing the demand for virgin resources and minimizing waste sent to landfills.
In terms of end-of-life considerations, silicone rubber is non-toxic and does not leach harmful chemicals into the environment when disposed of properly. This characteristic makes it a safer option for both human health and ecological systems compared to some other synthetic materials.
The versatility of silicone rubber also contributes to its sustainability profile. Its ability to be molded into various shapes and forms allows for efficient material use and design optimization. This versatility enables designers to create products that are not only functional but also minimize material waste during production.
As the focus on sustainability in product design continues to grow, silicone rubber's environmental attributes position it as a material of choice for human-centric design. Its combination of durability, energy-efficient production, recyclability, and safety aligns well with the increasing demand for sustainable materials in various industries, from consumer goods to medical devices and beyond.
One of the key sustainability advantages of silicone rubber is its durability and longevity. Products made from silicone rubber typically have a longer lifespan than those made from other materials, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This durability contributes to a reduction in waste generation and resource consumption over time, aligning with circular economy principles.
Furthermore, silicone rubber is highly resistant to extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. This resistance allows products to maintain their integrity and performance even in harsh environments, extending their useful life and reducing the environmental impact associated with premature product failure or degradation.
The production process of silicone rubber also offers sustainability benefits. It requires less energy compared to the production of many other synthetic materials, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. Additionally, silicone rubber production generates fewer harmful byproducts and emissions, contributing to cleaner manufacturing practices.
Silicone rubber's recyclability is another important sustainability aspect. While not as easily recyclable as some thermoplastics, silicone rubber can be recycled through specialized processes. These processes allow for the recovery and reuse of the material, reducing the demand for virgin resources and minimizing waste sent to landfills.
In terms of end-of-life considerations, silicone rubber is non-toxic and does not leach harmful chemicals into the environment when disposed of properly. This characteristic makes it a safer option for both human health and ecological systems compared to some other synthetic materials.
The versatility of silicone rubber also contributes to its sustainability profile. Its ability to be molded into various shapes and forms allows for efficient material use and design optimization. This versatility enables designers to create products that are not only functional but also minimize material waste during production.
As the focus on sustainability in product design continues to grow, silicone rubber's environmental attributes position it as a material of choice for human-centric design. Its combination of durability, energy-efficient production, recyclability, and safety aligns well with the increasing demand for sustainable materials in various industries, from consumer goods to medical devices and beyond.
Regulatory Compliance
The regulatory landscape surrounding silicone rubber in human-centric design is complex and evolving. As this material gains prominence in various applications, manufacturers and designers must navigate a web of regulations to ensure compliance and safety.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating silicone rubber products that come into contact with food or are used in medical devices. The FDA's 21 CFR 177.2600 specifically addresses rubber articles intended for repeated use in food contact applications, setting guidelines for composition and testing requirements. For medical devices, the FDA's premarket approval (PMA) process or 510(k) clearance may be necessary, depending on the device classification and intended use.
The European Union's regulatory framework is equally stringent. The EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation impacts the use of silicone rubber, requiring manufacturers to register substances and provide safety data. Additionally, the EU's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) set standards for medical devices incorporating silicone rubber components.
In the consumer products sector, regulations such as the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA) in the US and the General Product Safety Directive (GPSD) in the EU apply to silicone rubber products. These regulations focus on ensuring product safety, particularly for items intended for use by children.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in regulatory compliance. Many jurisdictions are implementing stricter regulations on the disposal and recycling of silicone rubber products. The EU's Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive, for instance, impacts the end-of-life management of products containing silicone rubber components.
As human-centric design often involves wearable technology and smart devices, data protection regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US become relevant when silicone rubber products incorporate sensors or data collection capabilities.
Manufacturers must also consider industry-specific standards and certifications. For example, in the automotive industry, silicone rubber components may need to meet standards set by organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
Compliance with these diverse regulations requires a comprehensive approach. Companies must invest in robust quality management systems, conduct thorough testing and documentation, and stay informed about regulatory changes across different markets. As silicone rubber continues to drive innovation in human-centric design, navigating this complex regulatory landscape will be crucial for successful product development and market entry.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating silicone rubber products that come into contact with food or are used in medical devices. The FDA's 21 CFR 177.2600 specifically addresses rubber articles intended for repeated use in food contact applications, setting guidelines for composition and testing requirements. For medical devices, the FDA's premarket approval (PMA) process or 510(k) clearance may be necessary, depending on the device classification and intended use.
The European Union's regulatory framework is equally stringent. The EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation impacts the use of silicone rubber, requiring manufacturers to register substances and provide safety data. Additionally, the EU's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) set standards for medical devices incorporating silicone rubber components.
In the consumer products sector, regulations such as the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA) in the US and the General Product Safety Directive (GPSD) in the EU apply to silicone rubber products. These regulations focus on ensuring product safety, particularly for items intended for use by children.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in regulatory compliance. Many jurisdictions are implementing stricter regulations on the disposal and recycling of silicone rubber products. The EU's Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive, for instance, impacts the end-of-life management of products containing silicone rubber components.
As human-centric design often involves wearable technology and smart devices, data protection regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US become relevant when silicone rubber products incorporate sensors or data collection capabilities.
Manufacturers must also consider industry-specific standards and certifications. For example, in the automotive industry, silicone rubber components may need to meet standards set by organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
Compliance with these diverse regulations requires a comprehensive approach. Companies must invest in robust quality management systems, conduct thorough testing and documentation, and stay informed about regulatory changes across different markets. As silicone rubber continues to drive innovation in human-centric design, navigating this complex regulatory landscape will be crucial for successful product development and market entry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!