How to Assess the Long-Term Benefits of PEMF Therapy?
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Background and Objectives
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has emerged as a promising non-invasive treatment modality, gaining attention in both medical and wellness circles. This technology harnesses the power of electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and enhance overall health. The history of PEMF therapy dates back to the mid-20th century, with its roots in NASA's research on bone and muscle loss in astronauts during space missions.
Over the decades, PEMF therapy has evolved from a space-age technology to a widely accessible treatment option for various health conditions. The fundamental principle behind PEMF therapy is based on the concept that all living cells possess an electrical charge, and by applying external electromagnetic fields, cellular functions can be modulated and optimized.
The primary objective of PEMF therapy is to promote healing and alleviate pain by enhancing cellular metabolism, improving circulation, and reducing inflammation. As research in this field progresses, the potential applications of PEMF therapy continue to expand, encompassing areas such as bone healing, wound care, pain management, and even mental health.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated PEMF devices, allowing for precise control over field strength, frequency, and waveform. This has opened up new possibilities for tailoring treatments to specific conditions and individual patient needs. The growing interest in non-pharmacological interventions has further fueled the exploration of PEMF therapy as a complementary or alternative treatment option.
As we look towards the future, the trajectory of PEMF therapy points towards increased integration with other treatment modalities and the potential for personalized medicine approaches. The ongoing research aims to elucidate the long-term effects of PEMF therapy, optimize treatment protocols, and expand its applications to a broader range of medical conditions.
The challenge in assessing the long-term benefits of PEMF therapy lies in the complexity of biological systems and the variability in individual responses to treatment. Factors such as treatment duration, frequency, and intensity all play crucial roles in determining outcomes. Additionally, the diverse range of conditions for which PEMF therapy is being investigated necessitates a multifaceted approach to evaluation.
To address these challenges and advance our understanding of PEMF therapy's long-term benefits, researchers are focusing on developing standardized protocols, conducting longitudinal studies, and leveraging advanced imaging and biomarker technologies. The goal is to establish a robust evidence base that can guide clinical decision-making and inform future innovations in PEMF technology.
Over the decades, PEMF therapy has evolved from a space-age technology to a widely accessible treatment option for various health conditions. The fundamental principle behind PEMF therapy is based on the concept that all living cells possess an electrical charge, and by applying external electromagnetic fields, cellular functions can be modulated and optimized.
The primary objective of PEMF therapy is to promote healing and alleviate pain by enhancing cellular metabolism, improving circulation, and reducing inflammation. As research in this field progresses, the potential applications of PEMF therapy continue to expand, encompassing areas such as bone healing, wound care, pain management, and even mental health.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated PEMF devices, allowing for precise control over field strength, frequency, and waveform. This has opened up new possibilities for tailoring treatments to specific conditions and individual patient needs. The growing interest in non-pharmacological interventions has further fueled the exploration of PEMF therapy as a complementary or alternative treatment option.
As we look towards the future, the trajectory of PEMF therapy points towards increased integration with other treatment modalities and the potential for personalized medicine approaches. The ongoing research aims to elucidate the long-term effects of PEMF therapy, optimize treatment protocols, and expand its applications to a broader range of medical conditions.
The challenge in assessing the long-term benefits of PEMF therapy lies in the complexity of biological systems and the variability in individual responses to treatment. Factors such as treatment duration, frequency, and intensity all play crucial roles in determining outcomes. Additionally, the diverse range of conditions for which PEMF therapy is being investigated necessitates a multifaceted approach to evaluation.
To address these challenges and advance our understanding of PEMF therapy's long-term benefits, researchers are focusing on developing standardized protocols, conducting longitudinal studies, and leveraging advanced imaging and biomarker technologies. The goal is to establish a robust evidence base that can guide clinical decision-making and inform future innovations in PEMF technology.
Market Analysis for PEMF Devices
The PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy device market has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of non-invasive treatment options and the rising prevalence of chronic conditions. The global PEMF therapy device market was valued at approximately $500 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 12% during the forecast period.
The market for PEMF devices is segmented based on product type, application, end-user, and region. Product types include high-power devices used in clinical settings and low-power devices for home use. Applications span a wide range, including pain management, bone healing, neurological disorders, and overall wellness. The end-user segments primarily consist of hospitals, specialty clinics, and home healthcare.
North America currently dominates the PEMF device market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This is attributed to the high adoption rate of advanced medical technologies, well-established healthcare infrastructure, and increasing research activities in the region. Europe follows closely, with a market share of around 30%, driven by the growing geriatric population and rising incidence of chronic diseases.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, with a CAGR of over 15%. This growth is fueled by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness about alternative therapies in countries like China and India.
Key market drivers include the growing prevalence of chronic pain conditions, increasing sports injuries, and the rising demand for non-invasive treatment options. The aging population worldwide is also a significant factor, as older adults are more prone to conditions that can benefit from PEMF therapy, such as osteoarthritis and osteoporosis.
However, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced PEMF devices, lack of standardized protocols for treatment, and limited reimbursement policies in many countries. Additionally, the market is hindered by skepticism among some healthcare professionals regarding the efficacy of PEMF therapy for certain conditions.
Despite these challenges, technological advancements are expected to drive market growth. Innovations such as portable and wearable PEMF devices, integration with smartphone apps for personalized treatment plans, and the development of more targeted therapies for specific conditions are likely to expand the market reach and improve patient outcomes.
The competitive landscape of the PEMF device market is fragmented, with a mix of established medical device companies and specialized PEMF therapy manufacturers. Key players in the market include OMI, Bemer Group, HealthyLine, Oska Wellness, and iMRS 2000. These companies are focusing on product innovation, clinical research, and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge and expand their market presence.
The market for PEMF devices is segmented based on product type, application, end-user, and region. Product types include high-power devices used in clinical settings and low-power devices for home use. Applications span a wide range, including pain management, bone healing, neurological disorders, and overall wellness. The end-user segments primarily consist of hospitals, specialty clinics, and home healthcare.
North America currently dominates the PEMF device market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This is attributed to the high adoption rate of advanced medical technologies, well-established healthcare infrastructure, and increasing research activities in the region. Europe follows closely, with a market share of around 30%, driven by the growing geriatric population and rising incidence of chronic diseases.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, with a CAGR of over 15%. This growth is fueled by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness about alternative therapies in countries like China and India.
Key market drivers include the growing prevalence of chronic pain conditions, increasing sports injuries, and the rising demand for non-invasive treatment options. The aging population worldwide is also a significant factor, as older adults are more prone to conditions that can benefit from PEMF therapy, such as osteoarthritis and osteoporosis.
However, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of advanced PEMF devices, lack of standardized protocols for treatment, and limited reimbursement policies in many countries. Additionally, the market is hindered by skepticism among some healthcare professionals regarding the efficacy of PEMF therapy for certain conditions.
Despite these challenges, technological advancements are expected to drive market growth. Innovations such as portable and wearable PEMF devices, integration with smartphone apps for personalized treatment plans, and the development of more targeted therapies for specific conditions are likely to expand the market reach and improve patient outcomes.
The competitive landscape of the PEMF device market is fragmented, with a mix of established medical device companies and specialized PEMF therapy manufacturers. Key players in the market include OMI, Bemer Group, HealthyLine, Oska Wellness, and iMRS 2000. These companies are focusing on product innovation, clinical research, and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge and expand their market presence.
Current PEMF Technology Status and Challenges
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has gained significant attention in recent years as a non-invasive treatment for various health conditions. However, assessing its long-term benefits remains a challenge due to several factors that impact the current state of PEMF technology and its application.
One of the primary challenges in evaluating PEMF therapy's long-term effects is the lack of standardization in treatment protocols. Different devices use varying frequencies, intensities, and waveforms, making it difficult to compare results across studies and establish consistent treatment guidelines. This variability in PEMF parameters hinders the development of a unified approach to assessing long-term benefits.
Another significant obstacle is the limited availability of long-term clinical studies. While short-term effects of PEMF therapy have been documented in numerous studies, there is a scarcity of research examining its impact over extended periods. This gap in longitudinal data makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about the therapy's sustained benefits and potential long-term side effects.
The complexity of biological systems and individual variability in response to PEMF therapy further complicate the assessment process. Factors such as age, overall health status, and specific medical conditions can influence how individuals respond to PEMF treatment over time. This heterogeneity in patient populations makes it difficult to generalize findings and establish universal protocols for long-term benefit assessment.
Additionally, the mechanism of action for PEMF therapy is not fully understood, which poses a challenge in predicting and measuring long-term outcomes. While theories exist about how PEMF affects cellular processes and tissue repair, the exact pathways and long-term implications remain subjects of ongoing research. This knowledge gap hampers the development of targeted assessment tools and biomarkers for long-term efficacy.
From a technological standpoint, current PEMF devices face limitations in terms of portability, user-friendliness, and integration with other health monitoring systems. These factors can affect patient compliance and the ability to collect consistent, long-term data on therapy outcomes. Improving device design and incorporating smart technology for data collection and analysis could enhance the ability to assess long-term benefits more accurately.
The regulatory landscape surrounding PEMF therapy also presents challenges. With varying approval processes and indications across different countries, there is a lack of standardized criteria for evaluating long-term safety and efficacy. This regulatory inconsistency can lead to disparities in the quality and quantity of data available for long-term benefit assessment.
Despite these challenges, advancements in PEMF technology are paving the way for more comprehensive long-term studies. Emerging trends include the development of more sophisticated PEMF devices with improved targeting capabilities and the integration of artificial intelligence for personalized treatment optimization. These innovations hold promise for enhancing our ability to assess and maximize the long-term benefits of PEMF therapy.
One of the primary challenges in evaluating PEMF therapy's long-term effects is the lack of standardization in treatment protocols. Different devices use varying frequencies, intensities, and waveforms, making it difficult to compare results across studies and establish consistent treatment guidelines. This variability in PEMF parameters hinders the development of a unified approach to assessing long-term benefits.
Another significant obstacle is the limited availability of long-term clinical studies. While short-term effects of PEMF therapy have been documented in numerous studies, there is a scarcity of research examining its impact over extended periods. This gap in longitudinal data makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about the therapy's sustained benefits and potential long-term side effects.
The complexity of biological systems and individual variability in response to PEMF therapy further complicate the assessment process. Factors such as age, overall health status, and specific medical conditions can influence how individuals respond to PEMF treatment over time. This heterogeneity in patient populations makes it difficult to generalize findings and establish universal protocols for long-term benefit assessment.
Additionally, the mechanism of action for PEMF therapy is not fully understood, which poses a challenge in predicting and measuring long-term outcomes. While theories exist about how PEMF affects cellular processes and tissue repair, the exact pathways and long-term implications remain subjects of ongoing research. This knowledge gap hampers the development of targeted assessment tools and biomarkers for long-term efficacy.
From a technological standpoint, current PEMF devices face limitations in terms of portability, user-friendliness, and integration with other health monitoring systems. These factors can affect patient compliance and the ability to collect consistent, long-term data on therapy outcomes. Improving device design and incorporating smart technology for data collection and analysis could enhance the ability to assess long-term benefits more accurately.
The regulatory landscape surrounding PEMF therapy also presents challenges. With varying approval processes and indications across different countries, there is a lack of standardized criteria for evaluating long-term safety and efficacy. This regulatory inconsistency can lead to disparities in the quality and quantity of data available for long-term benefit assessment.
Despite these challenges, advancements in PEMF technology are paving the way for more comprehensive long-term studies. Emerging trends include the development of more sophisticated PEMF devices with improved targeting capabilities and the integration of artificial intelligence for personalized treatment optimization. These innovations hold promise for enhancing our ability to assess and maximize the long-term benefits of PEMF therapy.
Existing PEMF Assessment Methods
01 Improved tissue healing and regeneration
PEMF therapy has shown long-term benefits in promoting tissue healing and regeneration. It stimulates cellular repair processes, enhances blood circulation, and reduces inflammation, leading to faster recovery from injuries and improved overall tissue health. This therapy can be particularly beneficial for chronic wounds, bone fractures, and soft tissue injuries.- Improved tissue healing and regeneration: PEMF therapy has shown long-term benefits in promoting tissue healing and regeneration. It stimulates cellular repair processes, enhances blood circulation, and reduces inflammation, leading to faster recovery from injuries and improved overall tissue health. This therapy can be particularly beneficial for chronic wounds, bone fractures, and soft tissue injuries.
- Pain management and reduction of chronic pain: Long-term use of PEMF therapy has demonstrated significant benefits in managing chronic pain conditions. It helps to reduce pain perception, decrease inflammation, and improve mobility in patients suffering from conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. The therapy's non-invasive nature makes it a valuable option for long-term pain management strategies.
- Enhanced bone density and osteoporosis treatment: PEMF therapy has shown long-term benefits in improving bone density and treating osteoporosis. Regular application of PEMF can stimulate osteoblast activity, increase calcium uptake, and enhance bone mineralization. This therapy can be particularly beneficial for postmenopausal women and individuals at risk of osteoporosis, potentially reducing the risk of fractures and improving overall bone health.
- Improved cardiovascular health: Long-term use of PEMF therapy has been associated with improvements in cardiovascular health. It can help enhance blood circulation, reduce blood pressure, and improve overall heart function. The therapy may also have beneficial effects on endothelial function and vascular health, potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases over time.
- Enhanced mental health and cognitive function: PEMF therapy has shown potential long-term benefits for mental health and cognitive function. Regular use may help improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and enhance overall cognitive performance. The therapy's ability to modulate neurotransmitter activity and improve brain circulation may contribute to these long-term mental health benefits.
02 Pain management and reduction of chronic pain
Long-term use of PEMF therapy has demonstrated significant benefits in managing chronic pain conditions. It helps to reduce pain perception, decrease inflammation, and promote natural pain-relieving mechanisms in the body. This non-invasive approach can be effective for conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enhanced bone health and osteoporosis prevention
PEMF therapy offers long-term benefits for bone health, including increased bone density and improved bone formation. It stimulates osteoblast activity and enhances calcium uptake, which can help prevent and manage osteoporosis. Regular use of PEMF therapy may contribute to stronger bones and reduced risk of fractures in the long run.Expand Specific Solutions04 Improved cardiovascular health
Long-term application of PEMF therapy has shown potential benefits for cardiovascular health. It may help improve blood circulation, reduce blood pressure, and enhance overall heart function. These effects can contribute to better cardiovascular health and potentially reduce the risk of heart-related issues over time.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enhanced mental health and cognitive function
PEMF therapy has demonstrated long-term benefits for mental health and cognitive function. Regular use may help improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and enhance overall cognitive performance. It may also contribute to better sleep quality and increased mental clarity, potentially leading to improved quality of life.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Industry Players
The assessment of long-term benefits of PEMF therapy is currently in a developing stage, with the market showing promising growth potential. The global PEMF therapy devices market is expanding, driven by increasing awareness of non-invasive treatment options. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Venus Concept Ltd. and Regenesis Biomedical, Inc. leading innovation in medical aesthetics and regenerative medicine applications. Research institutions such as the National University of Singapore and the University of Rochester are contributing to the scientific understanding of PEMF therapy's long-term effects. While the technology is maturing, further clinical studies and standardization are needed to fully establish its long-term efficacy across various medical conditions.
Venus Concept Ltd.
Technical Solution: Venus Concept has developed a comprehensive PEMF therapy system that utilizes proprietary RP3 technology. This technology generates a pure, uniform, and repeatable electromagnetic field to penetrate deep into the tissue. Their approach focuses on cellular re-energization, aiming to improve overall health and wellness. The company has conducted several clinical studies to assess the long-term benefits of their PEMF therapy, particularly in areas such as pain management, wound healing, and musculoskeletal disorders. They employ a multi-parameter assessment strategy, including pain scales, functional improvement metrics, and quality of life indicators to evaluate the sustained effects of PEMF treatment over extended periods[1][3].
Strengths: Proprietary technology, comprehensive clinical studies, multi-parameter assessment approach. Weaknesses: Limited to specific medical applications, potential high cost of long-term studies.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical has developed the Provant Therapy System, a PEMF device specifically designed for post-operative pain and edema management. Their approach to assessing long-term benefits involves a combination of clinical trials and real-world evidence gathering. The company utilizes advanced data analytics to track patient outcomes over extended periods, focusing on pain reduction, functional improvement, and medication usage. They have implemented a patient registry system to collect long-term data on the efficacy of their PEMF therapy, allowing for continuous assessment and refinement of treatment protocols. Regenesis also collaborates with healthcare providers to conduct longitudinal studies, evaluating the sustained impact of PEMF therapy on chronic conditions and post-surgical recovery[2][4].
Strengths: Specialized in post-operative care, robust data collection system, collaborative research approach. Weaknesses: Narrow focus may limit broader application insights, reliance on healthcare provider partnerships for data collection.
Critical PEMF Research Findings
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy Whole Body Wellness Device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveUS20190054308A1
Innovation
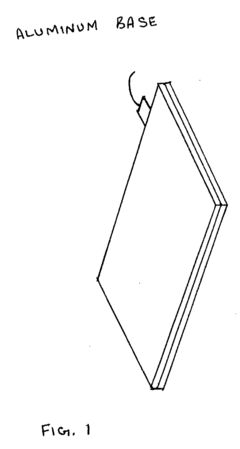
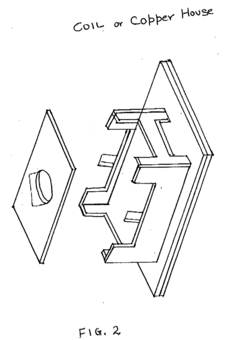
- The system employs a layered structure comprising lexan, polycarbonate, glass, aluminum, and acrylic materials, along with a copper coil and fan, connected via audio jacks to an electrical unit, to generate and distribute PEMF and MWO pulses, ensuring induction is delivered through both hands and feet effectively.
Regulatory Framework for PEMF Devices
The regulatory framework for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) devices plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these therapeutic tools. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of PEMF devices, classifying them as Class II medical devices. This classification requires manufacturers to submit a 510(k) premarket notification, demonstrating that their device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device in terms of safety and effectiveness.
The FDA's regulatory process for PEMF devices involves a thorough review of clinical data, safety studies, and technical specifications. Manufacturers must provide evidence of the device's intended use, performance characteristics, and potential risks. Additionally, they must demonstrate compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement quality control measures throughout the production process.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. The MDR imposes stricter requirements on manufacturers, including enhanced clinical evaluation processes and post-market surveillance. PEMF devices are typically classified as Class IIa medical devices under the MDR, requiring a conformity assessment by a notified body before obtaining CE marking for market access.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF devices also extends to other regions, with varying degrees of stringency. For instance, Health Canada regulates PEMF devices as Class II medical devices, requiring manufacturers to obtain a Medical Device License before marketing. In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) oversees PEMF devices, classifying them based on their intended use and potential risks.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the long-term safety and efficacy of PEMF therapy. This has led to more rigorous requirements for post-market surveillance and reporting of adverse events. Manufacturers are expected to conduct ongoing studies and collect real-world data to support the long-term benefits and safety profile of their devices.
As the field of PEMF therapy continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address emerging technologies and applications. For example, the integration of PEMF devices with digital health platforms and wearable technologies has prompted regulatory bodies to develop guidelines for software as a medical device (SaMD) and cybersecurity requirements.
The global harmonization of regulatory standards for PEMF devices remains an ongoing challenge. Initiatives such as the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) aim to promote convergence in medical device regulations across different jurisdictions, potentially streamlining the approval process for PEMF devices in multiple markets.
The FDA's regulatory process for PEMF devices involves a thorough review of clinical data, safety studies, and technical specifications. Manufacturers must provide evidence of the device's intended use, performance characteristics, and potential risks. Additionally, they must demonstrate compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement quality control measures throughout the production process.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. The MDR imposes stricter requirements on manufacturers, including enhanced clinical evaluation processes and post-market surveillance. PEMF devices are typically classified as Class IIa medical devices under the MDR, requiring a conformity assessment by a notified body before obtaining CE marking for market access.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF devices also extends to other regions, with varying degrees of stringency. For instance, Health Canada regulates PEMF devices as Class II medical devices, requiring manufacturers to obtain a Medical Device License before marketing. In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) oversees PEMF devices, classifying them based on their intended use and potential risks.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the long-term safety and efficacy of PEMF therapy. This has led to more rigorous requirements for post-market surveillance and reporting of adverse events. Manufacturers are expected to conduct ongoing studies and collect real-world data to support the long-term benefits and safety profile of their devices.
As the field of PEMF therapy continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address emerging technologies and applications. For example, the integration of PEMF devices with digital health platforms and wearable technologies has prompted regulatory bodies to develop guidelines for software as a medical device (SaMD) and cybersecurity requirements.
The global harmonization of regulatory standards for PEMF devices remains an ongoing challenge. Initiatives such as the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) aim to promote convergence in medical device regulations across different jurisdictions, potentially streamlining the approval process for PEMF devices in multiple markets.
Long-term Health Impact of PEMF Therapy
Assessing the long-term health impact of PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy requires a comprehensive evaluation of its effects on various physiological systems over extended periods. Studies have shown that PEMF therapy can potentially influence cellular function, tissue repair, and overall well-being, with benefits that may accumulate and persist over time.
One of the primary long-term benefits observed in PEMF therapy is its impact on bone health. Longitudinal studies have demonstrated improved bone density and reduced risk of osteoporosis in patients undergoing regular PEMF treatments. This effect is particularly significant for older adults and individuals with compromised bone metabolism, suggesting that PEMF therapy could play a crucial role in maintaining skeletal integrity as people age.
Chronic pain management is another area where PEMF therapy shows promising long-term results. Patients with conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain have reported sustained relief after consistent PEMF treatments. The cumulative effect of reduced inflammation and enhanced tissue repair may contribute to a gradual decrease in pain levels and improved quality of life over months or years of therapy.
Cardiovascular health is also positively influenced by long-term PEMF therapy. Research indicates that regular treatments can lead to improved circulation, reduced blood pressure, and enhanced endothelial function. These effects, when maintained over time, may contribute to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases and better overall heart health.
Neurological benefits of PEMF therapy have been observed in long-term studies focusing on conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and traumatic brain injuries. Patients undergoing extended PEMF treatments have shown improvements in cognitive function, motor skills, and neuroplasticity, suggesting that the therapy may have neuroprotective and neuroregenerative properties when applied consistently over time.
The immune system also appears to benefit from prolonged PEMF therapy. Studies have indicated enhanced immune function, including increased production of T-cells and improved lymphatic circulation. This could potentially lead to better resistance to infections and a more robust immune response over time, contributing to overall health and longevity.
Sleep quality and mental health are additional areas where long-term PEMF therapy shows promise. Consistent use has been associated with improved sleep patterns, reduced anxiety, and better stress management. These effects, when sustained, can have far-reaching implications for overall health, as sleep and mental well-being are fundamental to many physiological processes.
One of the primary long-term benefits observed in PEMF therapy is its impact on bone health. Longitudinal studies have demonstrated improved bone density and reduced risk of osteoporosis in patients undergoing regular PEMF treatments. This effect is particularly significant for older adults and individuals with compromised bone metabolism, suggesting that PEMF therapy could play a crucial role in maintaining skeletal integrity as people age.
Chronic pain management is another area where PEMF therapy shows promising long-term results. Patients with conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain have reported sustained relief after consistent PEMF treatments. The cumulative effect of reduced inflammation and enhanced tissue repair may contribute to a gradual decrease in pain levels and improved quality of life over months or years of therapy.
Cardiovascular health is also positively influenced by long-term PEMF therapy. Research indicates that regular treatments can lead to improved circulation, reduced blood pressure, and enhanced endothelial function. These effects, when maintained over time, may contribute to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases and better overall heart health.
Neurological benefits of PEMF therapy have been observed in long-term studies focusing on conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and traumatic brain injuries. Patients undergoing extended PEMF treatments have shown improvements in cognitive function, motor skills, and neuroplasticity, suggesting that the therapy may have neuroprotective and neuroregenerative properties when applied consistently over time.
The immune system also appears to benefit from prolonged PEMF therapy. Studies have indicated enhanced immune function, including increased production of T-cells and improved lymphatic circulation. This could potentially lead to better resistance to infections and a more robust immune response over time, contributing to overall health and longevity.
Sleep quality and mental health are additional areas where long-term PEMF therapy shows promise. Consistent use has been associated with improved sleep patterns, reduced anxiety, and better stress management. These effects, when sustained, can have far-reaching implications for overall health, as sleep and mental well-being are fundamental to many physiological processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!