How to Enhance Alkyl Catalyst Performance?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Catalyst Evolution and Objectives
Alkyl catalysts have played a pivotal role in the chemical industry for decades, revolutionizing various processes and enabling the production of essential compounds. The evolution of these catalysts has been marked by continuous improvements in performance, selectivity, and efficiency. From their initial discovery in the mid-20th century to the present day, alkyl catalysts have undergone significant transformations, driven by the need for more sustainable and economically viable chemical processes.
The journey of alkyl catalyst development began with simple organometallic compounds, which demonstrated the ability to catalyze alkylation reactions. As research progressed, scientists discovered more complex and effective catalyst systems, incorporating transition metals and tailored ligands. This evolution led to the development of highly active and selective catalysts capable of promoting a wide range of reactions, including polymerization, hydroformylation, and cross-coupling.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing the performance of alkyl catalysts to meet the growing demands of modern industry. Key objectives in this pursuit include increasing catalytic activity, improving selectivity, extending catalyst lifetime, and reducing environmental impact. Researchers are exploring various strategies to achieve these goals, such as fine-tuning catalyst structure, optimizing reaction conditions, and developing novel support materials.
One of the primary objectives in alkyl catalyst enhancement is to increase their turnover frequency and number, allowing for more efficient and cost-effective processes. This involves designing catalysts with improved stability under harsh reaction conditions and the ability to maintain high activity over extended periods. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on developing catalysts that can operate at lower temperatures and pressures, reducing energy consumption and improving overall process sustainability.
Another critical objective is to enhance the selectivity of alkyl catalysts, enabling the production of desired products with minimal side reactions and waste generation. This requires a deep understanding of reaction mechanisms and the ability to control the electronic and steric properties of the catalyst. Researchers are investigating the use of advanced computational methods and high-throughput experimentation to accelerate the discovery and optimization of highly selective catalysts.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, there is an increasing focus on developing greener alkyl catalysts. This includes exploring bio-inspired catalysts, utilizing abundant and non-toxic metals, and designing catalysts that can operate in environmentally benign solvents or solvent-free conditions. The ultimate goal is to create catalytic systems that align with the principles of green chemistry, minimizing waste and reducing the carbon footprint of chemical processes.
In conclusion, the evolution of alkyl catalysts has been driven by the continuous pursuit of enhanced performance and sustainability. The objectives for future development are clear: to create more active, selective, and environmentally friendly catalysts that can meet the challenges of modern chemical manufacturing while addressing global sustainability goals.
The journey of alkyl catalyst development began with simple organometallic compounds, which demonstrated the ability to catalyze alkylation reactions. As research progressed, scientists discovered more complex and effective catalyst systems, incorporating transition metals and tailored ligands. This evolution led to the development of highly active and selective catalysts capable of promoting a wide range of reactions, including polymerization, hydroformylation, and cross-coupling.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing the performance of alkyl catalysts to meet the growing demands of modern industry. Key objectives in this pursuit include increasing catalytic activity, improving selectivity, extending catalyst lifetime, and reducing environmental impact. Researchers are exploring various strategies to achieve these goals, such as fine-tuning catalyst structure, optimizing reaction conditions, and developing novel support materials.
One of the primary objectives in alkyl catalyst enhancement is to increase their turnover frequency and number, allowing for more efficient and cost-effective processes. This involves designing catalysts with improved stability under harsh reaction conditions and the ability to maintain high activity over extended periods. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on developing catalysts that can operate at lower temperatures and pressures, reducing energy consumption and improving overall process sustainability.
Another critical objective is to enhance the selectivity of alkyl catalysts, enabling the production of desired products with minimal side reactions and waste generation. This requires a deep understanding of reaction mechanisms and the ability to control the electronic and steric properties of the catalyst. Researchers are investigating the use of advanced computational methods and high-throughput experimentation to accelerate the discovery and optimization of highly selective catalysts.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, there is an increasing focus on developing greener alkyl catalysts. This includes exploring bio-inspired catalysts, utilizing abundant and non-toxic metals, and designing catalysts that can operate in environmentally benign solvents or solvent-free conditions. The ultimate goal is to create catalytic systems that align with the principles of green chemistry, minimizing waste and reducing the carbon footprint of chemical processes.
In conclusion, the evolution of alkyl catalysts has been driven by the continuous pursuit of enhanced performance and sustainability. The objectives for future development are clear: to create more active, selective, and environmentally friendly catalysts that can meet the challenges of modern chemical manufacturing while addressing global sustainability goals.
Market Demand Analysis for Enhanced Catalysts
The market demand for enhanced alkyl catalysts has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing need for more efficient and sustainable chemical processes across various industries. The global catalyst market, valued at $33.9 billion in 2020, is projected to reach $47.9 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%. Within this market, alkyl catalysts play a crucial role in numerous applications, including petrochemicals, polymers, and fine chemicals production.
The push for improved alkyl catalyst performance is primarily fueled by the petrochemical industry's quest for higher yields, reduced energy consumption, and minimized waste generation. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, there is a growing emphasis on developing catalysts that can operate efficiently under milder conditions, thereby reducing the overall carbon footprint of chemical processes.
In the polymer industry, enhanced alkyl catalysts are sought after for their potential to improve the quality and properties of plastics, elastomers, and other synthetic materials. The demand for high-performance polymers with specific characteristics, such as increased durability, heat resistance, and recyclability, is driving research into more advanced catalytic systems.
The fine chemicals sector, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, is another key driver of the demand for enhanced alkyl catalysts. These industries require catalysts capable of facilitating complex, multi-step syntheses with high selectivity and yield. The ability to produce chiral compounds efficiently is particularly valuable in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where stereochemistry plays a crucial role in drug efficacy and safety.
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are also shaping the market demand for improved alkyl catalysts. There is a growing focus on developing catalysts that can enable the use of renewable feedstocks, such as biomass-derived materials, in chemical production. Additionally, catalysts that can facilitate the recycling and upcycling of plastics are gaining attention as part of the circular economy initiatives.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric vehicles has created new opportunities for alkyl catalyst applications in battery technologies. Enhanced catalysts are needed for the production of advanced battery materials and the recycling of spent batteries, driving further research and development in this area.
In conclusion, the market demand for enhanced alkyl catalysts is robust and multifaceted, spanning across various industries and applications. The drive for improved efficiency, sustainability, and product quality is expected to continue fueling innovation in this field, presenting significant opportunities for catalyst developers and manufacturers in the coming years.
The push for improved alkyl catalyst performance is primarily fueled by the petrochemical industry's quest for higher yields, reduced energy consumption, and minimized waste generation. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, there is a growing emphasis on developing catalysts that can operate efficiently under milder conditions, thereby reducing the overall carbon footprint of chemical processes.
In the polymer industry, enhanced alkyl catalysts are sought after for their potential to improve the quality and properties of plastics, elastomers, and other synthetic materials. The demand for high-performance polymers with specific characteristics, such as increased durability, heat resistance, and recyclability, is driving research into more advanced catalytic systems.
The fine chemicals sector, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, is another key driver of the demand for enhanced alkyl catalysts. These industries require catalysts capable of facilitating complex, multi-step syntheses with high selectivity and yield. The ability to produce chiral compounds efficiently is particularly valuable in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where stereochemistry plays a crucial role in drug efficacy and safety.
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are also shaping the market demand for improved alkyl catalysts. There is a growing focus on developing catalysts that can enable the use of renewable feedstocks, such as biomass-derived materials, in chemical production. Additionally, catalysts that can facilitate the recycling and upcycling of plastics are gaining attention as part of the circular economy initiatives.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric vehicles has created new opportunities for alkyl catalyst applications in battery technologies. Enhanced catalysts are needed for the production of advanced battery materials and the recycling of spent batteries, driving further research and development in this area.
In conclusion, the market demand for enhanced alkyl catalysts is robust and multifaceted, spanning across various industries and applications. The drive for improved efficiency, sustainability, and product quality is expected to continue fueling innovation in this field, presenting significant opportunities for catalyst developers and manufacturers in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Catalyst Technology
Alkyl catalysts play a crucial role in various industrial processes, particularly in organic synthesis and petrochemical applications. However, the technology faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and optimal performance.
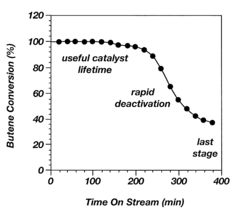
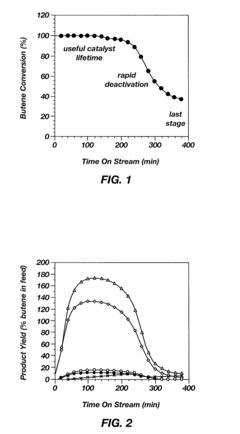
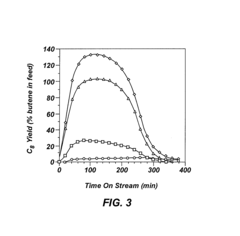
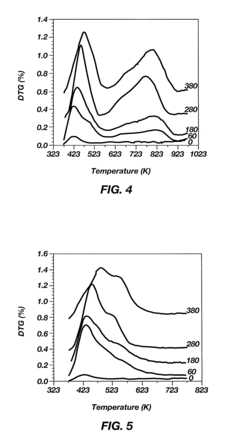
One of the primary challenges is catalyst stability. Alkyl catalysts often suffer from rapid deactivation due to various factors, including coking, sintering, and poisoning. This instability leads to reduced catalytic activity over time, necessitating frequent catalyst replacement and increasing operational costs. Developing more stable alkyl catalysts that can withstand harsh reaction conditions for extended periods remains a key focus area for researchers.
Another major challenge is selectivity. While alkyl catalysts can facilitate numerous reactions, achieving high selectivity towards desired products is often difficult. Side reactions and the formation of unwanted by-products can significantly reduce the efficiency of the catalytic process. Enhancing the selectivity of alkyl catalysts without compromising their activity is a delicate balance that researchers are striving to achieve.
The issue of catalyst recovery and recyclability also poses a significant challenge. Many alkyl catalysts are homogeneous, making their separation from the reaction mixture and subsequent reuse problematic. This not only increases the cost of the catalytic process but also raises environmental concerns due to potential metal contamination in the final products. Developing efficient methods for catalyst recovery or designing heterogeneous alkyl catalysts with comparable activity to their homogeneous counterparts is an active area of research.
Furthermore, the limited substrate scope of many alkyl catalysts restricts their applicability across a wide range of reactions. Expanding the substrate scope while maintaining high catalytic performance is crucial for broadening the utility of alkyl catalysts in various industrial processes.
The scalability of alkyl catalyst technology also presents challenges. While many catalytic systems show promising results at the laboratory scale, translating these successes to industrial-scale applications often encounters difficulties. Issues such as mass transfer limitations, heat management, and maintaining catalyst performance at larger scales need to be addressed to facilitate the widespread adoption of alkyl catalyst technology.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of alkyl catalysts remains a significant hurdle. Many high-performance alkyl catalysts rely on expensive noble metals or complex ligand systems, making them economically unfeasible for large-scale industrial applications. Developing equally effective catalysts based on more abundant and less expensive materials is a key challenge that researchers are actively pursuing.
One of the primary challenges is catalyst stability. Alkyl catalysts often suffer from rapid deactivation due to various factors, including coking, sintering, and poisoning. This instability leads to reduced catalytic activity over time, necessitating frequent catalyst replacement and increasing operational costs. Developing more stable alkyl catalysts that can withstand harsh reaction conditions for extended periods remains a key focus area for researchers.
Another major challenge is selectivity. While alkyl catalysts can facilitate numerous reactions, achieving high selectivity towards desired products is often difficult. Side reactions and the formation of unwanted by-products can significantly reduce the efficiency of the catalytic process. Enhancing the selectivity of alkyl catalysts without compromising their activity is a delicate balance that researchers are striving to achieve.
The issue of catalyst recovery and recyclability also poses a significant challenge. Many alkyl catalysts are homogeneous, making their separation from the reaction mixture and subsequent reuse problematic. This not only increases the cost of the catalytic process but also raises environmental concerns due to potential metal contamination in the final products. Developing efficient methods for catalyst recovery or designing heterogeneous alkyl catalysts with comparable activity to their homogeneous counterparts is an active area of research.
Furthermore, the limited substrate scope of many alkyl catalysts restricts their applicability across a wide range of reactions. Expanding the substrate scope while maintaining high catalytic performance is crucial for broadening the utility of alkyl catalysts in various industrial processes.
The scalability of alkyl catalyst technology also presents challenges. While many catalytic systems show promising results at the laboratory scale, translating these successes to industrial-scale applications often encounters difficulties. Issues such as mass transfer limitations, heat management, and maintaining catalyst performance at larger scales need to be addressed to facilitate the widespread adoption of alkyl catalyst technology.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of alkyl catalysts remains a significant hurdle. Many high-performance alkyl catalysts rely on expensive noble metals or complex ligand systems, making them economically unfeasible for large-scale industrial applications. Developing equally effective catalysts based on more abundant and less expensive materials is a key challenge that researchers are actively pursuing.
Existing Alkyl Catalyst Enhancement Methods
01 Alkyl catalyst composition and structure
Alkyl catalysts are designed with specific compositions and structures to enhance their performance. These catalysts often include metal components and support materials that are carefully selected to optimize catalytic activity, selectivity, and stability. The structure of the catalyst, including particle size and surface area, plays a crucial role in determining its overall performance.- Alkyl catalyst composition and structure: Various alkyl catalysts are developed with specific compositions and structures to enhance performance. These catalysts often include metal components and support materials, designed to improve activity, selectivity, and stability in different chemical reactions.
- Catalyst performance in olefin polymerization: Alkyl catalysts play a crucial role in olefin polymerization processes. Research focuses on improving catalyst efficiency, controlling polymer properties, and enhancing the overall polymerization performance through catalyst modifications and process optimizations.
- Catalyst regeneration and lifetime extension: Methods for regenerating and extending the lifetime of alkyl catalysts are developed to improve their long-term performance and economic viability. These techniques involve removing deactivating species, restoring active sites, and maintaining catalyst activity over multiple cycles.
- Environmental and sustainable catalysis: Research is conducted on developing environmentally friendly and sustainable alkyl catalysts. This includes the use of non-toxic materials, improved atom efficiency, and catalysts that operate under milder conditions to reduce energy consumption and waste generation.
- Catalyst performance in specific chemical processes: Alkyl catalysts are tailored for specific chemical processes to enhance their performance. This includes optimizing catalysts for reactions such as alkylation, isomerization, and hydrogenation, focusing on improving yield, selectivity, and reaction rates in these processes.
02 Catalyst performance in alkylation reactions
Alkyl catalysts are widely used in various alkylation reactions, such as the production of alkylbenzenes or alkylation of olefins. The performance of these catalysts is evaluated based on factors like conversion rate, product selectivity, and catalyst lifetime. Optimizing reaction conditions and catalyst properties can significantly improve the efficiency of alkylation processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Catalyst regeneration and lifetime extension
Extending the lifetime of alkyl catalysts is crucial for improving their overall performance and economic viability. Various regeneration techniques have been developed to restore catalyst activity and selectivity after deactivation. These methods may involve thermal treatments, chemical treatments, or a combination of both to remove coke deposits and other contaminants from the catalyst surface.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel alkyl catalyst development
Research efforts are focused on developing novel alkyl catalysts with improved performance characteristics. This includes the exploration of new catalyst materials, such as bimetallic or multimetallic systems, as well as the incorporation of promoters or modifiers to enhance catalytic activity and selectivity. Advanced synthesis techniques are employed to create catalysts with tailored properties for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process optimization for alkyl catalyst performance
Optimizing process conditions is essential for maximizing alkyl catalyst performance. This involves adjusting parameters such as temperature, pressure, feed composition, and residence time to achieve the desired product distribution and catalyst efficiency. Advanced process control strategies and modeling techniques are employed to maintain optimal operating conditions and predict catalyst behavior under various scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Catalyst Industry
The competition landscape for enhancing alkyl catalyst performance is characterized by a mature market with significant ongoing research and development efforts. The global catalyst market, valued at over $30 billion, is experiencing steady growth driven by increasing demand in petrochemicals and environmental applications. Major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Shell Oil Co., and ExxonMobil Chemical Patents Inc. are at the forefront of innovation, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and industry expertise. Academic institutions such as China Petroleum University Beijing and the University of Tokyo collaborate with industry leaders, contributing to technological advancements. The field is highly competitive, with companies like BASF Corp. and Bayer AG also making significant strides in catalyst technology development.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a novel alkylation catalyst system that combines solid acid catalysts with ionic liquids. This hybrid system enhances the catalytic performance by increasing the active sites and improving mass transfer. The solid acid component provides a high surface area and strong acidity, while the ionic liquid acts as a co-catalyst and solvent, facilitating the alkylation reaction. Sinopec's research has shown that this system can achieve conversion rates of up to 95% and selectivity exceeding 90% for target alkylate products[1][3]. The catalyst also demonstrates improved stability, with a lifespan of over 1000 hours without significant deactivation[2].
Strengths: High conversion rates and selectivity, improved catalyst stability, and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional liquid acid catalysts. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs and complexity in catalyst preparation and regeneration.
Shell Oil Co.
Technical Solution: Shell Oil Co. has pioneered the development of a next-generation solid acid alkylation catalyst technology. Their approach focuses on a highly porous, structured catalyst material that maximizes the accessible surface area for reactants. The catalyst incorporates advanced metal oxides and zeolites, engineered at the nanoscale to optimize acid site distribution and strength. Shell's proprietary manufacturing process ensures uniform catalyst particle size and pore structure, leading to enhanced mass transfer and reduced diffusion limitations. In pilot plant studies, this catalyst has demonstrated alkylate yields of up to 98% and octane numbers consistently above 96 RON[4]. Additionally, Shell has implemented an in-situ regeneration process that extends catalyst life by up to 50% compared to conventional systems[5].
Strengths: High alkylate yield and octane number, extended catalyst lifespan, and potential for continuous operation. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs and potential challenges in scaling up to commercial production.
Innovative Approaches in Catalyst Design
Enhancement of alkylation catalysts for improved supercritical fluid regeneration
PatentInactiveUS7858069B2
Innovation
- The method involves modifying the alkylation catalyst by selectively poisoning strongly acidic active sites, adjusting the pore size distribution, and reducing the number of strongly acidic sites to prevent the formation of condensed hydrocarbon species, thereby enhancing regeneration efficiency through supercritical fluid regeneration.
Process for the production of alkenyl esters of lower carboxylic acids and process for the production of alkenyl alcohols
PatentInactiveEP1641738A1
Innovation
- A process involving a catalyst with a support containing palladium, alkali metal or alkaline earth metal, and Group 11 elements, where the outflow of alkali metal and alkaline earth metal components is controlled and compensated, maintaining catalyst activity and stability over time.
Environmental Impact of Alkyl Catalysts
The environmental impact of alkyl catalysts is a critical consideration in their development and application. These catalysts, while essential for numerous industrial processes, can have significant effects on ecosystems and human health if not properly managed. The primary environmental concerns associated with alkyl catalysts include air and water pollution, soil contamination, and potential long-term ecological disruptions.
Alkyl catalysts often involve the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals, which can be released into the atmosphere during production and use. These emissions contribute to air quality degradation, potentially leading to smog formation and respiratory issues in affected areas. Furthermore, the production and disposal of alkyl catalysts may result in the release of harmful substances into water systems, posing risks to aquatic life and potentially contaminating drinking water sources.
Soil contamination is another significant environmental concern. Improper handling or disposal of alkyl catalysts can lead to soil pollution, affecting plant growth and soil microorganisms. This contamination can persist for extended periods, potentially entering the food chain and causing long-term ecological damage.
However, recent advancements in alkyl catalyst technology have focused on mitigating these environmental impacts. Green chemistry principles are increasingly being applied to catalyst design, emphasizing the use of less toxic materials and more environmentally benign processes. For instance, researchers are developing water-soluble alkyl catalysts that reduce the need for organic solvents, thereby minimizing VOC emissions and improving overall environmental performance.
Recycling and regeneration of alkyl catalysts have also become key strategies in reducing their environmental footprint. By extending the life cycle of these catalysts, industries can significantly decrease waste generation and resource consumption. Advanced recovery techniques are being developed to efficiently separate and purify used catalysts, allowing for their reuse in subsequent reactions.
Moreover, the shift towards more sustainable alkyl catalysts is driving innovation in biocatalysis. Enzyme-based catalysts derived from biological sources offer a promising alternative, often operating under milder conditions and producing fewer harmful by-products. These bio-inspired catalysts not only reduce environmental impact but also open up new possibilities for more selective and efficient chemical transformations.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, the development of eco-friendly alkyl catalysts is becoming a priority for both researchers and industry. This focus on sustainability is not only addressing immediate environmental concerns but also paving the way for more responsible and efficient chemical processes in the future.
Alkyl catalysts often involve the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals, which can be released into the atmosphere during production and use. These emissions contribute to air quality degradation, potentially leading to smog formation and respiratory issues in affected areas. Furthermore, the production and disposal of alkyl catalysts may result in the release of harmful substances into water systems, posing risks to aquatic life and potentially contaminating drinking water sources.
Soil contamination is another significant environmental concern. Improper handling or disposal of alkyl catalysts can lead to soil pollution, affecting plant growth and soil microorganisms. This contamination can persist for extended periods, potentially entering the food chain and causing long-term ecological damage.
However, recent advancements in alkyl catalyst technology have focused on mitigating these environmental impacts. Green chemistry principles are increasingly being applied to catalyst design, emphasizing the use of less toxic materials and more environmentally benign processes. For instance, researchers are developing water-soluble alkyl catalysts that reduce the need for organic solvents, thereby minimizing VOC emissions and improving overall environmental performance.
Recycling and regeneration of alkyl catalysts have also become key strategies in reducing their environmental footprint. By extending the life cycle of these catalysts, industries can significantly decrease waste generation and resource consumption. Advanced recovery techniques are being developed to efficiently separate and purify used catalysts, allowing for their reuse in subsequent reactions.
Moreover, the shift towards more sustainable alkyl catalysts is driving innovation in biocatalysis. Enzyme-based catalysts derived from biological sources offer a promising alternative, often operating under milder conditions and producing fewer harmful by-products. These bio-inspired catalysts not only reduce environmental impact but also open up new possibilities for more selective and efficient chemical transformations.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, the development of eco-friendly alkyl catalysts is becoming a priority for both researchers and industry. This focus on sustainability is not only addressing immediate environmental concerns but also paving the way for more responsible and efficient chemical processes in the future.
Economic Feasibility of Catalyst Improvements
The economic feasibility of catalyst improvements in alkyl catalysis is a critical consideration for industrial applications. Enhancing alkyl catalyst performance can lead to significant cost savings and increased productivity, making it an attractive prospect for chemical manufacturers. However, the economic viability of such improvements must be carefully evaluated against the investment required for research, development, and implementation.
One of the primary economic drivers for catalyst improvements is the potential for increased yield and selectivity. By enhancing catalyst performance, manufacturers can produce more desired products with fewer raw materials, reducing overall production costs. This efficiency gain can translate into substantial savings, especially in large-scale operations where even small improvements can have a significant impact on the bottom line.
Another economic benefit of improved alkyl catalysts is the potential for reduced energy consumption. Catalysts that operate more efficiently at lower temperatures or pressures can lead to decreased energy requirements, resulting in lower operational costs and a reduced carbon footprint. This dual benefit of cost savings and environmental sustainability can provide a competitive advantage in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The longevity of catalysts is also a crucial factor in economic feasibility. Developing catalysts with extended lifespans can reduce the frequency of catalyst replacement, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. This aspect is particularly important in continuous production processes where interruptions can be costly.
However, the economic benefits must be weighed against the costs of developing and implementing new catalyst technologies. Research and development expenses, including laboratory equipment, materials, and personnel, can be substantial. Additionally, scaling up from laboratory to industrial production may require significant capital investment in new equipment or modifications to existing processes.
The time-to-market for new catalyst technologies is another critical economic consideration. Lengthy development cycles can delay the realization of benefits and may impact the overall return on investment. Companies must assess whether the projected improvements justify the time and resources required for development and implementation.
Market dynamics also play a role in the economic feasibility of catalyst improvements. The demand for the end products, price volatility of raw materials, and competitive landscape all influence the potential return on investment. A thorough market analysis is essential to ensure that the improved catalyst technology aligns with current and future market needs.
In conclusion, while the potential economic benefits of enhancing alkyl catalyst performance are significant, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is crucial. Companies must carefully evaluate the projected improvements in yield, energy efficiency, and catalyst longevity against the investment required and market conditions to determine the true economic feasibility of catalyst improvements.
One of the primary economic drivers for catalyst improvements is the potential for increased yield and selectivity. By enhancing catalyst performance, manufacturers can produce more desired products with fewer raw materials, reducing overall production costs. This efficiency gain can translate into substantial savings, especially in large-scale operations where even small improvements can have a significant impact on the bottom line.
Another economic benefit of improved alkyl catalysts is the potential for reduced energy consumption. Catalysts that operate more efficiently at lower temperatures or pressures can lead to decreased energy requirements, resulting in lower operational costs and a reduced carbon footprint. This dual benefit of cost savings and environmental sustainability can provide a competitive advantage in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The longevity of catalysts is also a crucial factor in economic feasibility. Developing catalysts with extended lifespans can reduce the frequency of catalyst replacement, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. This aspect is particularly important in continuous production processes where interruptions can be costly.
However, the economic benefits must be weighed against the costs of developing and implementing new catalyst technologies. Research and development expenses, including laboratory equipment, materials, and personnel, can be substantial. Additionally, scaling up from laboratory to industrial production may require significant capital investment in new equipment or modifications to existing processes.
The time-to-market for new catalyst technologies is another critical economic consideration. Lengthy development cycles can delay the realization of benefits and may impact the overall return on investment. Companies must assess whether the projected improvements justify the time and resources required for development and implementation.
Market dynamics also play a role in the economic feasibility of catalyst improvements. The demand for the end products, price volatility of raw materials, and competitive landscape all influence the potential return on investment. A thorough market analysis is essential to ensure that the improved catalyst technology aligns with current and future market needs.
In conclusion, while the potential economic benefits of enhancing alkyl catalyst performance are significant, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is crucial. Companies must carefully evaluate the projected improvements in yield, energy efficiency, and catalyst longevity against the investment required and market conditions to determine the true economic feasibility of catalyst improvements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!