How to Evaluate Alkyl Impact on Biocompatible Materials?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl-Biocompatibility Evaluation Background
The evaluation of alkyl impact on biocompatible materials has become increasingly important in the field of biomaterials and medical device development. This area of research focuses on understanding how the presence and characteristics of alkyl groups affect the overall biocompatibility of materials intended for use in biological systems. The background of this evaluation stems from the growing need for advanced materials that can seamlessly integrate with living tissues without causing adverse reactions or compromising their intended functions.
Historically, the development of biocompatible materials has been driven by the demand for improved medical implants, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering scaffolds. As researchers delved deeper into material-tissue interactions, they recognized the significant role that surface chemistry plays in determining a material's biocompatibility. Alkyl groups, being ubiquitous in organic compounds and polymers, emerged as a critical factor influencing these interactions.
The evolution of this field has been marked by several key milestones. Early studies primarily focused on the hydrophobic nature of alkyl groups and their impact on protein adsorption and cell adhesion. As analytical techniques advanced, researchers began to investigate more nuanced effects, such as the influence of alkyl chain length, branching, and density on cellular responses and immune system activation.
Recent years have seen a shift towards a more comprehensive understanding of alkyl-biocompatibility relationships. This includes exploring the interplay between alkyl groups and other surface functionalities, as well as their role in modulating the release of bioactive compounds from materials. The advent of high-throughput screening methods and computational modeling has accelerated the pace of discovery, allowing researchers to systematically evaluate a wide range of alkyl modifications and their biological effects.
The current landscape of alkyl-biocompatibility evaluation encompasses a multidisciplinary approach, combining elements of materials science, surface chemistry, cell biology, and immunology. Researchers are now focusing on developing standardized protocols for assessing the impact of alkyl groups on various aspects of biocompatibility, including protein adsorption kinetics, cell adhesion strength, inflammatory responses, and long-term tissue integration.
As the field continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the observed biological responses to alkyl-modified surfaces. This deeper mechanistic insight is crucial for designing next-generation biocompatible materials with tailored surface properties that can meet the specific requirements of diverse biomedical applications.
Historically, the development of biocompatible materials has been driven by the demand for improved medical implants, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering scaffolds. As researchers delved deeper into material-tissue interactions, they recognized the significant role that surface chemistry plays in determining a material's biocompatibility. Alkyl groups, being ubiquitous in organic compounds and polymers, emerged as a critical factor influencing these interactions.
The evolution of this field has been marked by several key milestones. Early studies primarily focused on the hydrophobic nature of alkyl groups and their impact on protein adsorption and cell adhesion. As analytical techniques advanced, researchers began to investigate more nuanced effects, such as the influence of alkyl chain length, branching, and density on cellular responses and immune system activation.
Recent years have seen a shift towards a more comprehensive understanding of alkyl-biocompatibility relationships. This includes exploring the interplay between alkyl groups and other surface functionalities, as well as their role in modulating the release of bioactive compounds from materials. The advent of high-throughput screening methods and computational modeling has accelerated the pace of discovery, allowing researchers to systematically evaluate a wide range of alkyl modifications and their biological effects.
The current landscape of alkyl-biocompatibility evaluation encompasses a multidisciplinary approach, combining elements of materials science, surface chemistry, cell biology, and immunology. Researchers are now focusing on developing standardized protocols for assessing the impact of alkyl groups on various aspects of biocompatibility, including protein adsorption kinetics, cell adhesion strength, inflammatory responses, and long-term tissue integration.
As the field continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the observed biological responses to alkyl-modified surfaces. This deeper mechanistic insight is crucial for designing next-generation biocompatible materials with tailored surface properties that can meet the specific requirements of diverse biomedical applications.
Market Analysis for Alkylated Biomaterials
The market for alkylated biomaterials has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for biocompatible materials in various industries, particularly in healthcare and medical devices. The global biocompatible materials market, which includes alkylated biomaterials, was valued at approximately $14.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $29.7 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 10.5% during the forecast period.
Alkylated biomaterials have gained traction due to their enhanced properties, such as improved biocompatibility, reduced immunogenicity, and increased stability. These materials find applications in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, implantable devices, and wound healing products. The healthcare sector remains the primary consumer of alkylated biomaterials, accounting for over 60% of the market share.
The North American region dominates the alkylated biomaterials market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high investment in research and development. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and growing awareness of advanced medical technologies.
Key factors driving the market growth include the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the increasing demand for minimally invasive surgical procedures. Additionally, the growing focus on personalized medicine and regenerative therapies has created new opportunities for alkylated biomaterials in tailored medical solutions.
However, the market faces challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements and the high cost associated with the development and manufacturing of alkylated biomaterials. These factors may hinder market growth to some extent, particularly in developing regions.
The competitive landscape of the alkylated biomaterials market is characterized by the presence of both established players and innovative start-ups. Major companies in this space are investing heavily in research and development to introduce novel products and gain a competitive edge. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry players are also becoming increasingly common, fostering innovation and accelerating product development.
In conclusion, the market for alkylated biomaterials presents significant opportunities for growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing applications in healthcare. As research continues to uncover new potential uses for these materials, the market is expected to expand further, with a focus on developing more sophisticated and tailored solutions for various medical applications.
Alkylated biomaterials have gained traction due to their enhanced properties, such as improved biocompatibility, reduced immunogenicity, and increased stability. These materials find applications in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, implantable devices, and wound healing products. The healthcare sector remains the primary consumer of alkylated biomaterials, accounting for over 60% of the market share.
The North American region dominates the alkylated biomaterials market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high investment in research and development. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and growing awareness of advanced medical technologies.
Key factors driving the market growth include the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the increasing demand for minimally invasive surgical procedures. Additionally, the growing focus on personalized medicine and regenerative therapies has created new opportunities for alkylated biomaterials in tailored medical solutions.
However, the market faces challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements and the high cost associated with the development and manufacturing of alkylated biomaterials. These factors may hinder market growth to some extent, particularly in developing regions.
The competitive landscape of the alkylated biomaterials market is characterized by the presence of both established players and innovative start-ups. Major companies in this space are investing heavily in research and development to introduce novel products and gain a competitive edge. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry players are also becoming increasingly common, fostering innovation and accelerating product development.
In conclusion, the market for alkylated biomaterials presents significant opportunities for growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing applications in healthcare. As research continues to uncover new potential uses for these materials, the market is expected to expand further, with a focus on developing more sophisticated and tailored solutions for various medical applications.
Current Challenges in Alkyl-Biocompatibility Assessment
The evaluation of alkyl impact on biocompatible materials presents several significant challenges in the current research landscape. One of the primary difficulties lies in the complexity of interactions between alkyl groups and biological systems. These interactions are often multifaceted, involving various molecular mechanisms that are not yet fully understood.
A major challenge is the lack of standardized protocols for assessing alkyl-biocompatibility. Different research groups employ diverse methodologies, making it difficult to compare results across studies. This inconsistency hampers the establishment of reliable benchmarks and slows down the progress in the field.
Another critical issue is the limited availability of long-term in vivo studies. While short-term evaluations provide valuable insights, they often fail to capture the full spectrum of biological responses to alkyl-modified materials over extended periods. This gap in knowledge raises concerns about the potential long-term effects of these materials in medical applications.
The variability in biological responses among different individuals and species further complicates the assessment process. What may be biocompatible in one model system might elicit adverse reactions in another, necessitating extensive cross-species validation studies.
Additionally, the dynamic nature of biological environments poses a significant challenge. Alkyl-modified materials may undergo changes over time due to factors such as degradation, protein adsorption, or cellular interactions. These temporal variations make it difficult to predict long-term biocompatibility based on initial assessments.
The development of sensitive and specific analytical techniques for detecting subtle changes in biological responses to alkyl-modified materials remains an ongoing challenge. Current methods may not be sufficiently refined to capture all relevant biological interactions, potentially overlooking important biocompatibility factors.
Furthermore, the ethical considerations and regulatory requirements associated with biocompatibility testing create additional hurdles. Balancing the need for comprehensive evaluations with ethical constraints and regulatory compliance adds complexity to the assessment process.
Lastly, the rapidly evolving field of materials science continually introduces new alkyl-modified materials, outpacing the development of corresponding biocompatibility evaluation methods. This lag creates a constant need for updating and adapting assessment protocols to keep pace with material innovations.
A major challenge is the lack of standardized protocols for assessing alkyl-biocompatibility. Different research groups employ diverse methodologies, making it difficult to compare results across studies. This inconsistency hampers the establishment of reliable benchmarks and slows down the progress in the field.
Another critical issue is the limited availability of long-term in vivo studies. While short-term evaluations provide valuable insights, they often fail to capture the full spectrum of biological responses to alkyl-modified materials over extended periods. This gap in knowledge raises concerns about the potential long-term effects of these materials in medical applications.
The variability in biological responses among different individuals and species further complicates the assessment process. What may be biocompatible in one model system might elicit adverse reactions in another, necessitating extensive cross-species validation studies.
Additionally, the dynamic nature of biological environments poses a significant challenge. Alkyl-modified materials may undergo changes over time due to factors such as degradation, protein adsorption, or cellular interactions. These temporal variations make it difficult to predict long-term biocompatibility based on initial assessments.
The development of sensitive and specific analytical techniques for detecting subtle changes in biological responses to alkyl-modified materials remains an ongoing challenge. Current methods may not be sufficiently refined to capture all relevant biological interactions, potentially overlooking important biocompatibility factors.
Furthermore, the ethical considerations and regulatory requirements associated with biocompatibility testing create additional hurdles. Balancing the need for comprehensive evaluations with ethical constraints and regulatory compliance adds complexity to the assessment process.
Lastly, the rapidly evolving field of materials science continually introduces new alkyl-modified materials, outpacing the development of corresponding biocompatibility evaluation methods. This lag creates a constant need for updating and adapting assessment protocols to keep pace with material innovations.
Existing Alkyl-Biocompatibility Evaluation Methods
01 Biocompatible alkyl-containing polymers
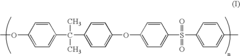
Alkyl-containing polymers are used in biocompatible materials due to their ability to enhance material properties and biocompatibility. These polymers can be modified to improve their interaction with biological systems, making them suitable for various medical applications such as drug delivery systems, implants, and tissue engineering scaffolds.- Biocompatible alkyl-containing polymers: Alkyl-containing polymers are used in biocompatible materials due to their ability to enhance material properties and biocompatibility. These polymers can be modified to improve their interaction with biological systems, making them suitable for various medical applications such as drug delivery systems, implants, and tissue engineering scaffolds.
- Alkyl-modified surface treatments for medical devices: Surface treatments incorporating alkyl groups are applied to medical devices to improve their biocompatibility and performance. These treatments can enhance the device's resistance to protein adsorption, reduce bacterial adhesion, and improve overall integration with surrounding tissues.
- Alkyl-based drug delivery systems: Alkyl-based compounds are utilized in the development of drug delivery systems to improve the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of therapeutic agents. These systems can include alkyl-modified nanoparticles, liposomes, or other carrier molecules designed to enhance drug efficacy and reduce side effects.
- Alkyl impact on biocompatible coatings: The incorporation of alkyl groups in biocompatible coatings can significantly impact their properties and performance. These coatings may exhibit improved adhesion to substrates, enhanced durability, and better control over the release of bioactive compounds, making them suitable for various medical and biotechnological applications.
- Alkyl-functionalized hydrogels for tissue engineering: Alkyl-functionalized hydrogels are developed for tissue engineering applications, offering improved mechanical properties and cell adhesion characteristics. These materials can be tailored to mimic the extracellular matrix, providing a suitable environment for cell growth and tissue regeneration.
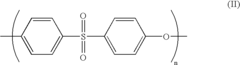
02 Alkyl-modified surface treatments for medical devices
Surface treatments incorporating alkyl groups are applied to medical devices to improve their biocompatibility and performance. These treatments can enhance the device's resistance to protein adsorption, reduce bacterial adhesion, and improve overall integration with surrounding tissues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl-based drug delivery systems
Alkyl-based compounds are utilized in the development of drug delivery systems to improve the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of therapeutic agents. These systems can include alkyl-modified nanoparticles, liposomes, or other carrier molecules designed to enhance drug efficacy and reduce side effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Impact of alkyl chain length on biocompatibility
The length of alkyl chains in biocompatible materials significantly affects their properties and interactions with biological systems. Researchers investigate the optimal alkyl chain lengths for specific applications, considering factors such as hydrophobicity, biodegradation rate, and cellular response.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alkyl-functionalized hydrogels for tissue engineering
Hydrogels functionalized with alkyl groups are developed for tissue engineering applications. These materials combine the biocompatibility of hydrogels with the enhanced mechanical properties and cell adhesion characteristics provided by alkyl modifications, creating scaffolds that better mimic natural tissue environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Biocompatible Materials Research
The evaluation of alkyl impact on biocompatible materials is a rapidly evolving field within the broader context of biomaterials research. The market is in its growth phase, with increasing demand for advanced biocompatible materials in medical devices and implants. The global biocompatible materials market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like F. Hoffmann-La Roche, DuPont de Nemours, and Merck & Co. leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as MIT and Emory University are also contributing to the knowledge base. The technology is maturing, but there's still room for innovation, particularly in understanding the long-term effects of alkyl groups on material performance and biocompatibility.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: Roche has developed a comprehensive approach to evaluate alkyl impact on biocompatible materials, focusing on their drug delivery systems and medical devices. Their method involves a multi-step process: 1) Synthesis of alkylated biomaterials using controlled polymerization techniques[1]. 2) Characterization of surface properties through advanced spectroscopic methods, including X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS)[2]. 3) Assessment of protein adsorption and cell adhesion on alkylated surfaces using quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) and fluorescence microscopy[3]. 4) In vitro cytotoxicity and hemocompatibility tests to evaluate biocompatibility[4]. 5) In vivo studies in animal models to assess long-term performance and tissue response[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach covering synthesis to in vivo testing; Advanced analytical techniques for detailed surface characterization. Weaknesses: Time-consuming and resource-intensive process; May not fully predict long-term in vivo performance.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed a systematic approach to evaluate alkyl impact on biocompatible materials, particularly focusing on their range of polymers and biomaterials. Their methodology includes: 1) Synthesis of alkylated materials using controlled radical polymerization and click chemistry[1]. 2) Surface characterization using atomic force microscopy (AFM) and contact angle measurements to assess topography and wettability changes[2]. 3) Chemical analysis using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to confirm alkyl group incorporation[3]. 4) Protein adsorption studies using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to evaluate the impact of alkylation on protein-surface interactions[4]. 5) Cell culture experiments to assess cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation on alkylated surfaces[5]. 6) Mechanical testing to determine the effect of alkylation on material properties such as tensile strength and elasticity.
Strengths: Comprehensive physicochemical and biological evaluation; Strong focus on material properties and performance. Weaknesses: May not fully capture the complexity of in vivo environments; Limited long-term in vivo studies.
Innovative Approaches in Alkyl Impact Assessment
Method of evaluating biocompatibility
PatentInactiveUS20040241690A1
Innovation
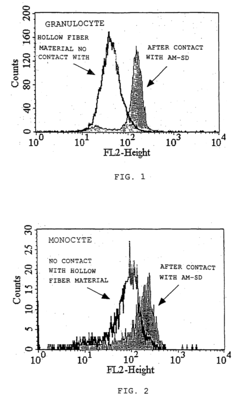
- A method involving in-vitro contact of leukocytes with medical materials, followed by RNA extraction and real-time PCR or DNA array analysis to quantify the expression levels of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor gene and protein, allowing for sensitive and quantitative evaluation of biocompatibility without requiring clinical blood samples and minimizing endotoxin contamination.
Compositions and methods for implantation of processed adipose tissue and processed adipose tissue products
PatentInactiveUS20220073881A1
Innovation
- Processed adipose tissue compositions are developed, including decellularized adipose tissue extracellular matrix that is cross-linked and combined with biopolymers, which are designed to be non-immunogenic and retain the native architecture and bioactivity of adipose tissue, allowing for predictable and long-lasting soft tissue reconstruction.
Regulatory Framework for Biocompatible Materials
The regulatory framework for biocompatible materials plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices and implants. When evaluating the impact of alkyl groups on biocompatible materials, it is essential to consider the existing regulations and guidelines set forth by various regulatory bodies worldwide.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory agency responsible for overseeing the safety and effectiveness of medical devices. The FDA has established a comprehensive framework for evaluating biocompatible materials, including those containing alkyl groups. This framework includes guidance documents, such as the ISO 10993 series, which outlines the biological evaluation of medical devices.
The European Union has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR), which provide stringent requirements for biocompatible materials used in medical devices. These regulations emphasize the importance of risk assessment and management throughout the product lifecycle, including the evaluation of alkyl impacts on biocompatibility.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established its own set of guidelines for evaluating biocompatible materials, which align closely with international standards. These guidelines include specific considerations for assessing the impact of chemical modifications, such as alkyl groups, on the overall biocompatibility of materials.
International standards, such as those developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), provide a harmonized approach to evaluating biocompatible materials. The ISO 10993 series, particularly ISO 10993-1, offers a systematic approach to biological evaluation and risk assessment, which can be applied to materials containing alkyl groups.
Regulatory bodies also require manufacturers to conduct specific tests to evaluate the biocompatibility of materials. These tests may include cytotoxicity assays, sensitization studies, and long-term implantation studies. When assessing the impact of alkyl groups, additional tests may be necessary to evaluate potential changes in material properties, degradation profiles, and interactions with biological systems.
It is important to note that regulatory requirements may vary depending on the intended use of the biocompatible material and the specific medical device application. Manufacturers must carefully consider the regulatory landscape in their target markets and ensure compliance with all relevant guidelines and standards when evaluating the impact of alkyl groups on biocompatible materials.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory agency responsible for overseeing the safety and effectiveness of medical devices. The FDA has established a comprehensive framework for evaluating biocompatible materials, including those containing alkyl groups. This framework includes guidance documents, such as the ISO 10993 series, which outlines the biological evaluation of medical devices.
The European Union has implemented the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR), which provide stringent requirements for biocompatible materials used in medical devices. These regulations emphasize the importance of risk assessment and management throughout the product lifecycle, including the evaluation of alkyl impacts on biocompatibility.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established its own set of guidelines for evaluating biocompatible materials, which align closely with international standards. These guidelines include specific considerations for assessing the impact of chemical modifications, such as alkyl groups, on the overall biocompatibility of materials.
International standards, such as those developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), provide a harmonized approach to evaluating biocompatible materials. The ISO 10993 series, particularly ISO 10993-1, offers a systematic approach to biological evaluation and risk assessment, which can be applied to materials containing alkyl groups.
Regulatory bodies also require manufacturers to conduct specific tests to evaluate the biocompatibility of materials. These tests may include cytotoxicity assays, sensitization studies, and long-term implantation studies. When assessing the impact of alkyl groups, additional tests may be necessary to evaluate potential changes in material properties, degradation profiles, and interactions with biological systems.
It is important to note that regulatory requirements may vary depending on the intended use of the biocompatible material and the specific medical device application. Manufacturers must carefully consider the regulatory landscape in their target markets and ensure compliance with all relevant guidelines and standards when evaluating the impact of alkyl groups on biocompatible materials.
Sustainability in Alkylated Biomaterial Production
Sustainability in alkylated biomaterial production has become a critical focus in the biomedical industry, as the environmental impact of manufacturing processes gains increasing attention. The evaluation of alkyl impact on biocompatible materials plays a crucial role in developing sustainable production methods. This assessment involves analyzing the entire lifecycle of alkylated biomaterials, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life disposal.
One key aspect of sustainable production is the selection of alkyl sources. Traditional petroleum-based alkyl groups are being replaced by bio-based alternatives derived from renewable resources. These bio-based alkyl groups not only reduce the carbon footprint but also offer improved biodegradability. Researchers are exploring various plant-based oils and agricultural by-products as potential sources for sustainable alkyl groups.
The synthesis process of alkylated biomaterials also requires optimization for sustainability. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop more efficient and environmentally friendly reaction pathways. This includes the use of non-toxic solvents, catalysts with high selectivity, and reaction conditions that minimize energy consumption. Additionally, continuous flow chemistry techniques are being implemented to reduce waste and improve process efficiency.
Waste management and recycling strategies are integral to sustainable alkylated biomaterial production. Efforts are being made to develop closed-loop systems where by-products and waste materials can be repurposed or recycled. This not only reduces environmental impact but also improves resource utilization and economic viability.
The durability and longevity of alkylated biomaterials contribute significantly to their sustainability profile. Researchers are focusing on enhancing the stability of these materials to extend their useful life, thereby reducing the need for frequent replacements. This involves studying the degradation mechanisms of alkylated biomaterials under various environmental conditions and developing strategies to mitigate them.
Biodegradability is another crucial factor in sustainable production. While biocompatibility ensures safe interaction with biological systems, controlled biodegradation allows for the material to be naturally broken down after its intended use. Balancing these properties requires careful consideration of the alkyl group's structure and its integration into the biomaterial matrix.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) tools are being increasingly employed to evaluate the overall environmental impact of alkylated biomaterial production. These assessments consider factors such as energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and toxicity across all stages of production and use. The results of these LCAs guide further improvements in production processes and material design.
One key aspect of sustainable production is the selection of alkyl sources. Traditional petroleum-based alkyl groups are being replaced by bio-based alternatives derived from renewable resources. These bio-based alkyl groups not only reduce the carbon footprint but also offer improved biodegradability. Researchers are exploring various plant-based oils and agricultural by-products as potential sources for sustainable alkyl groups.
The synthesis process of alkylated biomaterials also requires optimization for sustainability. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop more efficient and environmentally friendly reaction pathways. This includes the use of non-toxic solvents, catalysts with high selectivity, and reaction conditions that minimize energy consumption. Additionally, continuous flow chemistry techniques are being implemented to reduce waste and improve process efficiency.
Waste management and recycling strategies are integral to sustainable alkylated biomaterial production. Efforts are being made to develop closed-loop systems where by-products and waste materials can be repurposed or recycled. This not only reduces environmental impact but also improves resource utilization and economic viability.
The durability and longevity of alkylated biomaterials contribute significantly to their sustainability profile. Researchers are focusing on enhancing the stability of these materials to extend their useful life, thereby reducing the need for frequent replacements. This involves studying the degradation mechanisms of alkylated biomaterials under various environmental conditions and developing strategies to mitigate them.
Biodegradability is another crucial factor in sustainable production. While biocompatibility ensures safe interaction with biological systems, controlled biodegradation allows for the material to be naturally broken down after its intended use. Balancing these properties requires careful consideration of the alkyl group's structure and its integration into the biomaterial matrix.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) tools are being increasingly employed to evaluate the overall environmental impact of alkylated biomaterial production. These assessments consider factors such as energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and toxicity across all stages of production and use. The results of these LCAs guide further improvements in production processes and material design.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!