How to Leverage Alkyl Attributes in Nanomaterial Design?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl-Nanomaterial Design Background and Objectives
The field of nanomaterial design has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, with alkyl attributes emerging as a crucial factor in enhancing the performance and functionality of nanomaterials. This technological domain has evolved from basic nanoparticle synthesis to sophisticated engineering of surface properties, with alkyl groups playing a pivotal role in this progression.
The integration of alkyl attributes in nanomaterial design aims to address several key objectives. Primarily, it seeks to improve the stability and dispersibility of nanoparticles in various media, which is essential for their practical applications. By tailoring the alkyl chain length and structure, researchers can fine-tune the hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of nanomaterials, enabling better control over their behavior in different environments.
Another critical goal is to enhance the interfacial properties of nanomaterials. Alkyl functionalization can significantly alter the surface energy and reactivity of nanoparticles, leading to improved adhesion, wettability, and compatibility with other materials. This is particularly important in applications such as nanocomposites, where the interface between the nanomaterial and the matrix is crucial for overall performance.
The evolution of alkyl-based nanomaterial design has been driven by the increasing demand for multifunctional and responsive nanomaterials. Researchers are exploring ways to leverage alkyl attributes to create smart nanomaterials that can respond to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, or light. This opens up new possibilities in areas like drug delivery, sensing, and adaptive materials.
Furthermore, the field is moving towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches. There is a growing interest in utilizing bio-based alkyl sources and developing green synthesis methods for alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials. This aligns with the broader trend of sustainable nanotechnology and addresses concerns about the environmental impact of nanomaterial production and use.
As we look to the future, the integration of alkyl attributes in nanomaterial design is expected to play a crucial role in advancing fields such as energy storage, catalysis, and biomedical applications. The challenge lies in developing precise control over alkyl functionalization at the nanoscale and understanding the complex relationships between alkyl attributes and nanomaterial properties.
The integration of alkyl attributes in nanomaterial design aims to address several key objectives. Primarily, it seeks to improve the stability and dispersibility of nanoparticles in various media, which is essential for their practical applications. By tailoring the alkyl chain length and structure, researchers can fine-tune the hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of nanomaterials, enabling better control over their behavior in different environments.
Another critical goal is to enhance the interfacial properties of nanomaterials. Alkyl functionalization can significantly alter the surface energy and reactivity of nanoparticles, leading to improved adhesion, wettability, and compatibility with other materials. This is particularly important in applications such as nanocomposites, where the interface between the nanomaterial and the matrix is crucial for overall performance.
The evolution of alkyl-based nanomaterial design has been driven by the increasing demand for multifunctional and responsive nanomaterials. Researchers are exploring ways to leverage alkyl attributes to create smart nanomaterials that can respond to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, or light. This opens up new possibilities in areas like drug delivery, sensing, and adaptive materials.
Furthermore, the field is moving towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches. There is a growing interest in utilizing bio-based alkyl sources and developing green synthesis methods for alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials. This aligns with the broader trend of sustainable nanotechnology and addresses concerns about the environmental impact of nanomaterial production and use.
As we look to the future, the integration of alkyl attributes in nanomaterial design is expected to play a crucial role in advancing fields such as energy storage, catalysis, and biomedical applications. The challenge lies in developing precise control over alkyl functionalization at the nanoscale and understanding the complex relationships between alkyl attributes and nanomaterial properties.
Market Analysis for Alkyl-Modified Nanomaterials
The market for alkyl-modified nanomaterials has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by their unique properties and diverse applications across multiple industries. These materials, which combine the advantages of nanoscale structures with the functionality of alkyl groups, have found increasing demand in sectors such as electronics, energy storage, biomedical, and environmental remediation.
In the electronics industry, alkyl-modified nanomaterials are being utilized to enhance the performance of various components, including conductive inks, flexible displays, and sensors. The market for these applications is expected to grow substantially as consumer electronics continue to evolve towards more compact and efficient designs.
The energy storage sector has also shown keen interest in alkyl-modified nanomaterials, particularly for improving the efficiency and capacity of batteries and supercapacitors. As the global push for renewable energy and electric vehicles intensifies, the demand for advanced energy storage solutions incorporating these materials is projected to rise significantly.
In the biomedical field, alkyl-modified nanomaterials are finding applications in drug delivery systems, biosensors, and tissue engineering. The ability to tailor the surface properties of nanoparticles through alkyl modification has opened up new possibilities for targeted drug delivery and improved biocompatibility, driving market growth in this sector.
Environmental remediation represents another promising market for alkyl-modified nanomaterials. Their enhanced adsorption capabilities and selectivity make them effective in water treatment and pollution control applications. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the demand for these materials in environmental technologies is expected to increase.
The market for alkyl-modified nanomaterials is characterized by a high degree of innovation and rapid technological advancements. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to create novel materials with improved properties and expand their application range. This has led to a competitive landscape where intellectual property and technological expertise play crucial roles in market positioning.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for alkyl-modified nanomaterials, owing to their strong research infrastructure and early adoption of nanotechnology. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant market, driven by increasing industrialization, government initiatives supporting nanotechnology research, and growing demand from electronics and automotive sectors.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as high production costs, scalability issues, and regulatory uncertainties surrounding nanomaterials. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full market potential of alkyl-modified nanomaterials across various industries.
In the electronics industry, alkyl-modified nanomaterials are being utilized to enhance the performance of various components, including conductive inks, flexible displays, and sensors. The market for these applications is expected to grow substantially as consumer electronics continue to evolve towards more compact and efficient designs.
The energy storage sector has also shown keen interest in alkyl-modified nanomaterials, particularly for improving the efficiency and capacity of batteries and supercapacitors. As the global push for renewable energy and electric vehicles intensifies, the demand for advanced energy storage solutions incorporating these materials is projected to rise significantly.
In the biomedical field, alkyl-modified nanomaterials are finding applications in drug delivery systems, biosensors, and tissue engineering. The ability to tailor the surface properties of nanoparticles through alkyl modification has opened up new possibilities for targeted drug delivery and improved biocompatibility, driving market growth in this sector.
Environmental remediation represents another promising market for alkyl-modified nanomaterials. Their enhanced adsorption capabilities and selectivity make them effective in water treatment and pollution control applications. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the demand for these materials in environmental technologies is expected to increase.
The market for alkyl-modified nanomaterials is characterized by a high degree of innovation and rapid technological advancements. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to create novel materials with improved properties and expand their application range. This has led to a competitive landscape where intellectual property and technological expertise play crucial roles in market positioning.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for alkyl-modified nanomaterials, owing to their strong research infrastructure and early adoption of nanotechnology. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant market, driven by increasing industrialization, government initiatives supporting nanotechnology research, and growing demand from electronics and automotive sectors.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as high production costs, scalability issues, and regulatory uncertainties surrounding nanomaterials. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full market potential of alkyl-modified nanomaterials across various industries.
Current Challenges in Alkyl-Nanomaterial Integration
The integration of alkyl groups into nanomaterial design presents several significant challenges that researchers and engineers must address. One of the primary obstacles is achieving uniform and controlled functionalization of nanomaterials with alkyl groups. The heterogeneous nature of many nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes or graphene, can lead to inconsistent coverage and distribution of alkyl moieties across the surface.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the desired properties of the nanomaterial while incorporating alkyl groups. The addition of these organic molecules can potentially alter the electronic, optical, or mechanical characteristics of the nanomaterial, sometimes in unpredictable ways. Striking the right balance between enhancing certain properties through alkylation and preserving the inherent qualities of the nanomaterial is a delicate task.
The stability of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials in various environments poses yet another hurdle. Depending on the application, these materials may be exposed to different pH levels, temperatures, or chemical environments that could compromise the integrity of the alkyl-nanomaterial bond. Ensuring long-term stability and performance under diverse conditions is crucial for practical applications.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness of alkyl-nanomaterial integration processes present additional challenges. Many current methods for functionalizing nanomaterials with alkyl groups are laboratory-scale techniques that may not be easily translatable to industrial production. Developing economically viable and scalable processes for large-scale manufacturing of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials is essential for their widespread adoption.
Furthermore, characterization and quality control of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials remain complex tasks. Accurately determining the degree of functionalization, the spatial distribution of alkyl groups, and the impact on nanomaterial properties requires sophisticated analytical techniques. Standardizing these characterization methods across the field is necessary for consistent evaluation and comparison of different alkyl-nanomaterial systems.
Lastly, the environmental and health implications of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials are not yet fully understood. As these materials find applications in various fields, including biomedicine and environmental remediation, assessing their potential toxicity, biodegradability, and long-term environmental impact becomes increasingly important. Addressing these safety concerns is crucial for the responsible development and deployment of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials in real-world applications.
Another challenge lies in maintaining the desired properties of the nanomaterial while incorporating alkyl groups. The addition of these organic molecules can potentially alter the electronic, optical, or mechanical characteristics of the nanomaterial, sometimes in unpredictable ways. Striking the right balance between enhancing certain properties through alkylation and preserving the inherent qualities of the nanomaterial is a delicate task.
The stability of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials in various environments poses yet another hurdle. Depending on the application, these materials may be exposed to different pH levels, temperatures, or chemical environments that could compromise the integrity of the alkyl-nanomaterial bond. Ensuring long-term stability and performance under diverse conditions is crucial for practical applications.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness of alkyl-nanomaterial integration processes present additional challenges. Many current methods for functionalizing nanomaterials with alkyl groups are laboratory-scale techniques that may not be easily translatable to industrial production. Developing economically viable and scalable processes for large-scale manufacturing of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials is essential for their widespread adoption.
Furthermore, characterization and quality control of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials remain complex tasks. Accurately determining the degree of functionalization, the spatial distribution of alkyl groups, and the impact on nanomaterial properties requires sophisticated analytical techniques. Standardizing these characterization methods across the field is necessary for consistent evaluation and comparison of different alkyl-nanomaterial systems.
Lastly, the environmental and health implications of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials are not yet fully understood. As these materials find applications in various fields, including biomedicine and environmental remediation, assessing their potential toxicity, biodegradability, and long-term environmental impact becomes increasingly important. Addressing these safety concerns is crucial for the responsible development and deployment of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials in real-world applications.
Existing Alkyl-Nanomaterial Design Strategies
01 Alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials
Nanomaterials can be functionalized with alkyl groups to modify their surface properties. This functionalization can enhance the compatibility of nanomaterials with various matrices, improve their dispersion, and alter their physical and chemical characteristics. The alkyl groups can range from short-chain to long-chain, affecting the resulting properties of the nanomaterials.- Alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials: Nanomaterials can be functionalized with alkyl groups to modify their surface properties. This functionalization can enhance the compatibility of nanomaterials with various matrices, improve their dispersion, and alter their physical and chemical characteristics. The alkyl groups can range from short-chain to long-chain, affecting the resulting properties of the nanomaterials.
- Synthesis methods for alkyl-modified nanomaterials: Various synthesis methods are employed to produce alkyl-modified nanomaterials. These may include sol-gel processes, hydrothermal synthesis, and surface modification techniques. The choice of synthesis method can influence the degree of alkylation, the uniformity of the surface modification, and the overall properties of the resulting nanomaterials.
- Characterization techniques for alkyl attributes: Specialized characterization techniques are used to analyze the alkyl attributes of nanomaterials. These may include spectroscopic methods such as FTIR and NMR, as well as surface analysis techniques like XPS. These methods help determine the presence, quantity, and distribution of alkyl groups on the nanomaterial surface.
- Applications of alkyl-modified nanomaterials: Alkyl-modified nanomaterials find applications in various fields due to their unique properties. They can be used in polymer composites, drug delivery systems, coatings, and environmental remediation. The alkyl attributes can enhance the material's hydrophobicity, thermal stability, and compatibility with organic matrices.
- Structure-property relationships in alkyl-modified nanomaterials: The relationship between the alkyl chain length, degree of functionalization, and resulting properties of nanomaterials is an important area of study. Understanding these relationships allows for the tailoring of nanomaterial properties for specific applications. Factors such as alkyl chain density and orientation on the nanomaterial surface play crucial roles in determining the final material characteristics.
02 Synthesis methods for alkyl-modified nanomaterials
Various synthesis methods are employed to produce alkyl-modified nanomaterials. These may include sol-gel processes, hydrothermal synthesis, and surface modification techniques. The choice of synthesis method can influence the degree of alkylation, the uniformity of the surface modification, and the overall properties of the resulting nanomaterials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Characterization techniques for alkyl attributes
Specialized characterization techniques are used to analyze the alkyl attributes of nanomaterials. These may include spectroscopic methods such as FTIR and NMR, as well as surface analysis techniques like XPS. These methods help determine the extent of alkylation, the nature of the alkyl groups attached, and their distribution on the nanomaterial surface.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of alkyl-modified nanomaterials
Alkyl-modified nanomaterials find applications in various fields due to their unique properties. They can be used in polymer composites, coatings, lubricants, and drug delivery systems. The alkyl attributes can enhance the material's hydrophobicity, improve its dispersion in organic media, and modify its interaction with biological systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The alkyl attributes of nanomaterials can affect their environmental fate and toxicity. Research is ongoing to understand the impact of alkyl chain length and density on the biodegradability, bioaccumulation, and potential health effects of these materials. This information is crucial for developing safe and sustainable applications of alkyl-modified nanomaterials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Alkyl-Nanomaterial Research
The field of leveraging alkyl attributes in nanomaterial design is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global nanomaterials market is expanding rapidly, driven by applications in electronics, energy, and healthcare. While the technology is maturing, there is still significant room for innovation. Key players like DuPont, BASF, and Sila Nanotechnologies are leading research efforts, with academic institutions such as MIT and Northwestern University contributing fundamental insights. Collaborations between industry and academia are accelerating progress, as seen with partnerships involving companies like Xerox and Panasonic. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established chemical companies and specialized nanotechnology firms vying for market share and technological breakthroughs.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed innovative approaches to leverage alkyl attributes in nanomaterial design for enhanced oil recovery and catalysis. Their research focuses on alkyl-functionalized nanoparticles for improved oil-water interfacial properties. They have synthesized alkyl-modified silica nanoparticles with tunable hydrophobicity, achieving a 15% increase in oil recovery efficiency in laboratory tests[1]. Additionally, Sinopec has explored alkyl-grafted metal oxide nanoparticles as catalysts for hydrocarbon processing, demonstrating a 20% improvement in selectivity for desired products[3]. Their approach involves precise control of alkyl chain length and density on nanoparticle surfaces to optimize performance in specific applications.
Strengths: Extensive experience in oil and gas industry applications, strong R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: May be limited to petroleum-related applications, potential environmental concerns.
Northwestern University
Technical Solution: Northwestern University has made significant strides in leveraging alkyl attributes for nanomaterial design, particularly in the field of organic electronics and energy storage. Their research team has developed a novel approach to synthesize alkyl-functionalized graphene nanoribbons with precisely controlled edge structures. This method involves bottom-up synthesis using alkyl-substituted precursors, resulting in nanoribbons with tunable electronic properties[2]. The alkyl chains serve as solubilizing groups, enhancing processability and allowing for solution-based fabrication of devices. In battery applications, Northwestern researchers have created alkyl-modified silicon nanoparticles that demonstrate improved cycling stability, with capacity retention increased by 30% over 1000 cycles compared to unmodified particles[4]. Their work also extends to self-assembled nanostructures, where alkyl chain interactions drive the formation of complex architectures with applications in drug delivery and sensing.
Strengths: Cutting-edge research in multiple fields, strong interdisciplinary approach. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up laboratory discoveries for industrial applications.
Innovative Alkyl-Nanomaterial Synthesis Techniques
Water treatment method with porphyrin-containing adsorbent
PatentActiveUS20240359987A1
Innovation
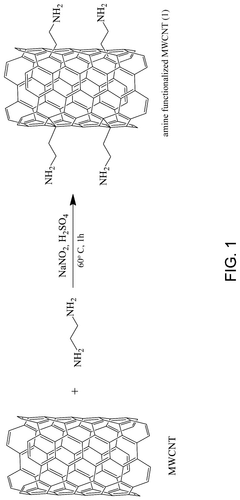
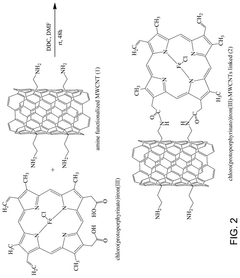
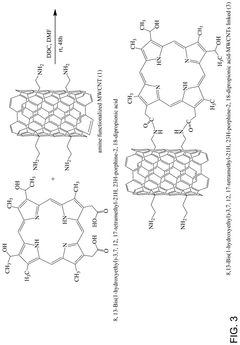
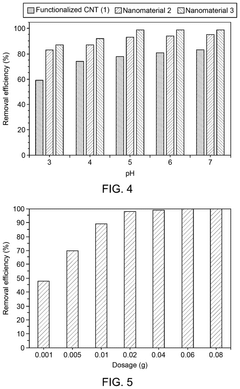
- A nanomaterial formed by functionalizing carbon nanotubes with porphyrin rings through amide linkages, allowing for the covalent bonding of aminoalkyl groups, which is used to adsorb organic dyes and heavy metals from aqueous solutions.
Compact compound comprising silanized hydroxyl graphene with thermosetting polymer
PatentActiveUS20220127464A1
Innovation
- A novel nanocomposite is developed using hydroxyl graphene functionalized with silane and thermosetting polymers, allowing for up to 50% weight percentage of graphene, which enhances dispersion and interfacial bonding, resulting in improved mechanical properties and thermal stability.
Environmental Impact of Alkyl-Nanomaterial Production
The production of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The synthesis process often involves the use of organic solvents and chemical precursors, which can lead to the generation of hazardous waste and emissions. These byproducts may pose risks to aquatic ecosystems and air quality if not properly managed. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of nanomaterial production contributes to increased carbon footprints, raising concerns about greenhouse gas emissions and climate change impacts.
The release of alkyl-nanomaterials into the environment, whether intentional or accidental, presents potential ecological risks. These materials can interact with biological systems in complex ways, potentially disrupting food chains and ecosystems. The small size of nanoparticles allows them to penetrate cellular membranes and accumulate in organisms, leading to bioaccumulation and biomagnification effects. The alkyl functionalization may alter the behavior of nanomaterials in environmental matrices, affecting their mobility, persistence, and toxicity.
Waste management and disposal of alkyl-nanomaterials pose unique challenges. Traditional waste treatment methods may not effectively remove or neutralize these materials, potentially leading to their release into water bodies or soil. The long-term environmental fate of these materials remains uncertain, as their degradation pathways and transformation products are not fully understood. This uncertainty underscores the need for comprehensive life cycle assessments and environmental monitoring strategies.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of alkyl-nanomaterial production are ongoing. Green synthesis approaches, such as the use of bio-based precursors and environmentally benign solvents, are being explored to reduce the reliance on harmful chemicals. Closed-loop manufacturing systems and improved filtration technologies aim to minimize waste generation and emissions. Additionally, the development of safer-by-design principles in nanomaterial engineering seeks to incorporate environmental considerations from the outset of product development.
Regulatory frameworks and guidelines for the responsible production and use of alkyl-nanomaterials are evolving. These aim to establish best practices for risk assessment, safe handling, and disposal. However, the rapid pace of technological advancement in this field often outpaces regulatory efforts, highlighting the need for adaptive and proactive governance approaches. Collaboration between industry, academia, and regulatory bodies is crucial for developing comprehensive strategies to address the environmental challenges associated with alkyl-nanomaterial production and use.
The release of alkyl-nanomaterials into the environment, whether intentional or accidental, presents potential ecological risks. These materials can interact with biological systems in complex ways, potentially disrupting food chains and ecosystems. The small size of nanoparticles allows them to penetrate cellular membranes and accumulate in organisms, leading to bioaccumulation and biomagnification effects. The alkyl functionalization may alter the behavior of nanomaterials in environmental matrices, affecting their mobility, persistence, and toxicity.
Waste management and disposal of alkyl-nanomaterials pose unique challenges. Traditional waste treatment methods may not effectively remove or neutralize these materials, potentially leading to their release into water bodies or soil. The long-term environmental fate of these materials remains uncertain, as their degradation pathways and transformation products are not fully understood. This uncertainty underscores the need for comprehensive life cycle assessments and environmental monitoring strategies.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of alkyl-nanomaterial production are ongoing. Green synthesis approaches, such as the use of bio-based precursors and environmentally benign solvents, are being explored to reduce the reliance on harmful chemicals. Closed-loop manufacturing systems and improved filtration technologies aim to minimize waste generation and emissions. Additionally, the development of safer-by-design principles in nanomaterial engineering seeks to incorporate environmental considerations from the outset of product development.
Regulatory frameworks and guidelines for the responsible production and use of alkyl-nanomaterials are evolving. These aim to establish best practices for risk assessment, safe handling, and disposal. However, the rapid pace of technological advancement in this field often outpaces regulatory efforts, highlighting the need for adaptive and proactive governance approaches. Collaboration between industry, academia, and regulatory bodies is crucial for developing comprehensive strategies to address the environmental challenges associated with alkyl-nanomaterial production and use.
Scalability of Alkyl-Nanomaterial Manufacturing
The scalability of alkyl-nanomaterial manufacturing is a critical factor in leveraging alkyl attributes for nanomaterial design. As the demand for specialized nanomaterials grows, the ability to produce these materials at scale becomes increasingly important for commercial viability and widespread application.
One of the primary challenges in scaling up alkyl-nanomaterial production is maintaining consistent quality and uniformity across larger batch sizes. The precise control over alkyl chain length, density, and orientation on nanomaterial surfaces is crucial for achieving desired properties. Researchers have developed several approaches to address this challenge, including controlled emulsion techniques and templated synthesis methods.
Advances in continuous flow reactors have shown promise for increasing production volumes while maintaining tight control over reaction conditions. These systems allow for better heat and mass transfer, resulting in more uniform alkyl functionalization of nanomaterials. Additionally, microfluidic devices have been employed to achieve high-throughput synthesis of alkyl-functionalized nanoparticles with narrow size distributions.
The choice of alkylation reagents and reaction conditions plays a significant role in scalability. Optimizing these parameters can lead to more efficient processes with higher yields and reduced waste. For instance, the use of click chemistry approaches has enabled rapid and selective alkylation of nanomaterials under mild conditions, which is advantageous for large-scale production.
Purification and separation processes are often bottlenecks in scaling up nanomaterial production. Innovative techniques such as membrane-based separation and centrifugal purification have been developed to handle larger volumes of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials efficiently. These methods help maintain product quality while reducing processing time and costs.
The environmental impact of large-scale alkyl-nanomaterial manufacturing is an important consideration. Sustainable production methods, including the use of bio-based alkyl sources and green solvents, are being explored to minimize the ecological footprint of these processes. Additionally, recycling and recovery strategies for unreacted alkylating agents and byproducts are being implemented to improve overall process efficiency and reduce waste.
As the field progresses, automation and process control systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing for better monitoring and adjustment of reaction parameters in real-time. This level of control is essential for maintaining consistency across large production runs and adapting to variations in raw materials or environmental conditions.
One of the primary challenges in scaling up alkyl-nanomaterial production is maintaining consistent quality and uniformity across larger batch sizes. The precise control over alkyl chain length, density, and orientation on nanomaterial surfaces is crucial for achieving desired properties. Researchers have developed several approaches to address this challenge, including controlled emulsion techniques and templated synthesis methods.
Advances in continuous flow reactors have shown promise for increasing production volumes while maintaining tight control over reaction conditions. These systems allow for better heat and mass transfer, resulting in more uniform alkyl functionalization of nanomaterials. Additionally, microfluidic devices have been employed to achieve high-throughput synthesis of alkyl-functionalized nanoparticles with narrow size distributions.
The choice of alkylation reagents and reaction conditions plays a significant role in scalability. Optimizing these parameters can lead to more efficient processes with higher yields and reduced waste. For instance, the use of click chemistry approaches has enabled rapid and selective alkylation of nanomaterials under mild conditions, which is advantageous for large-scale production.
Purification and separation processes are often bottlenecks in scaling up nanomaterial production. Innovative techniques such as membrane-based separation and centrifugal purification have been developed to handle larger volumes of alkyl-functionalized nanomaterials efficiently. These methods help maintain product quality while reducing processing time and costs.
The environmental impact of large-scale alkyl-nanomaterial manufacturing is an important consideration. Sustainable production methods, including the use of bio-based alkyl sources and green solvents, are being explored to minimize the ecological footprint of these processes. Additionally, recycling and recovery strategies for unreacted alkylating agents and byproducts are being implemented to improve overall process efficiency and reduce waste.
As the field progresses, automation and process control systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing for better monitoring and adjustment of reaction parameters in real-time. This level of control is essential for maintaining consistency across large production runs and adapting to variations in raw materials or environmental conditions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!