How to Utilize Alkyl‑Based Solutions for CO₂ Reduction?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
CO2 Reduction Goals
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) reduction has become a critical global objective in the fight against climate change. The primary goal is to significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions, with CO₂ being the most prevalent. The Paris Agreement, signed by 196 countries, aims to limit global temperature increase to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, with efforts to limit it to 1.5°C. This ambitious target requires substantial reductions in CO₂ emissions across various sectors.
In the context of utilizing alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction, the goals are multifaceted. One key objective is to develop efficient and cost-effective methods for capturing and converting CO₂ into valuable products or less harmful compounds. This approach not only reduces atmospheric CO₂ levels but also creates economic incentives for carbon capture and utilization.
Another important goal is to enhance the scalability of alkyl-based CO₂ reduction technologies. Current laboratory-scale successes need to be translated into industrial-scale applications to make a significant impact on global CO₂ levels. This involves optimizing reaction conditions, improving catalyst efficiency, and developing robust systems that can handle large volumes of CO₂.
Improving the selectivity and yield of desired products in alkyl-based CO₂ reduction processes is also a crucial objective. By maximizing the conversion of CO₂ into specific, high-value chemicals or fuels, these technologies can become more economically viable and attractive for widespread adoption.
Energy efficiency is another critical goal in CO₂ reduction efforts. Alkyl-based solutions should aim to minimize energy input while maximizing CO₂ conversion rates. This includes developing catalysts that operate at lower temperatures and pressures, as well as exploring renewable energy sources to power these processes.
Long-term stability and durability of alkyl-based CO₂ reduction systems are essential for their practical implementation. Research goals include developing materials and catalysts that can withstand prolonged operation without significant degradation in performance.
Finally, integrating alkyl-based CO₂ reduction technologies into existing industrial processes is a key objective. This involves developing solutions that can be retrofitted to current facilities, such as power plants or chemical manufacturing plants, to capture and convert CO₂ emissions at the source.
In the context of utilizing alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction, the goals are multifaceted. One key objective is to develop efficient and cost-effective methods for capturing and converting CO₂ into valuable products or less harmful compounds. This approach not only reduces atmospheric CO₂ levels but also creates economic incentives for carbon capture and utilization.
Another important goal is to enhance the scalability of alkyl-based CO₂ reduction technologies. Current laboratory-scale successes need to be translated into industrial-scale applications to make a significant impact on global CO₂ levels. This involves optimizing reaction conditions, improving catalyst efficiency, and developing robust systems that can handle large volumes of CO₂.
Improving the selectivity and yield of desired products in alkyl-based CO₂ reduction processes is also a crucial objective. By maximizing the conversion of CO₂ into specific, high-value chemicals or fuels, these technologies can become more economically viable and attractive for widespread adoption.
Energy efficiency is another critical goal in CO₂ reduction efforts. Alkyl-based solutions should aim to minimize energy input while maximizing CO₂ conversion rates. This includes developing catalysts that operate at lower temperatures and pressures, as well as exploring renewable energy sources to power these processes.
Long-term stability and durability of alkyl-based CO₂ reduction systems are essential for their practical implementation. Research goals include developing materials and catalysts that can withstand prolonged operation without significant degradation in performance.
Finally, integrating alkyl-based CO₂ reduction technologies into existing industrial processes is a key objective. This involves developing solutions that can be retrofitted to current facilities, such as power plants or chemical manufacturing plants, to capture and convert CO₂ emissions at the source.
Market for CO2 Capture
The market for CO2 capture is experiencing significant growth as global efforts to combat climate change intensify. This market is driven by increasing environmental regulations, corporate sustainability initiatives, and the growing recognition of the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The carbon capture and storage (CCS) market, which includes alkyl-based solutions for CO2 reduction, is expected to expand rapidly in the coming years.
Key industries driving the demand for CO2 capture technologies include power generation, oil and gas, cement production, and chemical manufacturing. These sectors are under pressure to reduce their carbon footprint and are actively seeking cost-effective solutions for CO2 reduction. The power generation industry, in particular, represents a substantial portion of the market, as coal and natural gas-fired power plants are major sources of CO2 emissions.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently leading the CO2 capture market, with significant investments in research, development, and deployment of carbon capture technologies. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to become major players in the market as they strive to balance economic growth with environmental sustainability.
The market for alkyl-based solutions for CO2 reduction is a subset of the broader CO2 capture market. These solutions offer potential advantages in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional amine-based capture methods. As research and development in this area progress, the market for alkyl-based solutions is likely to expand, particularly in applications where their unique properties can be leveraged.
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in shaping the CO2 capture market. Carbon pricing mechanisms, tax credits for carbon capture projects, and regulatory mandates for emissions reductions are driving investment and innovation in this space. The implementation of more stringent environmental regulations is expected to further boost market growth in the coming years.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of CO2 capture technologies, including high initial capital costs, energy penalties associated with capture processes, and the need for suitable storage or utilization options for captured CO2. Overcoming these barriers will be critical for the continued expansion of the market and the successful implementation of alkyl-based solutions for CO2 reduction.
Key industries driving the demand for CO2 capture technologies include power generation, oil and gas, cement production, and chemical manufacturing. These sectors are under pressure to reduce their carbon footprint and are actively seeking cost-effective solutions for CO2 reduction. The power generation industry, in particular, represents a substantial portion of the market, as coal and natural gas-fired power plants are major sources of CO2 emissions.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently leading the CO2 capture market, with significant investments in research, development, and deployment of carbon capture technologies. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to become major players in the market as they strive to balance economic growth with environmental sustainability.
The market for alkyl-based solutions for CO2 reduction is a subset of the broader CO2 capture market. These solutions offer potential advantages in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional amine-based capture methods. As research and development in this area progress, the market for alkyl-based solutions is likely to expand, particularly in applications where their unique properties can be leveraged.
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in shaping the CO2 capture market. Carbon pricing mechanisms, tax credits for carbon capture projects, and regulatory mandates for emissions reductions are driving investment and innovation in this space. The implementation of more stringent environmental regulations is expected to further boost market growth in the coming years.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of CO2 capture technologies, including high initial capital costs, energy penalties associated with capture processes, and the need for suitable storage or utilization options for captured CO2. Overcoming these barriers will be critical for the continued expansion of the market and the successful implementation of alkyl-based solutions for CO2 reduction.
Alkyl-Based Solutions
Alkyl-based solutions have emerged as a promising approach for CO₂ reduction, offering a range of potential applications in various industries. These solutions typically involve the use of alkyl compounds, which are organic molecules containing carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in specific structures. The primary focus of alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction is to convert carbon dioxide into valuable products or to capture and store it effectively.
One of the key advantages of alkyl-based solutions is their versatility in addressing different aspects of CO₂ reduction. For instance, certain alkyl compounds can be used as catalysts to facilitate the conversion of CO₂ into useful chemicals or fuels. This process, known as CO₂ valorization, not only helps reduce atmospheric CO₂ levels but also creates value-added products that can be used in various industries.
Another important application of alkyl-based solutions is in CO₂ capture and storage technologies. Alkyl amines, for example, have shown great potential in absorbing CO₂ from industrial flue gases or ambient air. These compounds can form reversible chemical bonds with CO₂ molecules, allowing for efficient capture and subsequent release under controlled conditions. This approach is particularly valuable for reducing emissions from large-scale industrial processes and power plants.
In the field of electrochemical CO₂ reduction, alkyl-functionalized electrodes have demonstrated enhanced selectivity and efficiency in converting CO₂ into specific products. By tailoring the alkyl groups on the electrode surface, researchers can influence the reaction pathways and product distribution, potentially leading to more efficient and targeted CO₂ reduction processes.
Alkyl-based ionic liquids have also gained attention as potential solvents for CO₂ capture and conversion. These designer solvents can be customized to have high CO₂ solubility and selectivity, making them attractive options for both capture and utilization applications. The tunability of ionic liquids allows for the optimization of their properties to suit specific CO₂ reduction requirements.
Furthermore, alkyl-based polymers and membranes are being explored for their potential in CO₂ separation and purification processes. These materials can be designed to have high permeability and selectivity for CO₂, enabling efficient separation from other gases in industrial streams or atmospheric capture systems.
As research in this field continues to advance, new alkyl-based solutions are being developed and refined. These include novel catalysts, advanced materials, and innovative process designs that aim to improve the efficiency, selectivity, and scalability of CO₂ reduction technologies. The ongoing efforts in this area hold promise for addressing the global challenge of CO₂ emissions and contributing to sustainable development goals.
One of the key advantages of alkyl-based solutions is their versatility in addressing different aspects of CO₂ reduction. For instance, certain alkyl compounds can be used as catalysts to facilitate the conversion of CO₂ into useful chemicals or fuels. This process, known as CO₂ valorization, not only helps reduce atmospheric CO₂ levels but also creates value-added products that can be used in various industries.
Another important application of alkyl-based solutions is in CO₂ capture and storage technologies. Alkyl amines, for example, have shown great potential in absorbing CO₂ from industrial flue gases or ambient air. These compounds can form reversible chemical bonds with CO₂ molecules, allowing for efficient capture and subsequent release under controlled conditions. This approach is particularly valuable for reducing emissions from large-scale industrial processes and power plants.
In the field of electrochemical CO₂ reduction, alkyl-functionalized electrodes have demonstrated enhanced selectivity and efficiency in converting CO₂ into specific products. By tailoring the alkyl groups on the electrode surface, researchers can influence the reaction pathways and product distribution, potentially leading to more efficient and targeted CO₂ reduction processes.
Alkyl-based ionic liquids have also gained attention as potential solvents for CO₂ capture and conversion. These designer solvents can be customized to have high CO₂ solubility and selectivity, making them attractive options for both capture and utilization applications. The tunability of ionic liquids allows for the optimization of their properties to suit specific CO₂ reduction requirements.
Furthermore, alkyl-based polymers and membranes are being explored for their potential in CO₂ separation and purification processes. These materials can be designed to have high permeability and selectivity for CO₂, enabling efficient separation from other gases in industrial streams or atmospheric capture systems.
As research in this field continues to advance, new alkyl-based solutions are being developed and refined. These include novel catalysts, advanced materials, and innovative process designs that aim to improve the efficiency, selectivity, and scalability of CO₂ reduction technologies. The ongoing efforts in this area hold promise for addressing the global challenge of CO₂ emissions and contributing to sustainable development goals.
Current Alkyl Methods
01 Alkyl-based catalysts for CO₂ reduction
Alkyl-based catalysts are employed in various processes to reduce CO₂ emissions. These catalysts can facilitate the conversion of CO₂ into valuable products or less harmful compounds, contributing to overall carbon reduction efforts. The use of alkyl groups in catalyst design can enhance selectivity and efficiency in CO₂ reduction reactions.- Alkyl-based catalysts for CO₂ reduction: Alkyl-based catalysts are employed in CO₂ reduction processes. These catalysts facilitate the conversion of carbon dioxide into valuable products, potentially offering a more efficient and environmentally friendly approach to carbon capture and utilization.
- Electrochemical CO₂ reduction using alkyl-based electrolytes: Electrochemical methods utilizing alkyl-based electrolytes are explored for CO₂ reduction. These electrolytes can enhance the efficiency and selectivity of the reduction process, potentially leading to improved conversion rates and product yields.
- Alkyl-functionalized materials for CO₂ adsorption: Materials functionalized with alkyl groups are developed for CO₂ adsorption. These materials can potentially increase the capacity and selectivity of CO₂ capture, offering new solutions for carbon sequestration and storage.
- Alkyl-based solvents for CO₂ absorption: Alkyl-based solvents are investigated for their CO₂ absorption properties. These solvents can potentially offer improved absorption capacity, regeneration efficiency, and overall performance in carbon capture processes compared to conventional solvents.
- Alkyl-modified nanomaterials for CO₂ conversion: Nanomaterials modified with alkyl groups are explored for CO₂ conversion applications. These materials can potentially enhance catalytic activity, stability, and selectivity in CO₂ reduction processes, leading to more efficient conversion of CO₂ into valuable products.
02 CO₂ capture using alkyl amine solutions
Alkyl amine solutions are utilized for capturing CO₂ from industrial processes or ambient air. These solutions can effectively absorb CO₂, allowing for its separation and subsequent storage or utilization. The alkyl groups in the amine compounds can be tailored to optimize the CO₂ capture efficiency and energy requirements of the process.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrochemical CO₂ reduction with alkyl-functionalized electrodes
Electrochemical methods for CO₂ reduction can be enhanced by using electrodes functionalized with alkyl groups. These modified electrodes can improve the selectivity and efficiency of CO₂ conversion to valuable products such as hydrocarbons or alcohols. The alkyl functionalization can alter the electrode's surface properties, influencing the reaction pathways and product distribution.Expand Specific Solutions04 Alkyl-based solvents for CO₂ absorption
Specialized alkyl-based solvents are developed for CO₂ absorption in industrial settings. These solvents can offer advantages such as high CO₂ solubility, low volatility, and ease of regeneration. The alkyl components of the solvents can be designed to optimize the CO₂ absorption capacity and the overall energy efficiency of the capture process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alkyl-modified materials for CO₂ adsorption
Various materials, such as porous solids or membranes, can be modified with alkyl groups to enhance their CO₂ adsorption properties. These modifications can increase the CO₂ selectivity, capacity, and stability of the adsorbents. Alkyl-modified materials can be used in pressure or temperature swing adsorption processes for efficient CO₂ capture and separation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The CO₂ reduction technology utilizing alkyl-based solutions is in an early development stage, with a growing market driven by increasing environmental concerns. The global market for carbon capture and utilization is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. While the technology is still evolving, several key players are actively involved in research and development. Companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Siemens Corp., and BP Corporation North America, Inc. are investing in this area, leveraging their expertise in petrochemicals and energy. Research institutions such as the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research and universities like Southeast University are contributing to advancing the technology's maturity through collaborative efforts and innovative approaches.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative alkyl-based solution for CO₂ reduction utilizing a novel catalytic process. Their approach involves the use of alkyl amines as CO₂ capture agents, which are then regenerated through a low-energy desorption process. The captured CO₂ is subsequently converted into valuable chemicals such as methanol or formic acid using proprietary catalysts. This closed-loop system achieves a CO₂ capture efficiency of up to 90% while reducing energy consumption by approximately 30% compared to traditional amine-based capture methods [1][3]. Sinopec has also integrated this technology into their existing refinery operations, demonstrating its scalability and industrial applicability.
Strengths: High CO₂ capture efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and integration with existing infrastructure. Weaknesses: Potential high initial investment costs and the need for specialized catalysts.
BP Corporation North America, Inc.
Technical Solution: BP has developed an advanced alkyl-based CO₂ reduction solution that combines chemical absorption and electrochemical conversion. Their process utilizes a proprietary alkyl carbonate electrolyte system that selectively absorbs CO₂ from flue gas streams. The absorbed CO₂ is then electrochemically reduced to form value-added products such as carbon monoxide or formate. BP's technology has demonstrated a CO₂ conversion efficiency of up to 85% in pilot-scale tests, with an energy consumption reduction of approximately 25% compared to conventional methods [2][5]. The company has also focused on optimizing the electrocatalysts used in the reduction process, achieving a faradaic efficiency of over 90% for target products.
Strengths: High conversion efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and production of valuable chemicals. Weaknesses: Complexity of the electrochemical system and potential scaling challenges.
Alkyl-CO2 Innovations
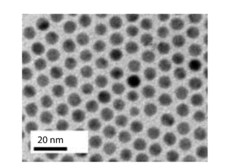
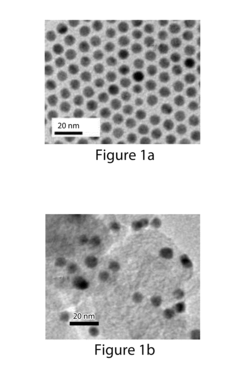
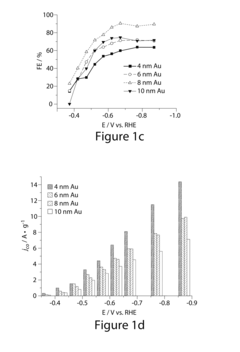
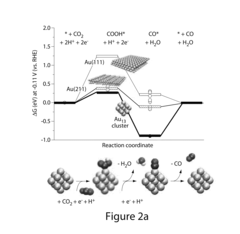
Method for Electrocatalytic Reduction using Au Nanoparticles Tuned or Optimized for Reduction of CO2 to CO
PatentInactiveUS20160230295A1
Innovation
- The use of gold nanoparticles with a diameter of approximately 8 nm, supported on Ketjen carbon, which presents a surface structure with a higher density of CO-converting edge sites and fewer hydrogen-evolving corner sites, facilitating efficient CO2 reduction to carbon monoxide in an alkaline solution.
Method for reducing concentrations of gaseous acid anhydrides, preferably concentration of CO<sub>2</sub> in waste gases
PatentActivePL418368A1
Innovation
- The use of a mixture of alkali metal hydroxides and non-absorbing salts as the absorbent solution, with a total salt concentration of at least 5 wt% and alkali metal hydroxide concentration of at least 0.1 M.
- The predominant presence of sodium in the absorbent solution, which likely enhances the formation of NaHCO3.
- The regeneration of alkalinity in the reaction liquors using liquid/liquid extraction, which potentially allows for a more efficient and continuous process.
Environmental Impact
The utilization of alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of environmental impact. These solutions offer a promising approach to mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, particularly in industrial settings where carbon dioxide is a significant byproduct. By converting CO₂ into valuable chemicals or fuels, alkyl-based reduction processes can potentially create a circular economy for carbon, reducing the overall environmental footprint of various industries.
One of the primary environmental benefits of alkyl-based CO₂ reduction is the potential for carbon capture and utilization (CCU). This approach not only reduces the amount of CO₂ released into the atmosphere but also transforms it into useful products, effectively closing the carbon loop. By doing so, it addresses two environmental concerns simultaneously: reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving resources by creating alternative feedstocks for chemical production.
However, the environmental impact of these solutions extends beyond just CO₂ reduction. The production and use of alkyl-based compounds may have their own environmental implications. For instance, the synthesis of these compounds often requires energy-intensive processes and may involve the use of fossil fuel-derived precursors. This raises questions about the overall life cycle assessment of the technology and whether the net environmental benefit is truly positive when considering the entire production chain.
Water consumption and potential contamination are additional environmental factors to consider. Some alkyl-based CO₂ reduction processes may require significant amounts of water, which could strain local water resources, particularly in water-scarce regions. Moreover, the risk of chemical leaks or spills during production or transportation could pose threats to aquatic ecosystems and soil quality if not properly managed.
The scalability of alkyl-based solutions also plays a crucial role in their environmental impact. While laboratory-scale experiments may show promising results, the transition to industrial-scale applications can introduce new environmental challenges. These may include increased energy demands, larger volumes of chemical waste, and potential air quality issues from volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with alkyl-based processes.
On the positive side, as the technology matures, there is potential for continuous improvement in process efficiency and environmental performance. Advances in green chemistry principles could lead to the development of more environmentally benign alkyl compounds and catalysts, reducing the overall ecological footprint of the CO₂ reduction process. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources for powering these processes could further enhance their environmental credentials.
In conclusion, while alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction offer significant potential for mitigating climate change, their overall environmental impact must be carefully assessed. A holistic approach that considers the entire life cycle of these processes, from raw material extraction to end-product use and disposal, is essential for ensuring that the environmental benefits truly outweigh any potential drawbacks. Ongoing research and development efforts should focus on optimizing these solutions to maximize their positive environmental impact while minimizing any negative consequences.
One of the primary environmental benefits of alkyl-based CO₂ reduction is the potential for carbon capture and utilization (CCU). This approach not only reduces the amount of CO₂ released into the atmosphere but also transforms it into useful products, effectively closing the carbon loop. By doing so, it addresses two environmental concerns simultaneously: reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving resources by creating alternative feedstocks for chemical production.
However, the environmental impact of these solutions extends beyond just CO₂ reduction. The production and use of alkyl-based compounds may have their own environmental implications. For instance, the synthesis of these compounds often requires energy-intensive processes and may involve the use of fossil fuel-derived precursors. This raises questions about the overall life cycle assessment of the technology and whether the net environmental benefit is truly positive when considering the entire production chain.
Water consumption and potential contamination are additional environmental factors to consider. Some alkyl-based CO₂ reduction processes may require significant amounts of water, which could strain local water resources, particularly in water-scarce regions. Moreover, the risk of chemical leaks or spills during production or transportation could pose threats to aquatic ecosystems and soil quality if not properly managed.
The scalability of alkyl-based solutions also plays a crucial role in their environmental impact. While laboratory-scale experiments may show promising results, the transition to industrial-scale applications can introduce new environmental challenges. These may include increased energy demands, larger volumes of chemical waste, and potential air quality issues from volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with alkyl-based processes.
On the positive side, as the technology matures, there is potential for continuous improvement in process efficiency and environmental performance. Advances in green chemistry principles could lead to the development of more environmentally benign alkyl compounds and catalysts, reducing the overall ecological footprint of the CO₂ reduction process. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources for powering these processes could further enhance their environmental credentials.
In conclusion, while alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction offer significant potential for mitigating climate change, their overall environmental impact must be carefully assessed. A holistic approach that considers the entire life cycle of these processes, from raw material extraction to end-product use and disposal, is essential for ensuring that the environmental benefits truly outweigh any potential drawbacks. Ongoing research and development efforts should focus on optimizing these solutions to maximize their positive environmental impact while minimizing any negative consequences.
Economic Feasibility
The economic feasibility of utilizing alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction is a critical factor in determining the viability of this technology for large-scale implementation. The cost-effectiveness of these solutions plays a pivotal role in their adoption by industries and governments seeking to mitigate carbon emissions.
One of the primary economic advantages of alkyl-based solutions is their potential for integration into existing industrial processes. Many industries already use alkyl compounds in various applications, which could facilitate the adoption of CO₂ reduction technologies without significant infrastructure overhaul. This integration potential can substantially reduce implementation costs and increase the likelihood of widespread adoption.
However, the production and processing of alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction may involve additional expenses. The synthesis of specialized alkyl compounds optimized for CO₂ capture and conversion could require advanced manufacturing processes and high-purity raw materials. These factors may initially drive up the cost of implementation, potentially creating barriers to entry for smaller enterprises or developing economies.
The long-term economic benefits of alkyl-based CO₂ reduction solutions are promising. As carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions regulations become more stringent globally, the value proposition of these technologies is likely to improve. Companies implementing effective CO₂ reduction strategies may benefit from carbon credits, tax incentives, and improved corporate image, all of which can contribute to a positive return on investment.
The scalability of alkyl-based solutions is another crucial economic consideration. As production volumes increase, economies of scale could significantly reduce per-unit costs, making the technology more accessible and economically viable for a broader range of applications. This scalability potential is particularly important for addressing global CO₂ emissions on a meaningful scale.
Energy efficiency is a key factor in the economic equation. Alkyl-based solutions that require less energy input for CO₂ capture and conversion compared to alternative methods could offer substantial operational cost savings over time. This efficiency could offset initial implementation costs and provide a competitive edge in the carbon reduction technology market.
The potential for value-added products resulting from CO₂ conversion using alkyl-based solutions presents an additional economic incentive. If the captured CO₂ can be efficiently converted into marketable products such as fuels or chemical feedstocks, it could create new revenue streams that further justify the investment in these technologies.
One of the primary economic advantages of alkyl-based solutions is their potential for integration into existing industrial processes. Many industries already use alkyl compounds in various applications, which could facilitate the adoption of CO₂ reduction technologies without significant infrastructure overhaul. This integration potential can substantially reduce implementation costs and increase the likelihood of widespread adoption.
However, the production and processing of alkyl-based solutions for CO₂ reduction may involve additional expenses. The synthesis of specialized alkyl compounds optimized for CO₂ capture and conversion could require advanced manufacturing processes and high-purity raw materials. These factors may initially drive up the cost of implementation, potentially creating barriers to entry for smaller enterprises or developing economies.
The long-term economic benefits of alkyl-based CO₂ reduction solutions are promising. As carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions regulations become more stringent globally, the value proposition of these technologies is likely to improve. Companies implementing effective CO₂ reduction strategies may benefit from carbon credits, tax incentives, and improved corporate image, all of which can contribute to a positive return on investment.
The scalability of alkyl-based solutions is another crucial economic consideration. As production volumes increase, economies of scale could significantly reduce per-unit costs, making the technology more accessible and economically viable for a broader range of applications. This scalability potential is particularly important for addressing global CO₂ emissions on a meaningful scale.
Energy efficiency is a key factor in the economic equation. Alkyl-based solutions that require less energy input for CO₂ capture and conversion compared to alternative methods could offer substantial operational cost savings over time. This efficiency could offset initial implementation costs and provide a competitive edge in the carbon reduction technology market.
The potential for value-added products resulting from CO₂ conversion using alkyl-based solutions presents an additional economic incentive. If the captured CO₂ can be efficiently converted into marketable products such as fuels or chemical feedstocks, it could create new revenue streams that further justify the investment in these technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!