How to Enhance HDR Content with ULED?
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED HDR Enhancement Background and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology has revolutionized the way we perceive visual content, offering a more lifelike and immersive viewing experience. As the demand for superior image quality continues to grow, the integration of Ultra LED (ULED) technology with HDR content enhancement has emerged as a promising solution to push the boundaries of display capabilities.
The evolution of display technologies has been driven by the pursuit of more accurate color reproduction, higher contrast ratios, and improved brightness levels. ULED, a proprietary technology developed by leading manufacturers, represents a significant advancement in LED backlighting systems. By combining ULED with HDR content enhancement techniques, the industry aims to deliver unprecedented visual quality that closely mimics the human eye's perception of the natural world.
The primary objective of enhancing HDR content with ULED is to maximize the potential of both technologies, creating a synergistic effect that results in superior image quality. This involves optimizing the dynamic range, expanding the color gamut, and improving local dimming capabilities to achieve deeper blacks and brighter highlights. By doing so, content creators and display manufacturers seek to provide viewers with a more engaging and realistic visual experience across various media platforms.
One of the key challenges in this technological pursuit is the need to address the limitations of current display hardware while ensuring compatibility with existing HDR content standards. As such, the development of ULED HDR enhancement techniques focuses on intelligent algorithms and advanced hardware solutions that can effectively process and render HDR content on ULED displays.
The market demand for enhanced HDR experiences is driven by several factors, including the proliferation of 4K and 8K content, the growing popularity of streaming services offering HDR content, and the increasing adoption of HDR-capable devices in both consumer and professional markets. This has created a competitive landscape where display manufacturers are constantly striving to differentiate their products through superior image quality and innovative features.
As we delve deeper into the technical aspects of ULED HDR enhancement, it is essential to consider the broader implications for the entertainment industry, content creation workflows, and consumer expectations. The successful implementation of these technologies has the potential to redefine visual standards across various applications, from home entertainment systems to professional studio monitors and digital signage solutions.
The evolution of display technologies has been driven by the pursuit of more accurate color reproduction, higher contrast ratios, and improved brightness levels. ULED, a proprietary technology developed by leading manufacturers, represents a significant advancement in LED backlighting systems. By combining ULED with HDR content enhancement techniques, the industry aims to deliver unprecedented visual quality that closely mimics the human eye's perception of the natural world.
The primary objective of enhancing HDR content with ULED is to maximize the potential of both technologies, creating a synergistic effect that results in superior image quality. This involves optimizing the dynamic range, expanding the color gamut, and improving local dimming capabilities to achieve deeper blacks and brighter highlights. By doing so, content creators and display manufacturers seek to provide viewers with a more engaging and realistic visual experience across various media platforms.
One of the key challenges in this technological pursuit is the need to address the limitations of current display hardware while ensuring compatibility with existing HDR content standards. As such, the development of ULED HDR enhancement techniques focuses on intelligent algorithms and advanced hardware solutions that can effectively process and render HDR content on ULED displays.
The market demand for enhanced HDR experiences is driven by several factors, including the proliferation of 4K and 8K content, the growing popularity of streaming services offering HDR content, and the increasing adoption of HDR-capable devices in both consumer and professional markets. This has created a competitive landscape where display manufacturers are constantly striving to differentiate their products through superior image quality and innovative features.
As we delve deeper into the technical aspects of ULED HDR enhancement, it is essential to consider the broader implications for the entertainment industry, content creation workflows, and consumer expectations. The successful implementation of these technologies has the potential to redefine visual standards across various applications, from home entertainment systems to professional studio monitors and digital signage solutions.
Market Demand for Advanced HDR Display Technologies
The demand for advanced HDR display technologies has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing consumer appetite for high-quality visual experiences across various platforms. As content creators and distributors continue to push the boundaries of image quality, there is a corresponding need for display technologies that can accurately reproduce this enhanced content.
In the television market, HDR-capable displays have become a standard feature in mid-range to high-end models. Consumer awareness of HDR technology has grown significantly, with many viewers now actively seeking out HDR content and compatible devices. This trend is particularly evident in the premium TV segment, where manufacturers are competing to offer the best HDR performance as a key differentiator.
The mobile device market has also seen a surge in demand for HDR display technologies. As smartphones and tablets increasingly become primary devices for content consumption, users are expecting cinema-quality visuals on their portable screens. This has led to a rapid adoption of HDR-capable displays in flagship and mid-range mobile devices.
In the professional sector, there is a growing demand for HDR displays in fields such as content creation, color grading, and medical imaging. These industries require displays that can accurately represent the full dynamic range and color gamut of HDR content, driving the development of specialized high-end monitors.
The gaming industry has emerged as another significant driver of HDR display technology adoption. With the latest generation of gaming consoles and high-end PCs supporting HDR rendering, gamers are seeking displays that can fully showcase the enhanced visual fidelity of modern games. This has led to an increase in HDR-capable gaming monitors and TVs designed specifically for gaming applications.
The automotive industry is also showing interest in HDR display technologies for in-vehicle infotainment systems and digital dashboards. As cars become more connected and autonomous, the quality of in-vehicle displays is becoming an important factor in user experience and safety.
Despite the growing demand, there are still challenges in the widespread adoption of advanced HDR display technologies. These include the higher cost of HDR-capable displays, the need for standardization across different HDR formats, and the limited availability of HDR content in some regions. However, as technology advances and economies of scale come into play, these barriers are expected to diminish over time.
In the television market, HDR-capable displays have become a standard feature in mid-range to high-end models. Consumer awareness of HDR technology has grown significantly, with many viewers now actively seeking out HDR content and compatible devices. This trend is particularly evident in the premium TV segment, where manufacturers are competing to offer the best HDR performance as a key differentiator.
The mobile device market has also seen a surge in demand for HDR display technologies. As smartphones and tablets increasingly become primary devices for content consumption, users are expecting cinema-quality visuals on their portable screens. This has led to a rapid adoption of HDR-capable displays in flagship and mid-range mobile devices.
In the professional sector, there is a growing demand for HDR displays in fields such as content creation, color grading, and medical imaging. These industries require displays that can accurately represent the full dynamic range and color gamut of HDR content, driving the development of specialized high-end monitors.
The gaming industry has emerged as another significant driver of HDR display technology adoption. With the latest generation of gaming consoles and high-end PCs supporting HDR rendering, gamers are seeking displays that can fully showcase the enhanced visual fidelity of modern games. This has led to an increase in HDR-capable gaming monitors and TVs designed specifically for gaming applications.
The automotive industry is also showing interest in HDR display technologies for in-vehicle infotainment systems and digital dashboards. As cars become more connected and autonomous, the quality of in-vehicle displays is becoming an important factor in user experience and safety.
Despite the growing demand, there are still challenges in the widespread adoption of advanced HDR display technologies. These include the higher cost of HDR-capable displays, the need for standardization across different HDR formats, and the limited availability of HDR content in some regions. However, as technology advances and economies of scale come into play, these barriers are expected to diminish over time.
Current ULED and HDR Technology Landscape
The current ULED and HDR technology landscape is characterized by rapid advancements and increasing market demand for high-quality visual experiences. ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology, developed by Hisense, represents a significant leap in display technology, offering enhanced brightness, contrast, and color performance compared to traditional LED displays.
ULED incorporates several key technologies, including local dimming, quantum dot color enhancement, and HDR (High Dynamic Range) processing. Local dimming allows for precise control of backlight zones, resulting in deeper blacks and improved contrast ratios. Quantum dot technology expands the color gamut, enabling more vibrant and accurate color reproduction.
HDR technology, on the other hand, has become a standard feature in modern displays, providing a wider range of luminance and color information. HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, and HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma) are the primary HDR formats currently in use, each offering different capabilities and compatibility with various devices and content.
The integration of ULED and HDR technologies has led to significant improvements in picture quality, with displays capable of achieving higher peak brightness levels, better contrast ratios, and more accurate color reproduction. This combination addresses many of the limitations of traditional LED displays, particularly in terms of dynamic range and color accuracy.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the potential of HDR content on ULED displays. One key issue is the limited availability of native HDR content, which necessitates the development of effective upscaling and tone-mapping algorithms to enhance standard dynamic range (SDR) content for HDR displays.
Another challenge lies in the standardization of HDR formats and metadata. The existence of multiple HDR standards can lead to compatibility issues and inconsistent viewing experiences across different devices and platforms. This fragmentation in the market creates obstacles for content creators and device manufacturers alike.
The current landscape also sees ongoing research and development in areas such as improved local dimming algorithms, enhanced color volume mapping, and more efficient HDR processing techniques. These efforts aim to further reduce artifacts, improve energy efficiency, and provide more consistent HDR performance across a wide range of content types.
As the technology continues to evolve, we are witnessing a trend towards higher peak brightness capabilities, wider color gamuts, and more sophisticated HDR processing engines. This progression is driven by the increasing demand for more immersive and lifelike visual experiences in both home entertainment and professional applications.
ULED incorporates several key technologies, including local dimming, quantum dot color enhancement, and HDR (High Dynamic Range) processing. Local dimming allows for precise control of backlight zones, resulting in deeper blacks and improved contrast ratios. Quantum dot technology expands the color gamut, enabling more vibrant and accurate color reproduction.
HDR technology, on the other hand, has become a standard feature in modern displays, providing a wider range of luminance and color information. HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, and HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma) are the primary HDR formats currently in use, each offering different capabilities and compatibility with various devices and content.
The integration of ULED and HDR technologies has led to significant improvements in picture quality, with displays capable of achieving higher peak brightness levels, better contrast ratios, and more accurate color reproduction. This combination addresses many of the limitations of traditional LED displays, particularly in terms of dynamic range and color accuracy.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the potential of HDR content on ULED displays. One key issue is the limited availability of native HDR content, which necessitates the development of effective upscaling and tone-mapping algorithms to enhance standard dynamic range (SDR) content for HDR displays.
Another challenge lies in the standardization of HDR formats and metadata. The existence of multiple HDR standards can lead to compatibility issues and inconsistent viewing experiences across different devices and platforms. This fragmentation in the market creates obstacles for content creators and device manufacturers alike.
The current landscape also sees ongoing research and development in areas such as improved local dimming algorithms, enhanced color volume mapping, and more efficient HDR processing techniques. These efforts aim to further reduce artifacts, improve energy efficiency, and provide more consistent HDR performance across a wide range of content types.
As the technology continues to evolve, we are witnessing a trend towards higher peak brightness capabilities, wider color gamuts, and more sophisticated HDR processing engines. This progression is driven by the increasing demand for more immersive and lifelike visual experiences in both home entertainment and professional applications.
Existing ULED-HDR Integration Solutions
01 HDR content processing for ULED displays
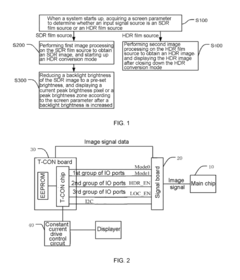
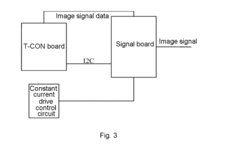
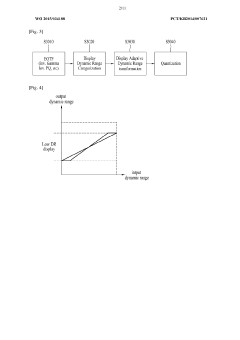
Methods for processing High Dynamic Range (HDR) content specifically for Ultra LED (ULED) displays. This involves techniques for enhancing contrast, brightness, and color gamut to fully utilize the capabilities of ULED technology, resulting in more vivid and lifelike images.- HDR content processing for ULED displays: ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) displays require specialized processing for HDR (High Dynamic Range) content. This involves techniques for enhancing contrast, brightness, and color gamut to fully utilize the capabilities of ULED technology. The processing may include tone mapping, color space conversion, and dynamic range adaptation to ensure optimal HDR content presentation on ULED screens.
- ULED backlight control for HDR content: Advanced backlight control mechanisms are crucial for displaying HDR content on ULED displays. This involves precise local dimming techniques, dynamic backlight adjustment, and intelligent luminance control to achieve high contrast ratios and deep black levels. The backlight control system works in tandem with content analysis to optimize the display output for each frame of HDR content.
- Color management for ULED HDR displays: Effective color management is essential for accurately reproducing HDR content on ULED displays. This includes advanced color mapping algorithms, wide color gamut processing, and color volume optimization. The system ensures that the expanded color range of HDR content is faithfully represented within the capabilities of the ULED display, maintaining color accuracy and vibrancy.
- HDR metadata processing for ULED displays: Processing HDR metadata is crucial for optimizing content display on ULED screens. This involves interpreting and applying content-specific metadata, such as mastering display information, maximum and minimum brightness levels, and color space data. The metadata is used to dynamically adjust display parameters, ensuring that the HDR content is rendered as intended by content creators on ULED displays.
- ULED panel calibration for HDR content: Precise calibration of ULED panels is necessary to ensure accurate HDR content reproduction. This includes methods for characterizing panel response, compensating for panel variations, and maintaining consistent performance over time. Calibration techniques may involve software algorithms, hardware-based solutions, or a combination of both to optimize the display for HDR content across its entire luminance and color range.
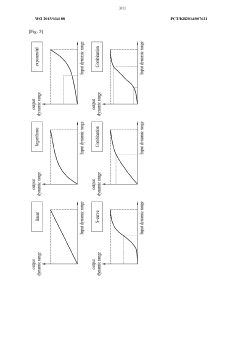
02 Tone mapping for HDR content on ULED screens
Techniques for tone mapping HDR content to optimize display on ULED screens. This includes algorithms for adjusting luminance levels and color spaces to match the specific characteristics of ULED displays, ensuring accurate representation of HDR content.Expand Specific Solutions03 ULED backlight control for HDR content
Methods for controlling ULED backlighting systems to enhance HDR content display. This involves precise local dimming techniques and dynamic backlight adjustment to improve contrast ratios and black levels, resulting in more impactful HDR imagery.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color management for HDR on ULED displays
Techniques for managing and enhancing color reproduction of HDR content on ULED displays. This includes methods for expanding color gamut, improving color accuracy, and optimizing color mapping to take full advantage of ULED's wide color capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions05 Adaptive content optimization for ULED HDR
Systems and methods for dynamically optimizing HDR content based on ULED display characteristics and viewing conditions. This involves real-time analysis and adjustment of content parameters to ensure optimal HDR performance across various ULED display models and environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ULED and HDR Display Industry
The HDR content enhancement with ULED technology is in a rapidly evolving phase, with significant market growth potential. The global HDR market is expanding, driven by increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences. Major players like LG Electronics, Samsung Electronics, and Dolby Laboratories are at the forefront, investing heavily in R&D. The technology's maturity varies, with established companies like Philips and Sharp offering advanced solutions, while emerging players such as Skyworth-RGB Electronics and TCL Digital Technology are quickly catching up. Chinese firms like Huawei and BOE Technology are also making significant strides, indicating a competitive and diverse landscape. The involvement of tech giants like Microsoft and AMD suggests broader applications beyond traditional display markets.
LG Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: LG's ULED HDR enhancement technology utilizes advanced local dimming algorithms and quantum dot color filters to significantly improve contrast and color accuracy. Their AI-powered processor analyzes and optimizes each frame in real-time, adjusting brightness and color levels to bring out the finest details in both bright and dark scenes. LG also implements dynamic tone mapping to preserve highlight details and expand the overall dynamic range of HDR content.
Strengths: Superior color accuracy and contrast; AI-driven real-time optimization. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost; may require specific hardware.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung's approach to enhancing HDR content with ULED technology involves their Quantum Matrix Technology Pro, which uses precise LED dimming and boosting to enhance contrast. Their Neural Quantum Processor upscales content to near-HDR quality and optimizes picture quality scene-by-scene. Samsung also employs a wide color gamut panel with quantum dots to produce more vivid and accurate colors, especially in HDR content.
Strengths: Excellent upscaling capabilities; precise contrast control. Weaknesses: Proprietary technology may limit compatibility; potentially higher power consumption.
Core Innovations in ULED-HDR Enhancement
Method for improving image effect and apparatus thereof
PatentActiveUS20180255225A1
Innovation
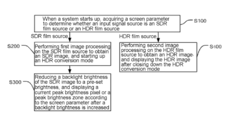
- A method that determines whether the input signal source is SDR or HDR upon startup, performs specific image processing, and adjusts backlight brightness to enhance the image effect, allowing SDR sources to be displayed with improved HDR-like quality by reducing backlight brightness and identifying peak brightness zones for localized dimming.
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving ultra-high definition broadcasting signal for high dynamic range representation in digital broadcasting system
PatentWO2015034188A1
Innovation
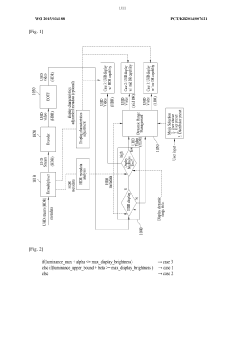
- A method and apparatus that include a receiver configured to receive UHD broadcast signals with wide dynamic range metadata, which converts the content to suit the display environment by comparing and adjusting the brightness ranges using different conversion methods for each section, including clipping and adaptive dynamic range transformation, ensuring optimal viewing experience.
Energy Efficiency Considerations in ULED-HDR Systems
Energy efficiency is a critical consideration in the development and implementation of ULED-HDR systems. As these technologies continue to advance, the focus on reducing power consumption while maintaining high-quality visual performance becomes increasingly important. ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology, when combined with HDR (High Dynamic Range) content, offers significant improvements in picture quality but also presents challenges in terms of energy management.
One of the primary concerns in ULED-HDR systems is the power required to achieve the high brightness levels necessary for HDR content. ULED displays are capable of producing extremely bright highlights, which is essential for HDR, but this can lead to increased energy consumption. To address this, manufacturers are developing more efficient LED backlighting systems that can deliver the required luminance while minimizing power usage.
Advanced local dimming techniques play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency. By precisely controlling individual LED zones, ULED-HDR systems can reduce power consumption in darker areas of the image while maintaining brightness in highlight regions. This selective dimming not only improves contrast but also significantly reduces overall energy usage.
The development of more efficient color filters and quantum dot technologies is another area of focus for improving energy efficiency in ULED-HDR systems. These advancements allow for better color reproduction with less light loss, meaning that less energy is required to achieve the same level of color performance and brightness.
Power management algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated in ULED-HDR displays. These algorithms dynamically adjust the display's power consumption based on the content being shown and ambient lighting conditions. For instance, in brighter environments, the display can increase its luminance to maintain visibility while reducing power in darker settings.
Heat management is another critical aspect of energy efficiency in ULED-HDR systems. Efficient heat dissipation not only prolongs the lifespan of the display but also reduces the energy wasted as heat. Manufacturers are exploring innovative cooling solutions, such as advanced heat sinks and thermal management materials, to improve overall system efficiency.
The integration of ambient light sensors and automatic brightness adjustment features further contributes to energy savings. These systems can automatically optimize the display's brightness based on the surrounding light conditions, reducing unnecessary power consumption while maintaining optimal viewing experiences.
As ULED-HDR technology continues to evolve, research into new materials and manufacturing processes that can improve energy efficiency is ongoing. This includes the development of more efficient LED phosphors, improved driver circuits, and optimized optical designs that can deliver superior HDR performance with reduced power requirements.
One of the primary concerns in ULED-HDR systems is the power required to achieve the high brightness levels necessary for HDR content. ULED displays are capable of producing extremely bright highlights, which is essential for HDR, but this can lead to increased energy consumption. To address this, manufacturers are developing more efficient LED backlighting systems that can deliver the required luminance while minimizing power usage.
Advanced local dimming techniques play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency. By precisely controlling individual LED zones, ULED-HDR systems can reduce power consumption in darker areas of the image while maintaining brightness in highlight regions. This selective dimming not only improves contrast but also significantly reduces overall energy usage.
The development of more efficient color filters and quantum dot technologies is another area of focus for improving energy efficiency in ULED-HDR systems. These advancements allow for better color reproduction with less light loss, meaning that less energy is required to achieve the same level of color performance and brightness.
Power management algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated in ULED-HDR displays. These algorithms dynamically adjust the display's power consumption based on the content being shown and ambient lighting conditions. For instance, in brighter environments, the display can increase its luminance to maintain visibility while reducing power in darker settings.
Heat management is another critical aspect of energy efficiency in ULED-HDR systems. Efficient heat dissipation not only prolongs the lifespan of the display but also reduces the energy wasted as heat. Manufacturers are exploring innovative cooling solutions, such as advanced heat sinks and thermal management materials, to improve overall system efficiency.
The integration of ambient light sensors and automatic brightness adjustment features further contributes to energy savings. These systems can automatically optimize the display's brightness based on the surrounding light conditions, reducing unnecessary power consumption while maintaining optimal viewing experiences.
As ULED-HDR technology continues to evolve, research into new materials and manufacturing processes that can improve energy efficiency is ongoing. This includes the development of more efficient LED phosphors, improved driver circuits, and optimized optical designs that can deliver superior HDR performance with reduced power requirements.
Standardization Efforts for ULED-HDR Technologies
Standardization efforts for ULED-HDR technologies are crucial for ensuring interoperability, consistency, and widespread adoption across the industry. Several organizations and consortia are actively working to develop and establish standards for ULED-HDR content creation, distribution, and display.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has been at the forefront of HDR standardization efforts, with its ITU-R BT.2100 recommendation serving as a foundation for HDR systems. This standard defines various aspects of HDR video, including transfer functions, color primaries, and metadata. As ULED technology advances, there is a growing need to incorporate its specific characteristics into existing or new standards.
The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) has also been instrumental in developing standards for HDR content production and distribution. Their ST 2084 standard, which defines the Perceptual Quantizer (PQ) transfer function, is widely used in HDR content creation. SMPTE is now exploring ways to extend these standards to accommodate the enhanced capabilities of ULED displays.
The Ultra HD Forum, a global organization dedicated to accelerating Ultra HD deployment, has been working on guidelines for HDR content delivery. They are now considering the inclusion of ULED-specific recommendations in their future releases, addressing issues such as brightness levels, color gamut, and dynamic range optimization for ULED displays.
The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) has been actively involved in defining HDR standards for consumer electronics. They are now exploring the possibility of creating a certification program for ULED-HDR displays, which would help consumers identify products that meet specific performance criteria.
In the realm of content delivery, the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is working on incorporating ULED-HDR considerations into video coding standards. This includes efforts to optimize compression techniques for the high brightness and wide color gamut capabilities of ULED displays.
Collaboration between display manufacturers, content creators, and broadcasters is essential for the development of comprehensive ULED-HDR standards. Industry forums and working groups are being established to facilitate discussions and reach consensus on key technical specifications and implementation guidelines.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, standardization efforts will need to remain flexible and adaptable. Future standards may need to address advanced features such as per-pixel local dimming, enhanced color volume mapping, and dynamic metadata for optimized content rendering on ULED displays.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has been at the forefront of HDR standardization efforts, with its ITU-R BT.2100 recommendation serving as a foundation for HDR systems. This standard defines various aspects of HDR video, including transfer functions, color primaries, and metadata. As ULED technology advances, there is a growing need to incorporate its specific characteristics into existing or new standards.
The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) has also been instrumental in developing standards for HDR content production and distribution. Their ST 2084 standard, which defines the Perceptual Quantizer (PQ) transfer function, is widely used in HDR content creation. SMPTE is now exploring ways to extend these standards to accommodate the enhanced capabilities of ULED displays.
The Ultra HD Forum, a global organization dedicated to accelerating Ultra HD deployment, has been working on guidelines for HDR content delivery. They are now considering the inclusion of ULED-specific recommendations in their future releases, addressing issues such as brightness levels, color gamut, and dynamic range optimization for ULED displays.
The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) has been actively involved in defining HDR standards for consumer electronics. They are now exploring the possibility of creating a certification program for ULED-HDR displays, which would help consumers identify products that meet specific performance criteria.
In the realm of content delivery, the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is working on incorporating ULED-HDR considerations into video coding standards. This includes efforts to optimize compression techniques for the high brightness and wide color gamut capabilities of ULED displays.
Collaboration between display manufacturers, content creators, and broadcasters is essential for the development of comprehensive ULED-HDR standards. Industry forums and working groups are being established to facilitate discussions and reach consensus on key technical specifications and implementation guidelines.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, standardization efforts will need to remain flexible and adaptable. Future standards may need to address advanced features such as per-pixel local dimming, enhanced color volume mapping, and dynamic metadata for optimized content rendering on ULED displays.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!