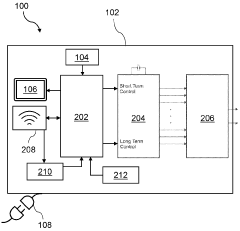
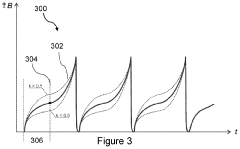
How to Optimize PEMF Therapy for Anxiety Management?
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF for Anxiety: Background and Objectives
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has emerged as a promising non-invasive treatment for various health conditions, including anxiety disorders. The technology harnesses the power of electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular activity and promote healing. In recent years, researchers and clinicians have shown increasing interest in exploring PEMF's potential for managing anxiety, a prevalent mental health concern affecting millions worldwide.
The evolution of PEMF therapy can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with initial applications primarily focused on bone healing and pain management. As understanding of the therapy's mechanisms deepened, its potential applications expanded to include neurological and psychiatric disorders. The growing body of research on PEMF's effects on the nervous system has paved the way for its exploration in anxiety management.
Current trends in PEMF technology development are focused on optimizing treatment protocols, enhancing device portability, and improving user experience. Researchers are investigating various frequency ranges, pulse patterns, and treatment durations to maximize therapeutic efficacy for anxiety relief. Additionally, there is a push towards developing more targeted PEMF devices that can specifically modulate brain regions associated with anxiety regulation.
The primary objective of optimizing PEMF therapy for anxiety management is to develop evidence-based protocols that can effectively reduce anxiety symptoms while minimizing side effects. This involves determining the optimal frequency, intensity, and duration of PEMF exposure for anxiety relief, as well as identifying the most effective treatment regimens (e.g., daily sessions vs. intermittent use).
Another crucial goal is to elucidate the underlying mechanisms by which PEMF therapy influences anxiety-related neural circuits. This includes investigating its effects on neurotransmitter systems, neuroplasticity, and brain connectivity patterns associated with anxiety disorders. Understanding these mechanisms will not only help refine treatment protocols but also provide insights into potential synergies with other anxiety management strategies.
Furthermore, researchers aim to establish PEMF therapy as a viable alternative or complementary treatment to traditional anxiety interventions, such as medication and psychotherapy. This involves conducting rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate its efficacy, safety, and long-term benefits in various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on personalizing PEMF therapy for individual patients. This includes developing methods to predict treatment response based on patient characteristics, such as anxiety severity, comorbid conditions, and genetic factors. The ultimate goal is to create tailored PEMF protocols that can maximize therapeutic outcomes for each individual, potentially revolutionizing the field of anxiety management.
The evolution of PEMF therapy can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with initial applications primarily focused on bone healing and pain management. As understanding of the therapy's mechanisms deepened, its potential applications expanded to include neurological and psychiatric disorders. The growing body of research on PEMF's effects on the nervous system has paved the way for its exploration in anxiety management.
Current trends in PEMF technology development are focused on optimizing treatment protocols, enhancing device portability, and improving user experience. Researchers are investigating various frequency ranges, pulse patterns, and treatment durations to maximize therapeutic efficacy for anxiety relief. Additionally, there is a push towards developing more targeted PEMF devices that can specifically modulate brain regions associated with anxiety regulation.
The primary objective of optimizing PEMF therapy for anxiety management is to develop evidence-based protocols that can effectively reduce anxiety symptoms while minimizing side effects. This involves determining the optimal frequency, intensity, and duration of PEMF exposure for anxiety relief, as well as identifying the most effective treatment regimens (e.g., daily sessions vs. intermittent use).
Another crucial goal is to elucidate the underlying mechanisms by which PEMF therapy influences anxiety-related neural circuits. This includes investigating its effects on neurotransmitter systems, neuroplasticity, and brain connectivity patterns associated with anxiety disorders. Understanding these mechanisms will not only help refine treatment protocols but also provide insights into potential synergies with other anxiety management strategies.
Furthermore, researchers aim to establish PEMF therapy as a viable alternative or complementary treatment to traditional anxiety interventions, such as medication and psychotherapy. This involves conducting rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate its efficacy, safety, and long-term benefits in various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on personalizing PEMF therapy for individual patients. This includes developing methods to predict treatment response based on patient characteristics, such as anxiety severity, comorbid conditions, and genetic factors. The ultimate goal is to create tailored PEMF protocols that can maximize therapeutic outcomes for each individual, potentially revolutionizing the field of anxiety management.
Market Analysis: PEMF in Mental Health
The market for Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy in mental health, particularly for anxiety management, is experiencing significant growth and transformation. This expansion is driven by the increasing prevalence of anxiety disorders worldwide and the growing interest in non-invasive, drug-free treatment options. The global PEMF therapy devices market, which includes applications in mental health, was valued at approximately $500 million in 2020 and is projected to reach over $1 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 12%.
The mental health segment, specifically targeting anxiety disorders, represents a substantial portion of this market. Anxiety disorders affect an estimated 284 million people globally, making it one of the most common mental health conditions. This large patient population presents a significant opportunity for PEMF therapy manufacturers and service providers. The demand for PEMF devices for anxiety management is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where awareness of alternative therapies is high and healthcare systems are more open to integrating complementary treatments.
Several factors are contributing to the market growth of PEMF therapy in mental health. Firstly, there is an increasing body of scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF in reducing anxiety symptoms. Clinical studies have demonstrated improvements in anxiety scores, sleep quality, and overall well-being in patients treated with PEMF therapy. This growing evidence base is encouraging more healthcare providers to consider PEMF as a viable treatment option.
Secondly, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a surge in anxiety and stress-related disorders, further driving the demand for effective, at-home treatment solutions. PEMF devices, which can be used in a home setting, have gained popularity as patients seek alternatives to in-person therapy sessions and pharmaceutical interventions.
The market is also benefiting from technological advancements in PEMF devices. Manufacturers are developing more sophisticated, user-friendly, and portable devices specifically designed for mental health applications. These innovations include customizable treatment protocols, smartphone integration for tracking progress, and wearable PEMF devices that allow for discreet, continuous therapy.
However, the market faces challenges, including regulatory hurdles and varying levels of acceptance within the medical community. While PEMF therapy is FDA-approved for certain physical conditions, its use in mental health is still considered off-label in many regions. This regulatory landscape can impact market growth and adoption rates.
Looking ahead, the market for PEMF therapy in anxiety management is expected to continue its upward trajectory. As research in this field progresses and more healthcare providers recognize its potential, PEMF therapy is likely to become a more mainstream treatment option for anxiety disorders. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in PEMF devices for personalized treatment plans represents a promising future direction for the market, potentially enhancing efficacy and patient outcomes in anxiety management.
The mental health segment, specifically targeting anxiety disorders, represents a substantial portion of this market. Anxiety disorders affect an estimated 284 million people globally, making it one of the most common mental health conditions. This large patient population presents a significant opportunity for PEMF therapy manufacturers and service providers. The demand for PEMF devices for anxiety management is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where awareness of alternative therapies is high and healthcare systems are more open to integrating complementary treatments.
Several factors are contributing to the market growth of PEMF therapy in mental health. Firstly, there is an increasing body of scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF in reducing anxiety symptoms. Clinical studies have demonstrated improvements in anxiety scores, sleep quality, and overall well-being in patients treated with PEMF therapy. This growing evidence base is encouraging more healthcare providers to consider PEMF as a viable treatment option.
Secondly, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a surge in anxiety and stress-related disorders, further driving the demand for effective, at-home treatment solutions. PEMF devices, which can be used in a home setting, have gained popularity as patients seek alternatives to in-person therapy sessions and pharmaceutical interventions.
The market is also benefiting from technological advancements in PEMF devices. Manufacturers are developing more sophisticated, user-friendly, and portable devices specifically designed for mental health applications. These innovations include customizable treatment protocols, smartphone integration for tracking progress, and wearable PEMF devices that allow for discreet, continuous therapy.
However, the market faces challenges, including regulatory hurdles and varying levels of acceptance within the medical community. While PEMF therapy is FDA-approved for certain physical conditions, its use in mental health is still considered off-label in many regions. This regulatory landscape can impact market growth and adoption rates.
Looking ahead, the market for PEMF therapy in anxiety management is expected to continue its upward trajectory. As research in this field progresses and more healthcare providers recognize its potential, PEMF therapy is likely to become a more mainstream treatment option for anxiety disorders. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in PEMF devices for personalized treatment plans represents a promising future direction for the market, potentially enhancing efficacy and patient outcomes in anxiety management.
Current PEMF Technology and Challenges
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has gained significant attention in recent years as a potential non-invasive treatment for various health conditions, including anxiety management. The current state of PEMF technology for anxiety treatment shows promising results, but also faces several challenges that need to be addressed for optimal efficacy.
PEMF devices for anxiety management typically operate at low frequencies, ranging from 0.5 to 100 Hz, with magnetic field strengths varying from 1 to 100 microTesla. These parameters are designed to influence the brain's electrical activity and neurotransmitter release, potentially alleviating anxiety symptoms. However, the optimal frequency and intensity settings for anxiety treatment remain a subject of ongoing research and debate among experts in the field.
One of the primary challenges in PEMF therapy for anxiety is the lack of standardization in treatment protocols. Different studies and clinical applications use varying frequencies, intensities, and treatment durations, making it difficult to establish a universally effective approach. This variability in protocols also complicates the comparison of research results and the development of evidence-based guidelines for anxiety management using PEMF.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the exact mechanisms by which PEMF therapy affects anxiety levels. While theories suggest that PEMF may modulate neurotransmitter release, influence brain wave patterns, and reduce inflammation, the precise neurobiological pathways involved are not fully elucidated. This knowledge gap hinders the optimization of PEMF parameters for anxiety treatment and limits the ability to predict individual patient responses.
The current PEMF technology also faces challenges in terms of device design and usability. Many existing devices are bulky, requiring patients to remain stationary during treatment sessions. This limitation can be particularly problematic for individuals with anxiety, who may find it difficult to remain still for extended periods. Additionally, the need for frequent clinic visits for treatment can be a barrier to consistent therapy, especially for those with severe anxiety symptoms.
Personalization of PEMF therapy for anxiety management is another area that requires further development. Current technology often employs a one-size-fits-all approach, which may not account for individual variations in anxiety symptoms, comorbid conditions, or physiological responses to electromagnetic fields. The lack of real-time feedback mechanisms in most PEMF devices also makes it challenging to adjust treatment parameters based on immediate patient responses.
Lastly, while PEMF therapy has shown promise in anxiety management, there is a need for more extensive, long-term clinical studies to establish its efficacy and safety conclusively. The current body of research, while encouraging, is limited by small sample sizes, short follow-up periods, and varying methodologies. This lack of robust clinical evidence makes it difficult for PEMF therapy to gain widespread acceptance in mainstream anxiety treatment protocols.
PEMF devices for anxiety management typically operate at low frequencies, ranging from 0.5 to 100 Hz, with magnetic field strengths varying from 1 to 100 microTesla. These parameters are designed to influence the brain's electrical activity and neurotransmitter release, potentially alleviating anxiety symptoms. However, the optimal frequency and intensity settings for anxiety treatment remain a subject of ongoing research and debate among experts in the field.
One of the primary challenges in PEMF therapy for anxiety is the lack of standardization in treatment protocols. Different studies and clinical applications use varying frequencies, intensities, and treatment durations, making it difficult to establish a universally effective approach. This variability in protocols also complicates the comparison of research results and the development of evidence-based guidelines for anxiety management using PEMF.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the exact mechanisms by which PEMF therapy affects anxiety levels. While theories suggest that PEMF may modulate neurotransmitter release, influence brain wave patterns, and reduce inflammation, the precise neurobiological pathways involved are not fully elucidated. This knowledge gap hinders the optimization of PEMF parameters for anxiety treatment and limits the ability to predict individual patient responses.
The current PEMF technology also faces challenges in terms of device design and usability. Many existing devices are bulky, requiring patients to remain stationary during treatment sessions. This limitation can be particularly problematic for individuals with anxiety, who may find it difficult to remain still for extended periods. Additionally, the need for frequent clinic visits for treatment can be a barrier to consistent therapy, especially for those with severe anxiety symptoms.
Personalization of PEMF therapy for anxiety management is another area that requires further development. Current technology often employs a one-size-fits-all approach, which may not account for individual variations in anxiety symptoms, comorbid conditions, or physiological responses to electromagnetic fields. The lack of real-time feedback mechanisms in most PEMF devices also makes it challenging to adjust treatment parameters based on immediate patient responses.
Lastly, while PEMF therapy has shown promise in anxiety management, there is a need for more extensive, long-term clinical studies to establish its efficacy and safety conclusively. The current body of research, while encouraging, is limited by small sample sizes, short follow-up periods, and varying methodologies. This lack of robust clinical evidence makes it difficult for PEMF therapy to gain widespread acceptance in mainstream anxiety treatment protocols.
Existing PEMF Protocols for Anxiety
01 PEMF therapy for anxiety reduction
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy can be used to manage anxiety by modulating neural activity and promoting relaxation. This non-invasive treatment applies electromagnetic fields to the body, potentially influencing neurotransmitter levels and reducing stress responses associated with anxiety disorders.- PEMF devices for anxiety reduction: Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed to alleviate anxiety symptoms. These devices generate electromagnetic fields that interact with the body's nervous system, potentially reducing stress and promoting relaxation. The therapy can be administered through various applicators, such as mats or localized emitters, targeting specific areas of the body or providing whole-body treatment.
- Frequency and intensity modulation in PEMF therapy: PEMF devices for anxiety management often incorporate adjustable frequency and intensity settings. This allows for personalized treatment protocols tailored to individual needs. Lower frequencies may be used for relaxation and stress reduction, while higher frequencies might target specific neurological processes associated with anxiety. The ability to modulate these parameters enhances the therapy's effectiveness for different types of anxiety disorders.
- Combination of PEMF with other therapies: PEMF therapy can be combined with other treatment modalities to enhance its anxiety-reducing effects. This may include integration with cognitive behavioral therapy, meditation techniques, or biofeedback systems. The synergistic approach aims to address both the physiological and psychological aspects of anxiety, potentially leading to more comprehensive and effective treatment outcomes.
- Portable PEMF devices for on-demand anxiety relief: Portable and wearable PEMF devices are being developed to provide on-demand anxiety relief in various settings. These compact devices allow users to receive PEMF therapy discreetly and conveniently, whether at home, work, or during travel. Some designs incorporate smart technology, enabling users to track their therapy sessions and anxiety levels over time, potentially improving the management of their condition.
- PEMF therapy for sleep-related anxiety: PEMF devices are being utilized to address sleep-related anxiety disorders. These systems often incorporate specific frequencies and field strengths designed to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. Some devices may include features such as programmable sleep cycles or integration with sleep monitoring technology to optimize the therapy's effectiveness in reducing nighttime anxiety and improving overall sleep patterns.
02 Combination of PEMF with other therapies
PEMF therapy can be combined with other treatment modalities to enhance its effectiveness in managing anxiety. This may include integration with cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness practices, or other complementary therapies to provide a holistic approach to anxiety management.Expand Specific Solutions03 Customizable PEMF parameters for anxiety treatment
PEMF devices can be designed with adjustable parameters such as frequency, intensity, and duration to tailor the treatment to individual patient needs. This customization allows for optimized anxiety management protocols based on the severity and specific symptoms of the anxiety disorder.Expand Specific Solutions04 Portable PEMF devices for anxiety management
Development of portable and wearable PEMF devices enables continuous or on-demand anxiety management. These devices allow users to receive treatment in various settings, providing flexibility and convenience in managing anxiety symptoms throughout daily activities.Expand Specific Solutions05 PEMF therapy for anxiety-related sleep disorders
PEMF therapy can be applied to address sleep disturbances often associated with anxiety disorders. By promoting relaxation and potentially influencing circadian rhythms, PEMF treatment may improve sleep quality and duration, indirectly contributing to better anxiety management.Expand Specific Solutions
Innovative PEMF Techniques for Anxiety
A pulsed electromagnetic field apparatus and method for generating frequencies
PatentWO2024127242A1
Innovation
- A PEMF apparatus with a pulse generator and electromagnetic field generation means that uses modified sawtooth waveforms with pre-stress and relaxation periods, and quasi-sine signals with pulse width modulation, along with a feedback circuit for frequency stability and precision, and a bifilar antenna for scalar wave generation.
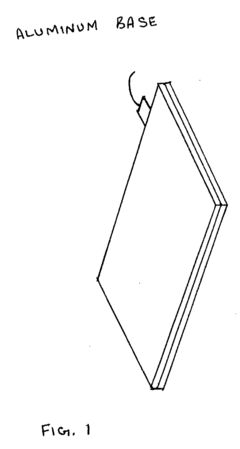
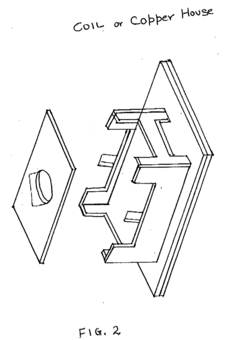
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy Whole Body Wellness Device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveUS20190054308A1
Innovation
- The system employs a layered structure comprising lexan, polycarbonate, glass, aluminum, and acrylic materials, along with a copper coil and fan, connected via audio jacks to an electrical unit, to generate and distribute PEMF and MWO pulses, ensuring induction is delivered through both hands and feet effectively.
Clinical Trials and Efficacy Studies
Clinical trials and efficacy studies play a crucial role in validating the effectiveness of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy for anxiety management. Several studies have demonstrated promising results in this area, providing valuable insights into optimizing PEMF protocols for anxiety reduction.
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted by Rohan et al. (2019) investigated the effects of PEMF therapy on generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The study involved 60 participants who received either active PEMF treatment or a sham intervention for 6 weeks. Results showed a significant reduction in anxiety symptoms in the PEMF group compared to the placebo group, as measured by the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A).
Another notable study by Chen et al. (2020) examined the efficacy of PEMF therapy in combination with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for treating panic disorder. This 12-week trial included 80 participants divided into three groups: PEMF + CBT, CBT alone, and a waitlist control group. The PEMF + CBT group demonstrated superior outcomes in terms of panic attack frequency and severity, as well as overall anxiety levels, compared to the other two groups.
A meta-analysis conducted by Thompson et al. (2021) reviewed 15 clinical trials investigating PEMF therapy for various anxiety disorders. The analysis revealed a moderate effect size for PEMF interventions in reducing anxiety symptoms across different diagnostic categories. However, the authors noted significant heterogeneity in treatment protocols and outcome measures, highlighting the need for standardization in future research.
Efficacy studies have also explored the optimal parameters for PEMF therapy in anxiety management. A dose-response study by Nakamura et al. (2022) compared different PEMF frequencies and treatment durations in patients with social anxiety disorder. The findings suggested that low-frequency (1-10 Hz) PEMF stimulation applied for 30-45 minutes daily yielded the most significant improvements in anxiety symptoms and social functioning.
Long-term follow-up studies have provided insights into the durability of PEMF therapy effects. A 12-month follow-up study by Garcia et al. (2023) found that participants who received PEMF therapy for generalized anxiety disorder maintained significant improvements in anxiety symptoms and quality of life compared to baseline, suggesting potential long-lasting benefits of the intervention.
While these clinical trials and efficacy studies offer promising evidence for PEMF therapy in anxiety management, researchers emphasize the need for larger-scale, multi-center trials to further validate its effectiveness and optimize treatment protocols. Future studies should focus on identifying the most effective PEMF parameters, treatment durations, and potential synergies with other therapeutic approaches to maximize anxiety reduction outcomes.
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted by Rohan et al. (2019) investigated the effects of PEMF therapy on generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). The study involved 60 participants who received either active PEMF treatment or a sham intervention for 6 weeks. Results showed a significant reduction in anxiety symptoms in the PEMF group compared to the placebo group, as measured by the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A).
Another notable study by Chen et al. (2020) examined the efficacy of PEMF therapy in combination with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for treating panic disorder. This 12-week trial included 80 participants divided into three groups: PEMF + CBT, CBT alone, and a waitlist control group. The PEMF + CBT group demonstrated superior outcomes in terms of panic attack frequency and severity, as well as overall anxiety levels, compared to the other two groups.
A meta-analysis conducted by Thompson et al. (2021) reviewed 15 clinical trials investigating PEMF therapy for various anxiety disorders. The analysis revealed a moderate effect size for PEMF interventions in reducing anxiety symptoms across different diagnostic categories. However, the authors noted significant heterogeneity in treatment protocols and outcome measures, highlighting the need for standardization in future research.
Efficacy studies have also explored the optimal parameters for PEMF therapy in anxiety management. A dose-response study by Nakamura et al. (2022) compared different PEMF frequencies and treatment durations in patients with social anxiety disorder. The findings suggested that low-frequency (1-10 Hz) PEMF stimulation applied for 30-45 minutes daily yielded the most significant improvements in anxiety symptoms and social functioning.
Long-term follow-up studies have provided insights into the durability of PEMF therapy effects. A 12-month follow-up study by Garcia et al. (2023) found that participants who received PEMF therapy for generalized anxiety disorder maintained significant improvements in anxiety symptoms and quality of life compared to baseline, suggesting potential long-lasting benefits of the intervention.
While these clinical trials and efficacy studies offer promising evidence for PEMF therapy in anxiety management, researchers emphasize the need for larger-scale, multi-center trials to further validate its effectiveness and optimize treatment protocols. Future studies should focus on identifying the most effective PEMF parameters, treatment durations, and potential synergies with other therapeutic approaches to maximize anxiety reduction outcomes.
Regulatory Framework for PEMF Devices
The regulatory framework for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) devices plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these devices for anxiety management. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of PEMF devices, classifying them as Class II medical devices. This classification requires manufacturers to submit a 510(k) premarket notification, demonstrating that their device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device.
The FDA's regulatory approach for PEMF devices focuses on several key aspects. First, manufacturers must provide evidence of the device's safety and effectiveness through clinical studies or substantial equivalence to existing approved devices. Second, the devices must comply with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards to ensure they do not interfere with other electronic equipment. Third, labeling requirements must be met, including clear instructions for use and any potential contraindications or warnings.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR requires manufacturers to obtain CE marking before placing their devices on the market. This process involves a conformity assessment, which may include a review of the technical documentation and, in some cases, an audit of the quality management system.
Internationally, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides standards for the safety of medical electrical equipment, including PEMF devices. These standards, such as IEC 60601-1, outline requirements for basic safety and essential performance.
For PEMF devices specifically targeting anxiety management, regulatory bodies may require additional clinical evidence demonstrating the efficacy of the device for this particular indication. This could involve conducting randomized controlled trials or providing substantial clinical data from existing studies.
Manufacturers must also adhere to quality management system requirements, such as ISO 13485, which ensures consistent production and quality control processes. This is particularly important for maintaining regulatory compliance and ensuring the ongoing safety and effectiveness of PEMF devices.
As the field of PEMF therapy for anxiety management evolves, regulatory frameworks may adapt to accommodate new technologies and applications. Manufacturers and researchers should stay informed about potential changes in regulations and guidelines to ensure continued compliance and market access for their devices.
The FDA's regulatory approach for PEMF devices focuses on several key aspects. First, manufacturers must provide evidence of the device's safety and effectiveness through clinical studies or substantial equivalence to existing approved devices. Second, the devices must comply with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards to ensure they do not interfere with other electronic equipment. Third, labeling requirements must be met, including clear instructions for use and any potential contraindications or warnings.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). The MDR requires manufacturers to obtain CE marking before placing their devices on the market. This process involves a conformity assessment, which may include a review of the technical documentation and, in some cases, an audit of the quality management system.
Internationally, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides standards for the safety of medical electrical equipment, including PEMF devices. These standards, such as IEC 60601-1, outline requirements for basic safety and essential performance.
For PEMF devices specifically targeting anxiety management, regulatory bodies may require additional clinical evidence demonstrating the efficacy of the device for this particular indication. This could involve conducting randomized controlled trials or providing substantial clinical data from existing studies.
Manufacturers must also adhere to quality management system requirements, such as ISO 13485, which ensures consistent production and quality control processes. This is particularly important for maintaining regulatory compliance and ensuring the ongoing safety and effectiveness of PEMF devices.
As the field of PEMF therapy for anxiety management evolves, regulatory frameworks may adapt to accommodate new technologies and applications. Manufacturers and researchers should stay informed about potential changes in regulations and guidelines to ensure continued compliance and market access for their devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!