How to Use PEMF Therapy as an Adjunct to Physical Therapy?
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Background and Objectives
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has emerged as a promising adjunctive treatment in physical therapy, with roots tracing back to the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing, PEMF therapy has evolved to address a wide range of musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. The technology leverages the principle that electromagnetic fields can influence cellular behavior and tissue repair processes.
The primary objective of integrating PEMF therapy into physical therapy is to enhance treatment outcomes by accelerating healing, reducing pain, and improving overall function. This non-invasive approach aims to complement traditional physical therapy techniques, potentially reducing recovery time and improving patient satisfaction. By stimulating cellular activity at the molecular level, PEMF therapy seeks to address underlying physiological processes that contribute to pain and dysfunction.
Recent advancements in PEMF technology have led to more sophisticated devices with adjustable parameters, allowing for targeted treatment of specific conditions. These developments have expanded the potential applications of PEMF therapy in physical therapy settings, ranging from acute injury management to chronic pain conditions and post-surgical rehabilitation.
The growing interest in PEMF therapy as an adjunct to physical therapy is driven by an increasing body of scientific evidence supporting its efficacy. Clinical studies have demonstrated positive outcomes in various areas, including osteoarthritis, fracture healing, and soft tissue injuries. This evidence base has contributed to the gradual acceptance of PEMF therapy within the medical community and its integration into comprehensive treatment protocols.
As the field of physical therapy continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on multimodal approaches to patient care. PEMF therapy aligns with this trend by offering a complementary treatment option that can be easily incorporated into existing therapy regimens. The non-pharmacological nature of PEMF therapy also makes it an attractive option in the context of rising concerns about opioid dependency and the side effects of long-term medication use.
Looking ahead, the objectives for PEMF therapy in physical therapy include further refinement of treatment protocols, expansion of its application to a broader range of conditions, and increased integration into standard care practices. Researchers and clinicians are working towards optimizing PEMF parameters for specific conditions, developing more portable and user-friendly devices, and exploring potential synergies with other therapeutic modalities.
The primary objective of integrating PEMF therapy into physical therapy is to enhance treatment outcomes by accelerating healing, reducing pain, and improving overall function. This non-invasive approach aims to complement traditional physical therapy techniques, potentially reducing recovery time and improving patient satisfaction. By stimulating cellular activity at the molecular level, PEMF therapy seeks to address underlying physiological processes that contribute to pain and dysfunction.
Recent advancements in PEMF technology have led to more sophisticated devices with adjustable parameters, allowing for targeted treatment of specific conditions. These developments have expanded the potential applications of PEMF therapy in physical therapy settings, ranging from acute injury management to chronic pain conditions and post-surgical rehabilitation.
The growing interest in PEMF therapy as an adjunct to physical therapy is driven by an increasing body of scientific evidence supporting its efficacy. Clinical studies have demonstrated positive outcomes in various areas, including osteoarthritis, fracture healing, and soft tissue injuries. This evidence base has contributed to the gradual acceptance of PEMF therapy within the medical community and its integration into comprehensive treatment protocols.
As the field of physical therapy continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on multimodal approaches to patient care. PEMF therapy aligns with this trend by offering a complementary treatment option that can be easily incorporated into existing therapy regimens. The non-pharmacological nature of PEMF therapy also makes it an attractive option in the context of rising concerns about opioid dependency and the side effects of long-term medication use.
Looking ahead, the objectives for PEMF therapy in physical therapy include further refinement of treatment protocols, expansion of its application to a broader range of conditions, and increased integration into standard care practices. Researchers and clinicians are working towards optimizing PEMF parameters for specific conditions, developing more portable and user-friendly devices, and exploring potential synergies with other therapeutic modalities.
Market Analysis for PEMF in Physical Therapy
The market for Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy as an adjunct to physical therapy is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of its potential benefits and a growing demand for non-invasive treatment options. The global PEMF therapy devices market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% from 2021 to 2028, with the physical therapy segment playing a crucial role in this growth.
Physical therapists are increasingly incorporating PEMF therapy into their treatment protocols, recognizing its potential to enhance traditional physical therapy outcomes. The market demand is particularly strong in regions with aging populations and high incidences of chronic pain, musculoskeletal disorders, and sports injuries. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific.
The integration of PEMF therapy in physical therapy practices is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing body of clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF in reducing pain, inflammation, and promoting tissue healing. This has led to increased acceptance among healthcare professionals and patients alike. Secondly, the non-invasive nature of PEMF therapy aligns well with the trend towards minimally invasive treatment options in healthcare.
Market analysis reveals that portable PEMF devices are gaining popularity in physical therapy settings due to their convenience and ability to provide targeted treatment. These devices allow for in-clinic use as well as home-based therapy, expanding the potential market reach. Additionally, there is a rising demand for PEMF devices that can be integrated with other physical therapy modalities, creating opportunities for innovative product development.
The competitive landscape of the PEMF therapy market in physical therapy is characterized by a mix of established medical device companies and specialized PEMF manufacturers. Key players are focusing on product innovation, clinical research, and strategic partnerships with healthcare providers to gain market share. There is also a trend towards developing user-friendly, app-controlled PEMF devices that allow for personalized treatment protocols and remote monitoring by physical therapists.
Challenges in the market include the need for more extensive clinical research to validate the long-term benefits of PEMF therapy in various physical therapy applications. Additionally, reimbursement policies for PEMF therapy vary across regions, which can impact market growth. However, as more insurance providers recognize the potential cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy in reducing the need for pharmaceutical interventions and surgical procedures, coverage is expected to improve.
In conclusion, the market analysis indicates a positive outlook for PEMF therapy as an adjunct to physical therapy. The growing acceptance among healthcare professionals, increasing patient demand for non-invasive treatments, and ongoing technological advancements are expected to drive market growth in the coming years. Companies that can demonstrate clinical efficacy, develop user-friendly devices, and navigate regulatory landscapes are likely to succeed in this expanding market.
Physical therapists are increasingly incorporating PEMF therapy into their treatment protocols, recognizing its potential to enhance traditional physical therapy outcomes. The market demand is particularly strong in regions with aging populations and high incidences of chronic pain, musculoskeletal disorders, and sports injuries. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific.
The integration of PEMF therapy in physical therapy practices is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing body of clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF in reducing pain, inflammation, and promoting tissue healing. This has led to increased acceptance among healthcare professionals and patients alike. Secondly, the non-invasive nature of PEMF therapy aligns well with the trend towards minimally invasive treatment options in healthcare.
Market analysis reveals that portable PEMF devices are gaining popularity in physical therapy settings due to their convenience and ability to provide targeted treatment. These devices allow for in-clinic use as well as home-based therapy, expanding the potential market reach. Additionally, there is a rising demand for PEMF devices that can be integrated with other physical therapy modalities, creating opportunities for innovative product development.
The competitive landscape of the PEMF therapy market in physical therapy is characterized by a mix of established medical device companies and specialized PEMF manufacturers. Key players are focusing on product innovation, clinical research, and strategic partnerships with healthcare providers to gain market share. There is also a trend towards developing user-friendly, app-controlled PEMF devices that allow for personalized treatment protocols and remote monitoring by physical therapists.
Challenges in the market include the need for more extensive clinical research to validate the long-term benefits of PEMF therapy in various physical therapy applications. Additionally, reimbursement policies for PEMF therapy vary across regions, which can impact market growth. However, as more insurance providers recognize the potential cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy in reducing the need for pharmaceutical interventions and surgical procedures, coverage is expected to improve.
In conclusion, the market analysis indicates a positive outlook for PEMF therapy as an adjunct to physical therapy. The growing acceptance among healthcare professionals, increasing patient demand for non-invasive treatments, and ongoing technological advancements are expected to drive market growth in the coming years. Companies that can demonstrate clinical efficacy, develop user-friendly devices, and navigate regulatory landscapes are likely to succeed in this expanding market.
Current PEMF Technology and Challenges
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has gained significant attention in recent years as a potential adjunct to physical therapy. The current state of PEMF technology is characterized by a diverse range of devices and applications, each with its own set of challenges and limitations.
PEMF devices typically consist of a control unit and applicators that generate electromagnetic fields. These fields are pulsed at specific frequencies and intensities, which can be adjusted based on the therapeutic goals. The technology has evolved from large, stationary machines to more portable and user-friendly devices, allowing for greater flexibility in treatment settings.
One of the primary challenges in PEMF therapy is the lack of standardization in treatment protocols. Different manufacturers produce devices with varying specifications, making it difficult for practitioners to determine the optimal parameters for specific conditions. This variability also complicates the comparison of research studies and clinical outcomes.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy exerts its effects on biological tissues. While numerous studies have demonstrated positive outcomes in areas such as pain reduction, inflammation control, and tissue healing, the underlying cellular and molecular processes are not fully elucidated. This gap in knowledge hinders the development of more targeted and efficient PEMF therapies.
The integration of PEMF therapy into existing physical therapy practices presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, PEMF devices can be easily incorporated into treatment sessions, potentially enhancing the effects of manual therapies and exercises. On the other hand, there is a learning curve for therapists to effectively utilize PEMF technology and interpret its effects in conjunction with other modalities.
Regulatory considerations also pose challenges for the widespread adoption of PEMF therapy. While some PEMF devices have received FDA clearance for specific indications, many remain classified as general wellness products. This regulatory landscape can create confusion among practitioners and patients regarding the appropriate use and expected outcomes of PEMF therapy.
The cost and accessibility of PEMF devices represent additional hurdles. High-quality, professional-grade equipment can be expensive, potentially limiting its availability in some clinical settings. Moreover, insurance coverage for PEMF therapy is often limited, which may restrict patient access to this treatment modality.
As research in PEMF therapy continues to advance, there is a growing need for more robust, large-scale clinical trials to establish its efficacy as an adjunct to physical therapy. Current evidence, while promising, is often based on small studies with varying methodologies, making it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about the optimal use of PEMF in different therapeutic contexts.
PEMF devices typically consist of a control unit and applicators that generate electromagnetic fields. These fields are pulsed at specific frequencies and intensities, which can be adjusted based on the therapeutic goals. The technology has evolved from large, stationary machines to more portable and user-friendly devices, allowing for greater flexibility in treatment settings.
One of the primary challenges in PEMF therapy is the lack of standardization in treatment protocols. Different manufacturers produce devices with varying specifications, making it difficult for practitioners to determine the optimal parameters for specific conditions. This variability also complicates the comparison of research studies and clinical outcomes.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy exerts its effects on biological tissues. While numerous studies have demonstrated positive outcomes in areas such as pain reduction, inflammation control, and tissue healing, the underlying cellular and molecular processes are not fully elucidated. This gap in knowledge hinders the development of more targeted and efficient PEMF therapies.
The integration of PEMF therapy into existing physical therapy practices presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, PEMF devices can be easily incorporated into treatment sessions, potentially enhancing the effects of manual therapies and exercises. On the other hand, there is a learning curve for therapists to effectively utilize PEMF technology and interpret its effects in conjunction with other modalities.
Regulatory considerations also pose challenges for the widespread adoption of PEMF therapy. While some PEMF devices have received FDA clearance for specific indications, many remain classified as general wellness products. This regulatory landscape can create confusion among practitioners and patients regarding the appropriate use and expected outcomes of PEMF therapy.
The cost and accessibility of PEMF devices represent additional hurdles. High-quality, professional-grade equipment can be expensive, potentially limiting its availability in some clinical settings. Moreover, insurance coverage for PEMF therapy is often limited, which may restrict patient access to this treatment modality.
As research in PEMF therapy continues to advance, there is a growing need for more robust, large-scale clinical trials to establish its efficacy as an adjunct to physical therapy. Current evidence, while promising, is often based on small studies with varying methodologies, making it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about the optimal use of PEMF in different therapeutic contexts.
PEMF Integration in Physical Therapy Protocols
01 PEMF devices for therapeutic applications
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and improve overall health. They can be used for pain management, tissue healing, and treating various medical conditions.- PEMF devices for therapeutic applications: Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular activity and promote healing. They can be used for pain management, tissue repair, and improving overall well-being.
- PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions: PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions. It has shown efficacy in managing chronic pain, accelerating bone healing, reducing inflammation, and improving circulation. The therapy can be tailored to address various health issues by adjusting the frequency and intensity of the electromagnetic fields.
- Portable and wearable PEMF devices: Advancements in PEMF technology have led to the development of portable and wearable devices. These compact units allow for convenient at-home use or on-the-go treatments. Wearable PEMF devices can be integrated into clothing or accessories, enabling continuous therapy throughout the day.
- Combination of PEMF with other therapies: PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This may include integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or other forms of electromagnetic stimulation. The synergistic effects of combined therapies can potentially improve treatment efficacy for various conditions.
- PEMF technology advancements and control systems: Ongoing research focuses on improving PEMF technology and control systems. This includes developing more precise field generation methods, optimizing treatment protocols, and creating user-friendly interfaces for device operation. Advanced control systems allow for personalized therapy settings and treatment tracking.
02 PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions
PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, bone fractures, and neurological disorders. The therapy aims to reduce inflammation, promote tissue regeneration, and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. Different frequencies and intensities of electromagnetic fields are applied depending on the targeted condition.Expand Specific Solutions03 Portable and wearable PEMF devices
Advancements in PEMF technology have led to the development of portable and wearable devices. These compact devices allow for convenient at-home use or continuous therapy throughout the day. They are designed to be user-friendly and can be applied to specific body parts for targeted treatment.Expand Specific Solutions04 PEMF therapy combined with other treatment modalities
PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic effects. This may include integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or traditional medical treatments. The combination approach aims to provide synergistic benefits and improve overall treatment outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions05 PEMF technology advancements and control systems
Ongoing research focuses on improving PEMF technology and control systems. This includes developing more precise electromagnetic field generation, optimizing treatment protocols, and creating smart devices with programmable settings. Advanced control systems allow for personalized therapy regimens and improved treatment efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Device Manufacturers and Providers
The competitive landscape for PEMF therapy as an adjunct to physical therapy is evolving rapidly. The market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across healthcare sectors. The global PEMF therapy devices market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by rising awareness of non-invasive treatment options. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Venus Concept Ltd. and Regenesis Biomedical, Inc. leading innovation in device development. Emerging players such as Galvanize Therapeutics, Inc. are also contributing to technological advancements, focusing on energy-based medical solutions. The industry is seeing a blend of established medical device manufacturers and specialized PEMF therapy companies, indicating a maturing but still dynamic market.
Venus Concept Ltd.
Technical Solution: Venus Concept has pioneered the integration of PEMF therapy with physical therapy through their Venus Heal system. This technology combines PEMF with other modalities such as massage and heat therapy to enhance overall treatment outcomes[4]. The Venus Heal device utilizes a patented RP3 technology, which generates a multi-polar magnetic field that penetrates deep into tissues, promoting cellular regeneration and reducing pain[5]. The system's design allows for hands-free operation, enabling physical therapists to simultaneously perform manual techniques while the PEMF therapy is applied[6].
Strengths: Multi-modal approach combining PEMF with other therapies, hands-free operation for therapist efficiency. Weaknesses: Limited to specific body areas due to applicator design, may require longer treatment sessions for comprehensive coverage.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical has developed the Provant Therapy System, which utilizes pulsed electromagnetic field technology specifically designed for physical therapy applications. The system employs a proprietary PEMF waveform that has been clinically proven to accelerate tissue repair and reduce pain in various musculoskeletal conditions[7]. Provant Therapy devices are portable and can be easily incorporated into existing physical therapy protocols, allowing for both in-clinic and at-home use[8]. The technology focuses on stimulating cellular activity at the mitochondrial level, enhancing ATP production and promoting faster healing of soft tissues and bones[9].
Strengths: Clinically proven efficacy, portable design for versatile use, specific focus on cellular-level healing. Weaknesses: May require longer treatment durations for chronic conditions, limited to specific PEMF waveform patterns.
PEMF Mechanisms and Efficacy Studies
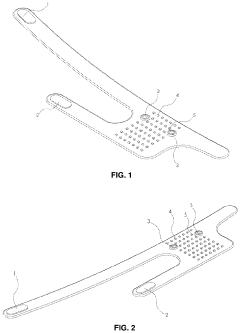
Flexible Photobiomodulation and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy Device
PatentPendingUS20230001222A1
Innovation
- A flexible wearable device that combines PEMF and PBM therapies, featuring a flexible substrate with electromagnetic coils and light-emitting diodes, controlled by a single module that can switch between pre-set frequency sequences, and is wirelessly enabled for remote control.
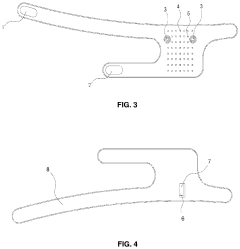
Method and apparatus for providing pulsed electromagnetic field therapy
PatentPendingUS20240278031A1
Innovation
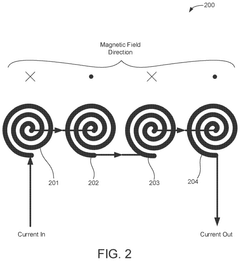
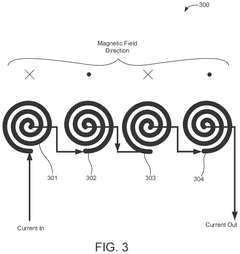
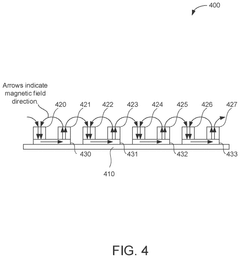
- The development of PEMF therapy applicators that include multiple PEMF emitter coils arranged to direct magnetic fields uniformly and additional therapy pads for providing heating, cooling, or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapies, with a ferromagnetic field director to enhance magnetic field strength and a substrate that can conform to body parts, allowing for directed and intensified magnetic field application.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations for PEMF Use
The safety and regulatory considerations for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy are crucial aspects that must be thoroughly addressed when integrating this technology into physical therapy practices. PEMF devices are classified as medical devices in many jurisdictions, including the United States, where they fall under the regulatory oversight of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The FDA has cleared several PEMF devices for various medical applications, including bone healing, pain management, and post-operative edema and bruising. However, it is essential to note that not all PEMF devices are FDA-cleared, and the specific indications for use may vary between devices. Physical therapists must ensure they are using FDA-cleared devices for their intended purposes to comply with regulatory requirements and maintain patient safety.
Safety considerations for PEMF therapy include contraindications and potential side effects. PEMF therapy is generally considered safe for most individuals, but it is contraindicated for patients with certain medical conditions or implanted electronic devices. Patients with pacemakers, implanted defibrillators, or other electronic implants should not undergo PEMF therapy due to the risk of interference with these devices.
Additionally, PEMF therapy is not recommended for pregnant women, as the effects on fetal development are not well-studied. Patients with active bleeding, cancer, or epilepsy should also avoid PEMF therapy unless specifically approved by their healthcare provider. Physical therapists must conduct thorough patient screenings and obtain comprehensive medical histories before administering PEMF therapy to ensure patient safety.
While side effects from PEMF therapy are generally mild and infrequent, some patients may experience temporary discomfort, such as mild pain, tingling sensations, or fatigue. These effects typically subside quickly and are not considered serious. However, physical therapists should monitor patients during treatment and adjust parameters as necessary to minimize any adverse reactions.
To ensure compliance with regulatory standards and maintain patient safety, physical therapy practices incorporating PEMF therapy should implement robust protocols and documentation procedures. This includes maintaining detailed records of device specifications, treatment parameters, patient assessments, and outcomes. Regular staff training on proper device operation, safety protocols, and emergency procedures is essential to minimize risks and ensure optimal patient care.
Furthermore, physical therapists should stay informed about ongoing research and regulatory updates related to PEMF therapy. As the field evolves, new safety guidelines or regulatory requirements may emerge, necessitating adjustments to clinical practices. Engaging in continuing education and professional development activities focused on PEMF therapy can help practitioners stay current with best practices and safety standards.
The FDA has cleared several PEMF devices for various medical applications, including bone healing, pain management, and post-operative edema and bruising. However, it is essential to note that not all PEMF devices are FDA-cleared, and the specific indications for use may vary between devices. Physical therapists must ensure they are using FDA-cleared devices for their intended purposes to comply with regulatory requirements and maintain patient safety.
Safety considerations for PEMF therapy include contraindications and potential side effects. PEMF therapy is generally considered safe for most individuals, but it is contraindicated for patients with certain medical conditions or implanted electronic devices. Patients with pacemakers, implanted defibrillators, or other electronic implants should not undergo PEMF therapy due to the risk of interference with these devices.
Additionally, PEMF therapy is not recommended for pregnant women, as the effects on fetal development are not well-studied. Patients with active bleeding, cancer, or epilepsy should also avoid PEMF therapy unless specifically approved by their healthcare provider. Physical therapists must conduct thorough patient screenings and obtain comprehensive medical histories before administering PEMF therapy to ensure patient safety.
While side effects from PEMF therapy are generally mild and infrequent, some patients may experience temporary discomfort, such as mild pain, tingling sensations, or fatigue. These effects typically subside quickly and are not considered serious. However, physical therapists should monitor patients during treatment and adjust parameters as necessary to minimize any adverse reactions.
To ensure compliance with regulatory standards and maintain patient safety, physical therapy practices incorporating PEMF therapy should implement robust protocols and documentation procedures. This includes maintaining detailed records of device specifications, treatment parameters, patient assessments, and outcomes. Regular staff training on proper device operation, safety protocols, and emergency procedures is essential to minimize risks and ensure optimal patient care.
Furthermore, physical therapists should stay informed about ongoing research and regulatory updates related to PEMF therapy. As the field evolves, new safety guidelines or regulatory requirements may emerge, necessitating adjustments to clinical practices. Engaging in continuing education and professional development activities focused on PEMF therapy can help practitioners stay current with best practices and safety standards.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of PEMF in Physical Therapy
The cost-benefit analysis of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy in physical therapy reveals a complex interplay of economic factors and therapeutic outcomes. Initial investment in PEMF equipment can be substantial, with high-quality devices ranging from $2,000 to $10,000 or more. However, this upfront cost should be weighed against the potential long-term benefits and cost savings.
One of the primary advantages of PEMF therapy is its non-invasive nature, which can lead to reduced medication costs for patients. Studies have shown that PEMF therapy can decrease the need for pain medications, particularly in cases of chronic pain management. This reduction in pharmaceutical expenses can offset the initial investment over time, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers.
PEMF therapy has demonstrated efficacy in accelerating healing processes, particularly in musculoskeletal injuries. Faster recovery times can translate to fewer physical therapy sessions required, potentially reducing overall treatment costs. Additionally, improved outcomes may lead to decreased likelihood of re-injury or chronic conditions, further reducing long-term healthcare expenses.
From a clinic's perspective, incorporating PEMF therapy can diversify service offerings, potentially attracting more patients and increasing revenue streams. The therapy's versatility in treating various conditions, from sports injuries to chronic pain, makes it a valuable addition to a physical therapy practice's toolkit.
However, it's important to consider ongoing costs associated with PEMF therapy. These may include maintenance of equipment, training staff in proper usage, and potential increases in energy consumption. These recurring expenses should be factored into the overall cost-benefit analysis.
Patient satisfaction and outcomes play a crucial role in the cost-benefit equation. Improved patient experiences and faster recovery times can lead to increased patient retention and referrals, indirectly contributing to the financial health of the practice.
Insurance reimbursement policies for PEMF therapy vary, which can impact its cost-effectiveness. While some insurance providers cover PEMF treatments, others may not, potentially limiting accessibility for some patients. This variability in coverage should be considered when evaluating the overall financial impact of implementing PEMF therapy.
In conclusion, while the initial investment in PEMF technology can be significant, the potential for improved patient outcomes, reduced medication costs, and diversified service offerings presents a compelling case for its integration into physical therapy practices. A thorough analysis of local market conditions, patient demographics, and reimbursement landscapes is essential for individual clinics to determine the specific cost-benefit ratio for their circumstances.
One of the primary advantages of PEMF therapy is its non-invasive nature, which can lead to reduced medication costs for patients. Studies have shown that PEMF therapy can decrease the need for pain medications, particularly in cases of chronic pain management. This reduction in pharmaceutical expenses can offset the initial investment over time, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers.
PEMF therapy has demonstrated efficacy in accelerating healing processes, particularly in musculoskeletal injuries. Faster recovery times can translate to fewer physical therapy sessions required, potentially reducing overall treatment costs. Additionally, improved outcomes may lead to decreased likelihood of re-injury or chronic conditions, further reducing long-term healthcare expenses.
From a clinic's perspective, incorporating PEMF therapy can diversify service offerings, potentially attracting more patients and increasing revenue streams. The therapy's versatility in treating various conditions, from sports injuries to chronic pain, makes it a valuable addition to a physical therapy practice's toolkit.
However, it's important to consider ongoing costs associated with PEMF therapy. These may include maintenance of equipment, training staff in proper usage, and potential increases in energy consumption. These recurring expenses should be factored into the overall cost-benefit analysis.
Patient satisfaction and outcomes play a crucial role in the cost-benefit equation. Improved patient experiences and faster recovery times can lead to increased patient retention and referrals, indirectly contributing to the financial health of the practice.
Insurance reimbursement policies for PEMF therapy vary, which can impact its cost-effectiveness. While some insurance providers cover PEMF treatments, others may not, potentially limiting accessibility for some patients. This variability in coverage should be considered when evaluating the overall financial impact of implementing PEMF therapy.
In conclusion, while the initial investment in PEMF technology can be significant, the potential for improved patient outcomes, reduced medication costs, and diversified service offerings presents a compelling case for its integration into physical therapy practices. A thorough analysis of local market conditions, patient demographics, and reimbursement landscapes is essential for individual clinics to determine the specific cost-benefit ratio for their circumstances.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!