Investigating Lamination Techniques for Enhanced Polypropylene Banner Materials
Lamination Evolution
The evolution of lamination techniques for polypropylene banner materials has been a journey of continuous innovation and refinement. In the early stages, simple heat-sealing methods were employed to join polypropylene sheets, providing basic protection and durability. However, these methods often resulted in weak bonds and limited material enhancement.
As the demand for more robust and versatile banner materials grew, the industry witnessed the introduction of adhesive-based lamination techniques. This marked a significant leap forward, allowing for the combination of different materials with polypropylene to enhance its properties. Cold lamination processes using pressure-sensitive adhesives became popular, offering improved flexibility and faster production times.
The next major milestone in lamination evolution came with the development of extrusion coating and lamination. This process involved applying a molten layer of polymer directly onto the polypropylene substrate, creating a strong, seamless bond. Extrusion lamination not only improved the overall strength of the banner material but also allowed for the incorporation of additional functional layers, such as UV-resistant coatings or vapor barriers.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards environmentally friendly lamination techniques. Water-based adhesives and solvent-free lamination processes have gained traction, addressing concerns about VOC emissions and sustainability. These eco-friendly approaches maintain the high performance standards required for banner materials while reducing environmental impact.
The advent of nanotechnology has ushered in a new era of lamination innovation. Nanocomposite coatings and nanostructured adhesives are being explored to enhance the mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of polypropylene banners. These advanced materials promise to deliver superior performance in terms of durability, weather resistance, and print quality.
Current research is exploring smart lamination techniques that incorporate functional elements directly into the lamination process. This includes the integration of conductive layers for interactive displays, photochromic materials for dynamic color-changing banners, and self-healing coatings that can repair minor damage automatically.
The evolution of lamination techniques for polypropylene banner materials reflects a constant drive towards improved performance, efficiency, and sustainability. From basic heat-sealing to cutting-edge nanotechnology applications, each advancement has contributed to the development of more versatile and durable banner materials. As the industry continues to innovate, we can expect further refinements in lamination technology, leading to even more advanced and multifunctional polypropylene banner materials in the future.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for enhanced polypropylene banner materials has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing need for durable, high-quality advertising and signage solutions across various industries. The global large format printing market, which includes banner materials, is projected to reach a substantial market value by 2025, with a significant portion attributed to polypropylene-based products.
The advertising and marketing sector remains the primary driver of demand for polypropylene banners, as businesses continually seek cost-effective and visually appealing ways to promote their products and services. Retail, events, and trade show industries also contribute significantly to the market growth, utilizing banners for temporary displays and promotional campaigns.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives have begun to shape market preferences, leading to increased demand for eco-friendly and recyclable banner materials. This trend has prompted manufacturers to explore innovative lamination techniques that can enhance the durability and performance of polypropylene banners while maintaining their recyclability.
The outdoor advertising segment, in particular, has shown robust growth, requiring banner materials that can withstand harsh weather conditions and maintain visual quality over extended periods. This has led to a surge in demand for advanced lamination techniques that can improve UV resistance, color fastness, and overall longevity of polypropylene banners.
Digital printing advancements have also influenced market demand, as customers now expect higher print quality and more vibrant colors on their banner materials. This has created a need for lamination techniques that can enhance color reproduction and protect printed surfaces from scratches and fading.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the market. While it initially caused a slowdown in demand due to reduced events and retail activities, it has also created new opportunities in sectors such as healthcare and education, where informational signage has become crucial.
As businesses adapt to post-pandemic realities, there is an emerging trend towards more frequent changes in advertising and promotional materials. This shift favors polypropylene banners due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of replacement, further driving the need for enhanced lamination techniques to improve their durability and reusability.
In conclusion, the market demand for enhanced polypropylene banner materials continues to grow, fueled by diverse industry needs, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. The development of innovative lamination techniques will be crucial in meeting these evolving market requirements and maintaining the competitiveness of polypropylene-based products in the banner materials sector.
Technical Challenges
The development of enhanced polypropylene banner materials through advanced lamination techniques faces several significant technical challenges. These challenges stem from the complex nature of the materials involved and the demanding requirements of the end product.
One of the primary challenges is achieving optimal adhesion between the polypropylene substrate and the laminate layer. Polypropylene's low surface energy and chemical inertness make it inherently difficult to bond with other materials. This necessitates the development of specialized adhesives or surface treatment methods to ensure strong and durable lamination. Techniques such as corona discharge treatment or plasma treatment are often employed, but these processes must be carefully controlled to avoid damaging the polypropylene substrate.
Another significant hurdle is maintaining the flexibility and durability of the laminated banner material. The lamination process must not compromise the inherent flexibility of polypropylene, which is crucial for banner applications. Simultaneously, the laminate layer needs to enhance the material's resistance to tearing, weathering, and UV radiation without adding excessive weight or stiffness. Striking this balance requires careful selection of laminate materials and precise control of the lamination process parameters.
The uniformity of the lamination across large banner surfaces presents another technical challenge. Ensuring consistent adhesion, thickness, and appearance over expansive areas demands highly controlled and scalable lamination processes. Any inconsistencies can lead to weak spots, visual defects, or premature failure of the banner material.
Environmental considerations add another layer of complexity to the lamination process. There is a growing demand for eco-friendly materials and processes in the banner industry. Developing lamination techniques that use sustainable adhesives, reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, and allow for easier recycling of the final product is a significant technical challenge. This often involves exploring bio-based adhesives or developing separation methods for the laminate layers at the end of the product's life cycle.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of the lamination process poses a considerable challenge. While enhanced properties are desirable, the lamination technique must be economically viable for large-scale production. This requires optimizing process speeds, minimizing material waste, and reducing energy consumption without compromising the quality of the final product. Balancing these factors with the performance requirements of the enhanced polypropylene banner material remains a complex technical challenge for researchers and manufacturers in this field.
Current Techniques
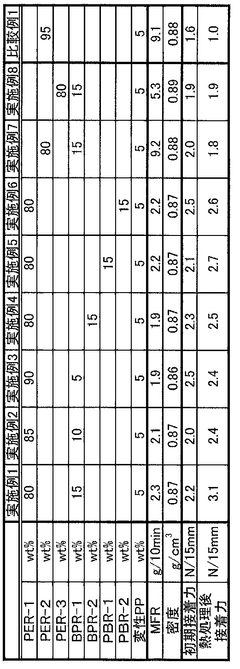
01 UV-resistant additives for polypropylene banners
Incorporating UV-resistant additives into polypropylene banner materials can significantly enhance their durability and longevity when exposed to outdoor conditions. These additives help prevent degradation caused by sunlight, maintaining the banner's color and structural integrity over time.- UV resistance enhancement: Improving the UV resistance of polypropylene banner materials is crucial for outdoor applications. This can be achieved by incorporating UV stabilizers or additives into the polypropylene composition. These additives help prevent degradation caused by sunlight exposure, extending the lifespan and maintaining the appearance of the banner material.
- Printing and color enhancement: Enhancing the printability and color retention of polypropylene banner materials is important for visual appeal. This can be accomplished by modifying the surface properties or adding specific coatings to improve ink adhesion and color vibrancy. Additionally, incorporating color-fast additives can help maintain the banner's appearance over time.
- Mechanical strength improvement: Increasing the mechanical strength of polypropylene banner materials is essential for durability. This can be achieved through various methods such as reinforcing the polymer structure, adding strengthening fibers, or optimizing the manufacturing process. Improved strength helps the banner withstand environmental stresses and prolongs its usable life.
- Weather resistance enhancement: Enhancing the weather resistance of polypropylene banner materials is crucial for outdoor applications. This involves improving resistance to factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and wind. Techniques may include incorporating water-repellent additives, optimizing the material's thermal properties, or developing multi-layer structures for better protection against environmental elements.
- Eco-friendly and recyclable improvements: Developing eco-friendly and recyclable polypropylene banner materials is becoming increasingly important. This involves using biodegradable additives, designing for easier recycling, or incorporating recycled polypropylene into the production process. These improvements aim to reduce the environmental impact of banner materials while maintaining their performance characteristics.
02 Flame retardant treatments for polypropylene banners
Applying flame retardant treatments to polypropylene banner materials improves their fire resistance properties. This enhancement is crucial for safety compliance in various indoor and outdoor applications, making the banners suitable for use in public spaces and events.Expand Specific Solutions03 Reinforcement techniques for polypropylene banners
Implementing reinforcement techniques, such as incorporating high-strength fibers or applying specialized coatings, can enhance the tensile strength and tear resistance of polypropylene banner materials. These improvements result in more durable and long-lasting banners suitable for various environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Printability enhancements for polypropylene banners
Developing surface treatments or coatings that improve the printability of polypropylene banner materials can enhance image quality and color vibrancy. These enhancements allow for better ink adhesion and higher resolution printing, resulting in more visually appealing and professional-looking banners.Expand Specific Solutions05 Eco-friendly additives for polypropylene banners
Incorporating eco-friendly additives into polypropylene banner materials can improve their environmental impact. These additives may include biodegradable components or recycled materials, making the banners more sustainable while maintaining their desired performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The lamination techniques for enhanced polypropylene banner materials market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for durable and high-quality advertising materials. The global market size is projected to expand significantly, fueled by advancements in printing technologies and the rising popularity of outdoor advertising. Technologically, the field is evolving rapidly, with companies like DuPont de Nemours, Mitsui Chemicals, and 3M Innovative Properties leading innovation. These firms are developing advanced lamination processes and materials to improve banner durability, print quality, and environmental sustainability. Emerging players such as Kingfa Sci. & Tech. and Japan Polypropylene Corp. are also contributing to technological advancements, intensifying competition in this dynamic sector.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Key Innovations
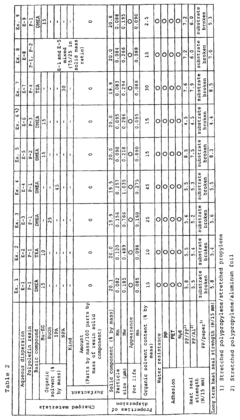
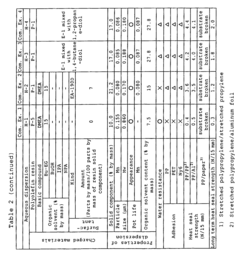
- A laminate manufacturing method involving a polypropylene adhesive layer with a specific composition, including 97-70% propylene copolymer (A) and 3-30% butene-derived copolymer (B), along with a polymer (C) containing unsaturated carboxylic acid units, and a base layer of polyester resin, which undergoes heat treatment at 80-140°C for 5-120 minutes to maintain adhesion and flexibility.
- Aqueous polyolefin resin dispersion with a specific composition containing 0.5 to 20% unsaturated carboxylic acid units, propylene, butene, and ethylene components, dispersed in an aqueous medium without high-boiling-point water-compatibilizing agents, achieving a particle size of 1 µm or smaller, and using a basic compound with a boiling point below 185°C to enhance adhesion and stability.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of lamination techniques for enhanced polypropylene banner materials is a critical consideration in the development and application of these products. Polypropylene banners are widely used in advertising and signage due to their durability and cost-effectiveness. However, the lamination process and the materials used can have significant environmental implications.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the use of adhesives in the lamination process. Many traditional adhesives contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks. Recent advancements in adhesive technology have led to the development of low-VOC and water-based adhesives, which significantly reduce harmful emissions during production and throughout the product lifecycle.
The energy consumption associated with lamination processes is another important factor. Thermal lamination techniques, which involve heat and pressure, can be energy-intensive. Manufacturers are increasingly exploring more energy-efficient methods, such as UV-cured lamination, which requires less heat and can reduce overall energy consumption. Additionally, improvements in equipment design and process optimization have led to more efficient lamination lines that minimize energy waste.
Waste generation and disposal are crucial aspects of the environmental impact assessment. The lamination process can produce off-cuts and rejected materials that often end up in landfills. To address this issue, some manufacturers have implemented recycling programs for production waste and are exploring ways to incorporate recycled content into new banner materials. However, the multi-layer nature of laminated polypropylene banners can make recycling challenging at the end of the product's life.
The durability of laminated polypropylene banners has both positive and negative environmental implications. On one hand, their longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, potentially lowering overall material consumption. On the other hand, their resistance to degradation means they can persist in the environment for extended periods if not properly disposed of or recycled.
Water usage and potential water pollution are also considerations in the lamination process. Some techniques require water for cooling or as part of the adhesive application. Manufacturers are increasingly implementing closed-loop water systems and water treatment processes to minimize consumption and prevent contamination of local water sources.
As environmental awareness grows, there is a push towards more sustainable lamination techniques and materials. Research is being conducted on bio-based adhesives and biodegradable laminating films that could reduce the environmental footprint of polypropylene banner materials. Additionally, life cycle assessments are becoming more common in the industry, helping manufacturers and consumers understand the full environmental impact of these products from production to disposal.
Quality Control
Quality control is a critical aspect of lamination techniques for enhanced polypropylene banner materials. The process involves several key steps to ensure the final product meets the required standards and specifications. Firstly, raw material inspection is essential. This includes checking the quality of the polypropylene film, adhesives, and any additional layers used in the lamination process. The materials must meet predetermined criteria for thickness, tensile strength, and chemical composition.
During the lamination process, continuous monitoring of temperature, pressure, and speed is crucial. These parameters directly affect the bond strength and overall quality of the laminated banner material. Advanced sensors and control systems are typically employed to maintain consistent conditions throughout the production run. Any deviations from the set parameters are immediately flagged and addressed to prevent defects.
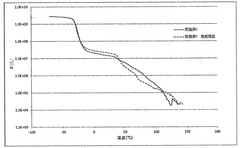
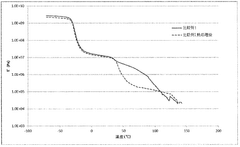
Post-lamination testing is another vital component of quality control. This involves a series of tests to evaluate the physical properties of the laminated material. Peel strength tests are conducted to assess the adhesion between layers, ensuring they can withstand environmental stresses and handling. Tensile strength and elongation tests measure the material's ability to resist tearing and stretching, which are crucial for durability in outdoor applications.
Visual inspection plays a significant role in quality control. Trained operators examine the laminated material for any visible defects such as bubbles, wrinkles, or uneven surfaces. Advanced imaging systems, including high-resolution cameras and machine vision technology, are often utilized to detect minute imperfections that may be missed by the human eye.
Weathering tests are particularly important for outdoor banner materials. Accelerated weathering chambers simulate various environmental conditions, including UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, and moisture. These tests help predict the material's performance and longevity in real-world applications. Color fastness and print quality are also evaluated to ensure the banner maintains its visual appeal over time.
Quality control documentation and traceability are essential for maintaining consistent standards and addressing any issues that may arise. Each batch of laminated material is typically assigned a unique identifier, allowing manufacturers to track its production history and test results. This information is valuable for continuous improvement efforts and addressing any customer concerns.
Implementing statistical process control (SPC) methods helps manufacturers identify trends and potential issues before they result in defective products. By analyzing data from various quality control checkpoints, producers can make proactive adjustments to their processes, ensuring consistent high-quality output of enhanced polypropylene banner materials.