How Polypropylene Permeability Transformation Aids Medical Packaging
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polypropylene Permeability Evolution and Objectives
Polypropylene has undergone significant evolution in its permeability characteristics, transforming its role in medical packaging over the years. Initially developed in the 1950s, polypropylene was primarily valued for its chemical resistance and mechanical properties. However, its high permeability to gases and moisture limited its use in sensitive medical applications.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the emergence of modified polypropylene formulations, incorporating additives and co-polymers to enhance barrier properties. These developments marked the beginning of polypropylene's journey towards becoming a viable option for medical packaging. Researchers focused on reducing oxygen and water vapor transmission rates, critical factors in preserving the efficacy of medical products.
By the 1990s, multilayer polypropylene films were introduced, combining the material's inherent strengths with enhanced barrier properties. This innovation significantly expanded polypropylene's applicability in medical packaging, particularly for moisture-sensitive products. The turn of the millennium brought nanotechnology into play, with nanocomposite polypropylene materials offering unprecedented improvements in gas barrier properties.
Recent advancements have centered on smart polypropylene packaging, incorporating active and intelligent features. These innovations aim to not only maintain product integrity but also provide real-time monitoring of package conditions. The integration of antimicrobial properties has further elevated polypropylene's value in medical applications, addressing concerns about bacterial contamination during storage and transport.
The primary objective in polypropylene permeability transformation for medical packaging is to achieve an optimal balance between barrier properties and other essential characteristics such as transparency, flexibility, and sterilizability. Researchers are striving to develop polypropylene formulations that can match or exceed the performance of traditional materials like glass and aluminum while offering the benefits of plastic packaging.
Another key goal is to enhance the sustainability profile of polypropylene medical packaging. This involves developing bio-based polypropylene variants and improving recyclability without compromising barrier properties. The industry is also focusing on reducing material thickness while maintaining or improving permeability characteristics, aiming to minimize environmental impact and reduce costs.
Looking ahead, the objectives for polypropylene permeability in medical packaging include the development of customizable barrier properties to suit specific product requirements, integration of smart technologies for enhanced product protection and traceability, and further improvements in sustainability metrics. These advancements are expected to solidify polypropylene's position as a preferred material in the evolving landscape of medical packaging solutions.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the emergence of modified polypropylene formulations, incorporating additives and co-polymers to enhance barrier properties. These developments marked the beginning of polypropylene's journey towards becoming a viable option for medical packaging. Researchers focused on reducing oxygen and water vapor transmission rates, critical factors in preserving the efficacy of medical products.
By the 1990s, multilayer polypropylene films were introduced, combining the material's inherent strengths with enhanced barrier properties. This innovation significantly expanded polypropylene's applicability in medical packaging, particularly for moisture-sensitive products. The turn of the millennium brought nanotechnology into play, with nanocomposite polypropylene materials offering unprecedented improvements in gas barrier properties.
Recent advancements have centered on smart polypropylene packaging, incorporating active and intelligent features. These innovations aim to not only maintain product integrity but also provide real-time monitoring of package conditions. The integration of antimicrobial properties has further elevated polypropylene's value in medical applications, addressing concerns about bacterial contamination during storage and transport.
The primary objective in polypropylene permeability transformation for medical packaging is to achieve an optimal balance between barrier properties and other essential characteristics such as transparency, flexibility, and sterilizability. Researchers are striving to develop polypropylene formulations that can match or exceed the performance of traditional materials like glass and aluminum while offering the benefits of plastic packaging.
Another key goal is to enhance the sustainability profile of polypropylene medical packaging. This involves developing bio-based polypropylene variants and improving recyclability without compromising barrier properties. The industry is also focusing on reducing material thickness while maintaining or improving permeability characteristics, aiming to minimize environmental impact and reduce costs.
Looking ahead, the objectives for polypropylene permeability in medical packaging include the development of customizable barrier properties to suit specific product requirements, integration of smart technologies for enhanced product protection and traceability, and further improvements in sustainability metrics. These advancements are expected to solidify polypropylene's position as a preferred material in the evolving landscape of medical packaging solutions.
Medical Packaging Market Demand Analysis
The medical packaging market has been experiencing significant growth due to increasing healthcare expenditure, rising demand for pharmaceutical products, and the growing prevalence of chronic diseases. The global medical packaging market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2021 to 2028, driven by the need for advanced packaging solutions that ensure product safety, sterility, and extended shelf life.
Polypropylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer, has emerged as a key material in medical packaging due to its excellent barrier properties, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The demand for polypropylene in medical packaging is expected to grow substantially, particularly in applications such as syringes, vials, and blister packs. This growth is fueled by the material's ability to maintain product integrity and prevent contamination, which is crucial in the healthcare sector.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for medical packaging, with a surge in the production of personal protective equipment (PPE), diagnostic kits, and vaccine packaging. This has led to increased adoption of polypropylene-based packaging solutions, as they offer superior protection against moisture and oxygen permeation.
In the pharmaceutical sector, there is a growing trend towards unit-dose packaging and blister packs, which require materials with enhanced barrier properties. Polypropylene, when modified to improve its permeability characteristics, addresses this need effectively. The market is witnessing a shift towards more sustainable packaging solutions, and polypropylene's recyclability aligns well with this trend.
The aging population in developed countries is another factor driving the demand for medical packaging. As the elderly population grows, there is an increased need for pharmaceutical products and medical devices, which in turn boosts the demand for high-quality, protective packaging materials like polypropylene.
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present significant growth opportunities for the medical packaging market. These regions are experiencing rapid urbanization, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increasing healthcare awareness, all of which contribute to the rising demand for advanced medical packaging solutions.
In conclusion, the medical packaging market is poised for substantial growth, with polypropylene playing a crucial role in meeting the industry's evolving needs. The material's ability to transform its permeability characteristics makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of medical packaging applications, addressing the market's demands for safety, efficacy, and sustainability.
Polypropylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer, has emerged as a key material in medical packaging due to its excellent barrier properties, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The demand for polypropylene in medical packaging is expected to grow substantially, particularly in applications such as syringes, vials, and blister packs. This growth is fueled by the material's ability to maintain product integrity and prevent contamination, which is crucial in the healthcare sector.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for medical packaging, with a surge in the production of personal protective equipment (PPE), diagnostic kits, and vaccine packaging. This has led to increased adoption of polypropylene-based packaging solutions, as they offer superior protection against moisture and oxygen permeation.
In the pharmaceutical sector, there is a growing trend towards unit-dose packaging and blister packs, which require materials with enhanced barrier properties. Polypropylene, when modified to improve its permeability characteristics, addresses this need effectively. The market is witnessing a shift towards more sustainable packaging solutions, and polypropylene's recyclability aligns well with this trend.
The aging population in developed countries is another factor driving the demand for medical packaging. As the elderly population grows, there is an increased need for pharmaceutical products and medical devices, which in turn boosts the demand for high-quality, protective packaging materials like polypropylene.
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present significant growth opportunities for the medical packaging market. These regions are experiencing rapid urbanization, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increasing healthcare awareness, all of which contribute to the rising demand for advanced medical packaging solutions.
In conclusion, the medical packaging market is poised for substantial growth, with polypropylene playing a crucial role in meeting the industry's evolving needs. The material's ability to transform its permeability characteristics makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of medical packaging applications, addressing the market's demands for safety, efficacy, and sustainability.
Current Challenges in Polypropylene Permeability
Polypropylene (PP) has become a staple material in medical packaging due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. However, its inherent permeability characteristics present significant challenges in maintaining the integrity and sterility of medical devices and pharmaceuticals. The primary challenge lies in balancing the need for a robust barrier against moisture, gases, and microorganisms while ensuring the material remains suitable for sterilization processes and long-term storage.
One of the most pressing issues is the relatively high oxygen transmission rate (OTR) of polypropylene compared to other packaging materials. This can lead to oxidation of sensitive medical products, potentially compromising their efficacy and safety. Additionally, the water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) of PP, while lower than some alternatives, still poses a risk to moisture-sensitive items, particularly in high-humidity environments or during long-term storage.
The sterilization compatibility of PP also presents challenges. While PP can withstand common sterilization methods such as ethylene oxide (EtO) and gamma irradiation, these processes can affect the material's permeability properties. Post-sterilization changes in the polymer structure may lead to increased permeability, potentially compromising the package's barrier function over time.
Another significant challenge is the variability in permeability across different grades and formulations of PP. This inconsistency makes it difficult for manufacturers to standardize packaging solutions across diverse product lines, often necessitating extensive testing and validation for each application. The lack of a one-size-fits-all solution increases development time and costs for medical device and pharmaceutical companies.
The growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions adds another layer of complexity. While PP is recyclable, the additives and modifications used to enhance its barrier properties can complicate recycling processes. Balancing environmental concerns with the stringent performance requirements of medical packaging remains a significant hurdle.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape surrounding medical packaging materials is becoming increasingly stringent. Demonstrating compliance with evolving standards for material safety, stability, and performance adds to the challenges faced by manufacturers using PP in medical packaging applications.
Lastly, the emergence of new medical technologies and therapies, such as biologics and personalized medicines, places even greater demands on packaging materials. These products often require exceptional barrier properties and stability over extended periods, pushing the limits of current PP technology and necessitating innovative solutions to enhance its permeability characteristics.
One of the most pressing issues is the relatively high oxygen transmission rate (OTR) of polypropylene compared to other packaging materials. This can lead to oxidation of sensitive medical products, potentially compromising their efficacy and safety. Additionally, the water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) of PP, while lower than some alternatives, still poses a risk to moisture-sensitive items, particularly in high-humidity environments or during long-term storage.
The sterilization compatibility of PP also presents challenges. While PP can withstand common sterilization methods such as ethylene oxide (EtO) and gamma irradiation, these processes can affect the material's permeability properties. Post-sterilization changes in the polymer structure may lead to increased permeability, potentially compromising the package's barrier function over time.
Another significant challenge is the variability in permeability across different grades and formulations of PP. This inconsistency makes it difficult for manufacturers to standardize packaging solutions across diverse product lines, often necessitating extensive testing and validation for each application. The lack of a one-size-fits-all solution increases development time and costs for medical device and pharmaceutical companies.
The growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions adds another layer of complexity. While PP is recyclable, the additives and modifications used to enhance its barrier properties can complicate recycling processes. Balancing environmental concerns with the stringent performance requirements of medical packaging remains a significant hurdle.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape surrounding medical packaging materials is becoming increasingly stringent. Demonstrating compliance with evolving standards for material safety, stability, and performance adds to the challenges faced by manufacturers using PP in medical packaging applications.
Lastly, the emergence of new medical technologies and therapies, such as biologics and personalized medicines, places even greater demands on packaging materials. These products often require exceptional barrier properties and stability over extended periods, pushing the limits of current PP technology and necessitating innovative solutions to enhance its permeability characteristics.
Existing Polypropylene Permeability Solutions
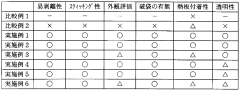
01 Modification of polypropylene structure
Altering the molecular structure of polypropylene through various methods such as copolymerization, blending, or adding fillers can significantly impact its permeability properties. These modifications can enhance or reduce gas and liquid permeability depending on the desired application.- Modification of polypropylene structure: Altering the molecular structure of polypropylene through various methods such as copolymerization, blending, or adding fillers can significantly impact its permeability properties. These modifications can enhance or reduce gas and vapor transmission rates, making the material suitable for specific applications.
- Barrier properties enhancement: Incorporating additives or creating multi-layer structures with polypropylene can improve its barrier properties against gases, moisture, and other substances. This is particularly useful in packaging applications where maintaining product freshness and extending shelf life are crucial.
- Permeability testing methods: Various techniques and equipment are used to measure and characterize the permeability of polypropylene materials. These methods help in assessing the material's performance under different conditions and for specific applications, ensuring quality control and product development.
- Environmental factors affecting permeability: Temperature, humidity, and pressure can significantly influence the permeability of polypropylene. Understanding these environmental factors is crucial for predicting and controlling the material's performance in various applications and storage conditions.
- Nanocomposite polypropylene materials: Incorporating nanoparticles or nanostructures into polypropylene can dramatically alter its permeability characteristics. These nanocomposites often exhibit improved barrier properties and can be tailored for specific gas or liquid permeation requirements.
02 Barrier properties enhancement
Techniques to improve the barrier properties of polypropylene, including the incorporation of nanoparticles, clay minerals, or other additives. These enhancements can reduce gas and moisture permeability, making the material more suitable for packaging and protective applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Permeability testing methods
Various methods and apparatus for measuring and characterizing the permeability of polypropylene materials. These include gas permeation tests, water vapor transmission rate measurements, and specialized equipment for assessing barrier properties under different conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Controlled permeability for specific applications
Tailoring polypropylene permeability for specific uses such as breathable fabrics, selective filtration membranes, or controlled release systems. This involves balancing permeability with other material properties to achieve desired functionality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental factors affecting permeability
Studies on how environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and pressure influence the permeability of polypropylene. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting material performance in various applications and storage conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Medical Packaging Materials
The polypropylene permeability transformation market for medical packaging is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced healthcare solutions. The market size is expanding, with key players like Becton, Dickinson & Co., Mitsui Chemicals, and DuPont de Nemours leading innovation. Technological maturity varies, with established companies like Borealis AG and Sinopec Shanghai Petrochemical Co. offering proven solutions, while newer entrants like Prime Polymer Co. Ltd. and Japan Polypropylene Corp. focus on developing cutting-edge technologies. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of global chemical conglomerates and specialized medical packaging firms, each leveraging their strengths to capture market share in this evolving sector.
Becton, Dickinson & Co.
Technical Solution: Becton, Dickinson & Co. has developed advanced polypropylene (PP) films with enhanced permeability for medical packaging. Their technology involves modifying the PP structure to create microporous channels, allowing controlled gas exchange while maintaining barrier properties against microorganisms. This transformation is achieved through a proprietary blend of PP with specific additives and a carefully controlled extrusion process. The resulting film exhibits improved sterilization efficiency, extended shelf life for medical devices, and reduced risk of package integrity issues during transportation and storage[1][3]. The company has also implemented a surface treatment technique to further enhance the film's printability and seal strength, crucial for medical packaging applications[5].
Strengths: Improved sterilization efficiency, extended product shelf life, and enhanced package integrity. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and the need for specialized manufacturing equipment.
Mitsui Chemicals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Mitsui Chemicals has pioneered a novel approach to polypropylene permeability transformation for medical packaging. Their technology involves the incorporation of nanoparticles into the PP matrix, creating a network of nanochannels that facilitate controlled gas permeation. This innovative method allows for precise tailoring of permeability characteristics to suit specific medical packaging requirements. The company has also developed a multi-layer film structure that combines the modified PP with other materials to achieve optimal barrier properties. Their research has shown a 30% improvement in oxygen transmission rates compared to conventional PP films, while maintaining excellent moisture barrier properties[2][4]. Additionally, Mitsui Chemicals has implemented a unique heat-treatment process that further enhances the film's dimensional stability and puncture resistance, critical factors in medical packaging applications[6].
Strengths: Highly customizable permeability, excellent barrier properties, and improved mechanical strength. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process and potential for increased material costs.
Core Innovations in Permeability Enhancement
Packaging container and medical packaging sheet
PatentWO2006013919A1
Innovation
- A packaging container with a laminate structure comprising a base layer of polypropylene resin and a surface layer of thermoplastic resin with a melting point of 130°C or higher, which functions as an adhesive layer, is heat-sealed along the periphery, using a porous film, nonwoven fabric, or sterilized paper as the lid material, ensuring improved heat resistance and easy peelability.
Polypropylene-based packaging material
PatentWO2023038148A1
Innovation
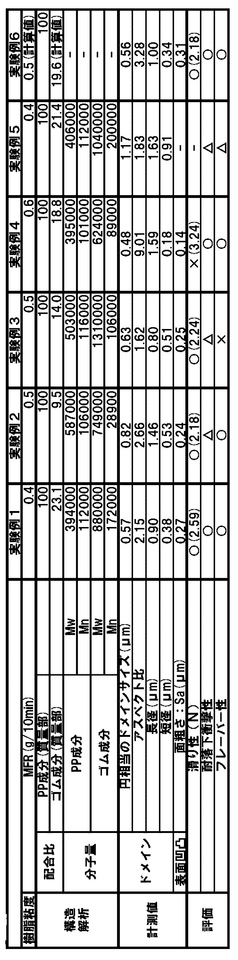
- A polypropylene packaging material with a phase-dispersed structure featuring spindle-shaped polypropylene elastomer domains in a polypropylene matrix, optimized by controlling domain size and molecular weight, and a laminate structure incorporating a polypropylene layer with specific surface roughness and layer configurations for enhanced performance.
Regulatory Framework for Medical Packaging
The regulatory framework for medical packaging plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices and pharmaceuticals. In the context of polypropylene permeability transformation for medical packaging, several key regulations and guidelines must be considered.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a primary regulatory body overseeing medical packaging. The FDA's 21 CFR Part 211 outlines current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) for finished pharmaceuticals, which includes requirements for packaging materials. Additionally, the FDA's guidance document on "Container Closure Systems for Packaging Human Drugs and Biologics" provides specific recommendations for evaluating and selecting appropriate packaging materials.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) govern medical packaging requirements. The EMA's guidelines on plastic immediate packaging materials (CPMP/QWP/4359/03) specifically address the use of plastic materials in pharmaceutical packaging, including polypropylene.
International standards also play a significant role in shaping the regulatory landscape. ISO 11607 sets global standards for packaging for terminally sterilized medical devices, covering both materials and packaging systems. This standard is widely recognized and often referenced by regulatory bodies worldwide.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) provides important standards for packaging materials, including USP <661> on plastic packaging systems and their materials of construction. These standards outline testing methods and acceptance criteria for various packaging materials, including polypropylene.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the environmental impact of medical packaging. The European Union's Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (94/62/EC) sets targets for the recovery and recycling of packaging materials, influencing the design and selection of medical packaging materials.
For polypropylene permeability transformation in medical packaging, manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these regulations and standards. This includes providing data on material properties, stability studies, and compatibility with the packaged product. The regulatory framework also requires manufacturers to implement quality management systems and maintain documentation of their packaging development and validation processes.
As the field of medical packaging evolves, regulatory bodies continue to update their guidelines to address new technologies and materials. Manufacturers and researchers working on polypropylene permeability transformation must stay informed about these regulatory changes and ensure their innovations align with current and emerging requirements.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a primary regulatory body overseeing medical packaging. The FDA's 21 CFR Part 211 outlines current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) for finished pharmaceuticals, which includes requirements for packaging materials. Additionally, the FDA's guidance document on "Container Closure Systems for Packaging Human Drugs and Biologics" provides specific recommendations for evaluating and selecting appropriate packaging materials.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) govern medical packaging requirements. The EMA's guidelines on plastic immediate packaging materials (CPMP/QWP/4359/03) specifically address the use of plastic materials in pharmaceutical packaging, including polypropylene.
International standards also play a significant role in shaping the regulatory landscape. ISO 11607 sets global standards for packaging for terminally sterilized medical devices, covering both materials and packaging systems. This standard is widely recognized and often referenced by regulatory bodies worldwide.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) provides important standards for packaging materials, including USP <661> on plastic packaging systems and their materials of construction. These standards outline testing methods and acceptance criteria for various packaging materials, including polypropylene.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the environmental impact of medical packaging. The European Union's Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (94/62/EC) sets targets for the recovery and recycling of packaging materials, influencing the design and selection of medical packaging materials.
For polypropylene permeability transformation in medical packaging, manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these regulations and standards. This includes providing data on material properties, stability studies, and compatibility with the packaged product. The regulatory framework also requires manufacturers to implement quality management systems and maintain documentation of their packaging development and validation processes.
As the field of medical packaging evolves, regulatory bodies continue to update their guidelines to address new technologies and materials. Manufacturers and researchers working on polypropylene permeability transformation must stay informed about these regulatory changes and ensure their innovations align with current and emerging requirements.
Sustainability in Medical Packaging Materials
Sustainability in medical packaging materials has become a critical focus in the healthcare industry, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The transformation of polypropylene permeability plays a significant role in advancing sustainable practices within medical packaging. This shift towards more eco-friendly solutions is reshaping the landscape of medical packaging materials and their environmental impact.
Polypropylene, a widely used material in medical packaging, has traditionally been known for its excellent barrier properties. However, its inherent impermeability has posed challenges in terms of recyclability and biodegradability. The transformation of polypropylene permeability addresses these issues by altering the material's structure to allow for controlled gas and moisture transmission while maintaining necessary protection for medical devices and pharmaceuticals.
This permeability transformation enables the development of packaging solutions that require less material overall, reducing waste and environmental footprint. By allowing for thinner packaging walls without compromising protection, manufacturers can significantly decrease the amount of plastic used in each package. Additionally, the improved permeability characteristics facilitate the use of sterilization methods that are more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, such as ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization, which requires gas penetration through the packaging material.
The sustainability benefits extend beyond material reduction and improved sterilization processes. Enhanced polypropylene permeability also contributes to the development of packaging that is more compatible with recycling streams. By allowing for easier separation of different components and improved breakdown of the material during recycling processes, these innovations help close the loop in the circular economy of medical packaging materials.
Furthermore, the transformation of polypropylene permeability opens up possibilities for incorporating bio-based additives and fillers into the packaging material. These additions can enhance biodegradability without compromising the essential barrier properties required for medical applications. This approach aligns with the growing demand for packaging solutions that have a reduced environmental impact at the end of their lifecycle.
As the healthcare industry continues to prioritize sustainability, the advancements in polypropylene permeability are driving innovation in medical packaging design. Manufacturers are exploring new ways to optimize packaging structures, combining transformed polypropylene with other sustainable materials to create hybrid solutions that offer the best of both worlds – robust protection and environmental responsibility.
In conclusion, the transformation of polypropylene permeability is a key enabler in the pursuit of more sustainable medical packaging materials. By addressing the limitations of traditional polypropylene while maintaining its beneficial properties, this innovation is paving the way for a new generation of medical packaging that meets stringent healthcare requirements while minimizing environmental impact.
Polypropylene, a widely used material in medical packaging, has traditionally been known for its excellent barrier properties. However, its inherent impermeability has posed challenges in terms of recyclability and biodegradability. The transformation of polypropylene permeability addresses these issues by altering the material's structure to allow for controlled gas and moisture transmission while maintaining necessary protection for medical devices and pharmaceuticals.
This permeability transformation enables the development of packaging solutions that require less material overall, reducing waste and environmental footprint. By allowing for thinner packaging walls without compromising protection, manufacturers can significantly decrease the amount of plastic used in each package. Additionally, the improved permeability characteristics facilitate the use of sterilization methods that are more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, such as ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization, which requires gas penetration through the packaging material.
The sustainability benefits extend beyond material reduction and improved sterilization processes. Enhanced polypropylene permeability also contributes to the development of packaging that is more compatible with recycling streams. By allowing for easier separation of different components and improved breakdown of the material during recycling processes, these innovations help close the loop in the circular economy of medical packaging materials.
Furthermore, the transformation of polypropylene permeability opens up possibilities for incorporating bio-based additives and fillers into the packaging material. These additions can enhance biodegradability without compromising the essential barrier properties required for medical applications. This approach aligns with the growing demand for packaging solutions that have a reduced environmental impact at the end of their lifecycle.
As the healthcare industry continues to prioritize sustainability, the advancements in polypropylene permeability are driving innovation in medical packaging design. Manufacturers are exploring new ways to optimize packaging structures, combining transformed polypropylene with other sustainable materials to create hybrid solutions that offer the best of both worlds – robust protection and environmental responsibility.
In conclusion, the transformation of polypropylene permeability is a key enabler in the pursuit of more sustainable medical packaging materials. By addressing the limitations of traditional polypropylene while maintaining its beneficial properties, this innovation is paving the way for a new generation of medical packaging that meets stringent healthcare requirements while minimizing environmental impact.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!