PEMF Therapy: Bridging Traditional and Modern Medicine
AUG 11, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Technology Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. The technology's roots can be traced back to the 1950s when scientists began exploring the effects of electromagnetic fields on biological systems. Initially, PEMF devices were large, cumbersome machines primarily used in clinical settings for bone healing and pain management.
The 1970s marked a crucial turning point in PEMF technology development. NASA's research into the use of pulsed electromagnetic fields to combat bone and muscle loss in astronauts during space missions led to significant advancements in the field. This research not only validated the therapeutic potential of PEMF but also paved the way for more compact and efficient devices.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, PEMF technology saw rapid improvements in both efficacy and portability. The introduction of microprocessors allowed for more precise control over field strength and frequency, enabling tailored treatments for various conditions. This period also witnessed the expansion of PEMF applications beyond bone healing to include soft tissue repair, pain relief, and even mental health treatments.
The early 2000s brought about a revolution in PEMF device design. Miniaturization of components and advancements in battery technology led to the development of portable, home-use PEMF devices. This shift democratized access to PEMF therapy, allowing patients to receive treatments outside of clinical settings and integrating the technology into daily wellness routines.
In recent years, the integration of PEMF technology with smart devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) has further enhanced its capabilities. Modern PEMF devices can now be controlled via smartphone apps, allowing for personalized treatment protocols and real-time monitoring of therapy sessions. This connectivity also facilitates data collection and analysis, contributing to ongoing research and refinement of PEMF protocols.
The latest frontier in PEMF technology evolution is the development of targeted therapies. Researchers are exploring ways to deliver electromagnetic pulses to specific tissues or organs with greater precision, potentially increasing efficacy while minimizing side effects. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining PEMF with other therapeutic modalities, such as photobiomodulation or ultrasound, to create synergistic healing effects.
As PEMF therapy continues to bridge the gap between traditional and modern medicine, ongoing research focuses on optimizing treatment parameters and expanding the range of treatable conditions. The technology's non-invasive nature and growing body of clinical evidence position it as a promising complementary therapy in integrative medicine approaches.
The 1970s marked a crucial turning point in PEMF technology development. NASA's research into the use of pulsed electromagnetic fields to combat bone and muscle loss in astronauts during space missions led to significant advancements in the field. This research not only validated the therapeutic potential of PEMF but also paved the way for more compact and efficient devices.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, PEMF technology saw rapid improvements in both efficacy and portability. The introduction of microprocessors allowed for more precise control over field strength and frequency, enabling tailored treatments for various conditions. This period also witnessed the expansion of PEMF applications beyond bone healing to include soft tissue repair, pain relief, and even mental health treatments.
The early 2000s brought about a revolution in PEMF device design. Miniaturization of components and advancements in battery technology led to the development of portable, home-use PEMF devices. This shift democratized access to PEMF therapy, allowing patients to receive treatments outside of clinical settings and integrating the technology into daily wellness routines.
In recent years, the integration of PEMF technology with smart devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) has further enhanced its capabilities. Modern PEMF devices can now be controlled via smartphone apps, allowing for personalized treatment protocols and real-time monitoring of therapy sessions. This connectivity also facilitates data collection and analysis, contributing to ongoing research and refinement of PEMF protocols.
The latest frontier in PEMF technology evolution is the development of targeted therapies. Researchers are exploring ways to deliver electromagnetic pulses to specific tissues or organs with greater precision, potentially increasing efficacy while minimizing side effects. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining PEMF with other therapeutic modalities, such as photobiomodulation or ultrasound, to create synergistic healing effects.
As PEMF therapy continues to bridge the gap between traditional and modern medicine, ongoing research focuses on optimizing treatment parameters and expanding the range of treatable conditions. The technology's non-invasive nature and growing body of clinical evidence position it as a promising complementary therapy in integrative medicine approaches.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy has been steadily growing as more individuals seek alternative and complementary treatments for various health conditions. This therapy, which bridges traditional and modern medicine, has gained traction due to its non-invasive nature and potential benefits in pain management, tissue repair, and overall wellness.
The global PEMF therapy devices market has shown significant expansion in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of its applications and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with projections indicating substantial growth over the next decade. This growth is attributed to factors such as the aging population, the surge in sports-related injuries, and the growing interest in non-pharmacological pain management solutions.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the increasing adoption of PEMF therapy in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Professional athletes and sports teams have begun incorporating PEMF devices into their recovery routines, citing improved healing times and reduced inflammation. This high-profile usage has contributed to broader public awareness and interest in the technology.
The healthcare sector has also shown a growing interest in PEMF therapy, with some hospitals and clinics integrating it into their treatment offerings. This integration is particularly notable in areas such as orthopedics, neurology, and pain management. The potential of PEMF therapy to reduce reliance on pain medications, including opioids, has made it an attractive option for both healthcare providers and patients seeking alternative pain management strategies.
Consumer demand for home-use PEMF devices has seen a notable uptick, especially in regions with high healthcare costs. This trend has been further accelerated by the global pandemic, which has led to increased interest in home-based health solutions. Manufacturers have responded by developing more user-friendly, portable PEMF devices designed for personal use, expanding the market beyond clinical settings.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain in market penetration. These include the need for more extensive clinical research to validate the efficacy of PEMF therapy across various conditions, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the relatively high cost of advanced PEMF devices. However, ongoing technological advancements and increasing research efforts are expected to address some of these challenges, potentially leading to wider acceptance and adoption of PEMF therapy in both clinical and consumer markets.
The global PEMF therapy devices market has shown significant expansion in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of its applications and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with projections indicating substantial growth over the next decade. This growth is attributed to factors such as the aging population, the surge in sports-related injuries, and the growing interest in non-pharmacological pain management solutions.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the increasing adoption of PEMF therapy in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Professional athletes and sports teams have begun incorporating PEMF devices into their recovery routines, citing improved healing times and reduced inflammation. This high-profile usage has contributed to broader public awareness and interest in the technology.
The healthcare sector has also shown a growing interest in PEMF therapy, with some hospitals and clinics integrating it into their treatment offerings. This integration is particularly notable in areas such as orthopedics, neurology, and pain management. The potential of PEMF therapy to reduce reliance on pain medications, including opioids, has made it an attractive option for both healthcare providers and patients seeking alternative pain management strategies.
Consumer demand for home-use PEMF devices has seen a notable uptick, especially in regions with high healthcare costs. This trend has been further accelerated by the global pandemic, which has led to increased interest in home-based health solutions. Manufacturers have responded by developing more user-friendly, portable PEMF devices designed for personal use, expanding the market beyond clinical settings.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain in market penetration. These include the need for more extensive clinical research to validate the efficacy of PEMF therapy across various conditions, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the relatively high cost of advanced PEMF devices. However, ongoing technological advancements and increasing research efforts are expected to address some of these challenges, potentially leading to wider acceptance and adoption of PEMF therapy in both clinical and consumer markets.
Current PEMF Challenges
Despite the growing popularity and potential of PEMF therapy, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption and integration into mainstream medical practice. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization in PEMF devices and treatment protocols. The wide variety of available devices, each with different frequencies, intensities, and waveforms, makes it difficult for healthcare providers to determine the most effective treatment parameters for specific conditions.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy exerts its therapeutic effects. While numerous studies have demonstrated positive outcomes, the underlying biological processes are not fully elucidated. This knowledge gap hampers the development of targeted treatments and impedes the optimization of PEMF therapy for different medical conditions.
The inconsistency in research methodologies and reporting standards across PEMF studies poses a substantial challenge to the scientific community. The lack of uniformity in experimental designs, treatment protocols, and outcome measures makes it challenging to compare results across studies and draw definitive conclusions about the efficacy of PEMF therapy for various conditions.
Regulatory hurdles also present a significant obstacle to the widespread adoption of PEMF therapy. The classification and approval processes for PEMF devices vary across different countries and regions, leading to inconsistencies in market availability and clinical application. This regulatory landscape creates barriers for manufacturers and limits patient access to potentially beneficial treatments.
The skepticism within the medical community regarding the efficacy of PEMF therapy remains a persistent challenge. Despite growing evidence supporting its therapeutic potential, many healthcare professionals are hesitant to incorporate PEMF therapy into their practice due to a perceived lack of robust clinical data and concerns about its scientific basis.
Additionally, the high cost of advanced PEMF devices and treatments poses a significant barrier to accessibility for many patients. The limited insurance coverage for PEMF therapy in many regions further exacerbates this issue, making it financially challenging for individuals to pursue this treatment option.
Lastly, the potential for electromagnetic interference with other medical devices and implants raises safety concerns that need to be addressed. Ensuring the compatibility of PEMF therapy with pacemakers, defibrillators, and other electronic medical devices is crucial for its safe and widespread application in clinical settings.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy exerts its therapeutic effects. While numerous studies have demonstrated positive outcomes, the underlying biological processes are not fully elucidated. This knowledge gap hampers the development of targeted treatments and impedes the optimization of PEMF therapy for different medical conditions.
The inconsistency in research methodologies and reporting standards across PEMF studies poses a substantial challenge to the scientific community. The lack of uniformity in experimental designs, treatment protocols, and outcome measures makes it challenging to compare results across studies and draw definitive conclusions about the efficacy of PEMF therapy for various conditions.
Regulatory hurdles also present a significant obstacle to the widespread adoption of PEMF therapy. The classification and approval processes for PEMF devices vary across different countries and regions, leading to inconsistencies in market availability and clinical application. This regulatory landscape creates barriers for manufacturers and limits patient access to potentially beneficial treatments.
The skepticism within the medical community regarding the efficacy of PEMF therapy remains a persistent challenge. Despite growing evidence supporting its therapeutic potential, many healthcare professionals are hesitant to incorporate PEMF therapy into their practice due to a perceived lack of robust clinical data and concerns about its scientific basis.
Additionally, the high cost of advanced PEMF devices and treatments poses a significant barrier to accessibility for many patients. The limited insurance coverage for PEMF therapy in many regions further exacerbates this issue, making it financially challenging for individuals to pursue this treatment option.
Lastly, the potential for electromagnetic interference with other medical devices and implants raises safety concerns that need to be addressed. Ensuring the compatibility of PEMF therapy with pacemakers, defibrillators, and other electronic medical devices is crucial for its safe and widespread application in clinical settings.
PEMF Treatment Modalities
01 PEMF devices for therapeutic applications
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular activity and promote healing. They can be used for pain management, tissue repair, and improving overall well-being.- PEMF devices for therapeutic applications: Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and improve overall health. They can be used for pain management, tissue healing, and treating various medical conditions.
- PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions: PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, bone fractures, and neurological disorders. The therapy aims to reduce inflammation, promote tissue regeneration, and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. Specialized PEMF devices are developed to target specific areas of the body or particular health issues.
- Wearable PEMF devices: Wearable PEMF devices are designed for convenient and continuous therapy. These devices can be worn on various parts of the body, allowing for targeted treatment while the user goes about their daily activities. Wearable PEMF devices often incorporate flexible materials and compact designs for improved comfort and usability.
- PEMF therapy combined with other treatments: PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic effects. This can include integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or other forms of electromagnetic stimulation. The combination of treatments aims to provide synergistic benefits and improve overall treatment outcomes.
- Advanced PEMF control systems: Advanced control systems for PEMF devices allow for precise manipulation of electromagnetic field parameters. These systems can adjust frequency, intensity, and waveform patterns to optimize treatment for specific conditions or individual patient needs. Some devices incorporate smart features such as programmable treatment protocols and real-time monitoring capabilities.
02 PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions
PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions. It has shown efficacy in managing chronic pain, reducing inflammation, accelerating bone healing, and improving circulation. The therapy can be tailored to address various health issues by adjusting the frequency and intensity of the electromagnetic fields.Expand Specific Solutions03 Portable and wearable PEMF devices
Advancements in PEMF technology have led to the development of portable and wearable devices. These compact units allow for convenient at-home use or on-the-go treatments. Wearable PEMF devices can be integrated into clothing or accessories, enabling continuous therapy throughout daily activities.Expand Specific Solutions04 PEMF therapy in veterinary and agricultural applications
PEMF therapy has expanded beyond human applications to include veterinary and agricultural uses. It is employed to treat injuries and promote healing in animals, as well as to enhance plant growth and crop yields. The technology has shown promise in improving animal health and agricultural productivity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination of PEMF with other therapies
PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic outcomes. Integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or traditional medical treatments can provide synergistic effects. This combinatorial approach aims to maximize the benefits of PEMF while addressing multiple aspects of health and wellness.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Industry Players
The PEMF therapy market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across medical and wellness sectors. The global market size is projected to expand significantly, driven by rising awareness of non-invasive treatments and technological advancements. While the technology is not new, its application in various medical fields is evolving, indicating a moderate level of technological maturity. Companies like Regenesis Biomedical and Venus Concept are at the forefront, developing innovative PEMF devices for pain management and aesthetic treatments. Research institutions such as the National University of Singapore and ETH Zurich are contributing to the scientific understanding of PEMF, potentially accelerating its integration into mainstream medicine. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established medical device manufacturers and emerging startups vying for market share.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical has developed a proprietary PEMF therapy system called Provant Therapy. This system utilizes a specific pulsed electromagnetic field to stimulate cellular repair and reduce pain. The technology is based on a patented signal that mimics the body's natural electrical signals, promoting tissue healing and reducing inflammation. Provant Therapy devices are designed for both clinical and home use, offering targeted treatment for various musculoskeletal conditions. The company has conducted clinical trials demonstrating the efficacy of their PEMF technology in reducing pain and improving function in patients with chronic wounds and post-operative recovery [1][3].
Strengths: Patented technology, FDA-cleared devices, proven clinical efficacy. Weaknesses: Limited to specific applications, may require longer treatment times compared to some competitors.
Venus Concept Ltd.
Technical Solution: Venus Concept has developed a range of PEMF therapy devices under their Venus Pulse line. Their technology combines PEMF with other modalities such as radiofrequency and magnetic pulse therapy for enhanced treatment outcomes. The Venus Pulse devices use proprietary RP3 technology, which delivers three types of pulses - biological, physical, and chemical - to stimulate various cellular processes. This multi-modal approach aims to improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue regeneration. Venus Concept's PEMF devices are primarily used in aesthetic medicine and pain management, with applications in wound healing and musculoskeletal disorders [2][4].
Strengths: Multi-modal technology, versatile applications in aesthetics and medicine. Weaknesses: Higher cost due to combined technologies, may require specialized training for optimal use.
PEMF Research Innovations
Treatment of conditions susceptible to pulsed electromagnetic field therapy
PatentActiveUS20170354830A1
Innovation
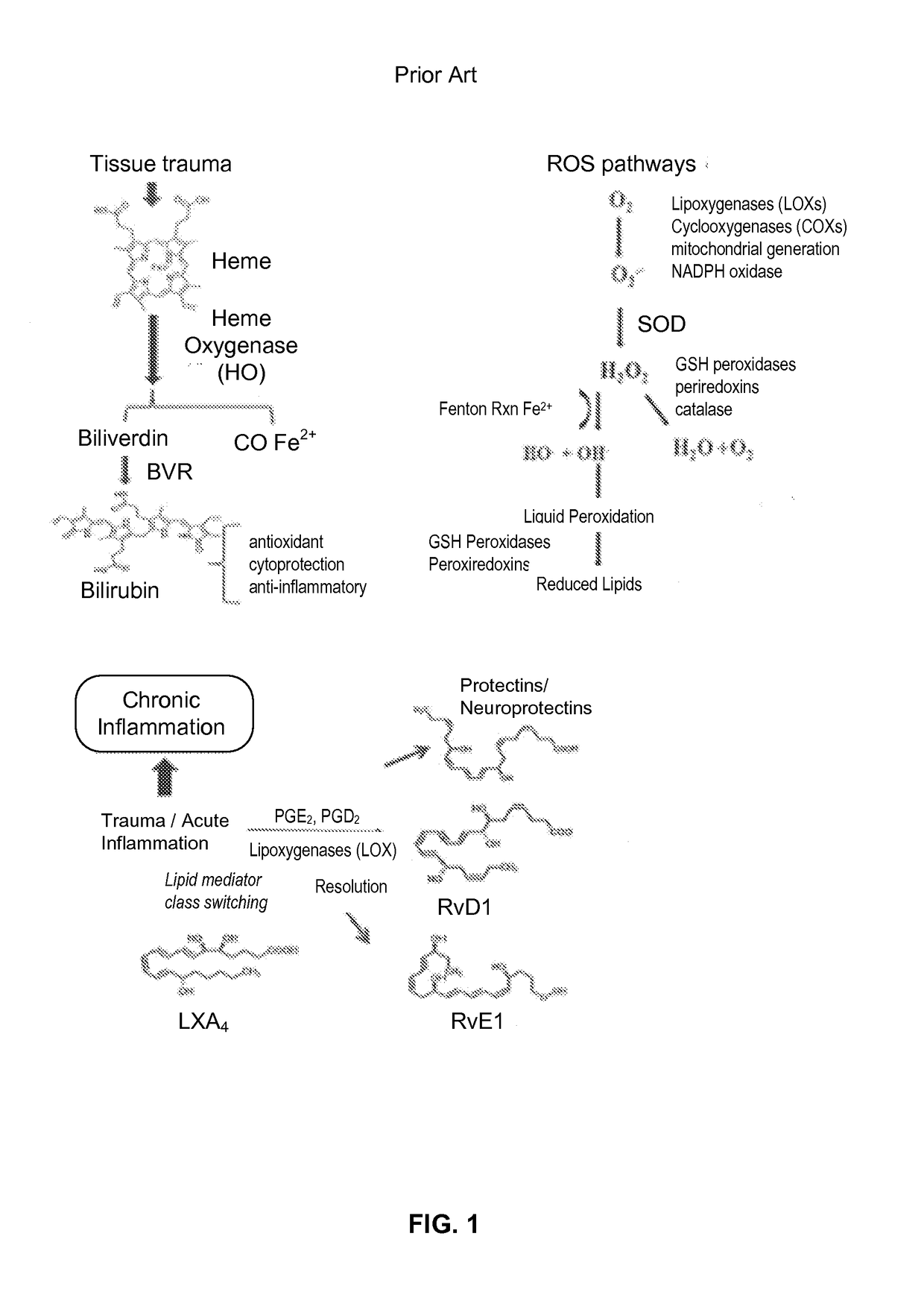
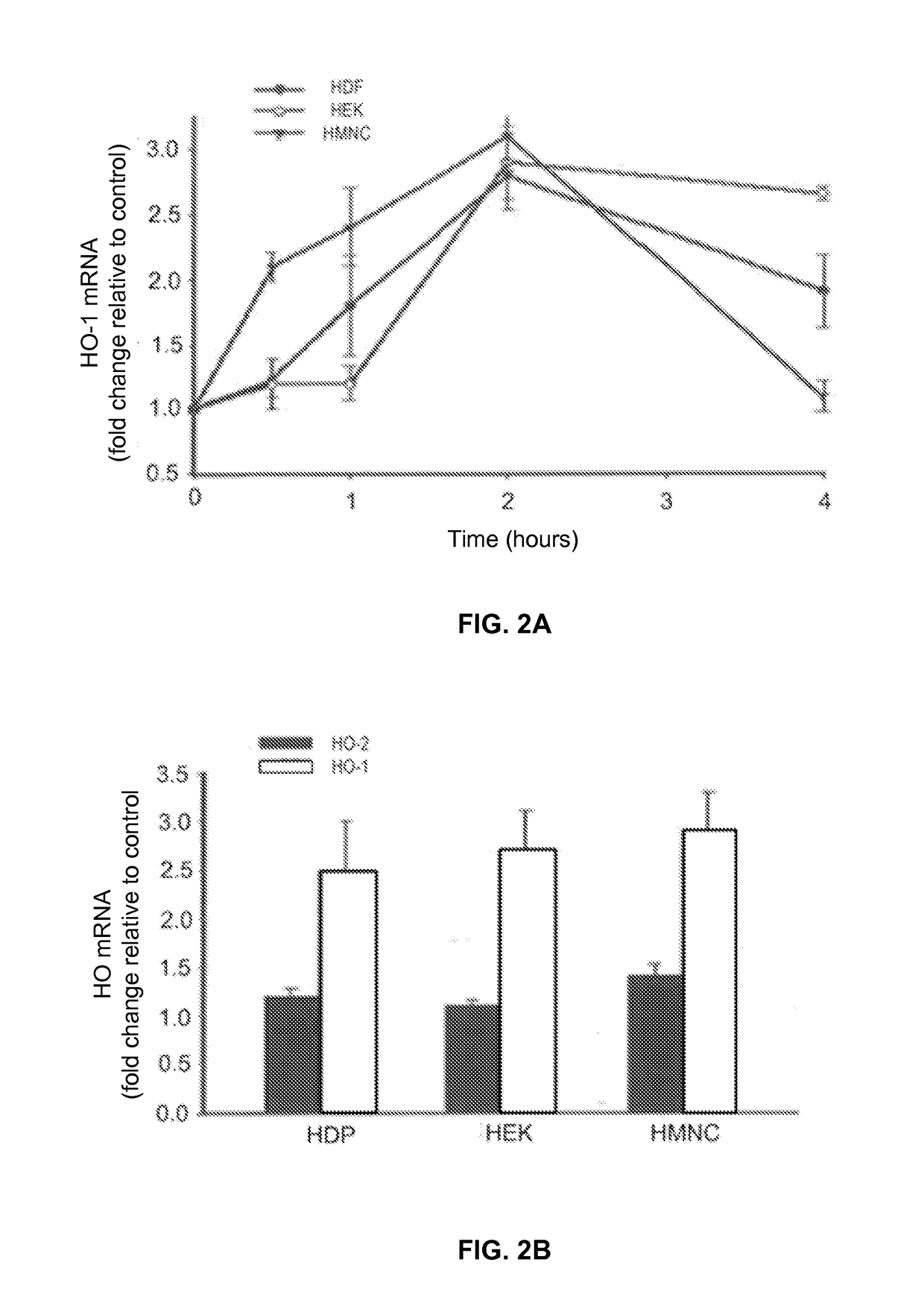
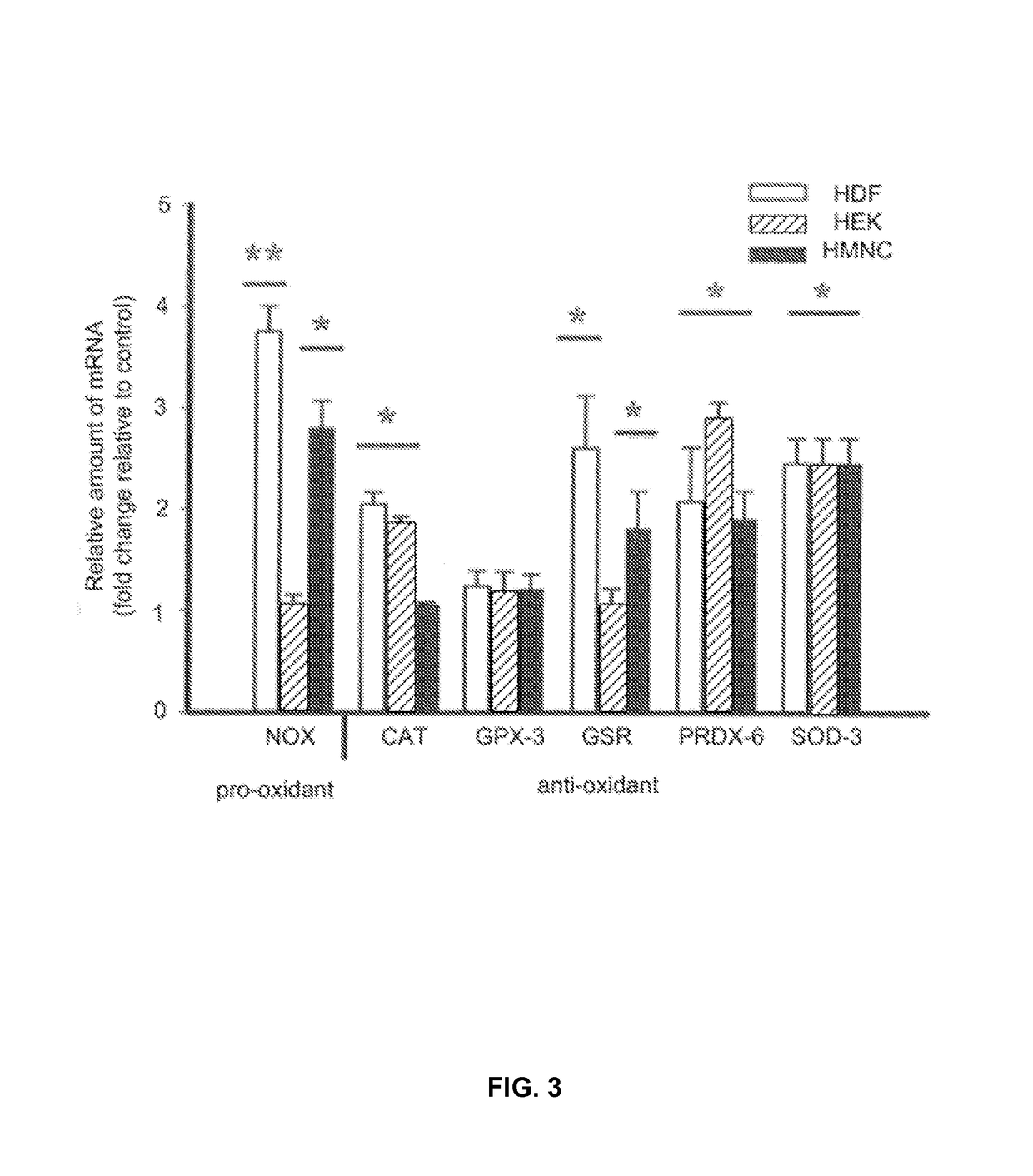
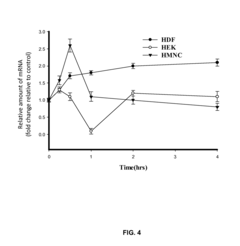
- PEMF therapy is administered to modulate gene expression associated with inflammation pathways, including heme oxygenase, antioxidant enzymes, lipid mediator biosynthesis, and cytokines, using specific parameters such as electric field strength, pulse rate, and duration to produce measurable clinical effects on pain, nerve function, and wound healing.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Devices Integrated into Adjustable Clothing
PatentPendingUS20230104434A1
Innovation
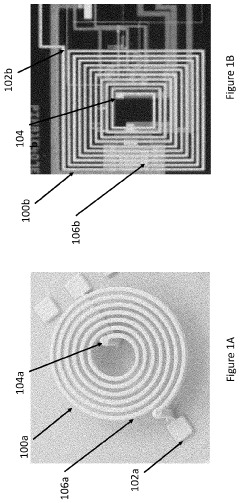
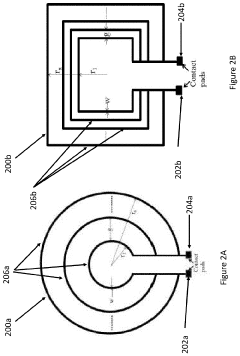
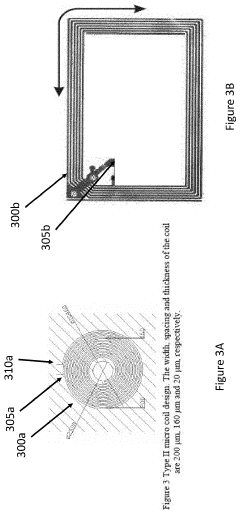
- A pulsed electromagnetic field device integrated into wearable clothing, using arrays of planar microcoils that generate controlled, homogenous magnetic fields, allowing for comfortable, long-term use and targeted treatment of various brain-related disorders and conditions.
Clinical Efficacy Studies
Clinical efficacy studies play a crucial role in validating the therapeutic potential of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy. These studies have been conducted across various medical conditions, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of PEMF as a treatment modality.
In the field of orthopedics, numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the positive effects of PEMF therapy on bone healing and pain management. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research showed significant improvements in pain reduction and functional outcomes for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee treated with PEMF therapy.
Neurological disorders have also been a focus of PEMF clinical research. A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry examined the efficacy of PEMF therapy in treating multiple sclerosis. The results indicated a moderate improvement in fatigue and quality of life measures for patients receiving PEMF treatment compared to control groups.
In the realm of chronic pain management, a multicenter, double-blind, randomized clinical trial published in Pain Research and Management evaluated the effects of PEMF therapy on fibromyalgia patients. The study reported significant reductions in pain intensity and improvements in overall well-being for the PEMF treatment group compared to the sham treatment group.
Wound healing has been another area of interest for PEMF therapy research. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial published in the Annals of Plastic Surgery investigated the effects of PEMF therapy on chronic wounds. The results showed accelerated wound closure and improved healing rates in the PEMF-treated group compared to the control group.
While these studies provide promising evidence for the efficacy of PEMF therapy, it is important to note that the quality and methodological rigor of clinical trials in this field vary. Some studies have been criticized for small sample sizes, inadequate blinding procedures, or short follow-up periods. Additionally, the optimal treatment parameters, such as frequency, intensity, and duration of PEMF exposure, remain subjects of ongoing research and debate.
Future clinical efficacy studies should focus on addressing these limitations by conducting larger, well-designed randomized controlled trials with longer follow-up periods. Standardization of PEMF treatment protocols and reporting methods would also enhance the comparability and reliability of research findings across different studies and medical conditions.
In the field of orthopedics, numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the positive effects of PEMF therapy on bone healing and pain management. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research showed significant improvements in pain reduction and functional outcomes for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee treated with PEMF therapy.
Neurological disorders have also been a focus of PEMF clinical research. A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry examined the efficacy of PEMF therapy in treating multiple sclerosis. The results indicated a moderate improvement in fatigue and quality of life measures for patients receiving PEMF treatment compared to control groups.
In the realm of chronic pain management, a multicenter, double-blind, randomized clinical trial published in Pain Research and Management evaluated the effects of PEMF therapy on fibromyalgia patients. The study reported significant reductions in pain intensity and improvements in overall well-being for the PEMF treatment group compared to the sham treatment group.
Wound healing has been another area of interest for PEMF therapy research. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial published in the Annals of Plastic Surgery investigated the effects of PEMF therapy on chronic wounds. The results showed accelerated wound closure and improved healing rates in the PEMF-treated group compared to the control group.
While these studies provide promising evidence for the efficacy of PEMF therapy, it is important to note that the quality and methodological rigor of clinical trials in this field vary. Some studies have been criticized for small sample sizes, inadequate blinding procedures, or short follow-up periods. Additionally, the optimal treatment parameters, such as frequency, intensity, and duration of PEMF exposure, remain subjects of ongoing research and debate.
Future clinical efficacy studies should focus on addressing these limitations by conducting larger, well-designed randomized controlled trials with longer follow-up periods. Standardization of PEMF treatment protocols and reporting methods would also enhance the comparability and reliability of research findings across different studies and medical conditions.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy is complex and varies significantly across different regions and countries. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared several PEMF devices for specific medical uses, such as bone healing and pain management. However, the regulatory status of PEMF devices can differ based on their intended use and claims made by manufacturers.
For medical applications, PEMF devices are typically classified as Class II or Class III medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) or premarket approval (PMA) respectively. The FDA evaluates the safety and efficacy of these devices through clinical trials and scientific evidence before granting clearance or approval.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Manufacturers must comply with CE marking requirements, which involve demonstrating the device's safety and performance through clinical evaluation and risk management processes. The classification of PEMF devices in the EU depends on their intended use and risk profile.
Regulatory bodies in other countries, such as Health Canada and Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), have their own frameworks for evaluating and approving PEMF devices. These agencies often consider international standards and guidelines when assessing the safety and efficacy of such devices.
One of the key regulatory challenges for PEMF therapy is the wide range of claims made by manufacturers. Regulatory bodies are particularly concerned with ensuring that marketing claims are supported by robust scientific evidence. This has led to increased scrutiny of PEMF devices, especially those marketed for general wellness or non-specific health benefits.
As PEMF therapy bridges traditional and modern medicine, regulators face the challenge of balancing innovation with patient safety. There is a growing need for standardized protocols and guidelines for PEMF therapy, which could help streamline the regulatory process and ensure consistent evaluation across different jurisdictions.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF therapy is evolving as more research emerges and the technology advances. Manufacturers and researchers must stay informed about changing regulations and work closely with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and facilitate the development of safe and effective PEMF devices.
For medical applications, PEMF devices are typically classified as Class II or Class III medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) or premarket approval (PMA) respectively. The FDA evaluates the safety and efficacy of these devices through clinical trials and scientific evidence before granting clearance or approval.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Manufacturers must comply with CE marking requirements, which involve demonstrating the device's safety and performance through clinical evaluation and risk management processes. The classification of PEMF devices in the EU depends on their intended use and risk profile.
Regulatory bodies in other countries, such as Health Canada and Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), have their own frameworks for evaluating and approving PEMF devices. These agencies often consider international standards and guidelines when assessing the safety and efficacy of such devices.
One of the key regulatory challenges for PEMF therapy is the wide range of claims made by manufacturers. Regulatory bodies are particularly concerned with ensuring that marketing claims are supported by robust scientific evidence. This has led to increased scrutiny of PEMF devices, especially those marketed for general wellness or non-specific health benefits.
As PEMF therapy bridges traditional and modern medicine, regulators face the challenge of balancing innovation with patient safety. There is a growing need for standardized protocols and guidelines for PEMF therapy, which could help streamline the regulatory process and ensure consistent evaluation across different jurisdictions.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF therapy is evolving as more research emerges and the technology advances. Manufacturers and researchers must stay informed about changing regulations and work closely with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and facilitate the development of safe and effective PEMF devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!