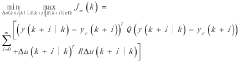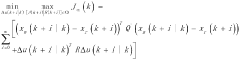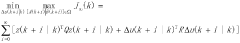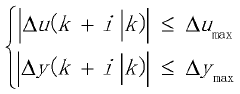Advanced Control Strategies For Industrial Processes - Eureka
JUN 17, 20254 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Advanced Control Strategies Overview and Objectives
The primary objective is to explore and evaluate advanced control strategies that can optimize and enhance the performance of industrial processes. This involves analyzing the current state of control technologies, identifying key challenges and limitations, and proposing innovative solutions to address these issues. The focus is on developing control algorithms and architectures that can improve process efficiency, product quality, energy consumption, and overall operational excellence. Potential areas of investigation include model predictive control, adaptive control, distributed control systems, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques for process monitoring and control optimization.
Market Demand for Industrial Process Control
- Increasing Demand for Automation
Industrial processes are becoming increasingly complex, driving the need for advanced control strategies to optimize efficiency, quality, and safety. Automation is crucial for meeting stringent production requirements and reducing human intervention. - Regulatory Compliance
Strict regulations and standards govern various industrial sectors, necessitating precise control systems to ensure compliance with environmental, safety, and quality norms. Advanced control strategies enable companies to meet these regulatory requirements. - Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
With rising energy costs and environmental concerns, there is a growing demand for control strategies that can optimize energy consumption and minimize waste in industrial processes. Advanced control techniques can significantly improve energy efficiency and support sustainability initiatives. - Process Optimization and Cost Reduction
Companies are constantly seeking ways to optimize their processes, reduce downtime, and minimize operational costs. Advanced control strategies can help achieve these goals by improving process stability, reducing variability, and enabling real-time adjustments. - Integration of Emerging Technologies
The adoption of emerging technologies, such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), big data analytics, and machine learning, is driving the need for advanced control strategies that can leverage these technologies for enhanced process monitoring, prediction, and optimization.
Current State and Challenges in Industrial Control Systems
- Legacy Control Systems
Many industrial facilities still rely on outdated control systems, which lack advanced features and are prone to failures and security vulnerabilities. - Lack of Integration
Different control systems and components often operate in silos, making it challenging to achieve seamless integration and data exchange across the entire production process. - Cybersecurity Risks
As industrial control systems become more connected, they face increased risks of cyber threats, such as malware attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access. - Limited Scalability
Existing control systems may struggle to accommodate rapid changes in production demands, hindering the ability to scale operations efficiently. - Skill Gaps
There is a shortage of skilled professionals who can design, implement, and maintain advanced industrial control systems, posing challenges for widespread adoption.
Existing Solutions for Industrial Process Control
01 Advanced Control Strategies
Various advanced control strategies, such as model predictive control, fuzzy logic control, and neural network-based control, have been developed to optimize and enhance industrial processes. These strategies aim to improve process efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and maintain product quality through advanced algorithms and real-time data analysis.- Advanced Process Control: Various advanced control strategies, such as model predictive control, fuzzy logic control, and optimization algorithms, have been developed to facilitate the control of industrial processes, improving process performance, efficiency, and robustness.
- Integrated Control Systems: Advanced control strategies can be integrated into industrial control systems, allowing for seamless implementation and coordination of various control modules and algorithms, enabling efficient and optimized control of complex industrial processes.
- Wastewater Treatment Control: Advanced control strategies have been applied to industrial wastewater treatment processes, enabling efficient pollutant removal, optimized resource utilization, and improved treatment performance through techniques like advanced oxidation processes and process optimization.
- Real-time Optimization: Advanced control strategies often involve real-time optimization and coordination techniques to ensure optimal process performance while considering economic factors, constraints, and process dynamics, aiming to maximize efficiency and profitability.
- Industrial Equipment Control: Advanced control strategies have been developed specifically for industrial equipment and machinery, enabling predictive maintenance, fault detection, and optimized operation through techniques like machine learning and data analytics.
02 Integrated Control Systems
Advanced control strategies can be integrated into industrial control systems, enabling seamless implementation and coordination of various control modules and algorithms. These integrated systems facilitate centralized monitoring and optimization across different processes or plant-wide operations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Wastewater Treatment Control
Advanced control strategies have been applied to industrial wastewater treatment processes to improve treatment efficiency, reduce operational costs, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. These strategies involve real-time monitoring, optimization algorithms, and process modeling.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cloud-based Control Strategies
With cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), advanced control strategies can be implemented using cloud-based platforms, leveraging remote data processing, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data exchange for process optimization, remote monitoring, and centralized control.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process Optimization Control
Advanced control strategies are employed to optimize various aspects of industrial processes, such as energy efficiency, product quality, and economic performance, through techniques like real-time optimization, constraint handling, and economic optimization algorithms.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial Control Systems
The competitive landscape for advanced control strategies in industrial processes is characterized by a mix of academic institutions and leading industrial companies. The industry is in a mature stage with significant market size, driven by the need for efficiency and automation.
ABB Group
Technical Solution: ABB Group offers advanced control strategies through its ABB Ability platform, integrating AI, machine learning, and real-time data analytics to optimize processes and reduce costs.
Strength: Comprehensive and scalable solutions. Weakness: High implementation cost.
Siemens AG
Technical Solution: Siemens AG provides advanced control strategies via its SIMATIC PCS 7 system, offering integrated automation solutions, process optimization, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring.
Strength: High reliability and flexibility. Weakness: Complexity in integration.
Core Innovations in Advanced Control Strategies
Advanced control method for industrial process constraint prediction
PatentActiveCN110045617A
Innovation
- A novel constrained predictive advanced control method is proposed to solve the control problem when actuators fail in industrial processes. The method extends the traditional single-input single-output model to an incremental form, introduces constraints on state error and output error, and introduces an objective function to track the reference trajectory. The method also introduces controller design to better control industrial processes
Regulatory and Compliance Issues in Industrial Control
Advanced control strategies for industrial processes aim to optimize process performance, improve efficiency, and enhance product quality. The key objectives include reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and ensuring consistent output within specified tolerances. This technology has evolved from classical control techniques like PID controllers to more sophisticated approaches like model predictive control (MPC), fuzzy logic control, and artificial intelligence-based methods. The market demand is driven by the need for automation, process intensification, and stringent regulatory requirements across various industries such as chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and energy sectors. The current challenges include handling complex nonlinear processes, dealing with uncertainties, and integrating advanced sensors and data analytics. Potential innovation directions involve developing hybrid control strategies, incorporating machine learning algorithms, and leveraging digital twins for virtual commissioning and optimization.
Environmental Impact of Industrial Control Technologies
Advanced control strategies for industrial processes aim to optimize process performance, improve efficiency, and enhance product quality. The key objectives include minimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and ensuring consistent output within specified tolerances. This technology leverages advanced algorithms, machine learning, and real-time data analytics to model complex process dynamics and implement adaptive control mechanisms. Potential innovations involve integrating multi-variable predictive control, reinforcement learning, and hybrid modeling techniques to handle nonlinearities and uncertainties in industrial processes. Emerging trends also explore the synergy between control strategies and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) for distributed monitoring and coordinated control across interconnected systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!