Half Wave Rectifiers in Power Supply Systems
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Half Wave Rectifier Background and Objectives
Half wave rectifiers have been a fundamental component in power supply systems since the early days of electronics. These devices play a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC), which is essential for powering various electronic devices and systems. The evolution of half wave rectifiers can be traced back to the invention of the vacuum tube diode in the early 20th century, which laid the foundation for modern rectification techniques.
The primary objective of researching half wave rectifiers in power supply systems is to enhance their efficiency, reliability, and overall performance. As power electronics continue to advance, there is a growing need for more compact, energy-efficient, and cost-effective rectification solutions. This research aims to address these challenges by exploring innovative materials, circuit designs, and control strategies.
One of the key trends in half wave rectifier technology is the shift towards semiconductor-based devices, particularly silicon and wide-bandgap materials such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN). These advanced materials offer superior electrical properties, including higher breakdown voltages, lower on-state resistance, and faster switching speeds, which can significantly improve the efficiency and power density of rectification circuits.
Another important aspect of half wave rectifier research is the development of smart control algorithms and adaptive systems. These innovations aim to optimize the rectification process in real-time, responding to variations in input voltage, load conditions, and environmental factors. By implementing intelligent control strategies, researchers seek to maximize energy conversion efficiency and minimize power losses across a wide range of operating conditions.
The integration of half wave rectifiers with other power electronic components, such as power factor correction (PFC) circuits and DC-DC converters, is also a significant area of focus. This holistic approach to power supply design aims to create more compact and efficient systems that can meet the demanding requirements of modern electronic devices, from consumer electronics to industrial equipment and renewable energy systems.
As the global emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability continues to grow, the development of eco-friendly and energy-efficient half wave rectifier technologies has become increasingly important. Researchers are exploring ways to reduce the environmental impact of these devices, including the use of recyclable materials, minimizing electromagnetic interference, and improving thermal management to extend the lifespan of power supply systems.
The primary objective of researching half wave rectifiers in power supply systems is to enhance their efficiency, reliability, and overall performance. As power electronics continue to advance, there is a growing need for more compact, energy-efficient, and cost-effective rectification solutions. This research aims to address these challenges by exploring innovative materials, circuit designs, and control strategies.
One of the key trends in half wave rectifier technology is the shift towards semiconductor-based devices, particularly silicon and wide-bandgap materials such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN). These advanced materials offer superior electrical properties, including higher breakdown voltages, lower on-state resistance, and faster switching speeds, which can significantly improve the efficiency and power density of rectification circuits.
Another important aspect of half wave rectifier research is the development of smart control algorithms and adaptive systems. These innovations aim to optimize the rectification process in real-time, responding to variations in input voltage, load conditions, and environmental factors. By implementing intelligent control strategies, researchers seek to maximize energy conversion efficiency and minimize power losses across a wide range of operating conditions.
The integration of half wave rectifiers with other power electronic components, such as power factor correction (PFC) circuits and DC-DC converters, is also a significant area of focus. This holistic approach to power supply design aims to create more compact and efficient systems that can meet the demanding requirements of modern electronic devices, from consumer electronics to industrial equipment and renewable energy systems.
As the global emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability continues to grow, the development of eco-friendly and energy-efficient half wave rectifier technologies has become increasingly important. Researchers are exploring ways to reduce the environmental impact of these devices, including the use of recyclable materials, minimizing electromagnetic interference, and improving thermal management to extend the lifespan of power supply systems.
Market Demand Analysis for Power Supply Systems
The market demand for power supply systems, particularly those incorporating half wave rectifiers, has been steadily growing across various industries. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing need for efficient and reliable power conversion solutions in both consumer electronics and industrial applications. The global power supply market, which includes rectifier technologies, is projected to reach significant market value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry averages.
In the consumer electronics sector, the demand for compact and energy-efficient power supplies has surged due to the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. Half wave rectifiers, known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, play a crucial role in these applications, especially in low-power charging systems and adapters. The automotive industry has also emerged as a key driver for power supply systems, with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) necessitating advanced power conversion technologies.
Industrial applications represent another significant market segment for power supply systems featuring half wave rectifiers. Manufacturing facilities, data centers, and telecommunications infrastructure require robust and efficient power conversion solutions to ensure uninterrupted operations and minimize energy losses. The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and power quality in industrial settings has further boosted the demand for advanced rectifier technologies.
The renewable energy sector has become a notable contributor to the market demand for power supply systems. As solar and wind energy installations continue to expand globally, there is an increasing need for efficient power conversion and grid integration solutions. Half wave rectifiers, along with more advanced rectifier technologies, play a vital role in converting and managing the power generated from these renewable sources.
Emerging technologies and trends are also shaping the market landscape for power supply systems. The Internet of Things (IoT) and the broader trend of digital transformation across industries have created new opportunities for smart, connected power supply solutions. These systems often require sophisticated power management capabilities, including efficient rectification and voltage regulation.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a dominant market for power supply systems, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of major electronics manufacturing hubs. North America and Europe follow closely, with strong demand from sectors such as healthcare, aerospace, and telecommunications. Developing economies in Latin America and Africa are also showing increased adoption of power supply technologies, particularly in infrastructure development projects.
In the consumer electronics sector, the demand for compact and energy-efficient power supplies has surged due to the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. Half wave rectifiers, known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, play a crucial role in these applications, especially in low-power charging systems and adapters. The automotive industry has also emerged as a key driver for power supply systems, with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) necessitating advanced power conversion technologies.
Industrial applications represent another significant market segment for power supply systems featuring half wave rectifiers. Manufacturing facilities, data centers, and telecommunications infrastructure require robust and efficient power conversion solutions to ensure uninterrupted operations and minimize energy losses. The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and power quality in industrial settings has further boosted the demand for advanced rectifier technologies.
The renewable energy sector has become a notable contributor to the market demand for power supply systems. As solar and wind energy installations continue to expand globally, there is an increasing need for efficient power conversion and grid integration solutions. Half wave rectifiers, along with more advanced rectifier technologies, play a vital role in converting and managing the power generated from these renewable sources.
Emerging technologies and trends are also shaping the market landscape for power supply systems. The Internet of Things (IoT) and the broader trend of digital transformation across industries have created new opportunities for smart, connected power supply solutions. These systems often require sophisticated power management capabilities, including efficient rectification and voltage regulation.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a dominant market for power supply systems, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of major electronics manufacturing hubs. North America and Europe follow closely, with strong demand from sectors such as healthcare, aerospace, and telecommunications. Developing economies in Latin America and Africa are also showing increased adoption of power supply technologies, particularly in infrastructure development projects.
Current State and Challenges in Rectification Technology
Half-wave rectification technology has seen significant advancements in recent years, yet it still faces several challenges in power supply systems. The current state of rectification technology is characterized by a balance between efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reliability. Modern half-wave rectifiers have improved significantly in terms of power conversion efficiency, with some designs achieving up to 95% efficiency under optimal conditions.
One of the primary challenges in half-wave rectification is the inherent pulsating nature of the output, which can lead to ripple in the DC voltage. This ripple can cause unwanted noise and interference in sensitive electronic systems. To address this issue, manufacturers have developed advanced filtering techniques, including the use of capacitors and inductors to smooth out the voltage fluctuations. However, these solutions often come at the cost of increased complexity and component count.
Another significant challenge is the management of heat dissipation in high-power applications. As power levels increase, the thermal stress on rectifying components becomes a critical factor. Researchers are exploring new materials and packaging techniques to enhance thermal management and improve the overall reliability of rectification systems.
The miniaturization of electronic devices has also posed challenges for half-wave rectifier design. As devices become smaller, the need for compact and efficient rectification solutions has grown. This has led to the development of integrated circuit-based rectifiers that combine multiple functions into a single chip, reducing size and improving performance.
In the realm of renewable energy systems, half-wave rectifiers play a crucial role in converting AC power from sources like solar panels and wind turbines into usable DC power. However, the variable nature of these energy sources presents unique challenges for rectification technology. Adaptive rectification systems that can handle fluctuating input voltages and maintain high efficiency across a wide range of operating conditions are an active area of research and development.
The increasing demand for high-frequency power supplies in applications such as wireless power transfer and RF energy harvesting has pushed the boundaries of traditional rectification technology. Researchers are investigating novel semiconductor materials and device structures to create rectifiers capable of operating efficiently at frequencies in the megahertz and gigahertz ranges.
Lastly, the global push for energy efficiency and sustainability has placed new demands on rectification technology. There is a growing focus on developing "green" rectifiers that minimize power losses and reduce electronic waste. This includes exploring biodegradable materials for rectifier components and designing circuits that consume less power in standby modes.
One of the primary challenges in half-wave rectification is the inherent pulsating nature of the output, which can lead to ripple in the DC voltage. This ripple can cause unwanted noise and interference in sensitive electronic systems. To address this issue, manufacturers have developed advanced filtering techniques, including the use of capacitors and inductors to smooth out the voltage fluctuations. However, these solutions often come at the cost of increased complexity and component count.
Another significant challenge is the management of heat dissipation in high-power applications. As power levels increase, the thermal stress on rectifying components becomes a critical factor. Researchers are exploring new materials and packaging techniques to enhance thermal management and improve the overall reliability of rectification systems.
The miniaturization of electronic devices has also posed challenges for half-wave rectifier design. As devices become smaller, the need for compact and efficient rectification solutions has grown. This has led to the development of integrated circuit-based rectifiers that combine multiple functions into a single chip, reducing size and improving performance.
In the realm of renewable energy systems, half-wave rectifiers play a crucial role in converting AC power from sources like solar panels and wind turbines into usable DC power. However, the variable nature of these energy sources presents unique challenges for rectification technology. Adaptive rectification systems that can handle fluctuating input voltages and maintain high efficiency across a wide range of operating conditions are an active area of research and development.
The increasing demand for high-frequency power supplies in applications such as wireless power transfer and RF energy harvesting has pushed the boundaries of traditional rectification technology. Researchers are investigating novel semiconductor materials and device structures to create rectifiers capable of operating efficiently at frequencies in the megahertz and gigahertz ranges.
Lastly, the global push for energy efficiency and sustainability has placed new demands on rectification technology. There is a growing focus on developing "green" rectifiers that minimize power losses and reduce electronic waste. This includes exploring biodegradable materials for rectifier components and designing circuits that consume less power in standby modes.
Existing Half Wave Rectifier Implementations
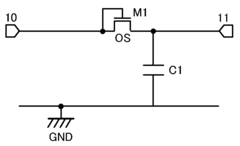
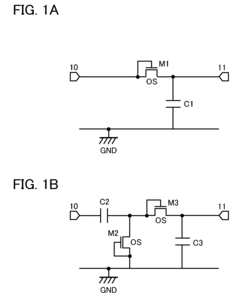
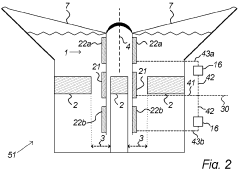
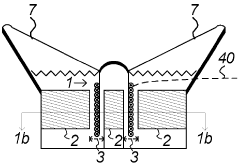
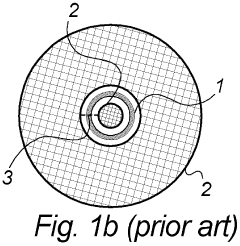
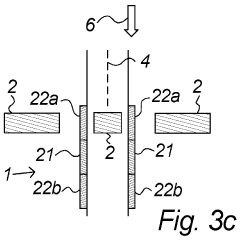
01 Circuit design for half-wave rectifiers
Half-wave rectifiers are designed to convert alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC) by allowing current flow in only one direction. The circuit typically includes a diode that conducts during the positive half-cycle of the AC input and blocks current during the negative half-cycle. This design is fundamental to power supply systems and various electronic applications.- Circuit design and topology: Half-wave rectifiers are designed with specific circuit topologies to convert AC to pulsating DC. These designs often include diodes, transformers, and capacitors to achieve efficient rectification. Various circuit configurations are employed to optimize performance and reduce ripple in the output voltage.
- Power supply applications: Half-wave rectifiers are commonly used in power supply systems for various electronic devices. They are integrated into AC-DC converters, battery chargers, and other power management circuits. These applications often require additional filtering and regulation to produce stable DC output from the rectified signal.
- Efficiency improvements: Researchers and engineers focus on improving the efficiency of half-wave rectifiers. This includes developing new semiconductor materials, optimizing component selection, and implementing advanced control strategies. Efforts are made to reduce power losses, improve thermal management, and enhance overall system performance.
- Integration with other circuits: Half-wave rectifiers are often integrated with other circuit elements to create more complex systems. This includes combining rectifiers with voltage regulators, filters, and protection circuits. Such integration aims to improve overall system functionality, reduce component count, and enhance reliability.
- Specialized applications: Half-wave rectifiers find use in specialized applications beyond general power supplies. These include RF signal detection, sensor circuits, and energy harvesting systems. In these applications, the rectifier's characteristics are tailored to meet specific requirements such as high-frequency operation or low-power consumption.
02 Efficiency improvements in half-wave rectifiers
Advancements in half-wave rectifier designs focus on improving efficiency and reducing power losses. This includes the use of high-performance diodes, optimized circuit layouts, and advanced control techniques. Some designs incorporate additional components or novel configurations to minimize voltage drops and enhance overall system performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of half-wave rectifiers in power supplies
Half-wave rectifiers are commonly integrated into various power supply designs, including switched-mode power supplies and voltage regulators. These integrated solutions often combine the rectification stage with other power conditioning components to create compact and efficient power conversion systems for a wide range of electronic devices and appliances.Expand Specific Solutions04 Protection and control mechanisms for half-wave rectifiers
To enhance reliability and safety, half-wave rectifier circuits often incorporate protection and control mechanisms. These may include overvoltage protection, current limiting features, and feedback control systems. Such additions help prevent damage to the rectifier and connected loads, while also improving the stability and performance of the power conversion process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of half-wave rectifiers in specific industries
Half-wave rectifiers find applications in various industries beyond general power supplies. They are used in specialized equipment such as welding machines, battery chargers, and certain types of motor controls. In these applications, the half-wave rectification process is tailored to meet specific requirements of the industry or equipment, often with modifications to improve performance or add functionality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Power Electronics Industry
The research on half wave rectifiers in power supply systems is in a mature stage, with established technologies and widespread applications. The market size is substantial, driven by the ubiquitous need for power conversion in various industries. Companies like Sanken Electric, Delta Electronics, and Huawei Technologies are key players, leveraging their expertise in semiconductor devices and power electronics. The technology's maturity is evident in the diverse product offerings from these firms, ranging from discrete components to integrated power management solutions. However, ongoing research by institutions like CNRS and universities continues to push the boundaries of efficiency and miniaturization in rectifier designs.
Sanken Electric Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sanken Electric has developed advanced half-wave rectifier solutions for power supply systems, focusing on high-efficiency and low-loss designs. Their technology incorporates silicon carbide (SiC) diodes, which offer faster switching speeds and lower forward voltage drops compared to traditional silicon diodes[1]. The company's half-wave rectifiers feature integrated thermal management systems to enhance reliability and longevity in high-power applications[2]. Sanken's designs also include advanced EMI suppression techniques to minimize electromagnetic interference, crucial for sensitive electronic systems[3].
Strengths: High efficiency, low power loss, and excellent thermal management. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to use of SiC technology, and limited to high-power applications.
Delta Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Delta Electronics has innovated in half-wave rectifier technology for power supply systems, particularly in the realm of compact and efficient designs. Their approach integrates advanced semiconductor materials and smart control algorithms to optimize power conversion efficiency[4]. Delta's half-wave rectifiers feature adaptive frequency modulation, which adjusts the switching frequency based on load conditions, reducing power losses during light-load operations[5]. The company has also implemented novel cooling solutions, including phase-change materials, to manage thermal issues in high-density power supplies[6].
Strengths: High power density, adaptive efficiency optimization, and innovative thermal management. Weaknesses: Complexity of control systems may increase maintenance requirements.
Core Innovations in Rectification Techniques
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
PatentInactiveUS20110216566A1
Innovation
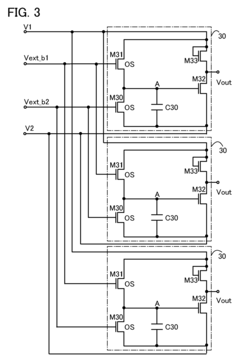
- A rectifier circuit utilizing transistors with oxide semiconductor channel formation regions, specifically indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO), which have significantly lower off-state currents, thereby reducing the risk of breakdown and improving reliability and efficiency by using a full-wave voltage doubler configuration and optimizing heat treatment processes to form high-quality oxide semiconductors.
A method and system for driving a voice coil of a loudspeaker
PatentActiveGB2591767A
Innovation
- A voice coil driving system with segmented voice coil sections, where a centre voice coil section and auxiliary voice coil sections are driven by centre and auxiliary driving signals, respectively, with rectifying units attenuating or blocking currents in specific directions to minimize power consumption and heating by only powering sections within the air gap.
Efficiency and Power Quality Considerations
Efficiency and power quality are critical considerations in the design and implementation of half-wave rectifiers in power supply systems. These factors significantly impact the overall performance and reliability of the system, as well as its compliance with regulatory standards.
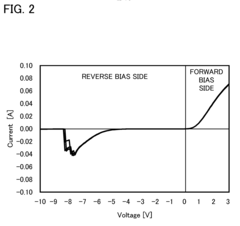
The efficiency of half-wave rectifiers is generally lower compared to full-wave rectifiers due to their inherent design. In a half-wave rectifier, only one half of the AC input waveform is utilized, resulting in a pulsating DC output with significant ripple. This inefficiency leads to increased power losses and heat generation, which can affect the longevity and reliability of the power supply components.
To improve efficiency, various techniques can be employed. One approach is the use of high-frequency switching techniques, which allow for smaller filter components and reduced conduction losses. Additionally, implementing synchronous rectification can further enhance efficiency by replacing diodes with actively controlled switches, such as MOSFETs, to reduce voltage drops and associated power losses.
Power quality is another crucial aspect of half-wave rectifiers. The pulsating nature of the output waveform introduces harmonics into the power system, which can lead to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and affect the performance of other connected devices. These harmonics also contribute to a poor power factor, increasing the apparent power drawn from the source and potentially violating power quality standards.
To address power quality issues, designers often incorporate passive or active filtering techniques. Passive filters, such as LC filters, can smooth out the rectified waveform and reduce harmonic content. Active power factor correction (PFC) circuits can be implemented to improve the power factor and reduce harmonic distortion, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as IEC 61000-3-2.
The trade-off between efficiency and power quality often presents challenges in half-wave rectifier design. Increasing filtering to improve power quality may lead to additional power losses, while attempts to maximize efficiency might compromise power quality. Therefore, a balanced approach is necessary, considering the specific application requirements and regulatory constraints.
Recent advancements in semiconductor technology and control strategies have led to improved efficiency and power quality in half-wave rectifier applications. The development of wide-bandgap semiconductors, such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), offers potential for higher switching frequencies and reduced losses, enabling more compact and efficient designs.
In conclusion, addressing efficiency and power quality considerations in half-wave rectifiers requires a multifaceted approach. Designers must carefully balance these factors to achieve optimal performance while meeting regulatory requirements and application-specific needs. Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to push the boundaries of what is achievable in terms of efficiency and power quality in half-wave rectifier-based power supply systems.
The efficiency of half-wave rectifiers is generally lower compared to full-wave rectifiers due to their inherent design. In a half-wave rectifier, only one half of the AC input waveform is utilized, resulting in a pulsating DC output with significant ripple. This inefficiency leads to increased power losses and heat generation, which can affect the longevity and reliability of the power supply components.
To improve efficiency, various techniques can be employed. One approach is the use of high-frequency switching techniques, which allow for smaller filter components and reduced conduction losses. Additionally, implementing synchronous rectification can further enhance efficiency by replacing diodes with actively controlled switches, such as MOSFETs, to reduce voltage drops and associated power losses.
Power quality is another crucial aspect of half-wave rectifiers. The pulsating nature of the output waveform introduces harmonics into the power system, which can lead to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and affect the performance of other connected devices. These harmonics also contribute to a poor power factor, increasing the apparent power drawn from the source and potentially violating power quality standards.
To address power quality issues, designers often incorporate passive or active filtering techniques. Passive filters, such as LC filters, can smooth out the rectified waveform and reduce harmonic content. Active power factor correction (PFC) circuits can be implemented to improve the power factor and reduce harmonic distortion, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards such as IEC 61000-3-2.
The trade-off between efficiency and power quality often presents challenges in half-wave rectifier design. Increasing filtering to improve power quality may lead to additional power losses, while attempts to maximize efficiency might compromise power quality. Therefore, a balanced approach is necessary, considering the specific application requirements and regulatory constraints.
Recent advancements in semiconductor technology and control strategies have led to improved efficiency and power quality in half-wave rectifier applications. The development of wide-bandgap semiconductors, such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), offers potential for higher switching frequencies and reduced losses, enabling more compact and efficient designs.
In conclusion, addressing efficiency and power quality considerations in half-wave rectifiers requires a multifaceted approach. Designers must carefully balance these factors to achieve optimal performance while meeting regulatory requirements and application-specific needs. Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to push the boundaries of what is achievable in terms of efficiency and power quality in half-wave rectifier-based power supply systems.
Environmental Impact of Rectifier Technologies
The environmental impact of rectifier technologies, particularly half-wave rectifiers in power supply systems, is a critical consideration in the broader context of sustainable energy solutions. These devices, while essential for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), can have significant environmental implications throughout their lifecycle.
The production of rectifiers involves the use of various materials, including semiconductors, metals, and plastics. The extraction and processing of these raw materials contribute to resource depletion and energy consumption. Additionally, the manufacturing process itself requires substantial energy input and may result in the release of pollutants and greenhouse gases.
During operation, half-wave rectifiers in power supply systems can impact energy efficiency. Their inherent design leads to the utilization of only one half of the AC waveform, potentially resulting in lower overall efficiency compared to full-wave rectifiers. This reduced efficiency translates to increased energy consumption and, consequently, higher carbon emissions from power generation sources.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated by rectifier circuits is another environmental concern. EMI can affect nearby electronic devices and potentially disrupt sensitive ecosystems, particularly in areas with high concentrations of electronic equipment or wildlife habitats sensitive to electromagnetic fields.
The heat generated by rectifiers during operation necessitates cooling systems, which may consume additional energy and potentially use refrigerants with high global warming potential. This thermal management aspect further contributes to the overall environmental footprint of power supply systems incorporating half-wave rectifiers.
End-of-life considerations for rectifiers also pose environmental challenges. The disposal of electronic components containing hazardous materials such as lead, cadmium, or mercury can lead to soil and water contamination if not properly managed. Recycling of these components, while beneficial, requires energy-intensive processes and specialized facilities.
However, ongoing research and development in rectifier technologies are addressing these environmental concerns. Advancements in semiconductor materials and circuit designs are improving the efficiency of half-wave rectifiers, reducing energy losses and associated emissions. The integration of smart control systems and power factor correction techniques further enhances the overall environmental performance of power supply systems.
Moreover, the shift towards more sustainable manufacturing processes and the use of eco-friendly materials in rectifier production are mitigating the environmental impact of their lifecycle. Innovations in recycling technologies are also improving the recoverability of valuable materials from discarded rectifiers, contributing to a more circular economy in the electronics industry.
The production of rectifiers involves the use of various materials, including semiconductors, metals, and plastics. The extraction and processing of these raw materials contribute to resource depletion and energy consumption. Additionally, the manufacturing process itself requires substantial energy input and may result in the release of pollutants and greenhouse gases.
During operation, half-wave rectifiers in power supply systems can impact energy efficiency. Their inherent design leads to the utilization of only one half of the AC waveform, potentially resulting in lower overall efficiency compared to full-wave rectifiers. This reduced efficiency translates to increased energy consumption and, consequently, higher carbon emissions from power generation sources.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated by rectifier circuits is another environmental concern. EMI can affect nearby electronic devices and potentially disrupt sensitive ecosystems, particularly in areas with high concentrations of electronic equipment or wildlife habitats sensitive to electromagnetic fields.
The heat generated by rectifiers during operation necessitates cooling systems, which may consume additional energy and potentially use refrigerants with high global warming potential. This thermal management aspect further contributes to the overall environmental footprint of power supply systems incorporating half-wave rectifiers.
End-of-life considerations for rectifiers also pose environmental challenges. The disposal of electronic components containing hazardous materials such as lead, cadmium, or mercury can lead to soil and water contamination if not properly managed. Recycling of these components, while beneficial, requires energy-intensive processes and specialized facilities.
However, ongoing research and development in rectifier technologies are addressing these environmental concerns. Advancements in semiconductor materials and circuit designs are improving the efficiency of half-wave rectifiers, reducing energy losses and associated emissions. The integration of smart control systems and power factor correction techniques further enhances the overall environmental performance of power supply systems.
Moreover, the shift towards more sustainable manufacturing processes and the use of eco-friendly materials in rectifier production are mitigating the environmental impact of their lifecycle. Innovations in recycling technologies are also improving the recoverability of valuable materials from discarded rectifiers, contributing to a more circular economy in the electronics industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!