The Economic Impact of Integrating PEMF Therapy in Healthcare
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing applications, PEMF therapy has expanded its reach across various medical domains. The therapy's evolution can be traced through several key phases, each marked by technological advancements and broadening applications.
In the 1950s, scientists first observed the piezoelectric effect in bones, leading to the development of early PEMF devices for bone healing. These initial applications focused primarily on non-union fractures and spinal fusion surgeries. The 1970s saw the FDA approval of PEMF devices for bone healing, marking a significant milestone in the therapy's acceptance within mainstream medicine.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed an expansion of PEMF research into other areas of medicine. Studies began exploring its potential in pain management, wound healing, and neurological disorders. This period also saw improvements in device design, with more portable and user-friendly PEMF systems becoming available.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era for PEMF therapy. Advancements in electronics and materials science led to the development of more sophisticated devices capable of delivering precise electromagnetic pulses. This technological progress enabled researchers to fine-tune treatment parameters, optimizing therapeutic outcomes across a wider range of conditions.
In recent years, PEMF therapy has gained traction in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Professional athletes and sports teams have adopted PEMF devices for faster recovery and injury prevention. Simultaneously, research has expanded into areas such as mental health, with studies exploring PEMF's potential in treating depression and anxiety.
The integration of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities has been a notable trend in its evolution. Combining PEMF with traditional physiotherapy, acupuncture, or pharmaceutical interventions has shown promising results in enhancing overall treatment efficacy. This integrative approach has opened new avenues for holistic patient care.
As PEMF therapy continues to evolve, current research is focusing on optimizing treatment protocols, understanding the underlying mechanisms of action, and exploring new applications. The development of wearable PEMF devices and the integration of smart technology for personalized treatment regimens represent the cutting edge of PEMF evolution. These advancements are poised to further expand the therapy's accessibility and effectiveness across various healthcare settings.
In the 1950s, scientists first observed the piezoelectric effect in bones, leading to the development of early PEMF devices for bone healing. These initial applications focused primarily on non-union fractures and spinal fusion surgeries. The 1970s saw the FDA approval of PEMF devices for bone healing, marking a significant milestone in the therapy's acceptance within mainstream medicine.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed an expansion of PEMF research into other areas of medicine. Studies began exploring its potential in pain management, wound healing, and neurological disorders. This period also saw improvements in device design, with more portable and user-friendly PEMF systems becoming available.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era for PEMF therapy. Advancements in electronics and materials science led to the development of more sophisticated devices capable of delivering precise electromagnetic pulses. This technological progress enabled researchers to fine-tune treatment parameters, optimizing therapeutic outcomes across a wider range of conditions.
In recent years, PEMF therapy has gained traction in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Professional athletes and sports teams have adopted PEMF devices for faster recovery and injury prevention. Simultaneously, research has expanded into areas such as mental health, with studies exploring PEMF's potential in treating depression and anxiety.
The integration of PEMF therapy with other treatment modalities has been a notable trend in its evolution. Combining PEMF with traditional physiotherapy, acupuncture, or pharmaceutical interventions has shown promising results in enhancing overall treatment efficacy. This integrative approach has opened new avenues for holistic patient care.
As PEMF therapy continues to evolve, current research is focusing on optimizing treatment protocols, understanding the underlying mechanisms of action, and exploring new applications. The development of wearable PEMF devices and the integration of smart technology for personalized treatment regimens represent the cutting edge of PEMF evolution. These advancements are poised to further expand the therapy's accessibility and effectiveness across various healthcare settings.
Healthcare Market Analysis
The healthcare market is experiencing significant growth and transformation, driven by technological advancements, changing demographics, and increasing healthcare demands. The global healthcare market size was valued at approximately $8.45 trillion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.9% from 2022 to 2030. This growth is attributed to factors such as the aging population, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and increased healthcare spending in both developed and developing countries.
Within this expanding market, there is a growing interest in alternative and complementary therapies, including Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy. The global PEMF therapy devices market was valued at $516.5 million in 2020 and is expected to reach $758.3 million by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period. This growth indicates a rising acceptance and integration of PEMF therapy in healthcare settings.
The integration of PEMF therapy in healthcare presents both opportunities and challenges for the market. On the opportunity side, PEMF therapy offers a non-invasive, drug-free treatment option for various conditions, including pain management, bone healing, and wound care. This aligns with the growing consumer demand for alternative therapies and personalized healthcare solutions. Additionally, as healthcare systems worldwide face increasing pressure to reduce costs and improve patient outcomes, PEMF therapy's potential to accelerate healing and reduce hospital stays could make it an attractive option for healthcare providers and insurers.
However, challenges exist in terms of market adoption and reimbursement. The lack of widespread clinical evidence and standardized protocols for PEMF therapy can hinder its acceptance by mainstream healthcare providers. Furthermore, the current reimbursement landscape for PEMF therapy varies significantly across different countries and insurance providers, which may limit patient access and market growth.
The economic impact of integrating PEMF therapy in healthcare extends beyond direct market size. It has the potential to reduce healthcare costs by decreasing the need for certain medications, shortening recovery times, and reducing the frequency of hospital visits for chronic conditions. For instance, studies have shown that PEMF therapy can reduce the use of pain medications in patients with osteoarthritis, potentially leading to significant cost savings in pain management.
Moreover, the integration of PEMF therapy could create new business models and revenue streams within the healthcare industry. This includes the development and sale of PEMF devices for home use, specialized PEMF therapy clinics, and the incorporation of PEMF treatments in existing healthcare facilities. The market also presents opportunities for innovation in device design, treatment protocols, and integration with other healthcare technologies, such as telemedicine and wearable devices.
Within this expanding market, there is a growing interest in alternative and complementary therapies, including Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy. The global PEMF therapy devices market was valued at $516.5 million in 2020 and is expected to reach $758.3 million by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period. This growth indicates a rising acceptance and integration of PEMF therapy in healthcare settings.
The integration of PEMF therapy in healthcare presents both opportunities and challenges for the market. On the opportunity side, PEMF therapy offers a non-invasive, drug-free treatment option for various conditions, including pain management, bone healing, and wound care. This aligns with the growing consumer demand for alternative therapies and personalized healthcare solutions. Additionally, as healthcare systems worldwide face increasing pressure to reduce costs and improve patient outcomes, PEMF therapy's potential to accelerate healing and reduce hospital stays could make it an attractive option for healthcare providers and insurers.
However, challenges exist in terms of market adoption and reimbursement. The lack of widespread clinical evidence and standardized protocols for PEMF therapy can hinder its acceptance by mainstream healthcare providers. Furthermore, the current reimbursement landscape for PEMF therapy varies significantly across different countries and insurance providers, which may limit patient access and market growth.
The economic impact of integrating PEMF therapy in healthcare extends beyond direct market size. It has the potential to reduce healthcare costs by decreasing the need for certain medications, shortening recovery times, and reducing the frequency of hospital visits for chronic conditions. For instance, studies have shown that PEMF therapy can reduce the use of pain medications in patients with osteoarthritis, potentially leading to significant cost savings in pain management.
Moreover, the integration of PEMF therapy could create new business models and revenue streams within the healthcare industry. This includes the development and sale of PEMF devices for home use, specialized PEMF therapy clinics, and the incorporation of PEMF treatments in existing healthcare facilities. The market also presents opportunities for innovation in device design, treatment protocols, and integration with other healthcare technologies, such as telemedicine and wearable devices.
PEMF Integration Challenges
The integration of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy into mainstream healthcare systems presents several significant challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization in PEMF devices and treatment protocols. The wide variety of available devices, each with different frequencies, intensities, and application methods, makes it difficult for healthcare providers to determine the most effective approach for specific conditions.
Another major challenge is the limited understanding of PEMF therapy among healthcare professionals. Many doctors and nurses are unfamiliar with the technology and its potential benefits, leading to skepticism and reluctance to adopt it in clinical practice. This knowledge gap extends to patients as well, who may be hesitant to try a treatment they perceive as unconventional or unproven.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF devices also poses a significant hurdle. In many countries, the approval process for medical devices is lengthy and costly, which can deter manufacturers from pursuing full medical certification. This results in many PEMF devices being marketed as wellness products rather than medical treatments, further complicating their integration into formal healthcare settings.
Financial considerations play a crucial role in the adoption of PEMF therapy. The initial investment in PEMF equipment can be substantial for healthcare facilities, and without clear reimbursement policies from insurance companies, many providers are hesitant to incorporate the technology. This economic barrier is compounded by the need for ongoing maintenance and staff training.
The lack of large-scale, long-term clinical studies on PEMF therapy's efficacy for various conditions is another significant challenge. While numerous small studies have shown promising results, the absence of comprehensive, multi-center trials makes it difficult to establish PEMF as a standard of care in many medical specialties.
Integration of PEMF therapy into existing treatment workflows and electronic health record systems presents technical and logistical challenges. Healthcare providers must determine how to incorporate PEMF sessions into patient care plans and how to track and document treatments effectively.
Lastly, there are concerns about potential interactions between PEMF therapy and other medical devices or treatments. For patients with implanted electronic devices such as pacemakers, or those undergoing certain types of cancer treatments, the safety and compatibility of PEMF therapy need to be carefully evaluated and managed.
Another major challenge is the limited understanding of PEMF therapy among healthcare professionals. Many doctors and nurses are unfamiliar with the technology and its potential benefits, leading to skepticism and reluctance to adopt it in clinical practice. This knowledge gap extends to patients as well, who may be hesitant to try a treatment they perceive as unconventional or unproven.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF devices also poses a significant hurdle. In many countries, the approval process for medical devices is lengthy and costly, which can deter manufacturers from pursuing full medical certification. This results in many PEMF devices being marketed as wellness products rather than medical treatments, further complicating their integration into formal healthcare settings.
Financial considerations play a crucial role in the adoption of PEMF therapy. The initial investment in PEMF equipment can be substantial for healthcare facilities, and without clear reimbursement policies from insurance companies, many providers are hesitant to incorporate the technology. This economic barrier is compounded by the need for ongoing maintenance and staff training.
The lack of large-scale, long-term clinical studies on PEMF therapy's efficacy for various conditions is another significant challenge. While numerous small studies have shown promising results, the absence of comprehensive, multi-center trials makes it difficult to establish PEMF as a standard of care in many medical specialties.
Integration of PEMF therapy into existing treatment workflows and electronic health record systems presents technical and logistical challenges. Healthcare providers must determine how to incorporate PEMF sessions into patient care plans and how to track and document treatments effectively.
Lastly, there are concerns about potential interactions between PEMF therapy and other medical devices or treatments. For patients with implanted electronic devices such as pacemakers, or those undergoing certain types of cancer treatments, the safety and compatibility of PEMF therapy need to be carefully evaluated and managed.
Current PEMF Applications
01 Economic impact of PEMF therapy on healthcare costs
PEMF therapy can potentially reduce healthcare costs by providing non-invasive treatment for various conditions, potentially decreasing the need for expensive surgical interventions and long-term medication use. This therapy may lead to shorter recovery times and fewer hospital visits, contributing to overall cost savings in the healthcare system.- Economic impact of PEMF therapy on healthcare costs: PEMF therapy can potentially reduce healthcare costs by providing non-invasive treatment for various conditions, potentially decreasing the need for expensive surgeries or long-term medication use. This therapy may lead to faster recovery times and fewer hospital visits, resulting in overall cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems.
- PEMF therapy devices and their market potential: The development and commercialization of PEMF therapy devices represent a growing market opportunity. These devices range from portable units for home use to more sophisticated clinical systems, potentially creating new revenue streams for medical device manufacturers and healthcare providers.
- Impact on workplace productivity and occupational health: PEMF therapy may contribute to improved workplace productivity by reducing absenteeism due to chronic pain or injuries. Its potential to accelerate healing and reduce recovery time could lead to economic benefits for employers and employees alike, as well as positively impact occupational health programs.
- Integration of PEMF therapy in telemedicine and digital health platforms: The incorporation of PEMF therapy into telemedicine and digital health platforms could create new economic opportunities in the healthcare technology sector. This integration may lead to the development of remote monitoring systems, AI-driven treatment protocols, and personalized therapy plans, potentially expanding the reach and efficiency of healthcare delivery.
- Economic implications of PEMF therapy research and development: Ongoing research and development in PEMF therapy could stimulate economic activity in the biotechnology and medical research sectors. This may include investments in clinical trials, development of new PEMF applications, and potential collaborations between academic institutions and private industry, fostering innovation and creating high-skilled job opportunities.
02 Market growth and economic opportunities in PEMF therapy
The PEMF therapy market is experiencing growth, creating economic opportunities for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and related industries. This expansion is driven by increasing awareness of non-invasive treatment options and technological advancements in PEMF devices, potentially leading to job creation and economic stimulation in the medical technology sector.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy compared to traditional treatments
PEMF therapy may offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional treatments for certain conditions. By potentially reducing the need for long-term medication or invasive procedures, PEMF therapy could lead to significant cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems over time.Expand Specific Solutions04 Impact of PEMF therapy on workplace productivity and economic output
The use of PEMF therapy in occupational health settings could potentially improve workplace productivity by reducing absenteeism due to chronic pain or injuries. This may lead to increased economic output and reduced costs associated with lost work time and disability claims.Expand Specific Solutions05 Economic implications of PEMF therapy in home healthcare
The adoption of PEMF therapy devices for home use could have significant economic implications. It may reduce the frequency of clinical visits, decrease the burden on healthcare facilities, and create a new market for personal medical devices, potentially stimulating economic activity in the consumer health sector.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Industry Players
The integration of PEMF therapy in healthcare is in its growth stage, with an expanding market driven by increasing awareness of non-invasive treatment options. The global PEMF therapy devices market is projected to reach significant value in the coming years, indicating substantial economic potential. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Venus Concept Ltd. and Regenesis Biomedical, Inc. leading innovation in medical aesthetics and regenerative medicine applications. Established players such as Medtronic and emerging companies like Galvanize Therapeutics are further driving technological maturity through research and development. The involvement of academic institutions like the National University of Singapore and Swiss Federal Institute of Technology suggests ongoing scientific exploration, potentially leading to new economic opportunities and healthcare applications.
Venus Concept Ltd.
Technical Solution: Venus Concept has developed a comprehensive PEMF therapy system called Venus Pulse. This system utilizes pulsed electromagnetic field technology to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration. The device delivers precise, targeted electromagnetic pulses to affected areas, promoting healing and reducing inflammation. Venus Concept's approach integrates PEMF therapy into various medical treatments, including pain management, wound healing, and post-surgical recovery. Their technology is designed to be user-friendly and adaptable to different healthcare settings, from hospitals to outpatient clinics[1][3]. The company has conducted clinical studies demonstrating the efficacy of their PEMF devices in improving patient outcomes and reducing recovery times[2].
Strengths: Versatile application across multiple medical fields, user-friendly design, and clinically proven results. Weaknesses: May require significant initial investment for healthcare providers, and long-term economic benefits may take time to materialize.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical has pioneered the Provant Therapy System, a PEMF device specifically designed for post-operative pain and edema management. Their technology utilizes a proprietary pulsed radio frequency energy (PRFE) signal to stimulate cellular activity and accelerate the body's natural healing processes. The Provant system is FDA-cleared and has been shown to reduce the need for pain medication, potentially leading to significant cost savings in post-operative care[4]. Regenesis has focused on integrating their PEMF technology into standard post-surgical protocols, aiming to reduce hospital readmissions and improve patient satisfaction scores. The company has conducted extensive research on the economic impact of their technology, demonstrating potential savings in both direct medical costs and indirect costs associated with faster recovery times[5].
Strengths: FDA-cleared technology, focused application in post-operative care, and demonstrated cost-saving potential. Weaknesses: Limited to specific medical applications, which may restrict broader market adoption.
PEMF Research Innovations
Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) therapy whole body wellness device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveIN201814011740A
Innovation
- A self-contained portable PEMF device, PEMF-DS100, generates pulsed electromagnetic fields that penetrate the body through the hands and feet, utilizing Multiple-Wave Oscillation technology to synchronize cellular vibrations, enhance energy potential, and promote self-healing, while being designed to avoid adaptation and maintain effectiveness over time.
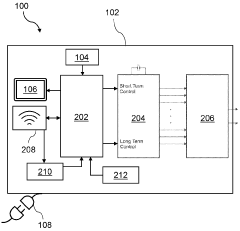
A pulsed electromagnetic field apparatus and method for generating frequencies
PatentWO2024127242A1
Innovation
- A PEMF apparatus with a pulse generator and electromagnetic field generation means that uses modified sawtooth waveforms with pre-stress and relaxation periods, and quasi-sine signals with pulse width modulation, along with a feedback circuit for frequency stability and precision, and a bifilar antenna for scalar wave generation.
Economic Impact Assessment
The integration of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy into healthcare systems has the potential to generate significant economic impacts across various sectors. This assessment examines the financial implications of widespread PEMF adoption, considering both direct and indirect economic effects.
From a healthcare cost perspective, PEMF therapy shows promise in reducing long-term expenses associated with chronic conditions. By potentially accelerating healing processes and managing pain more effectively, PEMF could decrease the need for prolonged treatments and medications. This shift may lead to substantial savings for healthcare providers and insurance companies, ultimately benefiting patients through reduced out-of-pocket expenses.
The implementation of PEMF technology in clinical settings could also drive economic growth within the medical device industry. As demand for PEMF devices increases, manufacturers and suppliers are likely to experience expanded market opportunities. This growth could stimulate job creation in research and development, manufacturing, and sales sectors related to PEMF technology.
Furthermore, the integration of PEMF therapy may contribute to improved workforce productivity. By potentially reducing recovery times and enhancing overall well-being, PEMF treatments could lead to fewer sick days and increased employee performance. This indirect economic benefit could translate into higher productivity levels across various industries, positively impacting national economic output.
The adoption of PEMF therapy could also influence healthcare infrastructure investments. Hospitals and clinics may need to allocate resources for equipment acquisition and staff training, potentially creating short-term economic stimuli in related sectors. However, these initial investments should be weighed against the long-term cost savings and improved patient outcomes.
Additionally, the expansion of PEMF therapy may create new opportunities in the field of personalized medicine. As research progresses, tailored PEMF treatments could emerge, potentially spawning a new subset of specialized healthcare services and fostering innovation in the medical technology sector.
It is important to note that the economic impact of PEMF integration will likely vary across different healthcare systems and economies. Factors such as regulatory environments, existing healthcare infrastructure, and cultural attitudes towards alternative therapies will influence the rate and extent of PEMF adoption, thereby affecting its economic implications.
In conclusion, while the full economic impact of integrating PEMF therapy into healthcare remains to be fully quantified, initial assessments suggest a multifaceted effect. From potential healthcare cost reductions to stimulating growth in related industries, PEMF integration presents both challenges and opportunities for economic development within the healthcare sector and beyond.
From a healthcare cost perspective, PEMF therapy shows promise in reducing long-term expenses associated with chronic conditions. By potentially accelerating healing processes and managing pain more effectively, PEMF could decrease the need for prolonged treatments and medications. This shift may lead to substantial savings for healthcare providers and insurance companies, ultimately benefiting patients through reduced out-of-pocket expenses.
The implementation of PEMF technology in clinical settings could also drive economic growth within the medical device industry. As demand for PEMF devices increases, manufacturers and suppliers are likely to experience expanded market opportunities. This growth could stimulate job creation in research and development, manufacturing, and sales sectors related to PEMF technology.
Furthermore, the integration of PEMF therapy may contribute to improved workforce productivity. By potentially reducing recovery times and enhancing overall well-being, PEMF treatments could lead to fewer sick days and increased employee performance. This indirect economic benefit could translate into higher productivity levels across various industries, positively impacting national economic output.
The adoption of PEMF therapy could also influence healthcare infrastructure investments. Hospitals and clinics may need to allocate resources for equipment acquisition and staff training, potentially creating short-term economic stimuli in related sectors. However, these initial investments should be weighed against the long-term cost savings and improved patient outcomes.
Additionally, the expansion of PEMF therapy may create new opportunities in the field of personalized medicine. As research progresses, tailored PEMF treatments could emerge, potentially spawning a new subset of specialized healthcare services and fostering innovation in the medical technology sector.
It is important to note that the economic impact of PEMF integration will likely vary across different healthcare systems and economies. Factors such as regulatory environments, existing healthcare infrastructure, and cultural attitudes towards alternative therapies will influence the rate and extent of PEMF adoption, thereby affecting its economic implications.
In conclusion, while the full economic impact of integrating PEMF therapy into healthcare remains to be fully quantified, initial assessments suggest a multifaceted effect. From potential healthcare cost reductions to stimulating growth in related industries, PEMF integration presents both challenges and opportunities for economic development within the healthcare sector and beyond.
Regulatory Considerations
The integration of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy into healthcare systems necessitates careful consideration of regulatory frameworks. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing medical devices, including PEMF devices. The FDA has classified PEMF devices into different categories based on their intended use and potential risks, with some devices requiring premarket approval while others may be cleared through the 510(k) process.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Health Canada have their own guidelines for PEMF devices. The European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) has introduced more stringent requirements for medical device manufacturers, potentially impacting the approval process for PEMF devices in European markets.
Compliance with these regulatory standards is essential for healthcare providers and manufacturers looking to integrate PEMF therapy into their offerings. This includes adhering to quality management systems, conducting clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy, and maintaining post-market surveillance.
The economic impact of regulatory compliance can be significant. Manufacturers must invest in research and development to meet regulatory standards, which can increase the overall cost of bringing PEMF devices to market. Healthcare providers may need to allocate resources for staff training and certification to ensure proper use of PEMF devices in accordance with regulatory guidelines.
However, regulatory compliance also presents opportunities for economic growth. Devices that meet stringent regulatory standards may gain a competitive edge in the market, potentially leading to increased adoption and revenue. Additionally, compliance with international standards can facilitate market expansion, allowing manufacturers to access a broader customer base.
As PEMF therapy gains traction, regulatory bodies may need to adapt their frameworks to accommodate emerging technologies and applications. This could involve developing new guidelines for combination therapies or updating existing regulations to address novel PEMF modalities. The evolving regulatory landscape may create both challenges and opportunities for stakeholders in the PEMF therapy ecosystem.
Stakeholders must stay informed about regulatory changes and engage in proactive dialogue with regulatory bodies to ensure smooth integration of PEMF therapy into healthcare systems. This collaborative approach can help shape regulations that balance innovation with patient safety, ultimately contributing to the economic viability and growth of PEMF therapy in healthcare.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Health Canada have their own guidelines for PEMF devices. The European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) has introduced more stringent requirements for medical device manufacturers, potentially impacting the approval process for PEMF devices in European markets.
Compliance with these regulatory standards is essential for healthcare providers and manufacturers looking to integrate PEMF therapy into their offerings. This includes adhering to quality management systems, conducting clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy, and maintaining post-market surveillance.
The economic impact of regulatory compliance can be significant. Manufacturers must invest in research and development to meet regulatory standards, which can increase the overall cost of bringing PEMF devices to market. Healthcare providers may need to allocate resources for staff training and certification to ensure proper use of PEMF devices in accordance with regulatory guidelines.
However, regulatory compliance also presents opportunities for economic growth. Devices that meet stringent regulatory standards may gain a competitive edge in the market, potentially leading to increased adoption and revenue. Additionally, compliance with international standards can facilitate market expansion, allowing manufacturers to access a broader customer base.
As PEMF therapy gains traction, regulatory bodies may need to adapt their frameworks to accommodate emerging technologies and applications. This could involve developing new guidelines for combination therapies or updating existing regulations to address novel PEMF modalities. The evolving regulatory landscape may create both challenges and opportunities for stakeholders in the PEMF therapy ecosystem.
Stakeholders must stay informed about regulatory changes and engage in proactive dialogue with regulatory bodies to ensure smooth integration of PEMF therapy into healthcare systems. This collaborative approach can help shape regulations that balance innovation with patient safety, ultimately contributing to the economic viability and growth of PEMF therapy in healthcare.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!