V8 Engine Linear Power Transfer: Understanding Mechanics
JUL 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V8 Engine Evolution
The V8 engine has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed to provide more power and smoother operation than inline engines, the V8 configuration has become synonymous with high-performance vehicles and heavy-duty applications.
The earliest V8 engines appeared in the 1900s, with notable examples including the 1910 De Dion-Bouton and the 1914 Cadillac L-Head V8. These early designs laid the foundation for the V8's reputation for power and reliability. The 1920s and 1930s saw widespread adoption of V8 engines in American automobiles, with Ford's introduction of the Flathead V8 in 1932 marking a significant milestone in making V8 power accessible to the mass market.
Post-World War II, V8 engines entered a golden age of development. The 1949 Oldsmobile Rocket V8, featuring overhead valves and high compression ratios, set new standards for performance and efficiency. This era also saw the birth of iconic V8s like the Chevrolet Small-Block, introduced in 1955, which became one of the most produced engines in history.
The 1960s and 1970s witnessed the pinnacle of V8 dominance in the automotive world, particularly in muscle cars and racing applications. However, the oil crises of the 1970s led to a shift towards more fuel-efficient designs, prompting manufacturers to explore ways to improve V8 efficiency without sacrificing power.
In recent decades, V8 evolution has focused on integrating advanced technologies to meet stringent emissions standards while maintaining performance. Innovations such as variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and cylinder deactivation have allowed V8 engines to remain relevant in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The latest frontier in V8 development involves hybridization and electrification. Many manufacturers are now pairing V8 engines with electric motors to create high-performance hybrid powertrains, combining the traditional appeal of V8 power with improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Throughout its evolution, the core principle of linear power transfer in V8 engines has remained constant. The V-configuration, with its two banks of four cylinders, allows for a compact design that efficiently transfers power from the pistons through the crankshaft. This arrangement has proven adaptable to various advancements in materials, fuel systems, and electronic controls, enabling the V8 to maintain its position as a benchmark for performance and engineering excellence.
The earliest V8 engines appeared in the 1900s, with notable examples including the 1910 De Dion-Bouton and the 1914 Cadillac L-Head V8. These early designs laid the foundation for the V8's reputation for power and reliability. The 1920s and 1930s saw widespread adoption of V8 engines in American automobiles, with Ford's introduction of the Flathead V8 in 1932 marking a significant milestone in making V8 power accessible to the mass market.
Post-World War II, V8 engines entered a golden age of development. The 1949 Oldsmobile Rocket V8, featuring overhead valves and high compression ratios, set new standards for performance and efficiency. This era also saw the birth of iconic V8s like the Chevrolet Small-Block, introduced in 1955, which became one of the most produced engines in history.
The 1960s and 1970s witnessed the pinnacle of V8 dominance in the automotive world, particularly in muscle cars and racing applications. However, the oil crises of the 1970s led to a shift towards more fuel-efficient designs, prompting manufacturers to explore ways to improve V8 efficiency without sacrificing power.
In recent decades, V8 evolution has focused on integrating advanced technologies to meet stringent emissions standards while maintaining performance. Innovations such as variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and cylinder deactivation have allowed V8 engines to remain relevant in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The latest frontier in V8 development involves hybridization and electrification. Many manufacturers are now pairing V8 engines with electric motors to create high-performance hybrid powertrains, combining the traditional appeal of V8 power with improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Throughout its evolution, the core principle of linear power transfer in V8 engines has remained constant. The V-configuration, with its two banks of four cylinders, allows for a compact design that efficiently transfers power from the pistons through the crankshaft. This arrangement has proven adaptable to various advancements in materials, fuel systems, and electronic controls, enabling the V8 to maintain its position as a benchmark for performance and engineering excellence.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for V8 engine linear power transfer technology has been steadily growing, driven by the automotive industry's pursuit of enhanced performance and efficiency. This technology, which focuses on optimizing the conversion of reciprocating motion into rotational motion, has garnered significant attention from both manufacturers and consumers.
In the high-performance vehicle segment, there is a strong demand for V8 engines that can deliver superior power output while maintaining fuel efficiency. The linear power transfer technology addresses this need by improving the overall engine dynamics and reducing energy losses. Sports car manufacturers and luxury vehicle brands are particularly interested in incorporating this technology to maintain their competitive edge in the market.
The commercial vehicle sector also shows promising market potential for V8 engine linear power transfer technology. Heavy-duty trucks and buses require robust and efficient powertrains, and the improved power delivery offered by this technology can lead to better fuel economy and reduced operating costs. Fleet operators and logistics companies are increasingly looking for solutions that can provide long-term cost savings through improved engine performance.
Moreover, the marine industry presents another significant market opportunity. Large boats and yachts often utilize V8 engines, and the demand for more efficient and powerful marine propulsion systems is on the rise. The linear power transfer technology can offer smoother operation and better fuel efficiency, which are crucial factors in marine applications.
The aftermarket and performance tuning sectors also contribute to the market demand. Enthusiasts and custom vehicle builders are constantly seeking ways to enhance engine performance, creating a niche market for advanced V8 engine components and technologies.
From a geographical perspective, North America and Europe lead in terms of market demand, given their strong automotive industries and consumer preference for high-performance vehicles. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are showing increased interest as their automotive sectors grow and diversify.
The global push for reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency is another factor driving the demand for advanced engine technologies. As regulatory standards become more stringent, manufacturers are compelled to invest in innovative solutions like linear power transfer to meet these requirements while maintaining performance levels.
In conclusion, the market demand for V8 engine linear power transfer technology is robust and multifaceted, spanning various industries and geographical regions. The technology's potential to enhance performance, improve efficiency, and meet regulatory standards positions it as a valuable innovation in the engine manufacturing landscape.
In the high-performance vehicle segment, there is a strong demand for V8 engines that can deliver superior power output while maintaining fuel efficiency. The linear power transfer technology addresses this need by improving the overall engine dynamics and reducing energy losses. Sports car manufacturers and luxury vehicle brands are particularly interested in incorporating this technology to maintain their competitive edge in the market.
The commercial vehicle sector also shows promising market potential for V8 engine linear power transfer technology. Heavy-duty trucks and buses require robust and efficient powertrains, and the improved power delivery offered by this technology can lead to better fuel economy and reduced operating costs. Fleet operators and logistics companies are increasingly looking for solutions that can provide long-term cost savings through improved engine performance.
Moreover, the marine industry presents another significant market opportunity. Large boats and yachts often utilize V8 engines, and the demand for more efficient and powerful marine propulsion systems is on the rise. The linear power transfer technology can offer smoother operation and better fuel efficiency, which are crucial factors in marine applications.
The aftermarket and performance tuning sectors also contribute to the market demand. Enthusiasts and custom vehicle builders are constantly seeking ways to enhance engine performance, creating a niche market for advanced V8 engine components and technologies.
From a geographical perspective, North America and Europe lead in terms of market demand, given their strong automotive industries and consumer preference for high-performance vehicles. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are showing increased interest as their automotive sectors grow and diversify.
The global push for reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency is another factor driving the demand for advanced engine technologies. As regulatory standards become more stringent, manufacturers are compelled to invest in innovative solutions like linear power transfer to meet these requirements while maintaining performance levels.
In conclusion, the market demand for V8 engine linear power transfer technology is robust and multifaceted, spanning various industries and geographical regions. The technology's potential to enhance performance, improve efficiency, and meet regulatory standards positions it as a valuable innovation in the engine manufacturing landscape.
Technical Challenges
The V8 engine linear power transfer system faces several technical challenges that require innovative solutions to enhance efficiency and performance. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent reciprocating motion of the pistons, which creates significant vibration and energy loss. This linear motion must be effectively converted into rotational motion to drive the crankshaft, a process that introduces friction and mechanical inefficiencies.
Another major challenge lies in the thermal management of the engine. The linear power transfer generates substantial heat, which can lead to thermal expansion and potential component failure if not properly managed. Engineers must develop advanced cooling systems and materials that can withstand high temperatures while maintaining optimal performance.
The issue of weight reduction presents a significant hurdle in V8 engine design. The linear power transfer system involves numerous heavy components, including pistons, connecting rods, and the crankshaft. Reducing the weight of these parts without compromising strength and durability is crucial for improving overall engine efficiency and vehicle performance.
Balancing the engine is another complex challenge. The linear motion of pistons in a V8 configuration creates inherent imbalances that can lead to increased vibration and wear. Sophisticated counterbalancing techniques and precision manufacturing are required to minimize these effects and ensure smooth operation across various engine speeds.
Fuel efficiency remains a persistent challenge in V8 engine design. The linear power transfer system's mechanical losses and the engine's overall size contribute to higher fuel consumption. Developing technologies to optimize combustion, reduce friction, and improve energy recovery from exhaust gases is essential for meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations.
The complexity of the V8 engine's valve train system poses additional challenges. Coordinating the opening and closing of multiple valves with precise timing is critical for optimal engine performance. Advanced valve control systems, such as variable valve timing and lift, add further complexity to the design and manufacturing process.
Lastly, the integration of modern technologies, such as hybrid systems and start-stop functionality, introduces new challenges in the linear power transfer system. Engineers must develop solutions that allow for seamless integration of these technologies while maintaining the V8 engine's characteristic performance and sound.
Another major challenge lies in the thermal management of the engine. The linear power transfer generates substantial heat, which can lead to thermal expansion and potential component failure if not properly managed. Engineers must develop advanced cooling systems and materials that can withstand high temperatures while maintaining optimal performance.
The issue of weight reduction presents a significant hurdle in V8 engine design. The linear power transfer system involves numerous heavy components, including pistons, connecting rods, and the crankshaft. Reducing the weight of these parts without compromising strength and durability is crucial for improving overall engine efficiency and vehicle performance.
Balancing the engine is another complex challenge. The linear motion of pistons in a V8 configuration creates inherent imbalances that can lead to increased vibration and wear. Sophisticated counterbalancing techniques and precision manufacturing are required to minimize these effects and ensure smooth operation across various engine speeds.
Fuel efficiency remains a persistent challenge in V8 engine design. The linear power transfer system's mechanical losses and the engine's overall size contribute to higher fuel consumption. Developing technologies to optimize combustion, reduce friction, and improve energy recovery from exhaust gases is essential for meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations.
The complexity of the V8 engine's valve train system poses additional challenges. Coordinating the opening and closing of multiple valves with precise timing is critical for optimal engine performance. Advanced valve control systems, such as variable valve timing and lift, add further complexity to the design and manufacturing process.
Lastly, the integration of modern technologies, such as hybrid systems and start-stop functionality, introduces new challenges in the linear power transfer system. Engineers must develop solutions that allow for seamless integration of these technologies while maintaining the V8 engine's characteristic performance and sound.
Current Linear Systems
01 Crankshaft and connecting rod assembly
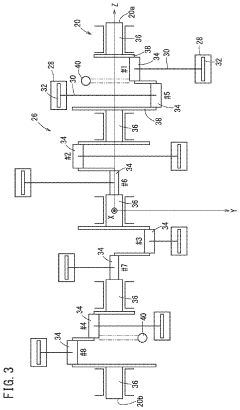
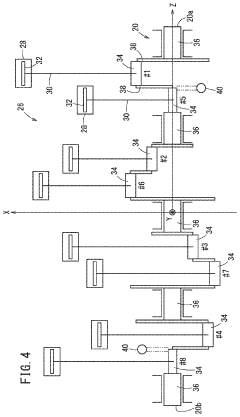
V8 engines utilize a crankshaft and connecting rod assembly to convert the reciprocating motion of pistons into rotational motion. This system is crucial for linear power transfer in V8 engines, as it efficiently translates the linear force generated by combustion into usable rotational energy.- Crankshaft and connecting rod design: V8 engines utilize a specific crankshaft and connecting rod design to convert the reciprocating motion of pistons into rotational motion. This design is crucial for efficient power transfer in V8 engines, optimizing the linear motion of pistons into usable rotational energy.
- Valve train and camshaft configuration: The valve train and camshaft configuration in V8 engines play a significant role in controlling the intake and exhaust of gases, thereby affecting the engine's power output and efficiency. Advanced designs can improve the linear power transfer by optimizing valve timing and lift.
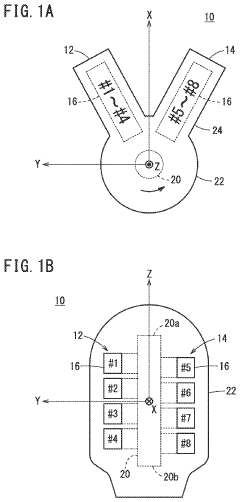
- Piston and cylinder arrangement: The arrangement of pistons and cylinders in a V8 engine is critical for balanced operation and efficient power transfer. Innovative designs focus on reducing friction, improving combustion efficiency, and enhancing the overall power output of the engine.
- Fuel injection and ignition systems: Advanced fuel injection and ignition systems in V8 engines contribute to improved power transfer by ensuring optimal fuel-air mixture and combustion timing. These systems can enhance engine performance, fuel efficiency, and power output.
- Power transmission and drivetrain integration: Efficient power transmission from the V8 engine to the drivetrain is essential for maximizing overall vehicle performance. This includes optimizing the design of components such as the transmission, driveshaft, and differential to ensure smooth and effective power transfer to the wheels.
02 Piston and cylinder arrangement
The V8 engine's unique piston and cylinder arrangement, with two banks of four cylinders in a V-shape, contributes to its linear power transfer characteristics. This configuration allows for balanced operation and smooth power delivery, enhancing overall engine performance and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Valve train and camshaft system
The valve train and camshaft system in V8 engines play a crucial role in linear power transfer by controlling the intake and exhaust of gases. Advanced designs in this area can optimize engine breathing, leading to improved power output and efficiency in the linear power transfer process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Fuel injection and ignition timing
Precise fuel injection and ignition timing are essential for maximizing linear power transfer in V8 engines. Advanced electronic control systems can optimize these parameters based on engine load and speed, ensuring efficient combustion and power delivery across various operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Power transmission and drivetrain integration
Effective linear power transfer in V8 engines also depends on the integration with the transmission and drivetrain. Advanced designs focus on minimizing power loss and optimizing the transfer of energy from the engine to the wheels, ensuring that the linear power generated by the V8 is efficiently utilized for vehicle propulsion.Expand Specific Solutions
Key V8 Manufacturers
The V8 Engine Linear Power Transfer technology is in a mature stage of development, with a competitive landscape dominated by established automotive manufacturers and suppliers. The market size is substantial, driven by the global automotive industry's demand for efficient power transfer systems. Companies like GM, Toyota, Honda, and Nissan are at the forefront, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and manufacturing expertise. The technology's maturity is evident in its widespread adoption across various vehicle models, with continuous refinements focusing on efficiency, performance, and emissions reduction. Smaller players and research institutions contribute to innovation, but major automakers maintain a significant advantage in commercialization and large-scale implementation.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM's V8 engine linear power transfer technology focuses on optimizing the conversion of reciprocating piston motion into rotational crankshaft motion. They employ advanced cylinder deactivation systems, allowing the engine to seamlessly switch between 8 and 4 cylinder operation for improved fuel efficiency[1]. GM's latest V8 engines feature direct injection and variable valve timing, enhancing power delivery and reducing fuel consumption[2]. The company has also developed a Dynamic Fuel Management system, which can deactivate cylinders in 17 different patterns to optimize power and efficiency based on driving conditions[3].
Strengths: Improved fuel efficiency, seamless power delivery, and adaptability to various driving conditions. Weaknesses: Complexity of the system may lead to higher maintenance costs and potential reliability issues in the long term.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honda's approach to V8 engine linear power transfer focuses on high-performance applications, particularly in racing. Their V8 engines, such as those used in IndyCar, feature a compact, lightweight design with a flat-plane crankshaft for higher revving capabilities[4]. Honda employs advanced materials like titanium for connecting rods and valves to reduce reciprocating mass and improve power transfer efficiency[5]. They also utilize a sophisticated engine management system that optimizes fuel injection and ignition timing for maximum power output across the RPM range[6].
Strengths: High-performance capabilities, lightweight design, and efficient power transfer. Weaknesses: Higher production costs and potentially reduced durability in non-racing applications.
Innovative Designs
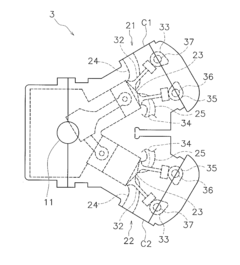
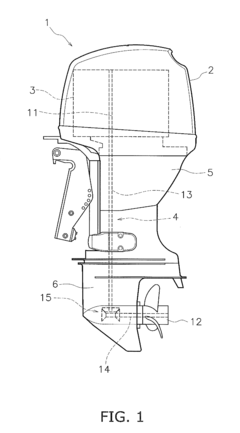
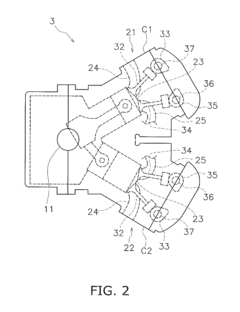
V8 engine and outboard motor
PatentActiveUS20160341097A1
Innovation
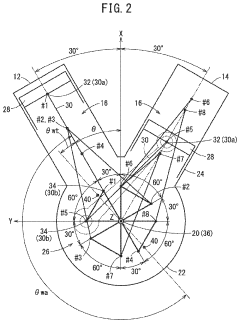
- A V8 engine design with a simple construction featuring aggregated exhaust pathways and adjustable exhaust cams, where the central angle of exhaust cams for each cylinder is optimized to minimize valve overlap and reduce exhaust interference, allowing for even firing intervals and improved exhaust gas management.
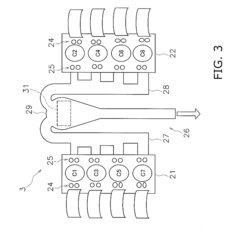
V8 engine
PatentActiveUS11821359B2
Innovation
- The V8 engine configuration features crank pins arranged at 90° intervals on one bank and offset by 60° on the other bank, allowing for cancellation of primary inertia couples without additional specialized parts by optimizing the arrangement of crank pins and connecting rods.
Emissions Regulations
Emissions regulations play a crucial role in shaping the development and implementation of V8 engine linear power transfer systems. These regulations, established by governmental bodies and environmental agencies, aim to reduce the environmental impact of internal combustion engines, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants.
In recent years, emissions standards have become increasingly stringent, forcing automotive manufacturers to innovate and adapt their engine designs. For V8 engines, this has led to a focus on improving the efficiency of power transfer systems to maximize fuel economy and minimize emissions. The linear power transfer mechanism in V8 engines has been subject to scrutiny and optimization to meet these regulatory requirements.
One of the primary challenges faced by V8 engine manufacturers is the need to balance performance with emissions compliance. The linear power transfer system must be designed to deliver optimal power output while simultaneously reducing fuel consumption and emissions. This has led to the development of advanced technologies such as variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and cylinder deactivation, all of which contribute to improved efficiency and reduced emissions.
Emissions regulations have also driven the adoption of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques in V8 engine design. Lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys and composites, are increasingly used to reduce overall engine weight, thereby improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Additionally, precision manufacturing processes have been implemented to ensure tighter tolerances and improved sealing, which contribute to better combustion efficiency and reduced emissions.
The impact of emissions regulations on V8 engine linear power transfer systems extends beyond the engine itself. Manufacturers have been compelled to integrate advanced aftertreatment systems, such as catalytic converters and particulate filters, to further reduce harmful emissions. These systems must be carefully integrated with the engine's power transfer mechanism to ensure optimal performance and compliance with regulations.
As emissions standards continue to evolve, the future of V8 engine linear power transfer systems remains uncertain. Some experts predict a shift towards hybrid and electric powertrains, while others believe that advancements in internal combustion engine technology will allow V8 engines to remain viable in the face of stricter regulations. Regardless of the outcome, it is clear that emissions regulations will continue to be a driving force in the development and refinement of V8 engine technology for years to come.
In recent years, emissions standards have become increasingly stringent, forcing automotive manufacturers to innovate and adapt their engine designs. For V8 engines, this has led to a focus on improving the efficiency of power transfer systems to maximize fuel economy and minimize emissions. The linear power transfer mechanism in V8 engines has been subject to scrutiny and optimization to meet these regulatory requirements.
One of the primary challenges faced by V8 engine manufacturers is the need to balance performance with emissions compliance. The linear power transfer system must be designed to deliver optimal power output while simultaneously reducing fuel consumption and emissions. This has led to the development of advanced technologies such as variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and cylinder deactivation, all of which contribute to improved efficiency and reduced emissions.
Emissions regulations have also driven the adoption of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques in V8 engine design. Lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys and composites, are increasingly used to reduce overall engine weight, thereby improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Additionally, precision manufacturing processes have been implemented to ensure tighter tolerances and improved sealing, which contribute to better combustion efficiency and reduced emissions.
The impact of emissions regulations on V8 engine linear power transfer systems extends beyond the engine itself. Manufacturers have been compelled to integrate advanced aftertreatment systems, such as catalytic converters and particulate filters, to further reduce harmful emissions. These systems must be carefully integrated with the engine's power transfer mechanism to ensure optimal performance and compliance with regulations.
As emissions standards continue to evolve, the future of V8 engine linear power transfer systems remains uncertain. Some experts predict a shift towards hybrid and electric powertrains, while others believe that advancements in internal combustion engine technology will allow V8 engines to remain viable in the face of stricter regulations. Regardless of the outcome, it is clear that emissions regulations will continue to be a driving force in the development and refinement of V8 engine technology for years to come.
Efficiency Benchmarks
Efficiency benchmarks for V8 engine linear power transfer systems provide crucial insights into the performance and optimization potential of these mechanical components. These benchmarks typically measure the ratio of power output to input, taking into account various factors such as friction, heat loss, and mechanical resistance.
Standard testing procedures involve measuring the power input at the crankshaft and comparing it to the power output at the wheels or drivetrain. This comparison allows engineers to quantify the efficiency of the power transfer system and identify areas for improvement. Typical efficiency ratings for modern V8 engines range from 25% to 35%, with high-performance engines achieving up to 40% efficiency under optimal conditions.
Factors influencing efficiency include engine design, materials used, lubrication systems, and operating conditions. Advanced materials such as low-friction coatings and high-strength alloys can significantly reduce power loss due to friction and heat. Similarly, optimized cooling systems and precision-engineered components contribute to higher efficiency ratings.
Comparative studies across different V8 engine models and manufacturers reveal interesting trends in efficiency improvements over time. For instance, advancements in computer-aided design and simulation have led to more precise tolerances and better-optimized power transfer systems, resulting in incremental efficiency gains of 1-2% per generation in some cases.
Real-world testing under various driving conditions provides valuable data on how efficiency varies with factors such as speed, load, and temperature. These tests often reveal that peak efficiency is achieved within specific operating ranges, highlighting the importance of matching engine characteristics to intended use cases.
Emerging technologies such as variable valve timing, cylinder deactivation, and advanced engine management systems have shown promising results in improving overall efficiency. Some studies indicate that these technologies can boost efficiency by up to 5% in certain driving scenarios, particularly in urban environments with frequent stops and starts.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, the focus on efficiency benchmarks has intensified. Manufacturers are increasingly using these metrics to guide research and development efforts, aiming to maximize power output while minimizing fuel consumption and emissions. This trend is likely to drive further innovations in V8 engine linear power transfer systems, potentially pushing efficiency ratings beyond current limits in the coming years.
Standard testing procedures involve measuring the power input at the crankshaft and comparing it to the power output at the wheels or drivetrain. This comparison allows engineers to quantify the efficiency of the power transfer system and identify areas for improvement. Typical efficiency ratings for modern V8 engines range from 25% to 35%, with high-performance engines achieving up to 40% efficiency under optimal conditions.
Factors influencing efficiency include engine design, materials used, lubrication systems, and operating conditions. Advanced materials such as low-friction coatings and high-strength alloys can significantly reduce power loss due to friction and heat. Similarly, optimized cooling systems and precision-engineered components contribute to higher efficiency ratings.
Comparative studies across different V8 engine models and manufacturers reveal interesting trends in efficiency improvements over time. For instance, advancements in computer-aided design and simulation have led to more precise tolerances and better-optimized power transfer systems, resulting in incremental efficiency gains of 1-2% per generation in some cases.
Real-world testing under various driving conditions provides valuable data on how efficiency varies with factors such as speed, load, and temperature. These tests often reveal that peak efficiency is achieved within specific operating ranges, highlighting the importance of matching engine characteristics to intended use cases.
Emerging technologies such as variable valve timing, cylinder deactivation, and advanced engine management systems have shown promising results in improving overall efficiency. Some studies indicate that these technologies can boost efficiency by up to 5% in certain driving scenarios, particularly in urban environments with frequent stops and starts.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, the focus on efficiency benchmarks has intensified. Manufacturers are increasingly using these metrics to guide research and development efforts, aiming to maximize power output while minimizing fuel consumption and emissions. This trend is likely to drive further innovations in V8 engine linear power transfer systems, potentially pushing efficiency ratings beyond current limits in the coming years.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!