How V8 Engines Affect Auto Industry Market Trends?
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V8 Engine Evolution and Objectives
The V8 engine has been a cornerstone of automotive engineering since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed to provide more power and smoother operation than inline engines, V8s quickly became synonymous with performance and luxury in the automotive industry. The evolution of V8 engines has been closely tied to advancements in materials science, fuel efficiency, and emissions control technologies.
In the 1950s and 1960s, V8 engines reached their zenith in terms of displacement and raw power output, particularly in American muscle cars. However, the oil crises of the 1970s forced a shift in focus towards fuel efficiency and emissions reduction. This led to the development of smaller, more efficient V8 engines with technologies like fuel injection and variable valve timing.
The 1980s and 1990s saw further refinements in V8 technology, with the introduction of overhead cam designs and more sophisticated engine management systems. These advancements allowed V8 engines to maintain their performance characteristics while meeting increasingly stringent emissions standards.
In recent years, the automotive industry has faced mounting pressure to reduce carbon emissions and improve fuel economy. This has led to a new phase in V8 engine evolution, characterized by the integration of technologies such as direct injection, turbocharging, and cylinder deactivation. These innovations have allowed V8 engines to deliver impressive power outputs from smaller displacements, maintaining their appeal in high-performance and luxury vehicle segments.
The primary objectives driving V8 engine development in the modern era are twofold. First, there is a continued focus on improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions to meet regulatory requirements and consumer demands for more environmentally friendly vehicles. Second, manufacturers aim to maintain the performance and prestige associated with V8 engines, which remain a key selling point for many premium and sports car brands.
Looking forward, the future of V8 engines in the auto industry is at a crossroads. While electrification is gaining momentum, there is still significant demand for the unique characteristics of V8 engines in certain market segments. As a result, manufacturers are exploring hybrid V8 powertrains and other innovative solutions to extend the viability of these iconic engines in an increasingly eco-conscious automotive landscape.
In the 1950s and 1960s, V8 engines reached their zenith in terms of displacement and raw power output, particularly in American muscle cars. However, the oil crises of the 1970s forced a shift in focus towards fuel efficiency and emissions reduction. This led to the development of smaller, more efficient V8 engines with technologies like fuel injection and variable valve timing.
The 1980s and 1990s saw further refinements in V8 technology, with the introduction of overhead cam designs and more sophisticated engine management systems. These advancements allowed V8 engines to maintain their performance characteristics while meeting increasingly stringent emissions standards.
In recent years, the automotive industry has faced mounting pressure to reduce carbon emissions and improve fuel economy. This has led to a new phase in V8 engine evolution, characterized by the integration of technologies such as direct injection, turbocharging, and cylinder deactivation. These innovations have allowed V8 engines to deliver impressive power outputs from smaller displacements, maintaining their appeal in high-performance and luxury vehicle segments.
The primary objectives driving V8 engine development in the modern era are twofold. First, there is a continued focus on improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions to meet regulatory requirements and consumer demands for more environmentally friendly vehicles. Second, manufacturers aim to maintain the performance and prestige associated with V8 engines, which remain a key selling point for many premium and sports car brands.
Looking forward, the future of V8 engines in the auto industry is at a crossroads. While electrification is gaining momentum, there is still significant demand for the unique characteristics of V8 engines in certain market segments. As a result, manufacturers are exploring hybrid V8 powertrains and other innovative solutions to extend the viability of these iconic engines in an increasingly eco-conscious automotive landscape.
Market Demand Analysis for V8-Powered Vehicles
The market demand for V8-powered vehicles has undergone significant shifts in recent years, reflecting changing consumer preferences, environmental concerns, and regulatory pressures. Traditionally, V8 engines have been synonymous with power, performance, and luxury in the automotive industry. These engines have long been favored in high-end sports cars, luxury sedans, and large SUVs, catering to consumers who prioritize acceleration, towing capacity, and a distinctive engine sound.
However, the global automotive market has witnessed a gradual decline in demand for V8-powered vehicles. This trend is primarily driven by increasing fuel efficiency standards and growing environmental awareness among consumers. Many countries have implemented stricter emissions regulations, pushing automakers to focus on smaller, more fuel-efficient engines. As a result, the market share of V8-powered vehicles has been steadily decreasing in most segments.
Despite this overall decline, certain niche markets continue to show strong demand for V8 engines. The luxury and high-performance vehicle segments, particularly in North America and the Middle East, still maintain a significant customer base for V8-powered cars. These consumers value the power and prestige associated with V8 engines, often viewing them as a status symbol.
The pickup truck market, especially in the United States, remains a stronghold for V8 engines. Many consumers in this segment prioritize towing capacity and payload, areas where V8 engines excel. However, even in this traditionally V8-dominated market, there is a growing trend towards more efficient V6 engines and hybrid powertrains that can match or exceed V8 performance while offering better fuel economy.
The sports car and muscle car segments also continue to see demand for V8 engines, with enthusiasts and collectors valuing the raw power and nostalgic appeal of these powerplants. However, this market is increasingly niche and faces pressure from high-performance electric and hybrid alternatives that offer comparable or superior acceleration.
Looking at regional variations, North America remains the largest market for V8-powered vehicles, followed by the Middle East. In contrast, European and Asian markets have seen a more rapid decline in V8 demand due to stricter emissions standards and higher fuel costs. This regional disparity has led some automakers to develop market-specific strategies, offering V8 options in certain regions while phasing them out in others.
The future market demand for V8-powered vehicles is likely to continue its downward trend as automotive technology advances. The rise of electric vehicles and the improvement of smaller turbocharged engines are providing alternatives that can match V8 performance with better efficiency. However, the V8 engine is expected to retain a loyal, albeit smaller, customer base in specific vehicle categories and regions for the foreseeable future.
However, the global automotive market has witnessed a gradual decline in demand for V8-powered vehicles. This trend is primarily driven by increasing fuel efficiency standards and growing environmental awareness among consumers. Many countries have implemented stricter emissions regulations, pushing automakers to focus on smaller, more fuel-efficient engines. As a result, the market share of V8-powered vehicles has been steadily decreasing in most segments.
Despite this overall decline, certain niche markets continue to show strong demand for V8 engines. The luxury and high-performance vehicle segments, particularly in North America and the Middle East, still maintain a significant customer base for V8-powered cars. These consumers value the power and prestige associated with V8 engines, often viewing them as a status symbol.
The pickup truck market, especially in the United States, remains a stronghold for V8 engines. Many consumers in this segment prioritize towing capacity and payload, areas where V8 engines excel. However, even in this traditionally V8-dominated market, there is a growing trend towards more efficient V6 engines and hybrid powertrains that can match or exceed V8 performance while offering better fuel economy.
The sports car and muscle car segments also continue to see demand for V8 engines, with enthusiasts and collectors valuing the raw power and nostalgic appeal of these powerplants. However, this market is increasingly niche and faces pressure from high-performance electric and hybrid alternatives that offer comparable or superior acceleration.
Looking at regional variations, North America remains the largest market for V8-powered vehicles, followed by the Middle East. In contrast, European and Asian markets have seen a more rapid decline in V8 demand due to stricter emissions standards and higher fuel costs. This regional disparity has led some automakers to develop market-specific strategies, offering V8 options in certain regions while phasing them out in others.
The future market demand for V8-powered vehicles is likely to continue its downward trend as automotive technology advances. The rise of electric vehicles and the improvement of smaller turbocharged engines are providing alternatives that can match V8 performance with better efficiency. However, the V8 engine is expected to retain a loyal, albeit smaller, customer base in specific vehicle categories and regions for the foreseeable future.
V8 Technology Status and Challenges
V8 engines have long been a symbol of power and performance in the automotive industry. However, their current status and challenges are shaped by evolving market trends, technological advancements, and environmental concerns. The global automotive market has seen a significant shift towards more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles, putting pressure on traditional V8 engines.
In terms of technological development, V8 engines have made considerable progress in recent years. Manufacturers have implemented advanced technologies such as direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. These innovations have allowed V8 engines to remain competitive in certain market segments, particularly in high-performance vehicles and luxury SUVs.
Despite these advancements, V8 engines face significant challenges in meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations worldwide. Many countries have implemented or are planning to implement stricter CO2 emission standards, which pose a substantial hurdle for V8 engines known for their higher fuel consumption and emissions compared to smaller, more efficient powertrains.
The rise of electric and hybrid vehicles presents another major challenge to V8 technology. As battery technology improves and charging infrastructure expands, electric vehicles are becoming more viable alternatives to traditional internal combustion engines, including V8s. This shift is particularly evident in the luxury and performance segments, where electric vehicles are increasingly matching or surpassing the performance capabilities of V8-powered cars.
From a geographical perspective, the development and adoption of V8 engines vary significantly across regions. In North America, V8 engines still maintain a strong presence, particularly in pickup trucks and muscle cars. However, in Europe and Asia, stricter emissions regulations and changing consumer preferences have led to a decline in V8 engine production and sales.
The main technical constraints facing V8 engines include improving fuel efficiency without sacrificing performance, reducing emissions to meet regulatory standards, and competing with the torque and acceleration capabilities of electric powertrains. Engineers are exploring various solutions, such as integrating mild hybrid systems, developing more advanced materials for weight reduction, and optimizing combustion processes.
In conclusion, while V8 engines continue to hold a place in certain market segments, they face significant technological and regulatory challenges. The future of V8 technology in the auto industry will depend on manufacturers' ability to innovate and adapt to changing market demands and environmental regulations. The coming years will likely see a continued decline in V8 engine production, with their use increasingly limited to niche markets and specialized applications.
In terms of technological development, V8 engines have made considerable progress in recent years. Manufacturers have implemented advanced technologies such as direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. These innovations have allowed V8 engines to remain competitive in certain market segments, particularly in high-performance vehicles and luxury SUVs.
Despite these advancements, V8 engines face significant challenges in meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations worldwide. Many countries have implemented or are planning to implement stricter CO2 emission standards, which pose a substantial hurdle for V8 engines known for their higher fuel consumption and emissions compared to smaller, more efficient powertrains.
The rise of electric and hybrid vehicles presents another major challenge to V8 technology. As battery technology improves and charging infrastructure expands, electric vehicles are becoming more viable alternatives to traditional internal combustion engines, including V8s. This shift is particularly evident in the luxury and performance segments, where electric vehicles are increasingly matching or surpassing the performance capabilities of V8-powered cars.
From a geographical perspective, the development and adoption of V8 engines vary significantly across regions. In North America, V8 engines still maintain a strong presence, particularly in pickup trucks and muscle cars. However, in Europe and Asia, stricter emissions regulations and changing consumer preferences have led to a decline in V8 engine production and sales.
The main technical constraints facing V8 engines include improving fuel efficiency without sacrificing performance, reducing emissions to meet regulatory standards, and competing with the torque and acceleration capabilities of electric powertrains. Engineers are exploring various solutions, such as integrating mild hybrid systems, developing more advanced materials for weight reduction, and optimizing combustion processes.
In conclusion, while V8 engines continue to hold a place in certain market segments, they face significant technological and regulatory challenges. The future of V8 technology in the auto industry will depend on manufacturers' ability to innovate and adapt to changing market demands and environmental regulations. The coming years will likely see a continued decline in V8 engine production, with their use increasingly limited to niche markets and specialized applications.
Current V8 Engine Design Solutions
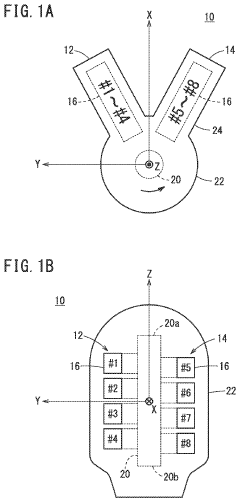
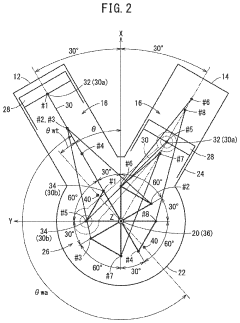
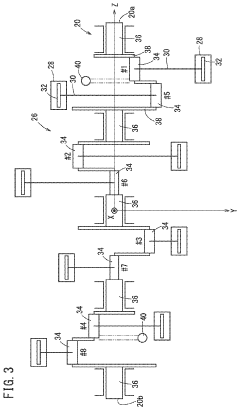
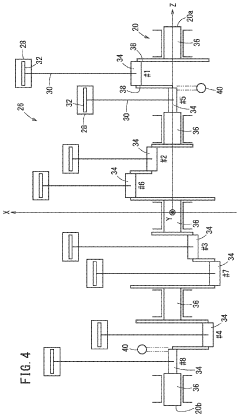
01 V8 Engine Design and Configuration
V8 engines are designed with eight cylinders arranged in two banks of four, forming a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact design, improved power output, and better balance compared to inline engines. Various aspects of V8 engine design, including cylinder arrangement, crankshaft configuration, and valve train systems, are continuously optimized for performance and efficiency.- V8 Engine Design and Configuration: V8 engines are designed with eight cylinders arranged in two banks of four, forming a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact design while providing high power output. The design often includes features for improved performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.
- Valve Train and Cylinder Head Improvements: Advancements in V8 engine valve trains and cylinder heads focus on optimizing airflow, combustion efficiency, and overall engine performance. These improvements may include variable valve timing, multi-valve configurations, and innovative cylinder head designs.
- Fuel Injection and Combustion Optimization: Modern V8 engines incorporate advanced fuel injection systems and combustion chamber designs to enhance fuel efficiency and power output. This includes direct injection technology, improved fuel atomization, and optimized combustion chamber geometry.
- Turbocharging and Supercharging Systems: V8 engines often utilize forced induction systems such as turbochargers or superchargers to increase power output and efficiency. These systems compress the intake air, allowing for more fuel to be burned and resulting in higher performance.
- Engine Management and Control Systems: Advanced electronic control systems are employed in V8 engines to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. These systems manage various engine parameters, including fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and valve actuation, to ensure optimal operation across different driving conditions.
02 Fuel Injection and Combustion Systems
Advanced fuel injection and combustion systems are crucial for V8 engine performance. These systems include direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation technologies. Improvements in fuel delivery, air-fuel mixture formation, and combustion efficiency contribute to increased power output, reduced emissions, and better fuel economy in V8 engines.Expand Specific Solutions03 Turbocharging and Supercharging
Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, are often employed in V8 engines to boost power output and efficiency. These systems compress the intake air, allowing more fuel to be burned and increasing engine performance. Various designs and configurations of turbochargers and superchargers are developed to optimize V8 engine performance across different operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Engine Management and Control Systems
Advanced engine management and control systems play a crucial role in optimizing V8 engine performance. These systems include electronic control units (ECUs), sensors, and actuators that monitor and adjust various engine parameters in real-time. Innovations in engine control algorithms, adaptive learning, and predictive maintenance contribute to improved efficiency, reliability, and performance of V8 engines.Expand Specific Solutions05 Materials and Manufacturing Techniques
Advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques contribute to the development of lighter, stronger, and more efficient V8 engines. The use of lightweight alloys, composite materials, and advanced manufacturing processes such as 3D printing and precision machining enables the production of engine components with improved durability, heat resistance, and performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions
Major V8 Engine Manufacturers and Automakers
The V8 engine market is in a mature stage, with established players dominating the landscape. The global V8 engine market size is estimated to be in the billions of dollars, driven by demand in high-performance vehicles and luxury segments. Technologically, V8 engines are well-developed, but facing challenges from stricter emissions regulations and the shift towards electrification. Key players like GM, Toyota, Honda, BMW, and Nissan are investing in improving V8 efficiency and performance while also diversifying into hybrid and electric powertrains. Smaller companies like Fuel Performance Solutions are focusing on niche innovations to enhance V8 fuel economy and emissions. Overall, the V8 market remains significant but is evolving rapidly due to regulatory and technological pressures.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has been at the forefront of V8 engine development, particularly with their Small Block V8 series. Their latest V8 engines incorporate advanced technologies such as Dynamic Fuel Management (DFM) and Active Fuel Management (AFM) to improve fuel efficiency without sacrificing power[1]. GM's V8 engines, such as the 6.2L V8 found in the Chevrolet Corvette, utilize direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation to achieve a balance of performance and efficiency[2]. The company has also been exploring ways to make V8 engines more environmentally friendly, including the development of a new generation of small-displacement V8s that can meet stringent emissions standards while still delivering the power and torque customers expect[3].
Strengths: Strong brand recognition for V8 performance, advanced fuel management systems, and a wide range of applications from sports cars to trucks. Weaknesses: Increasing pressure to shift towards electrification may impact long-term V8 development resources.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota's approach to V8 engines focuses on reliability and efficiency. Their UR series V8 engines, found in vehicles like the Toyota Tundra and Lexus models, incorporate dual overhead camshafts, variable valve timing, and direct injection technology[4]. Toyota has also developed a high-performance V8 for their Lexus F models, which uses a dual-intake system and titanium valves to achieve high power output while meeting emissions standards[5]. In response to market trends, Toyota has been gradually reducing its V8 offerings, focusing on turbocharged V6 engines and hybrid powertrains as alternatives. However, they continue to develop V8 engines for specific markets and applications where demand remains strong, such as in large SUVs and trucks[6].
Strengths: Reputation for reliability, efficient manufacturing processes, and a balanced approach to performance and fuel economy. Weaknesses: Limited focus on high-performance V8s compared to some competitors, and a stronger emphasis on alternative powertrains.
Key V8 Engine Innovations and Patents
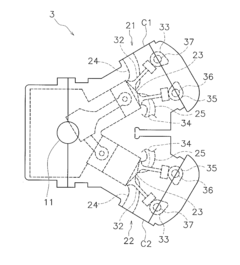
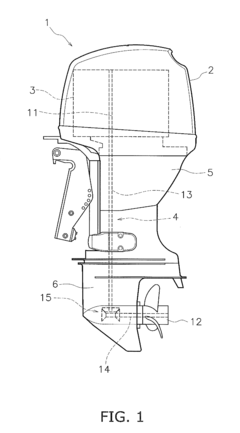
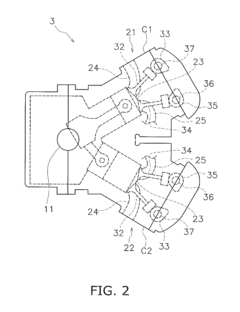
V8 engine and outboard motor
PatentActiveUS20160341097A1
Innovation
- A V8 engine design with a simple construction featuring aggregated exhaust pathways and adjustable exhaust cams, where the central angle of exhaust cams for each cylinder is optimized to minimize valve overlap and reduce exhaust interference, allowing for even firing intervals and improved exhaust gas management.
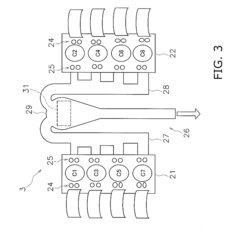
V8 engine
PatentActiveUS20230109196A1
Innovation
- The V8 engine configuration features crank pins arranged at 90° intervals on one bank and offset by 60° on the other bank, allowing for cancellation of primary inertia couples without additional specialized components by optimizing the arrangement of crank pins and connecting rods.
Environmental Impact of V8 Engines
The environmental impact of V8 engines has been a significant concern in the automotive industry for decades. These powerful engines, known for their high performance and distinctive sound, have long been associated with luxury vehicles and sports cars. However, their substantial fuel consumption and emissions have increasingly come under scrutiny in an era of growing environmental awareness and stricter regulations.
V8 engines typically produce higher levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to smaller, more fuel-efficient engines. This contributes to the overall greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector, which is a major contributor to global climate change. The increased fuel consumption of V8 engines also leads to greater extraction and processing of fossil fuels, further exacerbating environmental issues related to oil production and transportation.
In urban areas, V8 engines contribute to air pollution through the release of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and other harmful pollutants. These emissions can have severe health implications for local populations, including respiratory problems and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. The noise pollution generated by V8 engines, while appealing to some enthusiasts, can also negatively impact urban environments and wildlife habitats.
The manufacturing process of V8 engines itself has environmental implications. The production of larger, more complex engines requires more raw materials and energy, leading to increased industrial emissions and resource consumption. Additionally, the heavier weight of vehicles equipped with V8 engines results in increased tire wear, contributing to microplastic pollution in water systems and soil.
As environmental regulations become more stringent worldwide, automakers are facing pressure to reduce the environmental impact of their vehicles. This has led to innovations in V8 engine technology, including the development of more efficient fuel injection systems, cylinder deactivation technologies, and the integration of hybrid systems. These advancements aim to maintain the performance characteristics of V8 engines while reducing their environmental footprint.
Despite these improvements, the long-term sustainability of V8 engines in the automotive market remains uncertain. The shift towards electric vehicles and alternative powertrains is challenging the traditional dominance of high-displacement engines. As consumers become more environmentally conscious and governments implement stricter emissions standards, the role of V8 engines in the auto industry is likely to evolve, potentially becoming more niche or transitioning towards more sustainable technologies.
V8 engines typically produce higher levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to smaller, more fuel-efficient engines. This contributes to the overall greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector, which is a major contributor to global climate change. The increased fuel consumption of V8 engines also leads to greater extraction and processing of fossil fuels, further exacerbating environmental issues related to oil production and transportation.
In urban areas, V8 engines contribute to air pollution through the release of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and other harmful pollutants. These emissions can have severe health implications for local populations, including respiratory problems and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. The noise pollution generated by V8 engines, while appealing to some enthusiasts, can also negatively impact urban environments and wildlife habitats.
The manufacturing process of V8 engines itself has environmental implications. The production of larger, more complex engines requires more raw materials and energy, leading to increased industrial emissions and resource consumption. Additionally, the heavier weight of vehicles equipped with V8 engines results in increased tire wear, contributing to microplastic pollution in water systems and soil.
As environmental regulations become more stringent worldwide, automakers are facing pressure to reduce the environmental impact of their vehicles. This has led to innovations in V8 engine technology, including the development of more efficient fuel injection systems, cylinder deactivation technologies, and the integration of hybrid systems. These advancements aim to maintain the performance characteristics of V8 engines while reducing their environmental footprint.
Despite these improvements, the long-term sustainability of V8 engines in the automotive market remains uncertain. The shift towards electric vehicles and alternative powertrains is challenging the traditional dominance of high-displacement engines. As consumers become more environmentally conscious and governments implement stricter emissions standards, the role of V8 engines in the auto industry is likely to evolve, potentially becoming more niche or transitioning towards more sustainable technologies.
V8 Engine Regulations and Policies
V8 engine regulations and policies have significantly shaped the automotive industry landscape, influencing market trends and manufacturer strategies. These regulations primarily focus on emissions control and fuel efficiency standards, which have become increasingly stringent over the years.
In the United States, the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards have played a crucial role in regulating V8 engines. These standards, first introduced in 1975, have progressively tightened, pushing automakers to improve fuel efficiency across their vehicle lineups. As a result, manufacturers have been compelled to innovate and develop more efficient V8 engines or reduce their reliance on these powerplants altogether.
The European Union has implemented similar measures through its CO2 emissions regulations for new passenger cars. These regulations have set increasingly ambitious targets for reducing fleet-wide average emissions, indirectly impacting the viability of V8 engines in the European market. Consequently, many European automakers have shifted towards smaller, turbocharged engines or hybrid powertrains to meet these stringent requirements.
China, the world's largest automotive market, has also introduced policies aimed at reducing emissions and promoting fuel efficiency. The country's New Energy Vehicle (NEV) mandate and fuel consumption regulations have encouraged automakers to focus on electric and hybrid technologies, potentially limiting the future market for V8-powered vehicles in the region.
Global efforts to combat climate change have led to the introduction of carbon pricing mechanisms and tax incentives for low-emission vehicles in various countries. These policies have indirectly affected the market for V8 engines by making them less economically attractive to both manufacturers and consumers.
The implementation of stricter noise pollution regulations in urban areas has also impacted V8 engines. Many cities have introduced noise limits for vehicles, which can be challenging for high-performance V8 engines to meet without significant modifications.
Despite these regulatory challenges, some jurisdictions have introduced exemptions or special provisions for certain types of V8-powered vehicles. For instance, some countries offer exemptions for classic or historic vehicles, allowing enthusiasts to continue operating older V8-powered cars without meeting current emissions standards.
As the automotive industry transitions towards electrification, regulations surrounding V8 engines are likely to become even more stringent. Many countries have announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines entirely in the coming decades, which will have profound implications for the future of V8 engines in the global automotive market.
In the United States, the Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards have played a crucial role in regulating V8 engines. These standards, first introduced in 1975, have progressively tightened, pushing automakers to improve fuel efficiency across their vehicle lineups. As a result, manufacturers have been compelled to innovate and develop more efficient V8 engines or reduce their reliance on these powerplants altogether.
The European Union has implemented similar measures through its CO2 emissions regulations for new passenger cars. These regulations have set increasingly ambitious targets for reducing fleet-wide average emissions, indirectly impacting the viability of V8 engines in the European market. Consequently, many European automakers have shifted towards smaller, turbocharged engines or hybrid powertrains to meet these stringent requirements.
China, the world's largest automotive market, has also introduced policies aimed at reducing emissions and promoting fuel efficiency. The country's New Energy Vehicle (NEV) mandate and fuel consumption regulations have encouraged automakers to focus on electric and hybrid technologies, potentially limiting the future market for V8-powered vehicles in the region.
Global efforts to combat climate change have led to the introduction of carbon pricing mechanisms and tax incentives for low-emission vehicles in various countries. These policies have indirectly affected the market for V8 engines by making them less economically attractive to both manufacturers and consumers.
The implementation of stricter noise pollution regulations in urban areas has also impacted V8 engines. Many cities have introduced noise limits for vehicles, which can be challenging for high-performance V8 engines to meet without significant modifications.
Despite these regulatory challenges, some jurisdictions have introduced exemptions or special provisions for certain types of V8-powered vehicles. For instance, some countries offer exemptions for classic or historic vehicles, allowing enthusiasts to continue operating older V8-powered cars without meeting current emissions standards.
As the automotive industry transitions towards electrification, regulations surrounding V8 engines are likely to become even more stringent. Many countries have announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines entirely in the coming decades, which will have profound implications for the future of V8 engines in the global automotive market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!