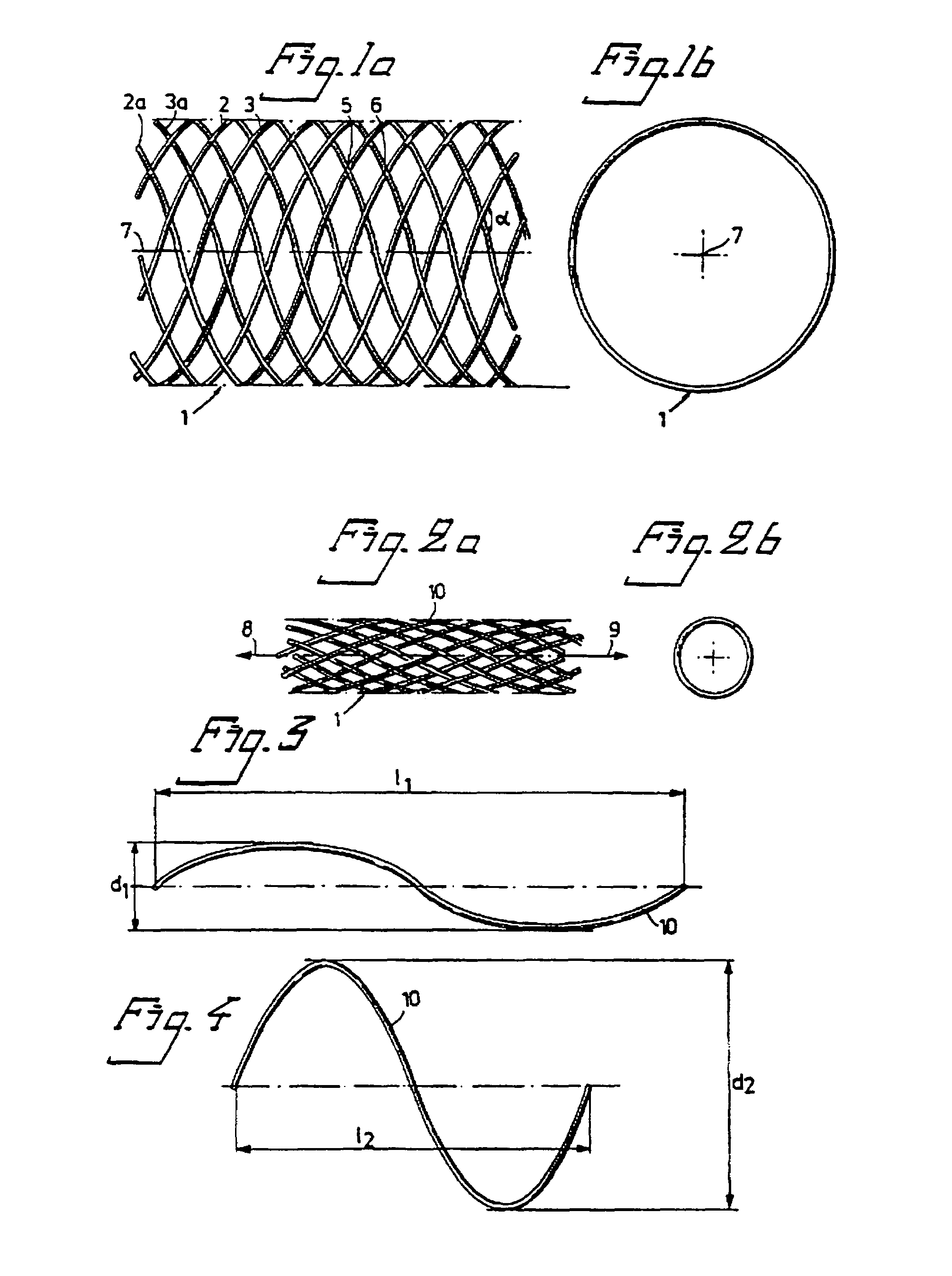
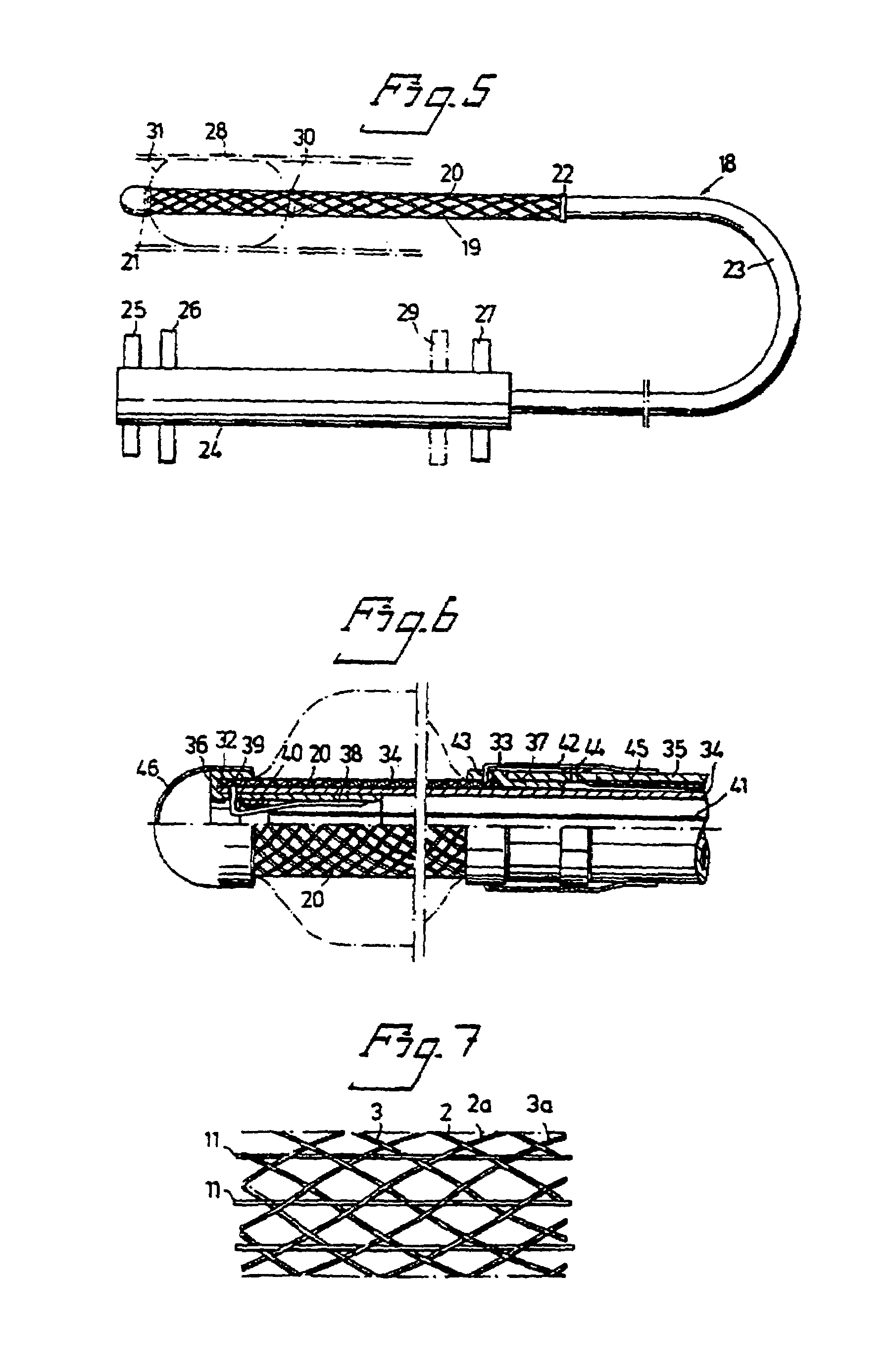
Patents
Literature
169results about How to "Improve radial strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
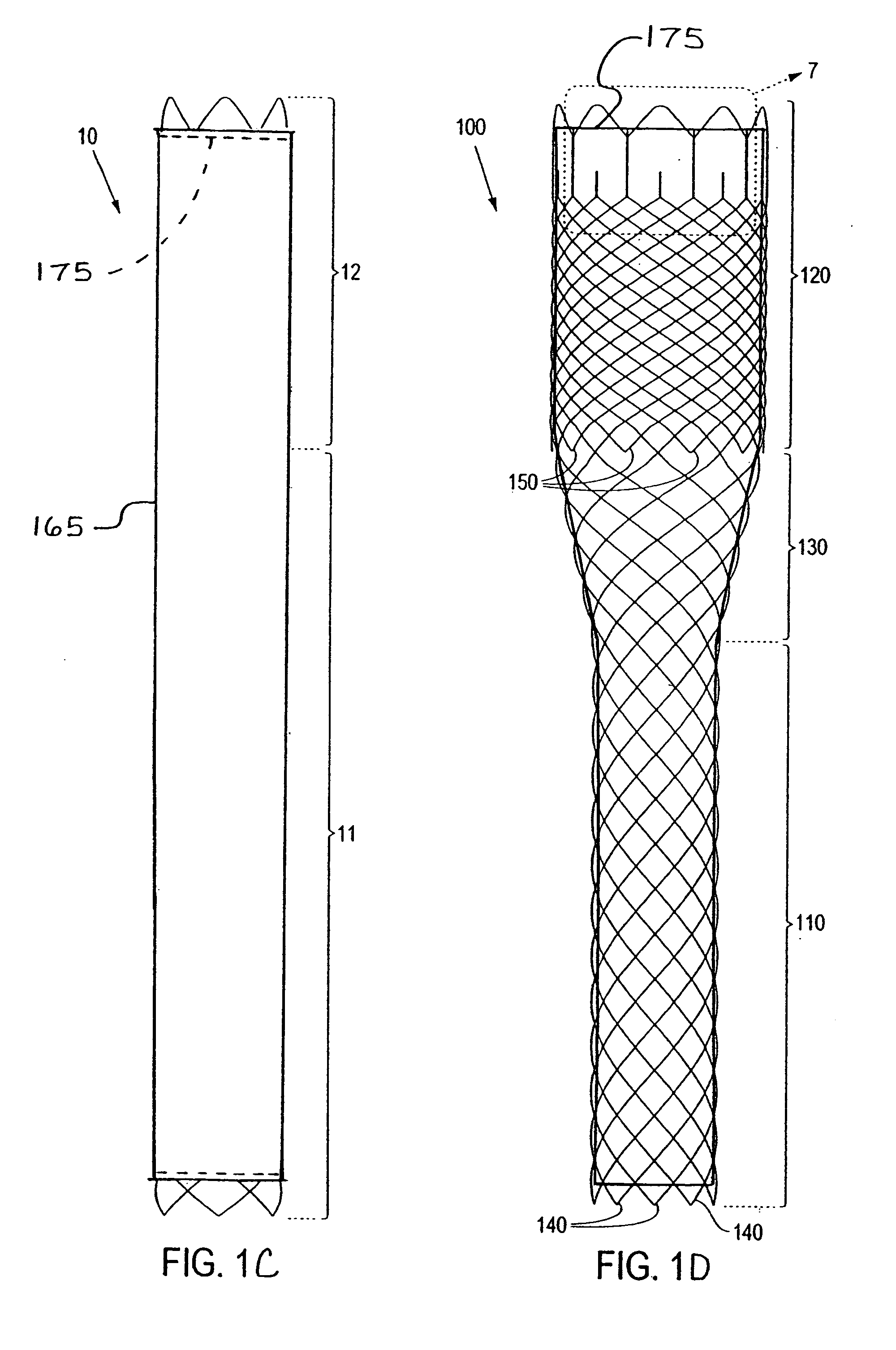
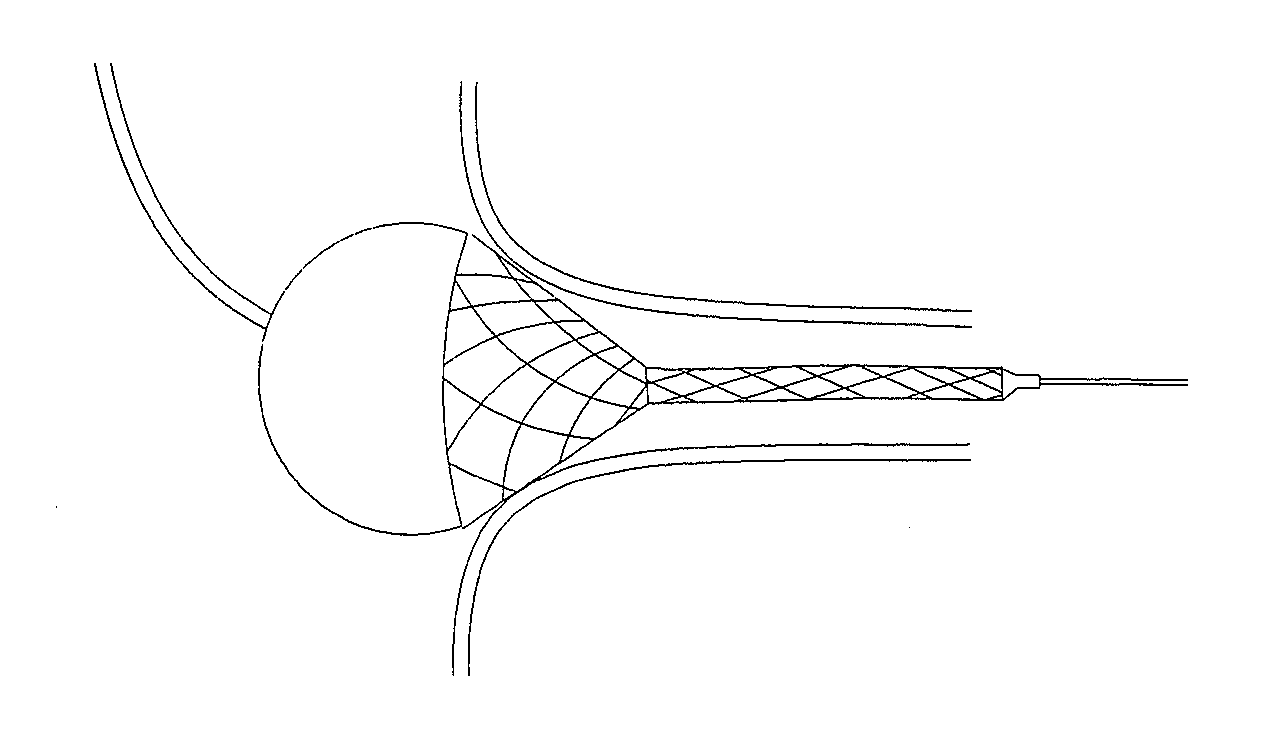
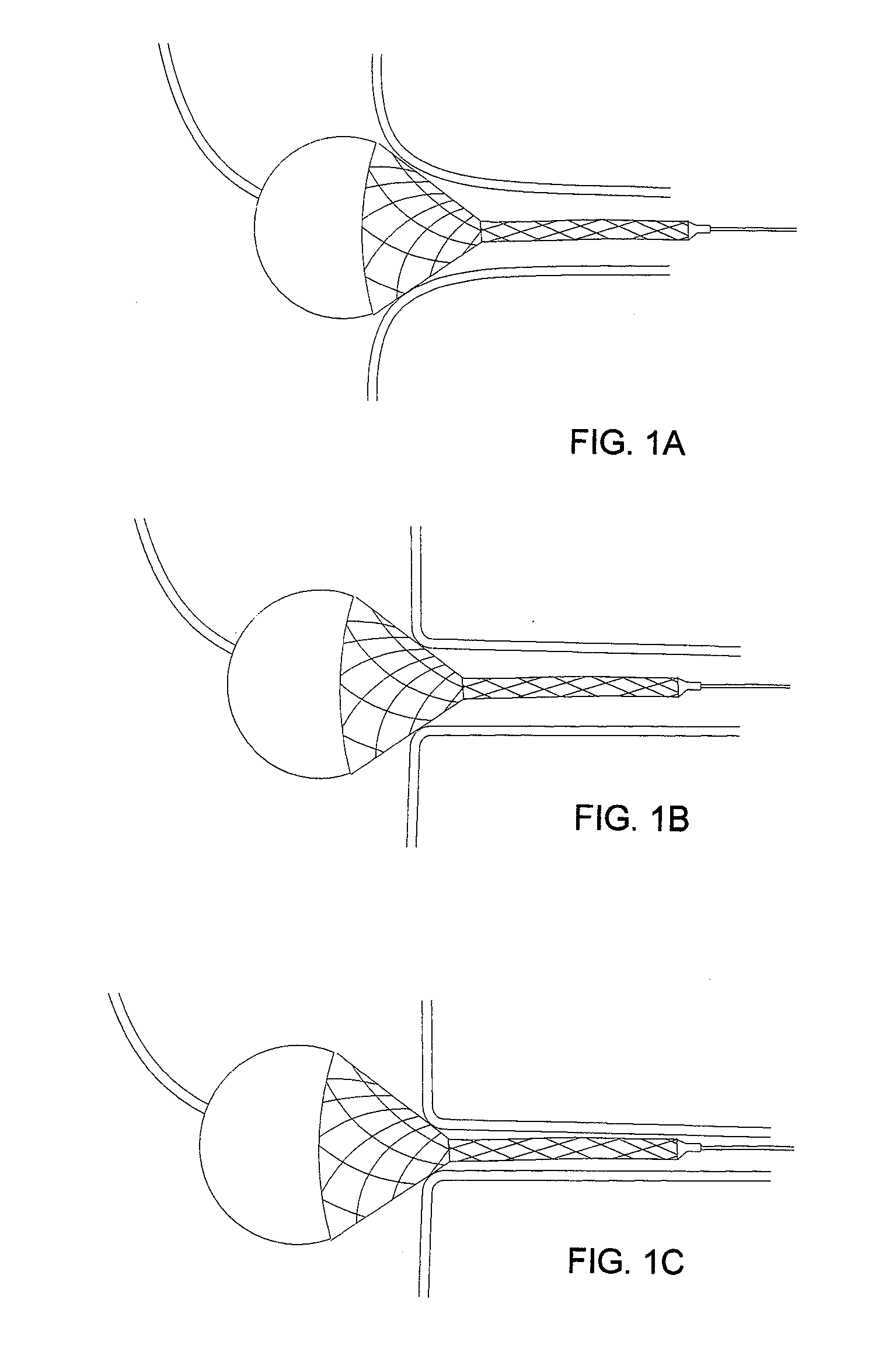
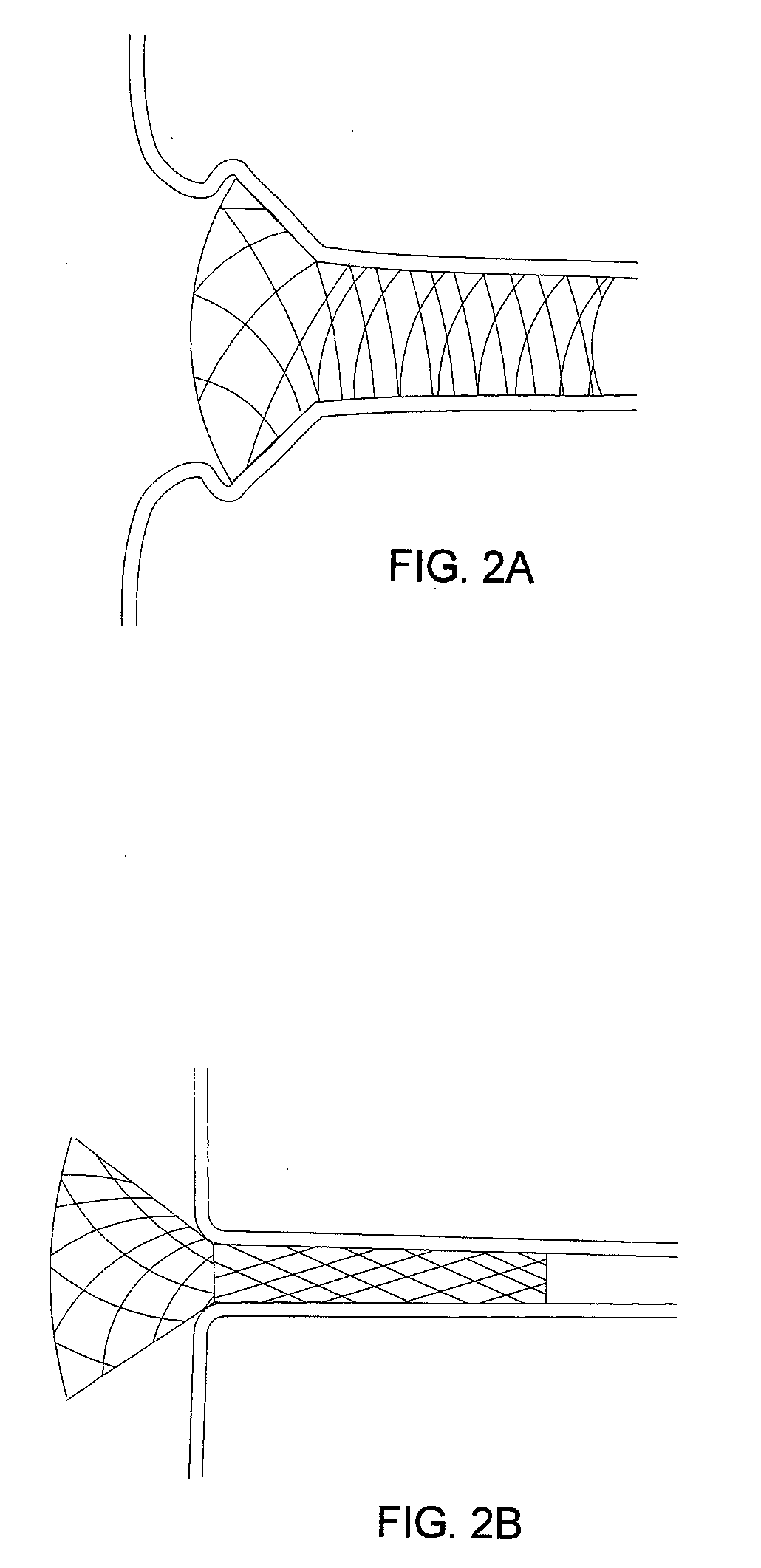
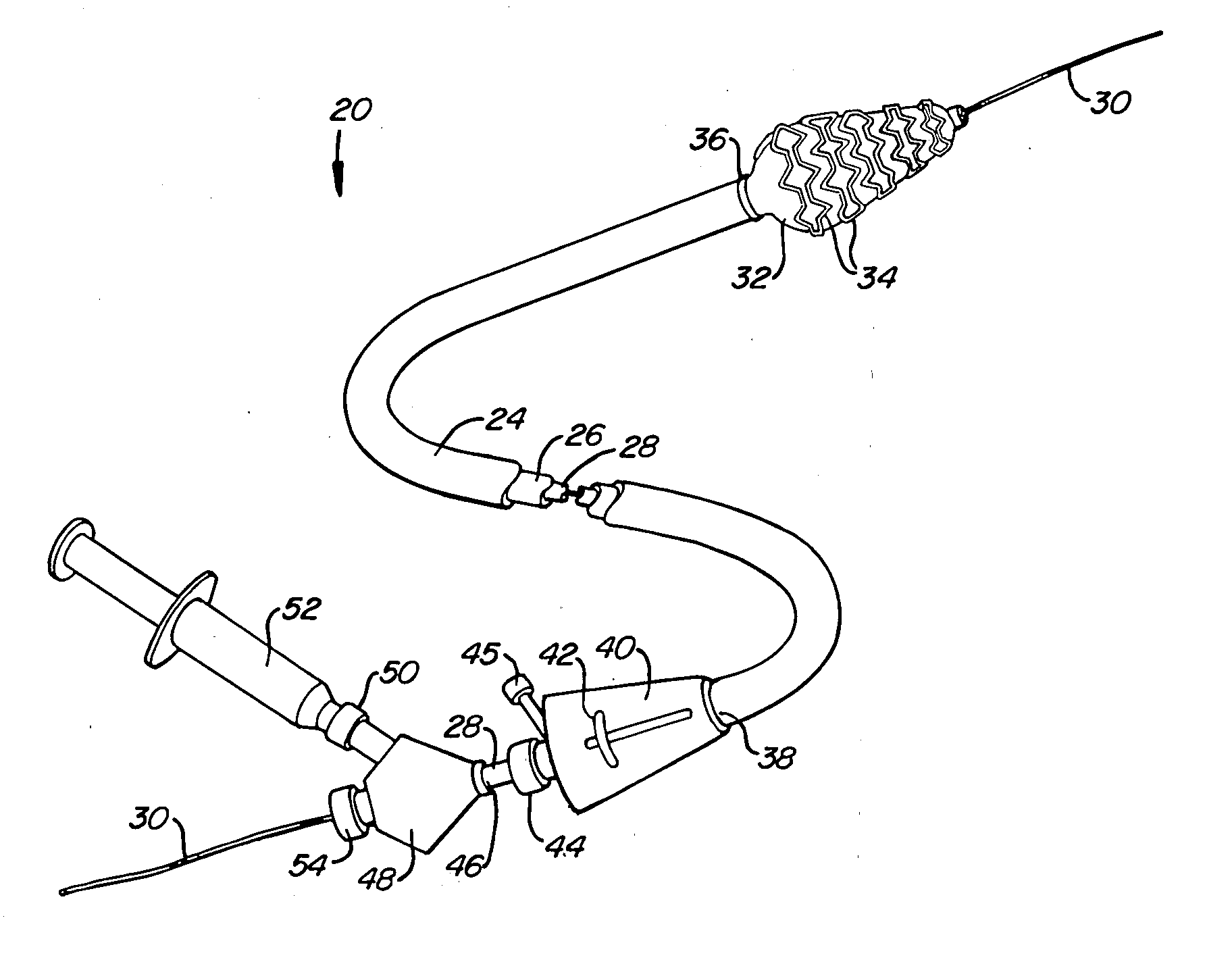
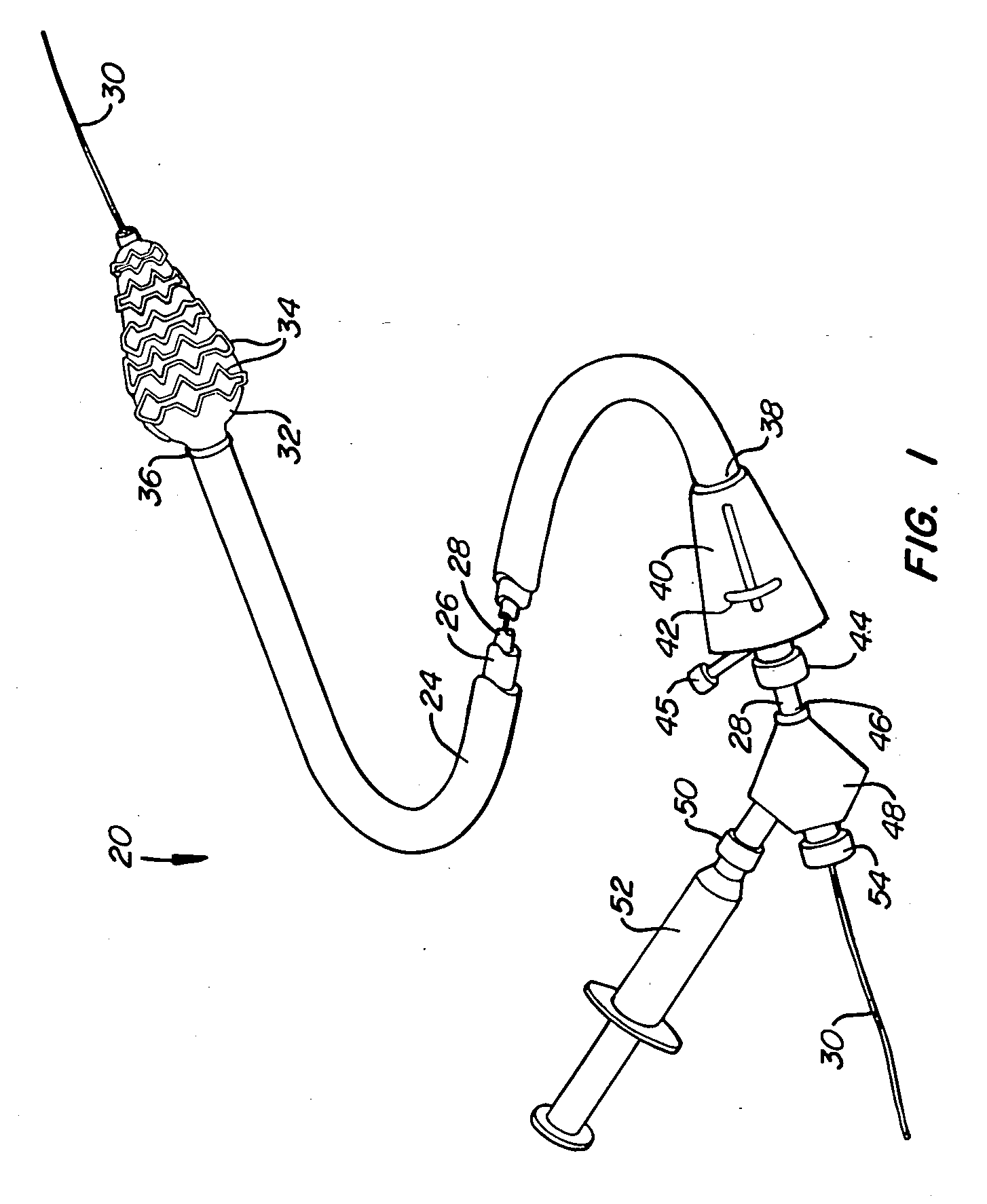
Externally Expandable Heart Valve Anchor and Method
InactiveUS20070010876A1Reduce leakageReduce regurgitationStentsBalloon catheterBlood vesselVALVE PORT
The invention includes methods of and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a heart valve of a patient. One aspect of the invention provides a method including the steps of endovascularly delivering a replacement valve and an expandable anchor to a vicinity of the heart valve in an unexpanded configuration; and applying an external non-hydraulic or non-pneumatic actuation force on the anchor to change the shape of the anchor, such as by applying proximally and / or distally directed force on the anchor using a releasable deployment tool to expand and contract the anchor or parts of the anchor.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
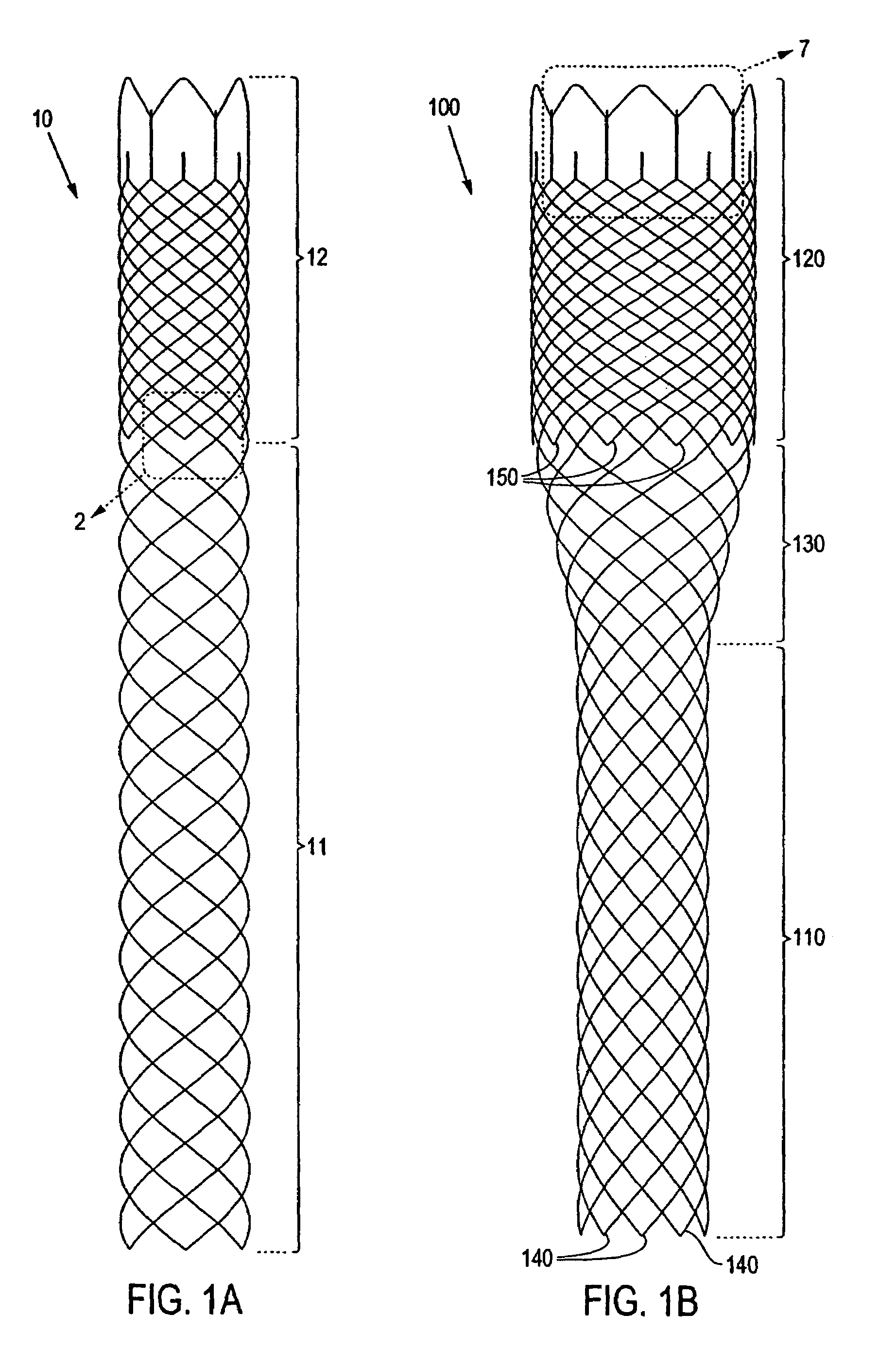
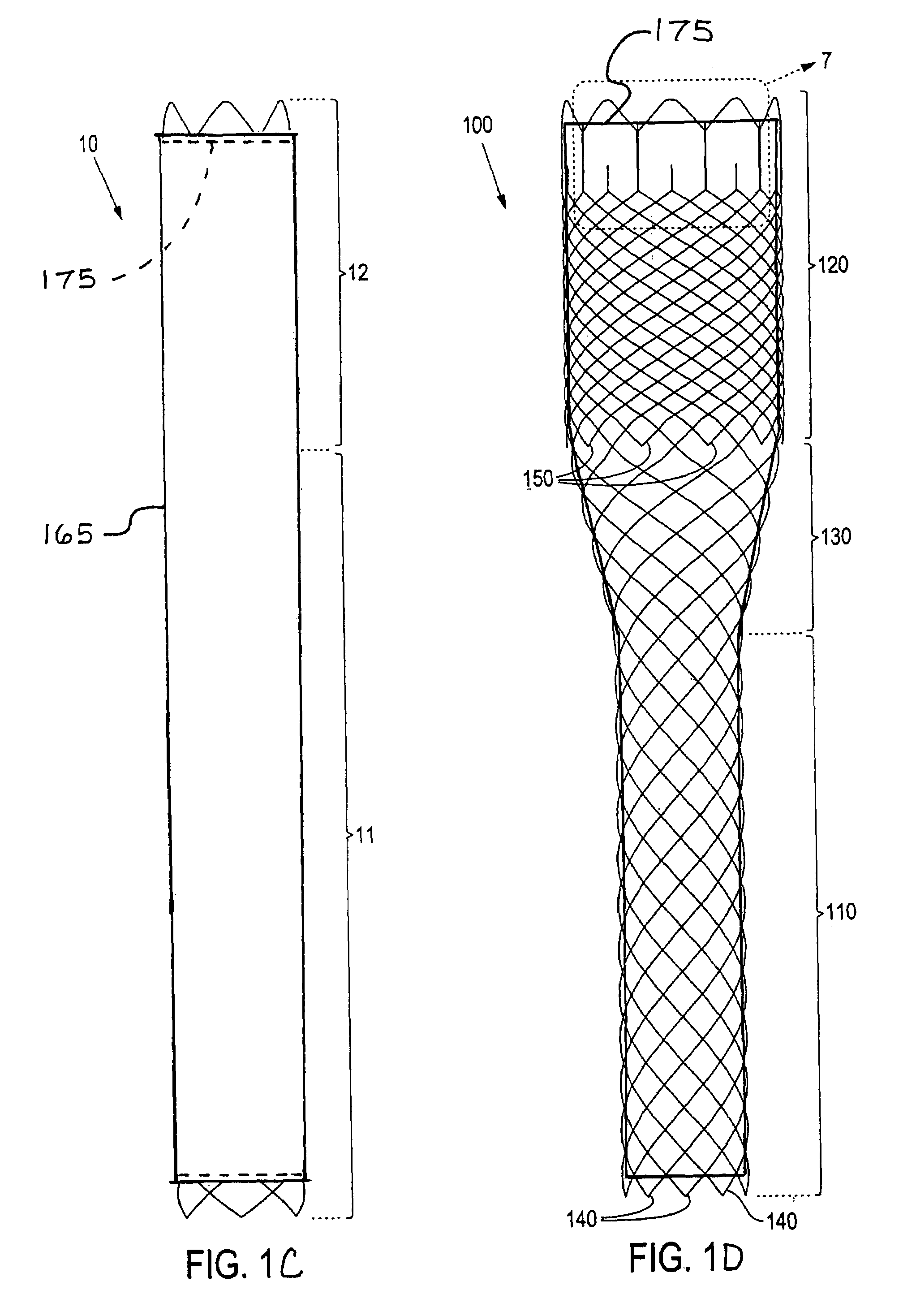
Prosthetic heart valves, scaffolding structures, and systems and methods for implantation of same
InactiveUS20050203617A1Improve radial strengthIncrease frictionBalloon catheterHeart valvesPercutaneous aortic valve replacementProsthetic valve
Prosthetic valves and their component parts are described, as are prosthetic valve delivery devices and methods for their use. The prosthetic valves are particularly adapted for use in percutaneous aortic valve replacement procedures. The delivery devices are particularly adapted for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:AORTX
Prosthetic heart valves, scaffolding structures, and systems and methods for implantation of same
InactiveUS20050203614A1Inhibit migrationGood tissue adhesionBalloon catheterEar treatmentProsthesisBiomedical engineering
Prosthetic valves and their component parts are described, as are prosthetic valve delivery devices and methods for their use. The prosthetic valves are particularly adapted for use in percutaneous aortic valve replacement procedures. The delivery devices are particularly adapted for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:AORTX
Prosthetic heart valves, scaffolding structures, and systems and methods for implantation of same
InactiveUS20050203615A1Inhibit migrationGood tissue adhesionBalloon catheterHeart valvesPercutaneous aortic valve replacementProsthetic valve
Prosthetic valves and their component parts are described, as are prosthetic valve delivery devices and methods for their use. The prosthetic valves are particularly adapted for use in percutaneous aortic valve replacement procedures. The delivery devices are particularly adapted for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:AORTX
Prosthetic heart valves, support structures and systems and methods for implanting same
InactiveUS20090210052A1Inhibit migrationGood tissue adhesionBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthetic valveProsthesis
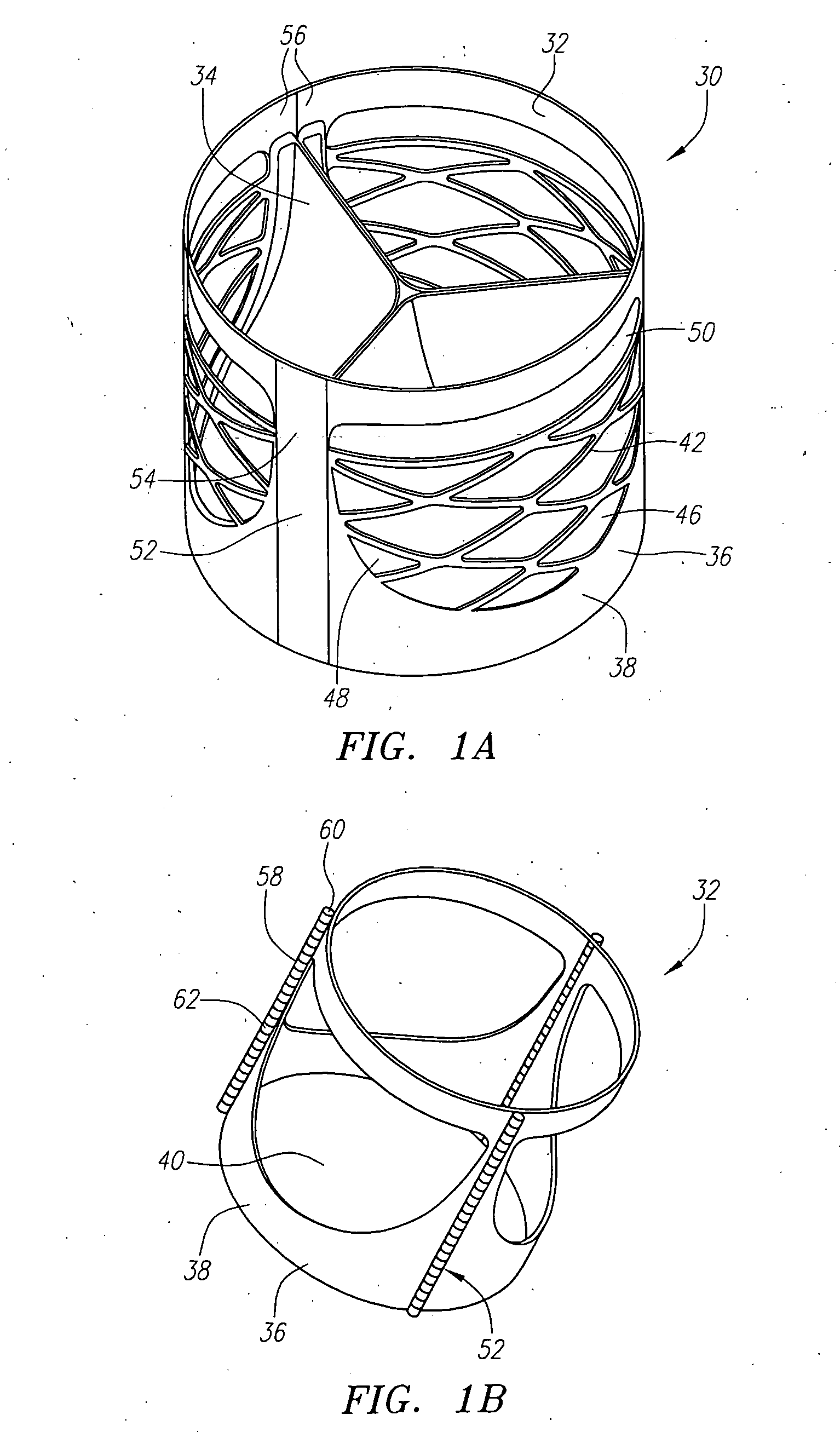
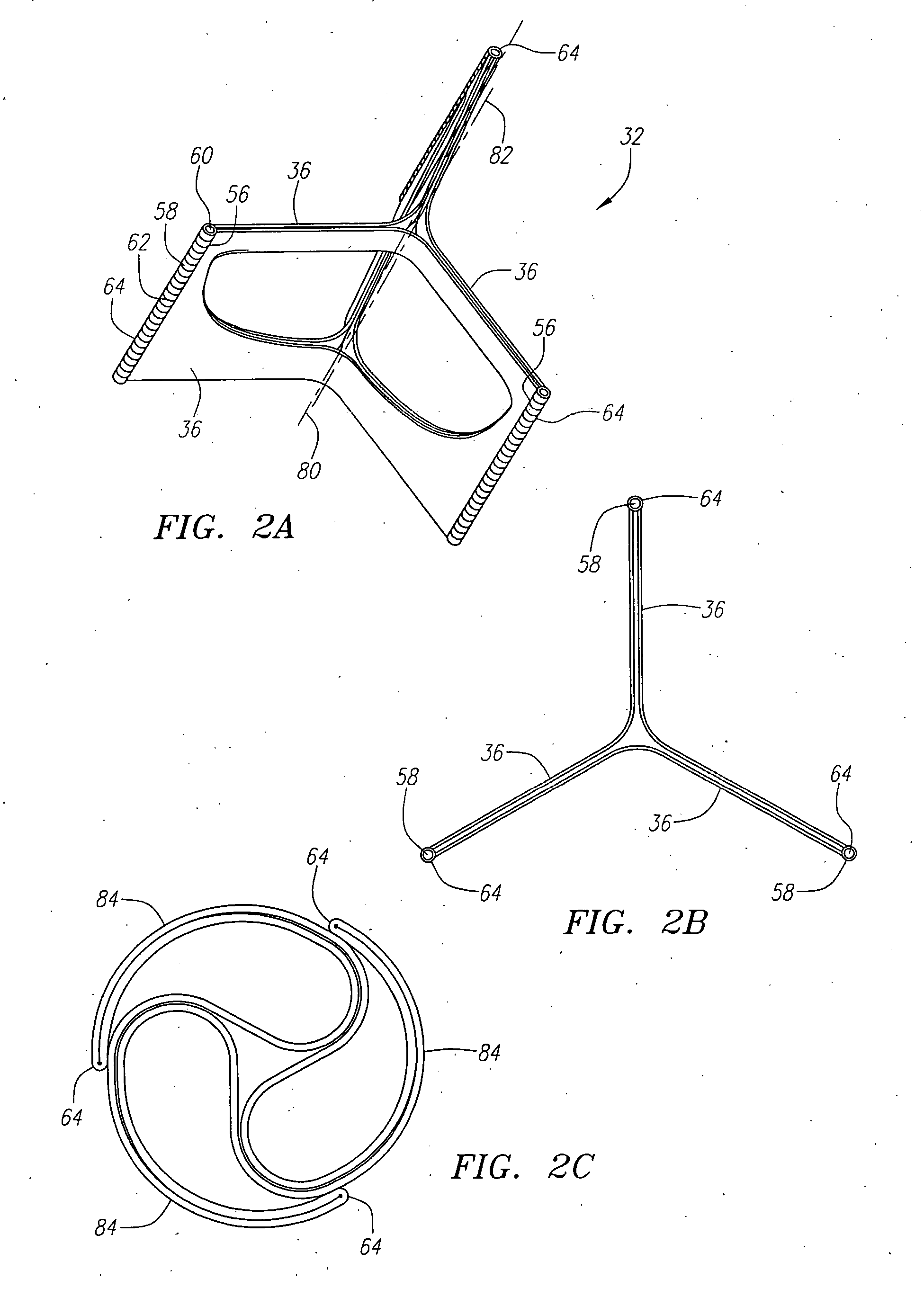
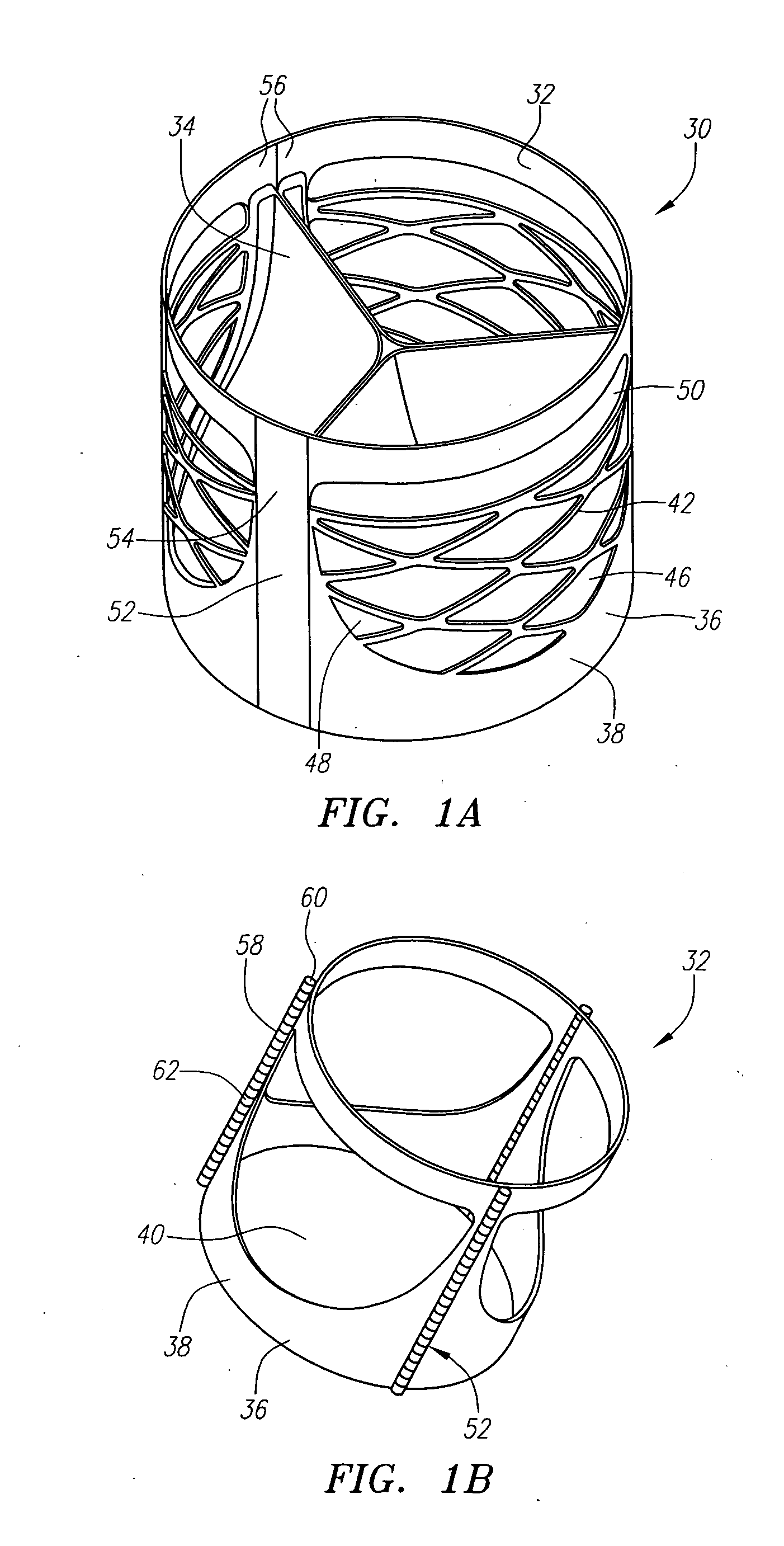
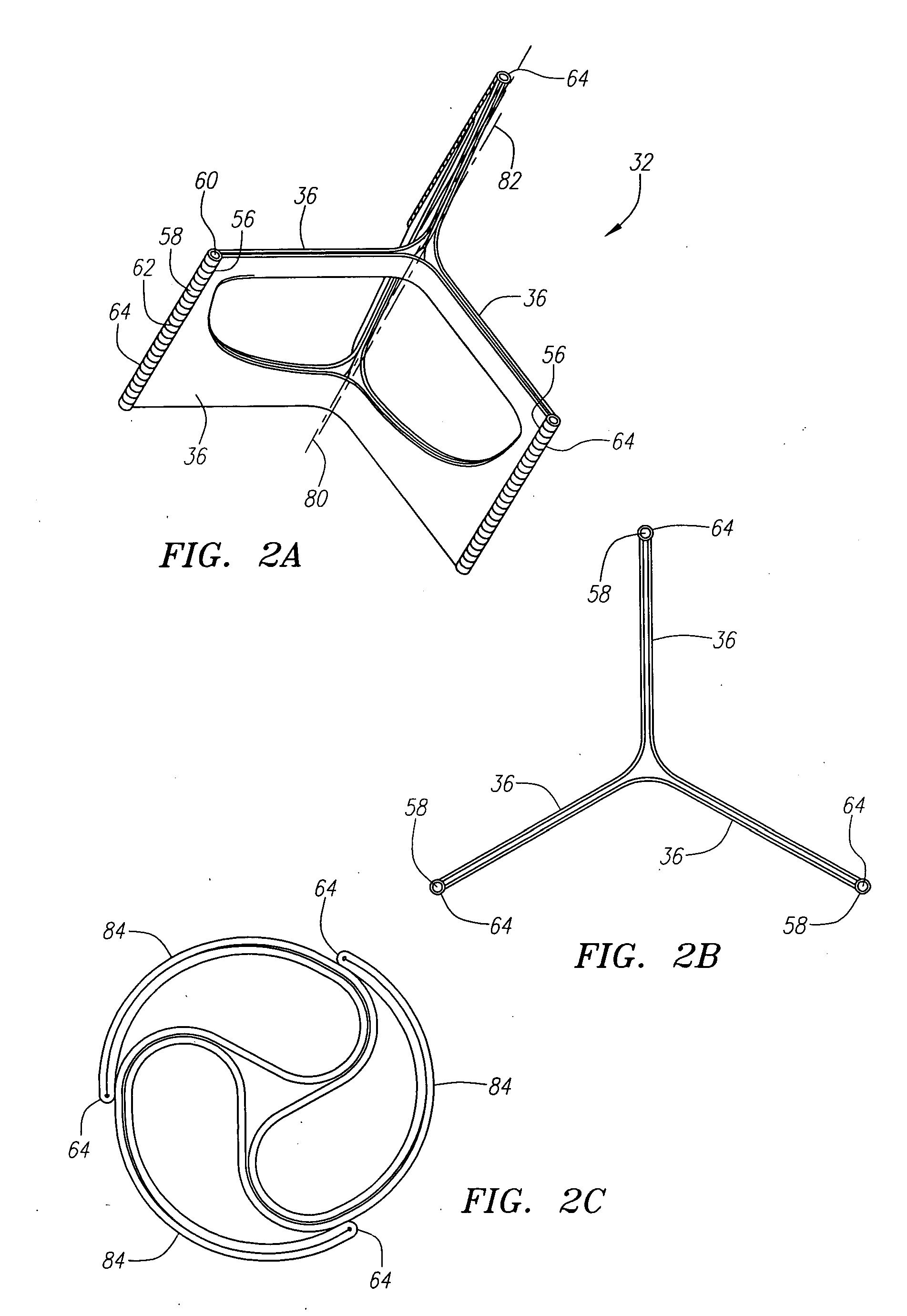
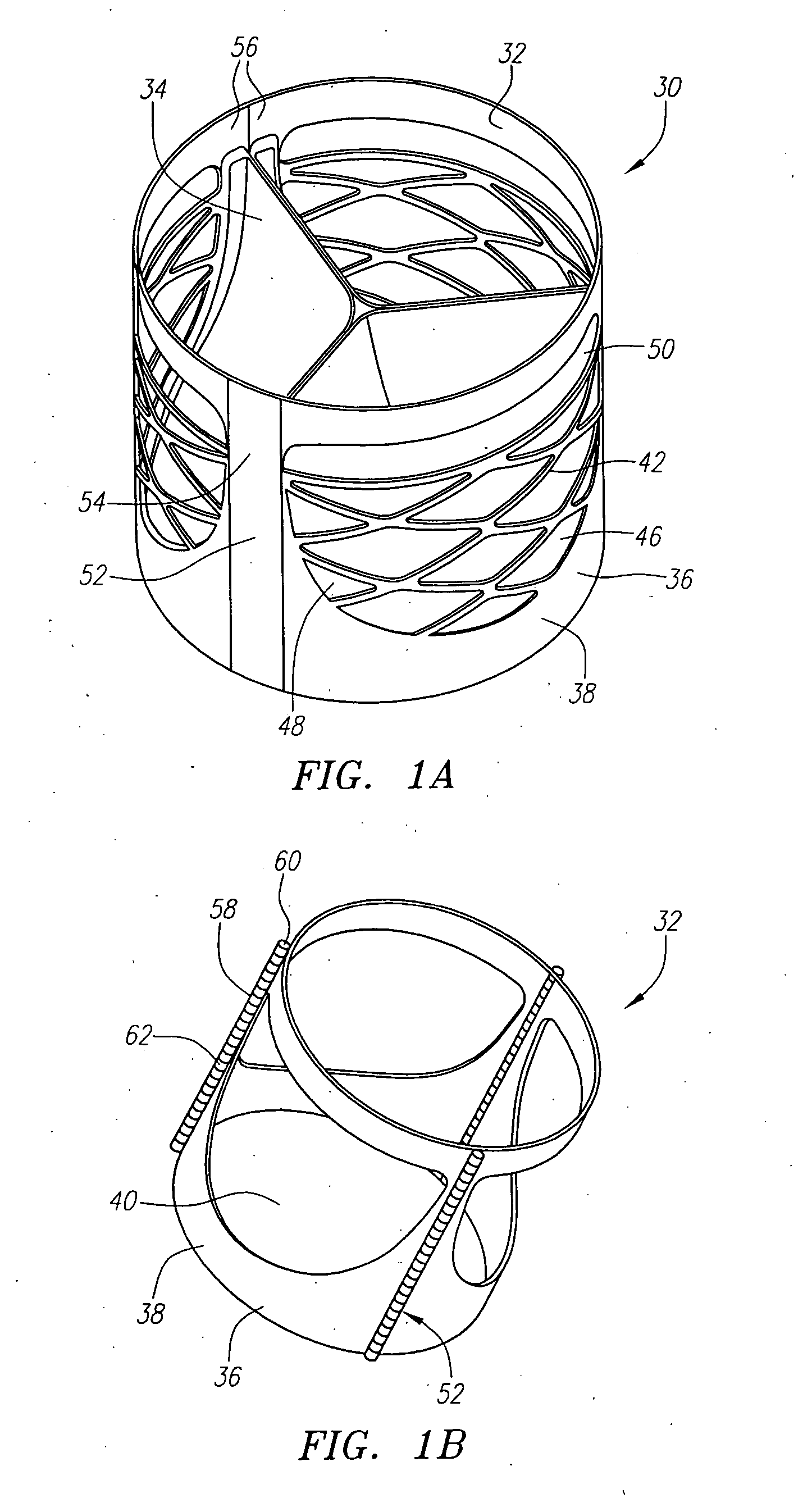
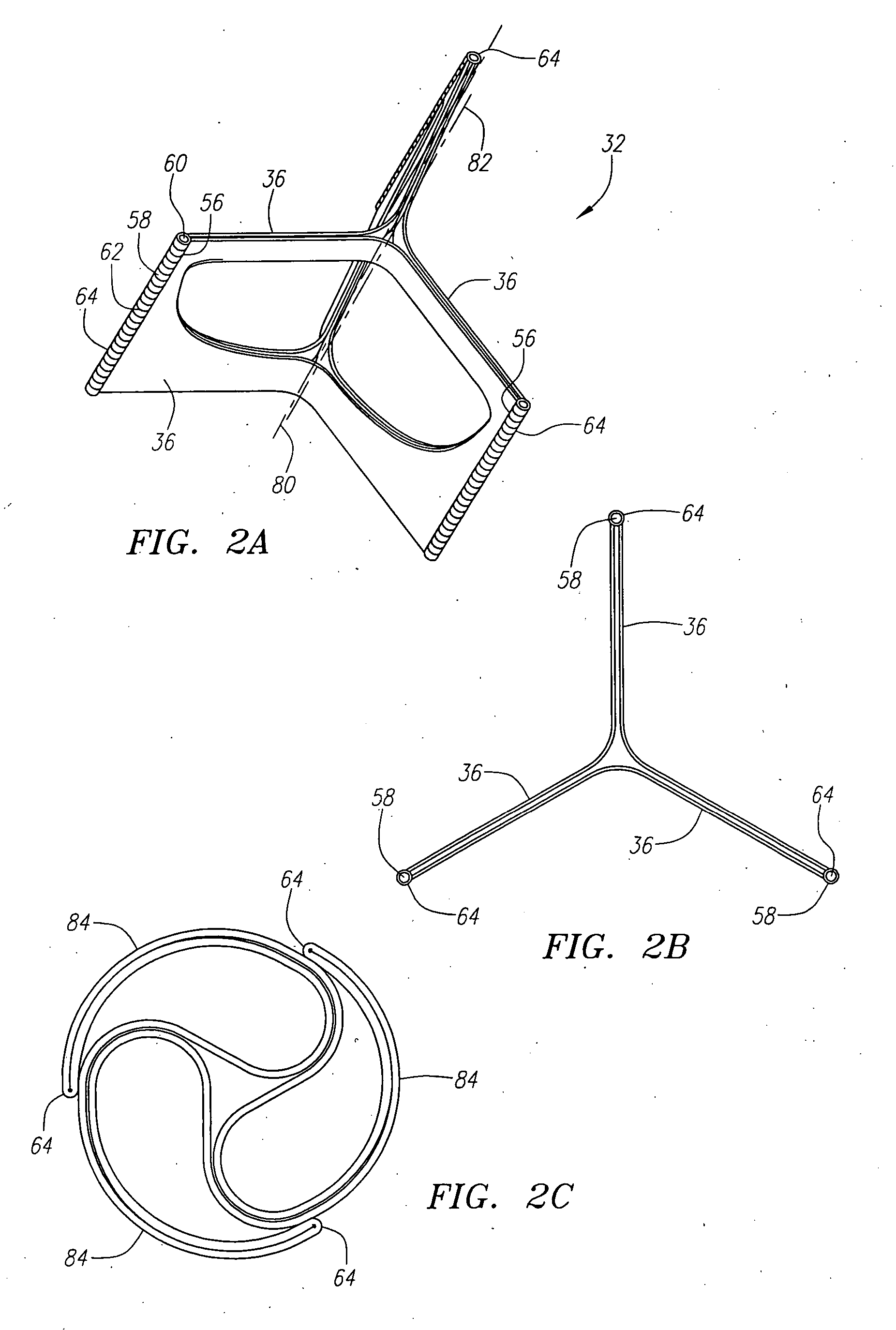
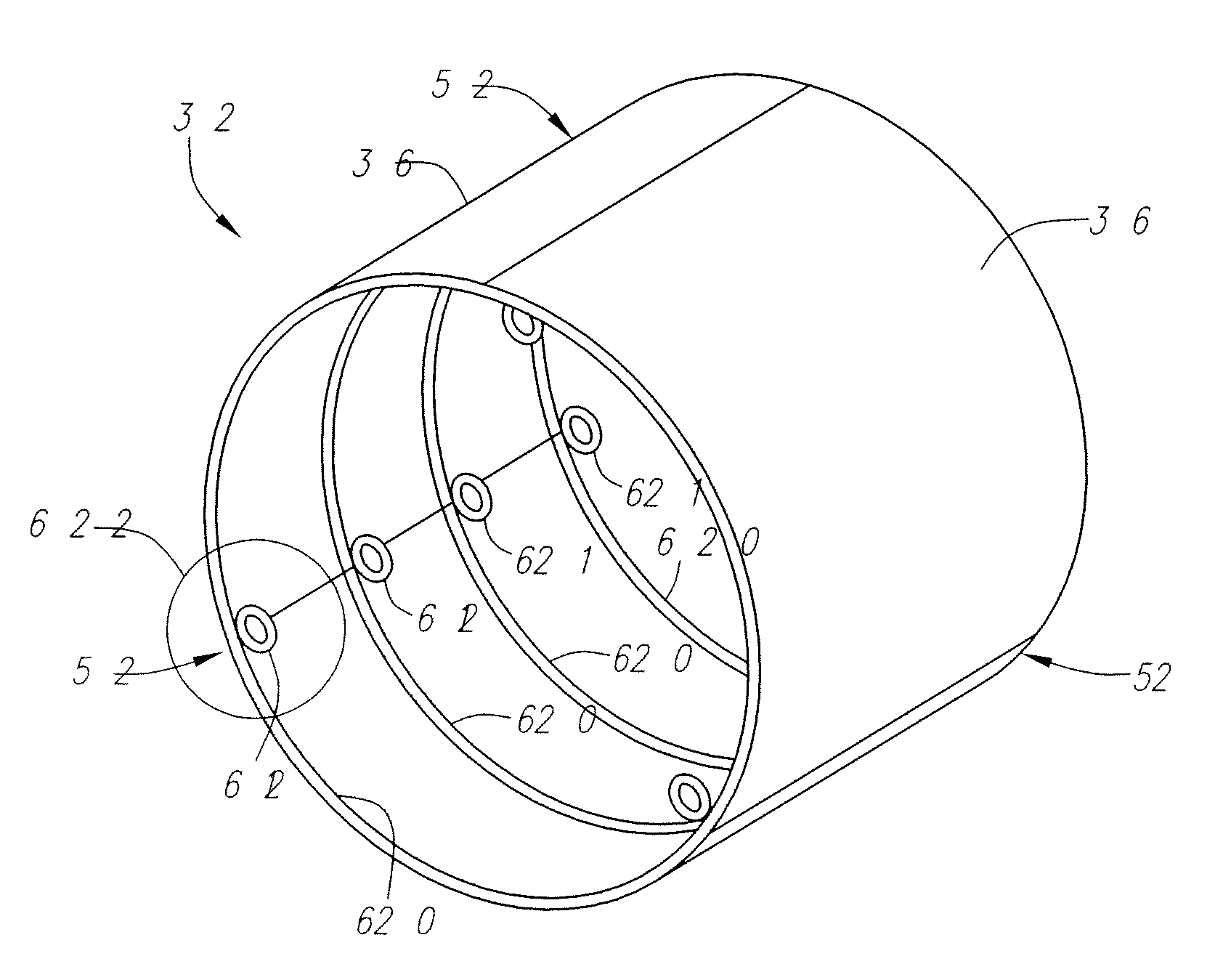
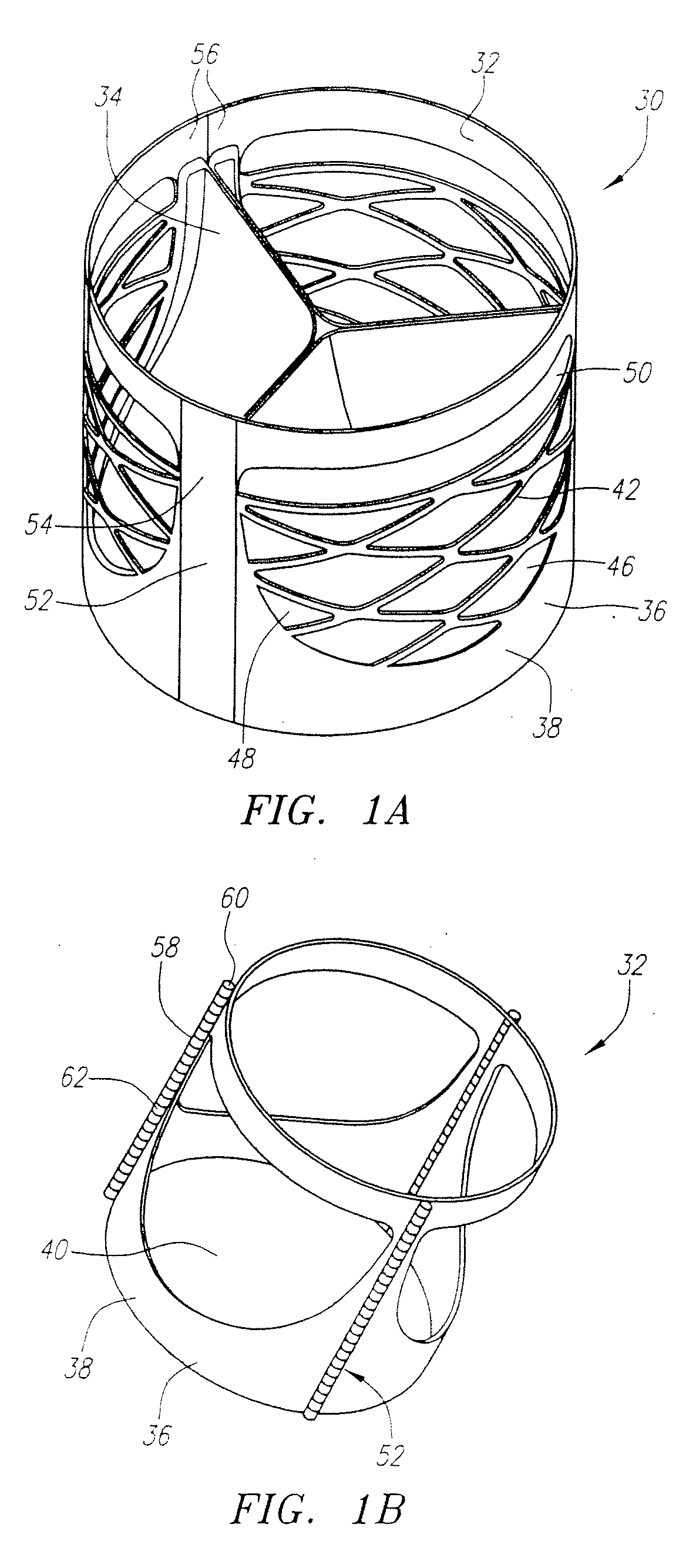
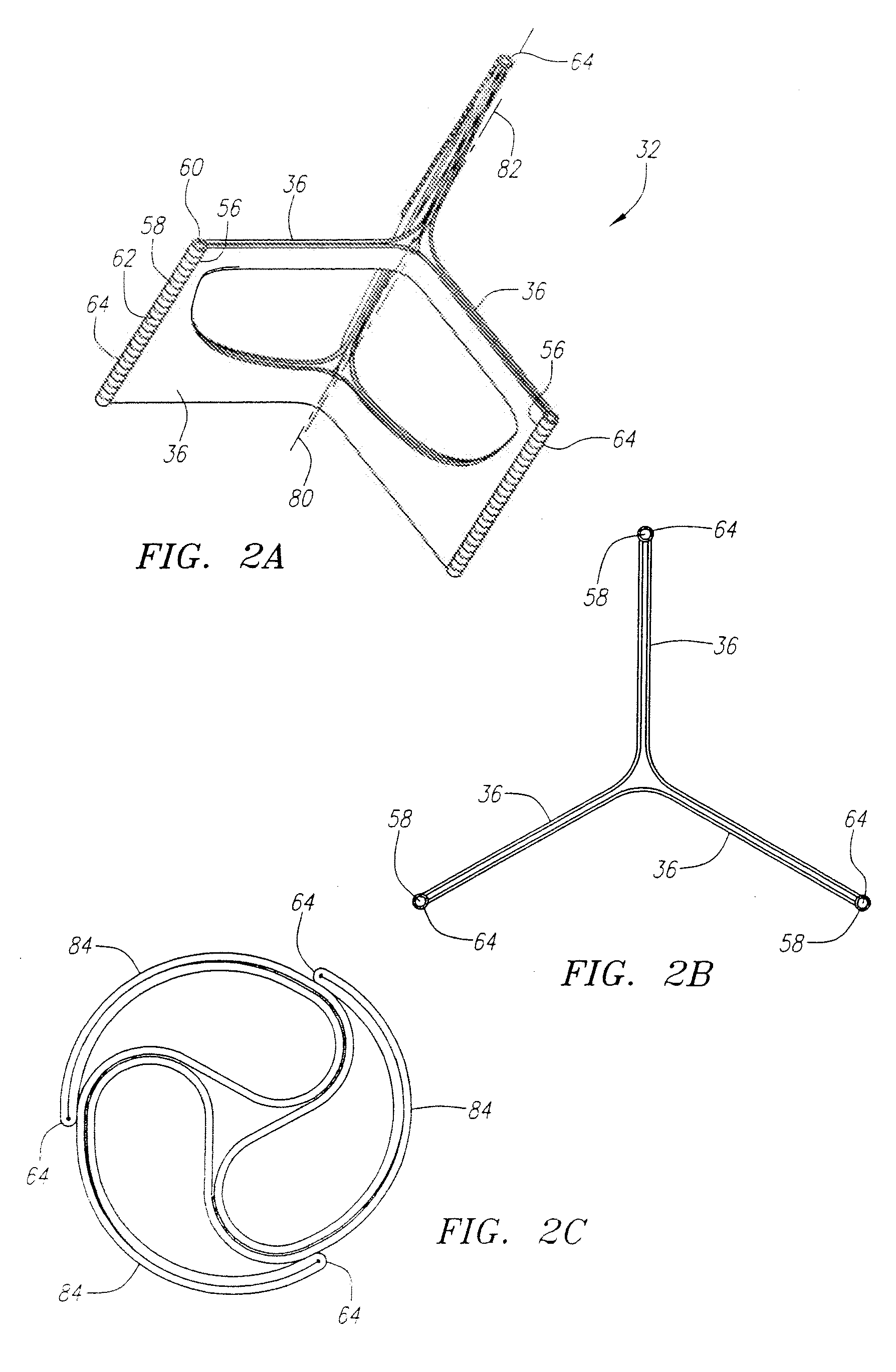
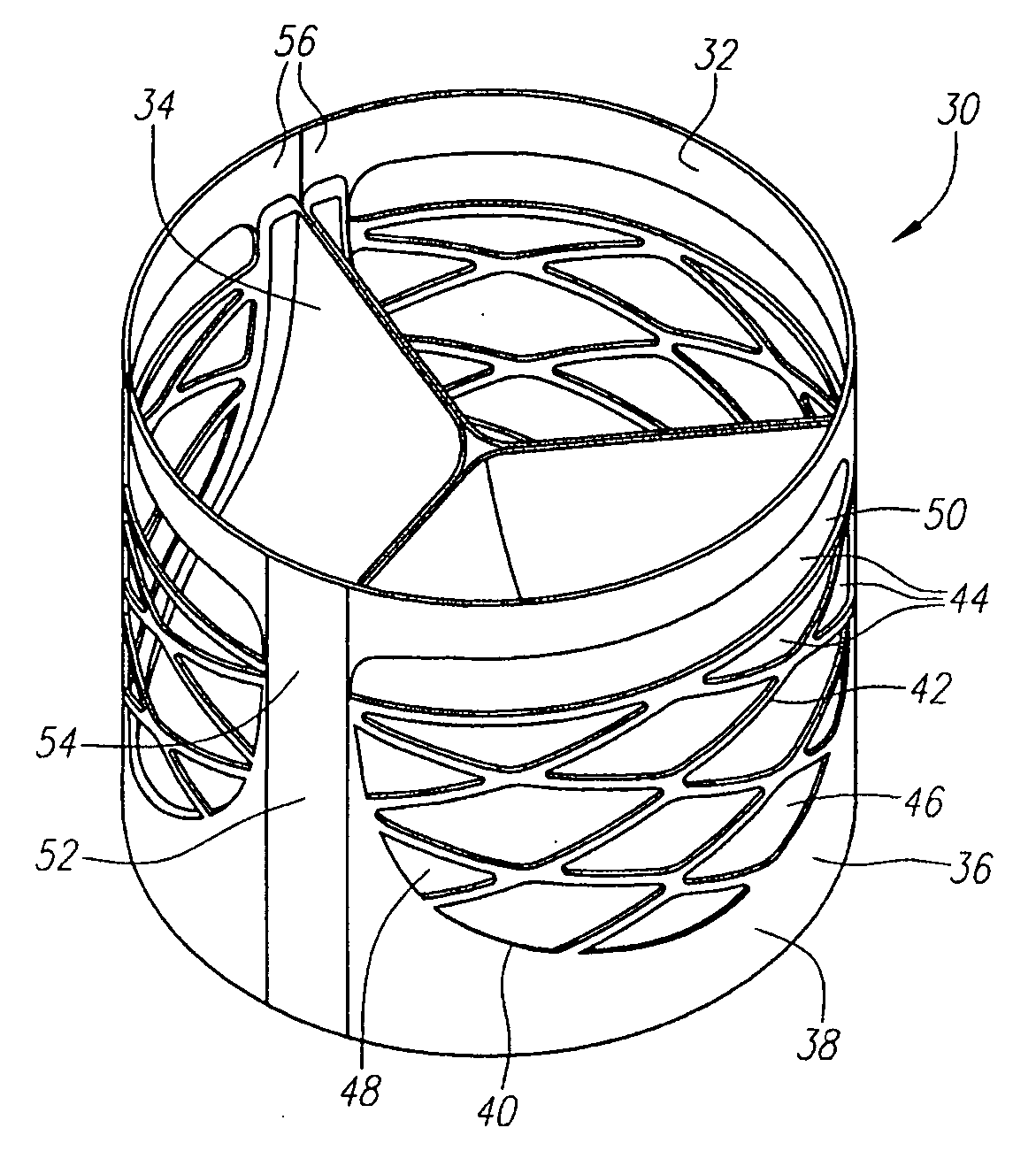
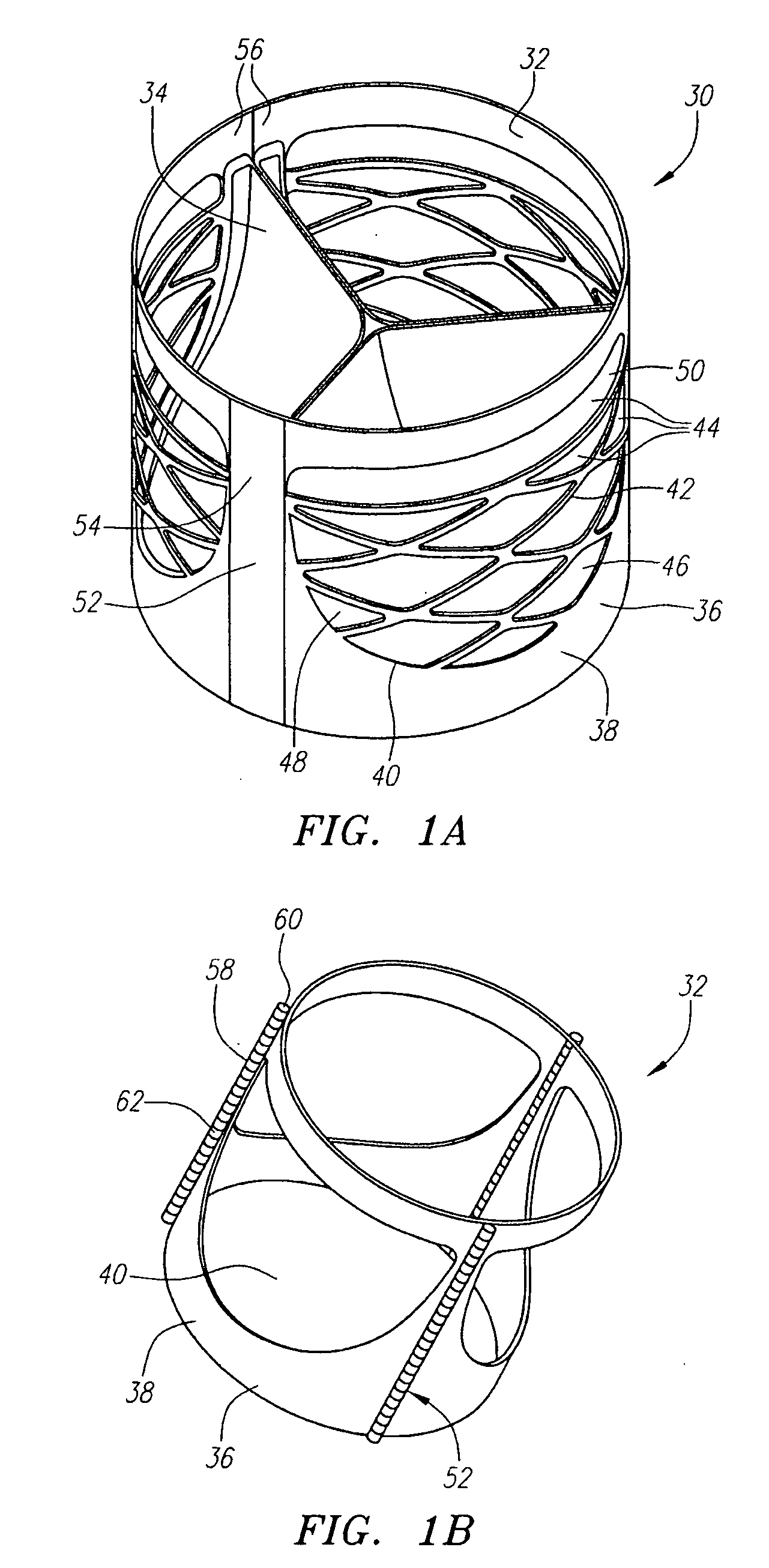
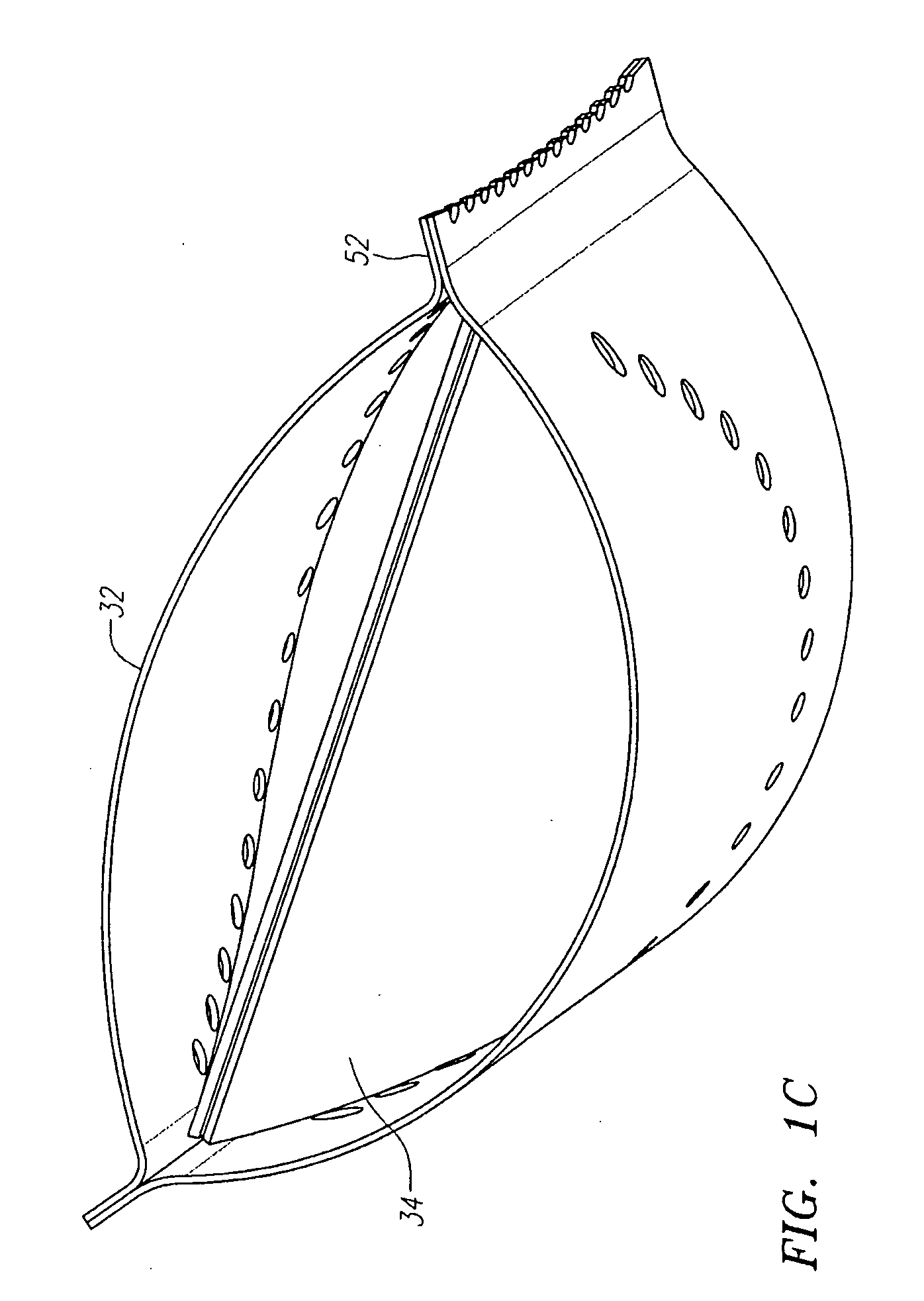
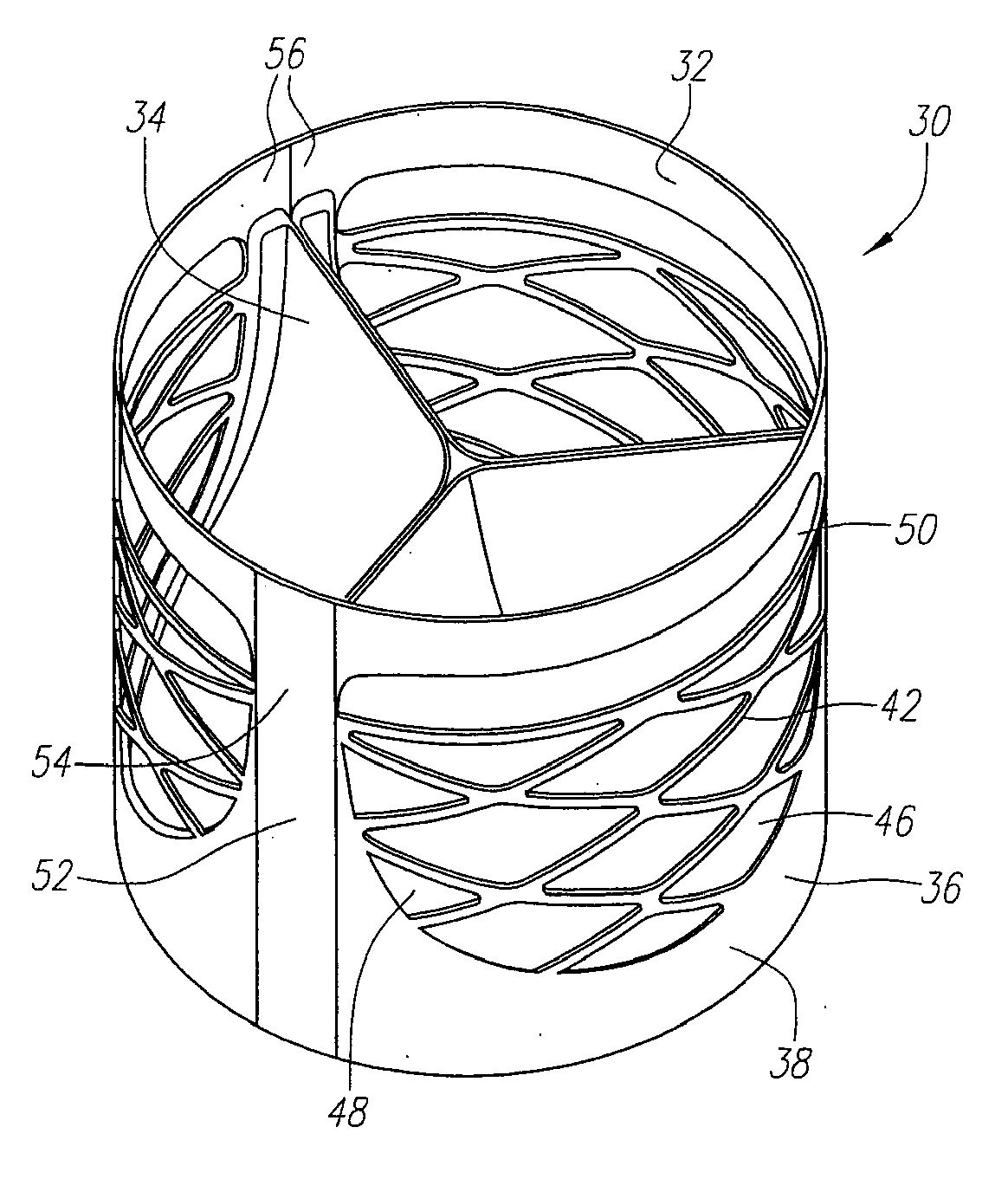
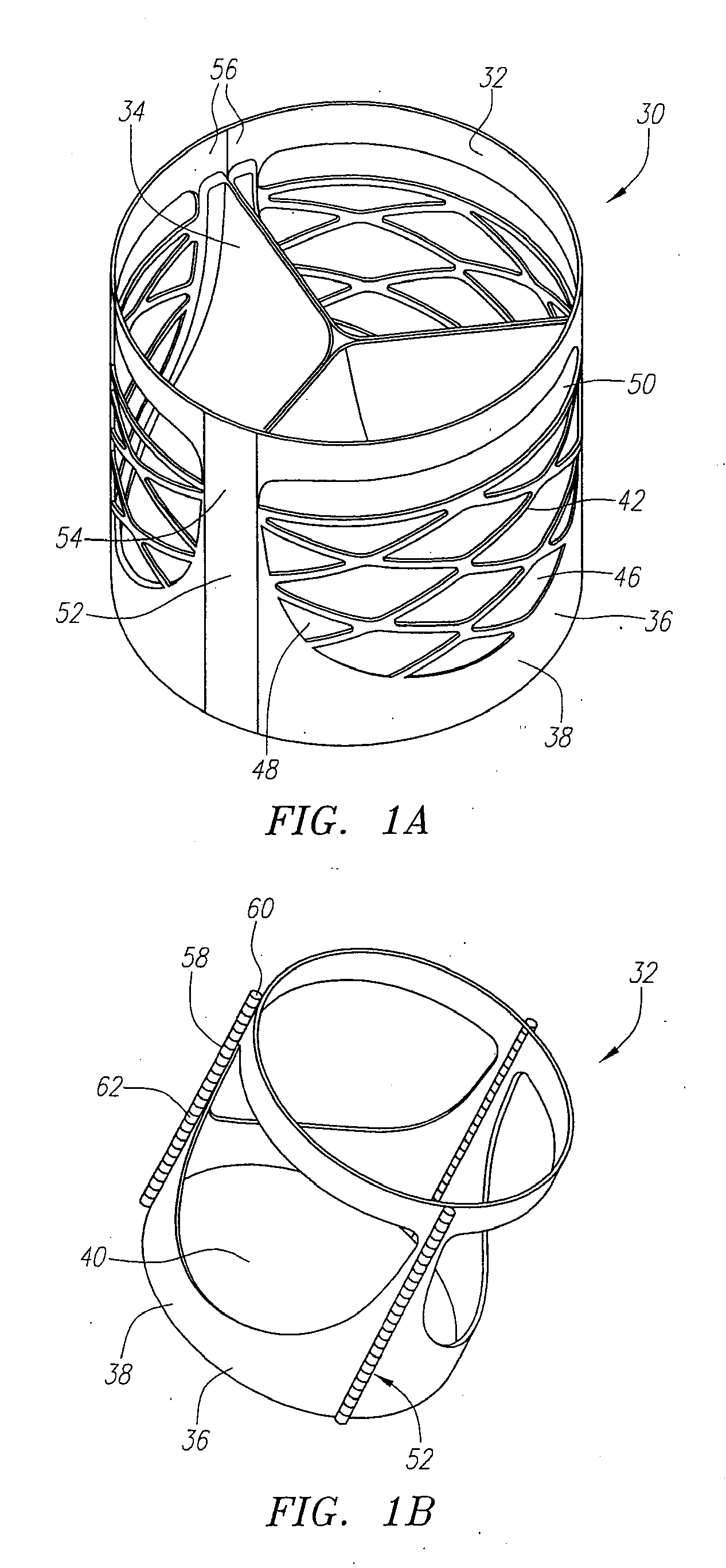
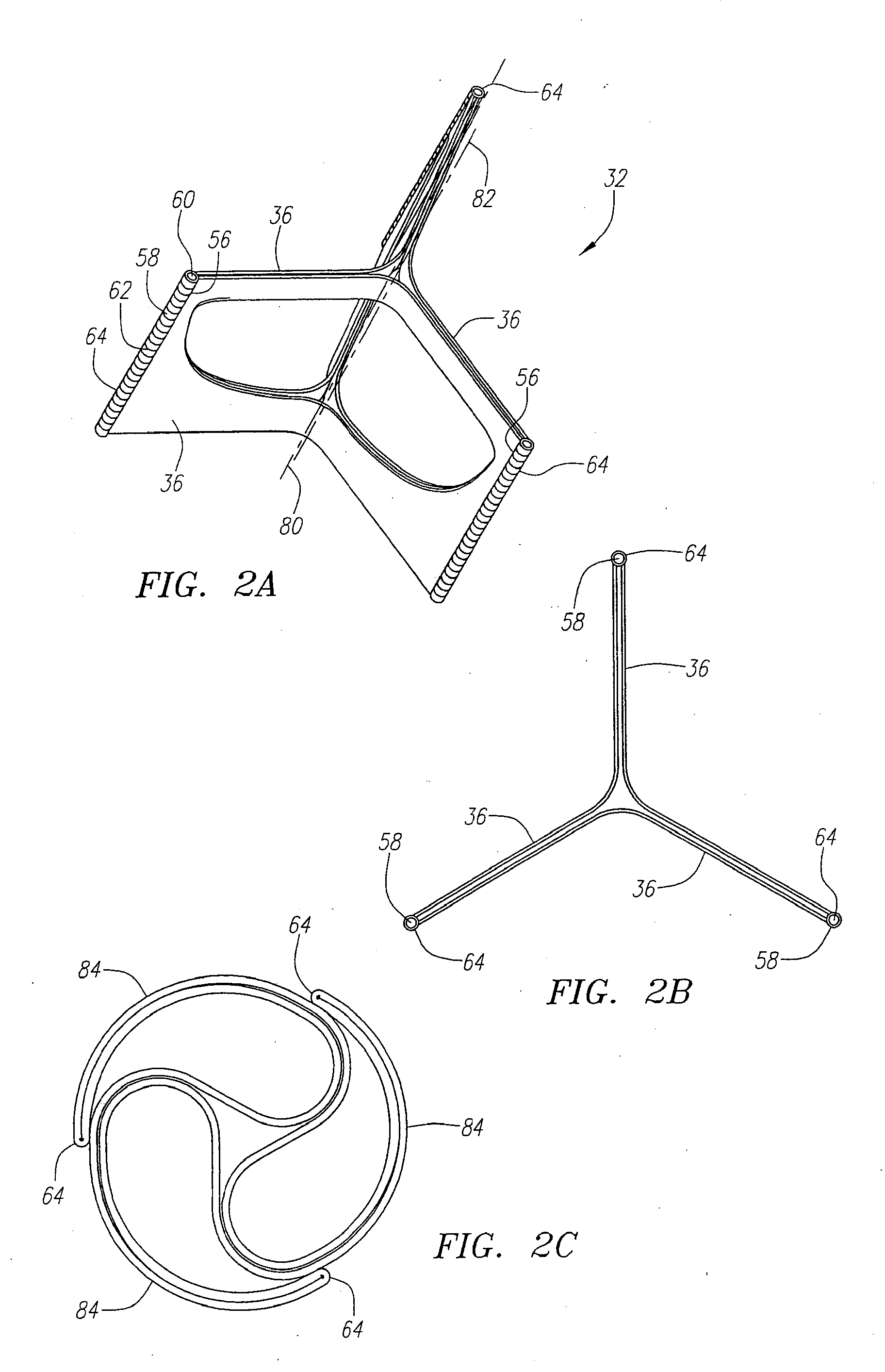
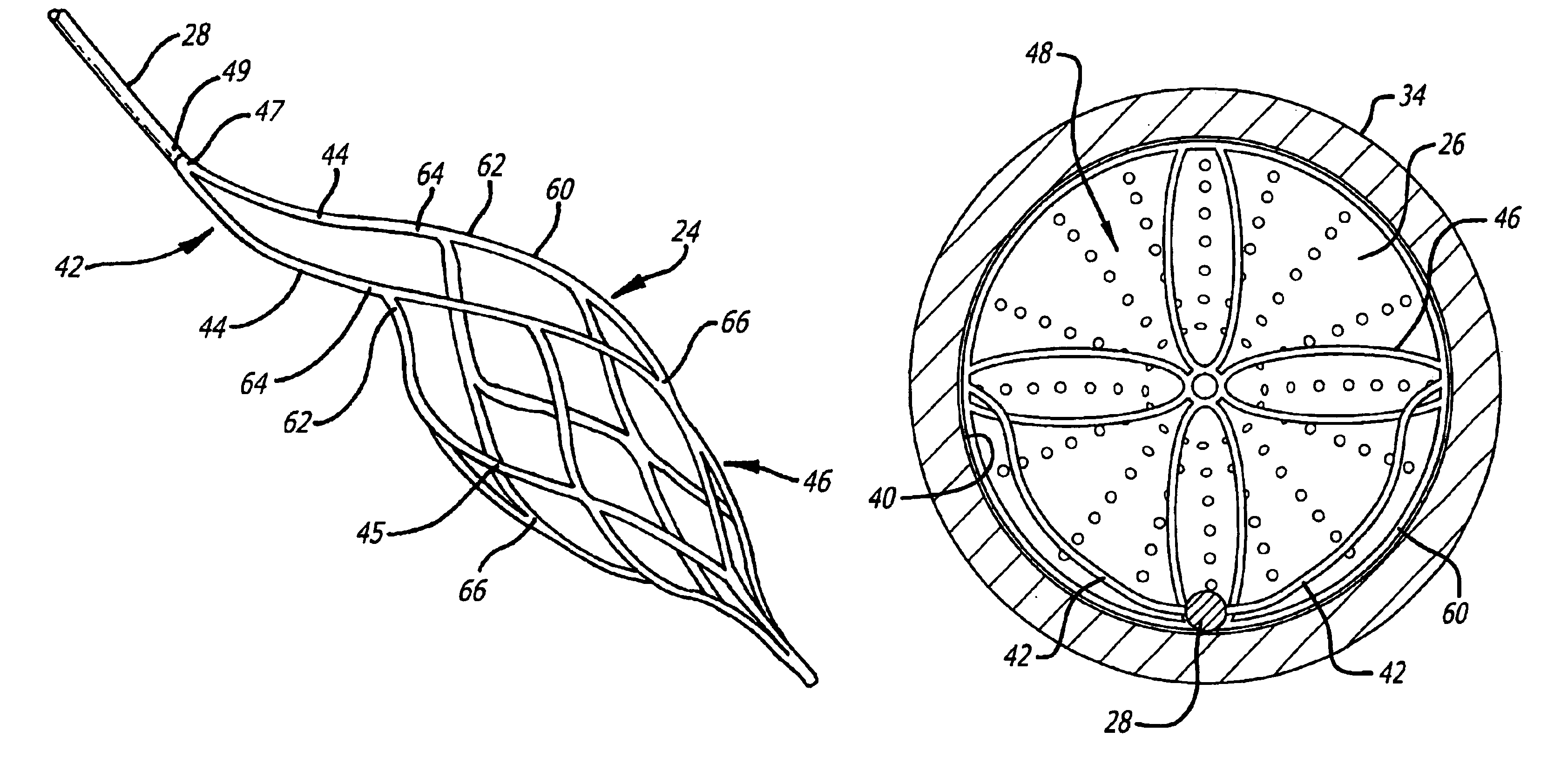
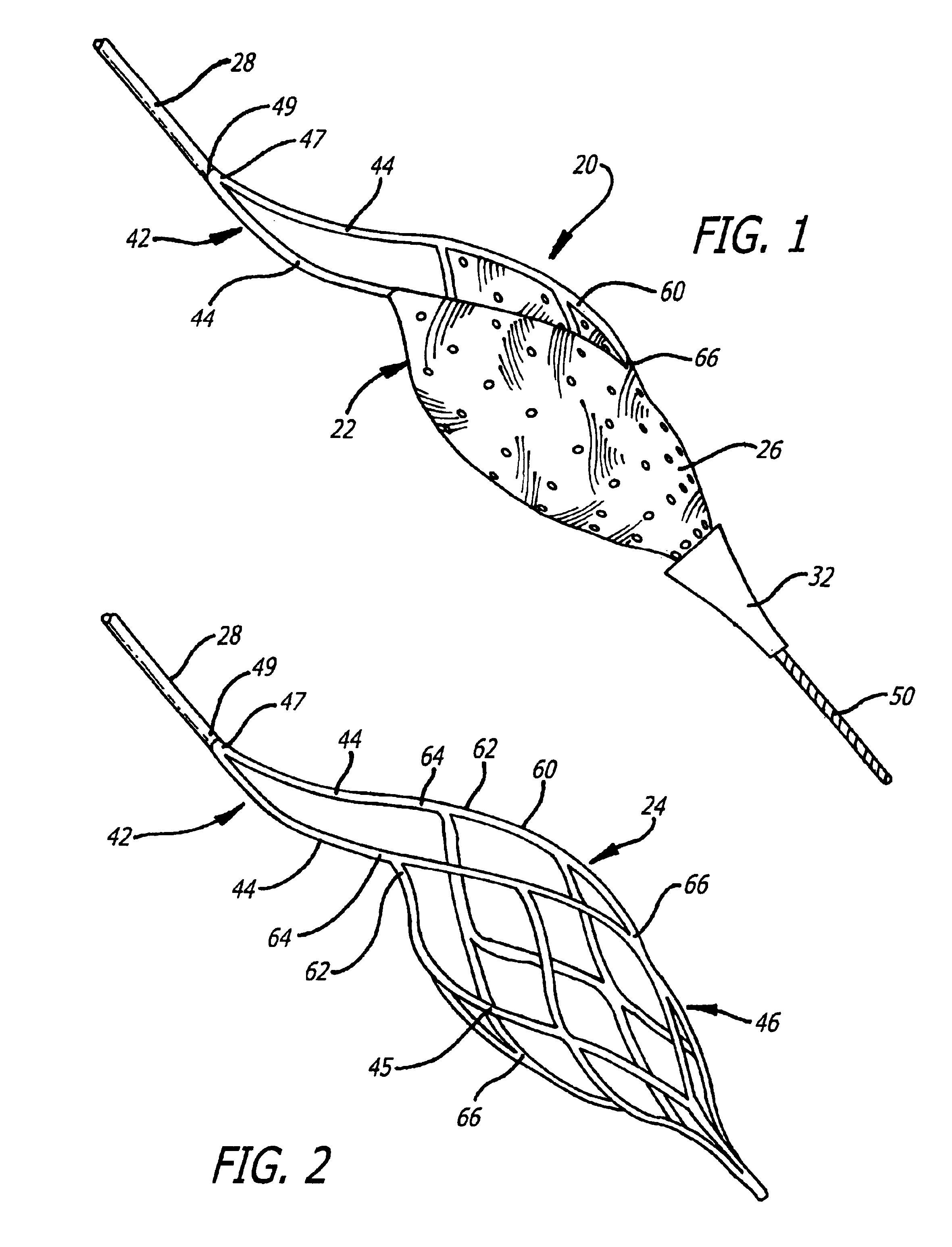
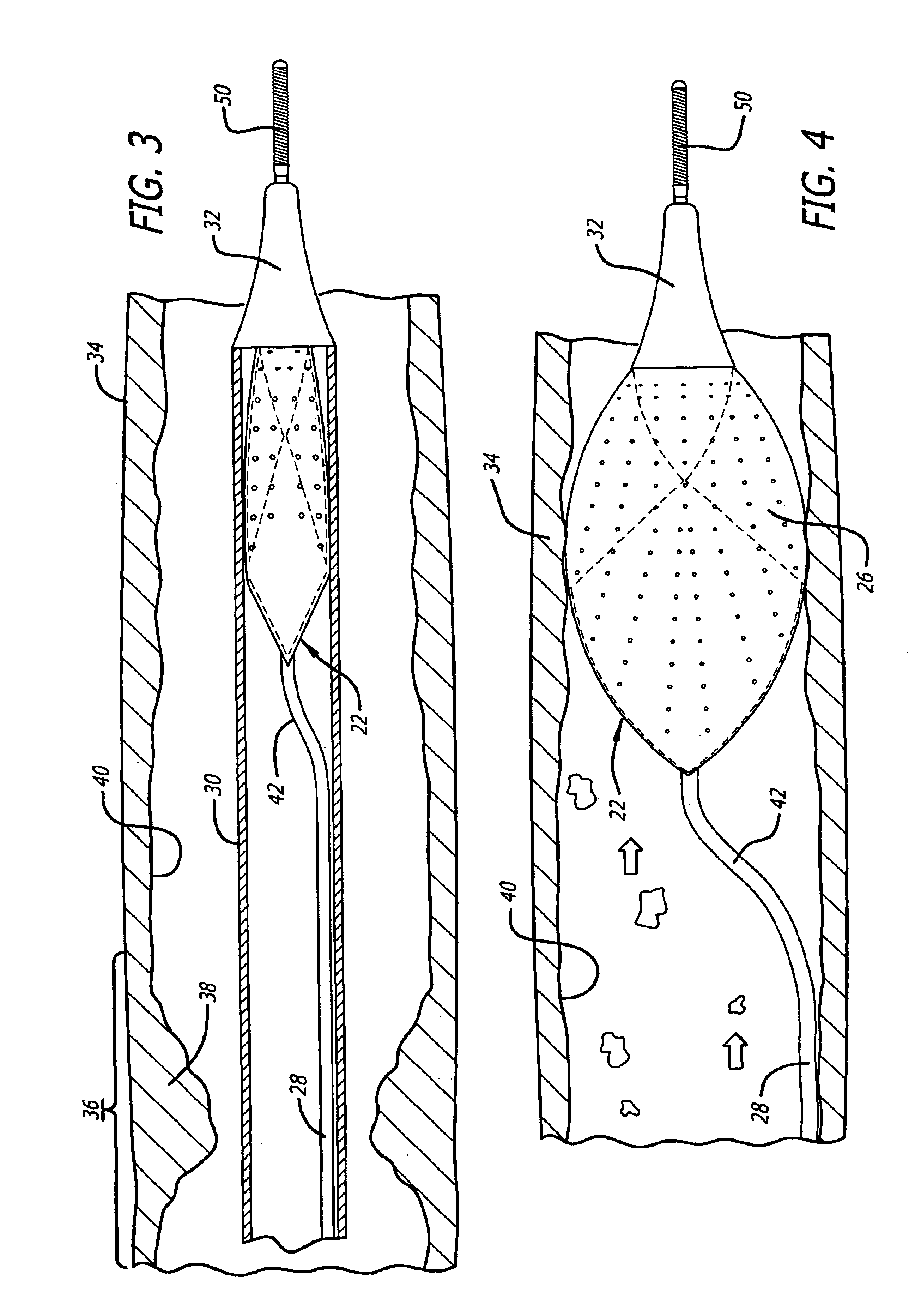
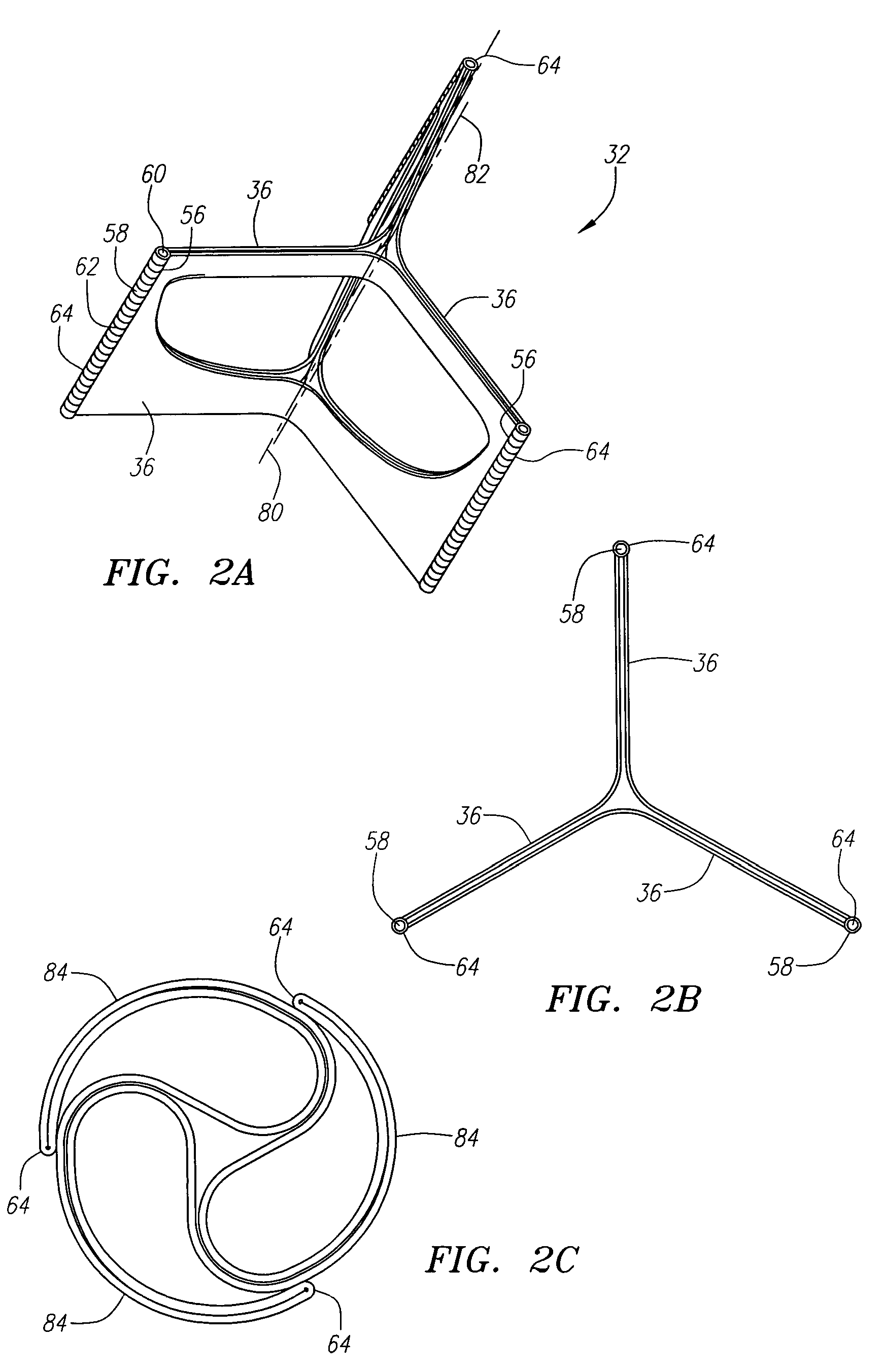
Described herein are systems and methods for operation of a prosthetic valve support structure (32) having additional reinforcement coupled with panels (36). Multiple support members (620) are distributed across the inner surface of the valve support structure (32) at regular intervals. Each support member (620) can include a looped portion (621) to act as a hinge (52). Each looped portion (621) is in a location coincidental with the interlace between adjacent panels (36).
Owner:AORTX
Prosthetic Heart Valves, Support Structures and Systems and Methods for Implanting the Same
InactiveUS20090132035A1Automatically deployingInhibit migrationBalloon catheterDiagnosticsPercutaneous aortic valve replacementProsthetic valve
Prosthetic valves and their component parts are described, as are prosthetic valve delivery devices and methods for their use. The prosthetic valves are particularly adapted for use in percutaneous aortic valve replacement procedures. The delivery devices may be adapted for use in minimally invasive or endovascular surgical procedures.
Owner:AORTX
Prosthetic Heart Valves, Support Structures And Systems And Methods For Implanting The Same
InactiveUS20070073387A1Improve radial strengthIncrease frictionStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic valvePercutaneous aortic valve replacement
Prosthetic valves and their component parts are described, as are prosthetic valve delivery devices and methods for their use. The prosthetic valves are particularly adapted for use in percutaneous aortic valve replacement procedures. The delivery devices are particularly adapted for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:AORTX
Offset proximal cage for embolic filtering devices
InactiveUS6939362B2Good flexibilityHigh strengthMaterial nanotechnologySurgeryCombined useExpandable cage
An expandable cage used in conjunction with an embolic filtering device has a strut configuration including a proximal strut assembly coupled to a distal strut assembly. A filter can be attached to the distal strut assembly which has an inlet opening. The proximal strut assembly is “offset” from the distal strut assembly in that these proximal struts extend substantially along the vessel wall of the patient, rather than being “centered” in the body vessel when the cage is expanded in a body vessel. As a result, there is little cage structure directly in front of the opening of the filter, resulting in a virtually unobstructed opening for the filter.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Stent deployment systems and methods
InactiveUS20070088420A1Facilitating in situ customizationImprove radial strengthStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentStent deployment
A stent deployment system includes a catheter shaft, an expandable member mounted to the catheter shaft, and one or more stents or stent segments slidably positioned on the expandable member. The stent deployment system is adapted for deployment of stents or stent segments in very long lesions and in tapered and curved vessels. The stent deployment system facilitates slidable movement of a stent in a distal direction relative to the expandable member while inhibiting slidable movement in a proximal direction relative to the expandable member.
Owner:XTENT INC
Stent-graft with bioabsorbable structural support
InactiveUS7108716B2Less open spacePrevent and limit tissue ingrowthStentsSurgeryStent graftingArterial fistula
The invention relates to a stent-graft with a bioabsorbable structure and a permanent graft for luminal support and ‘treatment of arterial fistulas, occlusive disease, and aneurysms. The bioabsorbable structure is formed from braided filaments of materials such as PLA, PLLA, PDLA, and PGA and the graft is formed from materials such as PET, ePTFE, PCU or PU.
Owner:SCHNEIDER (USA) INC
Bioabsorable medical devices
InactiveUS20060198869A1Facilitate deploymentImprove physical propertiesStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsYttriumMagnesium
Owner:ICON MEDICAL CORP
Stent segments axially connected by thin film
ActiveUS20090112306A1Improve radial strengthEasy to implantStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentBlood vessel
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a stent for insertion into a vessel of a patient. The stent has a front and back open ends and a longitudinal axis extending therebetween. The stent has a plurality of adjacent hoops that are held in alignment with the longitudinal axis between the front and back open ends by a thin film tube. The hoops are attached to either the inner or outer surface of the thin film tube. The stent is compressed into a first smaller diameter for insertion into the vessel with a delivery tube and a second larger diameter for deployment into the vessel. The inventive stent can be retracted into the delivery tube if it is improperly deployed.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Stent and stent delivery system for ostial locations in a conduit
ActiveUS7632302B2Improve radial strengthMaintaining dilated diameter of the renal vesselStentsBlood vesselsBalloon dilatationRenal vessels
Owner:EV3
Self-expanding, pseudo-braided intravascular device
InactiveUS20080109063A1Large expansion ratioIncrease flexibilityStentsHand lacing/braidingThrombusTubular stenosis
A self-expanding, pseudo-braided device embodying a high expansion ratio and flexibility as well as comformability and improved radial force. The pseudo-braided device is particularly suited for advancement through and deployment within highly tortuous and very distal vasculature. Various forms of the pseudo-braided device are adapted for the repair of aneurysms and stenoses as well as for use in thrombectomies and embolic protection therapy.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR TECH
Stent for blood flow improvement
InactiveUS8192484B2Avoid formingAvoids low shear stress flowStentsSpinal implantsInsertion stentHemodynamics
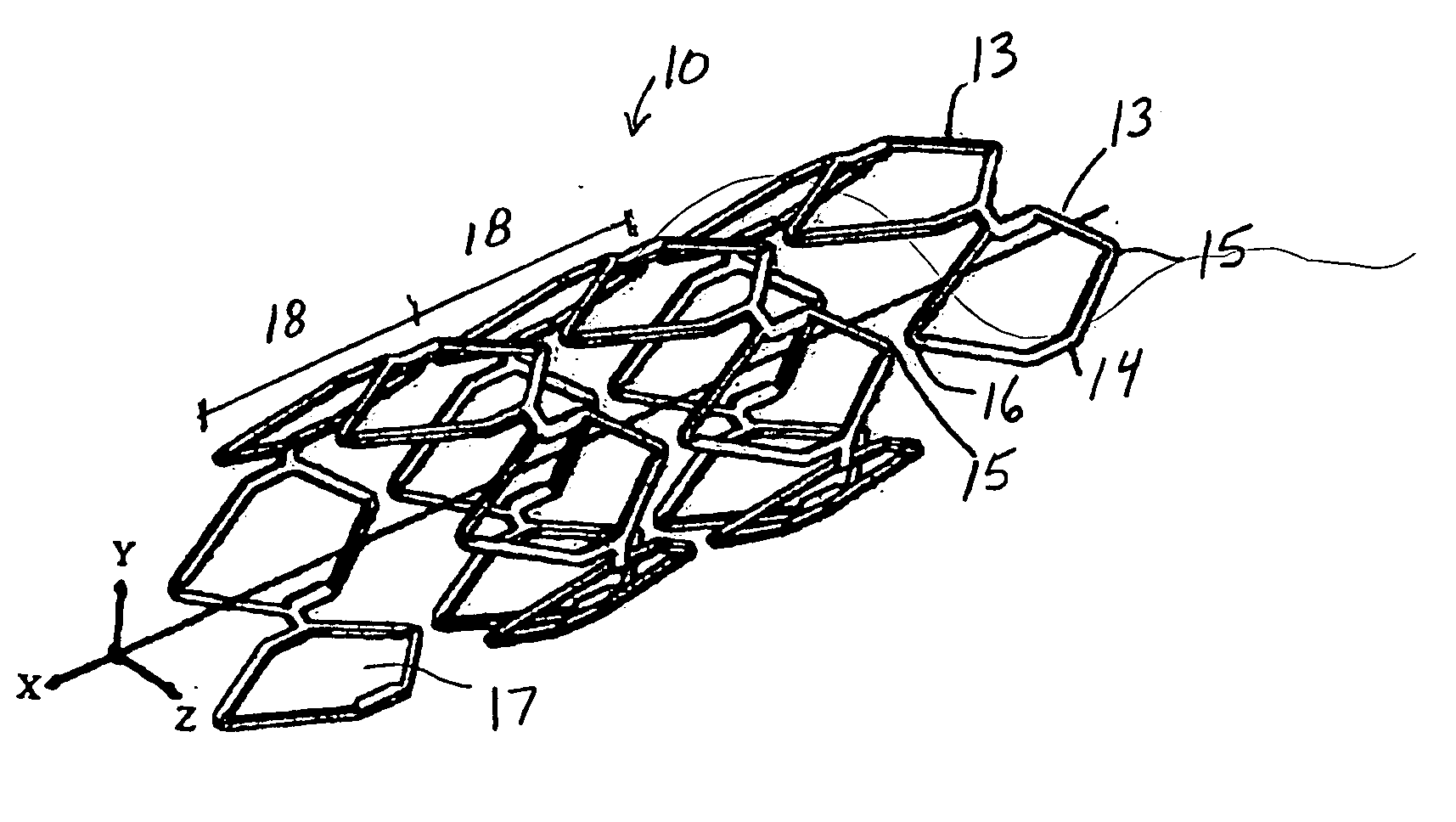
Luminal endoprosthesis formed of a multi-layer braided framework. The framework is devoid of any cover layer, and formed of a plurality of stabilized layers of biocompatible metal wires which are interlaced, forming a lattice, a plurality of wires of a given layer being integrated in the lattice of the adjacent layers. The mechanical characteristics of an outermost layer is so that when in place, the layer applies against a vessel wall, the other layers extending substantially along cylindrical surfaces distinct from the outermost layer so as to form a multi-layer mat which affects the haemodynamic of a flow of blood passing along or through this mat and preventing a growing of plaque.
Owner:CARDIATIS SA
Balloon expandable crush-recoverable stent device
InactiveUS7763065B2Improve radial strengthKeep openStentsBlood vesselsLocking mechanismShape-memory alloy
Owner:REVA MEDICAL
Removable sheath assembly for a polymer scaffold
ActiveUS20140379065A1Easy to disassembleMinimize damageStentsBalloon catheterHealth professionalsCatheter
A medical device includes a polymer scaffold crimped to a catheter having an expansion balloon. A sheath is placed over the crimped scaffold after crimping to reduce recoil of the crimped polymer scaffold and maintain scaffold-balloon engagement relied on to hold the scaffold to the balloon when the scaffold is being delivered to a target in a body. The sheath is removed by a health professional either by removing the sheath directly or using a tube containing the catheter.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Retrieval systems and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS20130317589A1Little strengthReduce dislodging portionStentsCannulasBiomedical engineeringFrictional resistance
The devices and methods described herein relate to improved structures for removing obstructions from body lumens. Such devices have applicability in through-out the body, including clearing of blockages within the vasculature, by addressing the frictional resistance on the obstruction prior to attempting to translate and / or mobilize the obstruction within the body lumen.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Prosthetic heart valves, scaffolding structures, and systems and methods for implantation of same
InactiveUS7785341B2Improve radial strengthIncrease frictionBalloon catheterEar treatmentPercutaneous aortic valve replacementProsthetic valve
Prosthetic valves and their component parts are described, as are prosthetic valve delivery devices and methods for their use. The prosthetic valves are particularly adapted for use in percutaneous aortic valve replacement procedures. The delivery devices are particularly adapted for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:AORTX
Fracture-resistant helical stent incorporating bistable cells and methods of use
InactiveUS20060217795A1Increased compressive loadPotent inhibitionStentsSurgeryVascular prosthesisLesion
Vascular prostheses and methods of use are provided, wherein the vascular prosthesis includes a plurality of bistable unit cells configured to form a helical structure. A visualization catheter also is provided for use ensuring accurate measurement of a lesion and ensuring delivery and placement of the vascular prosthesis.
Owner:CELONOVA STENT
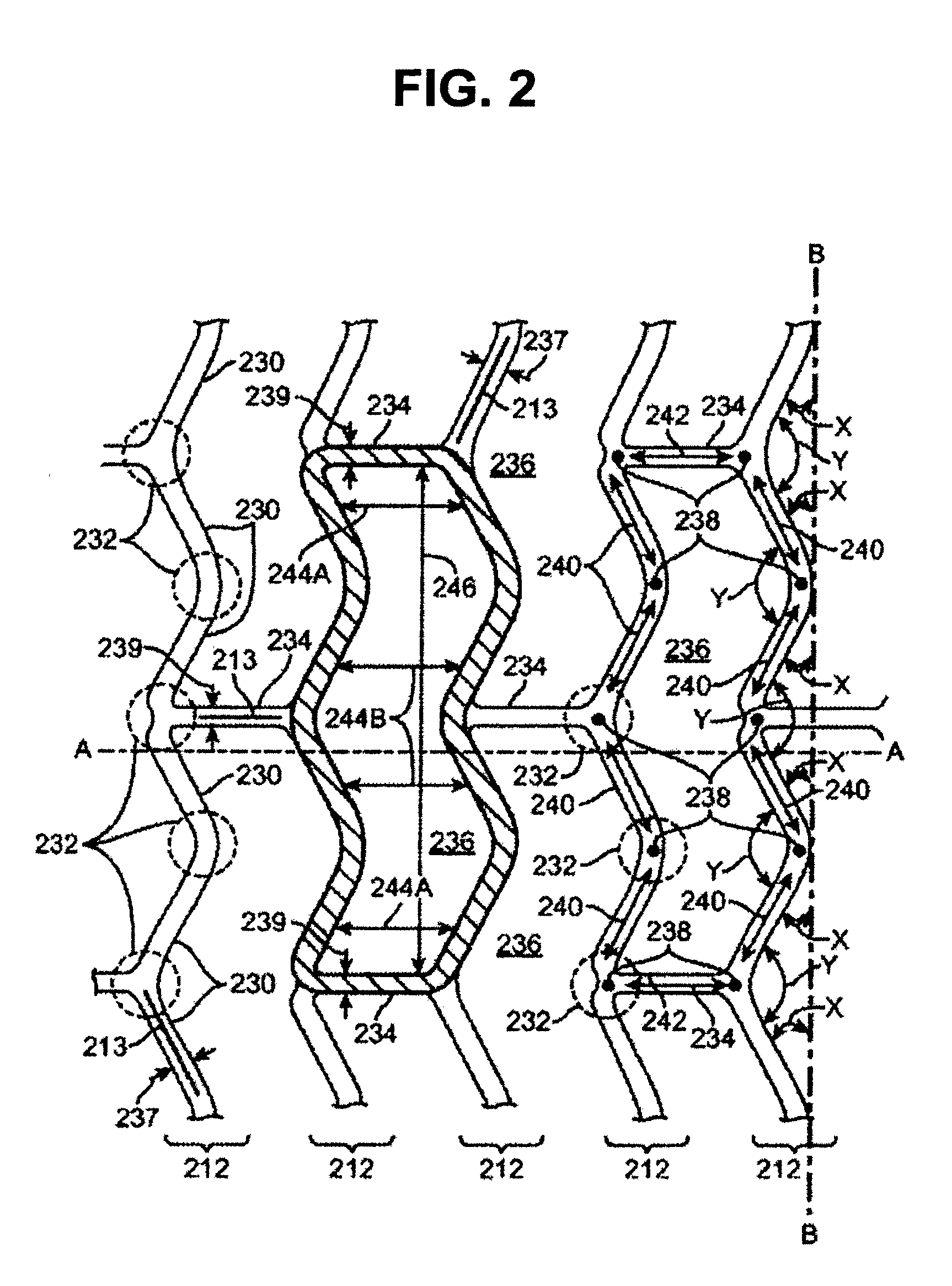
Stent
An expandable stent for use within a body passageway. The stent includes at least two struts and a connector securing together said two struts. At least one of said struts includes an elbow section and an undulating section. The apex of at least one strut can include at least one a dimple, divot and / or slot.
Owner:ICON MEDICAL CORP
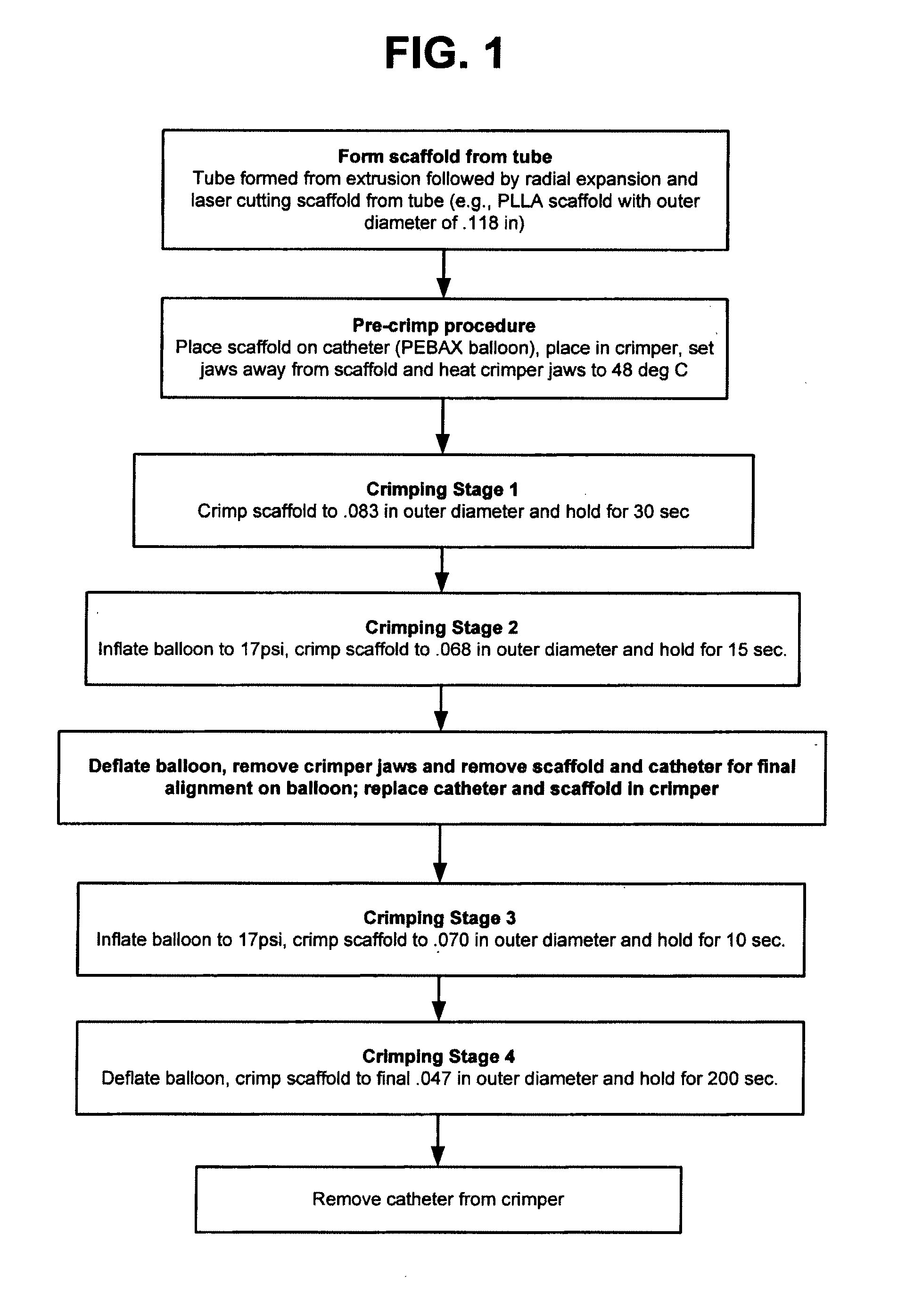
Methods for Crimping a Polymeric Stent Onto a Delivery Balloon
A medical device-includes a polymer stent crimped to a catheter having an expansion balloon. The stent is crimped to the balloon by a process that includes heating the stent to a temperature below the polymer's glass transition temperature to improve stent retention without adversely affecting the mechanical characteristics of the stent when later deployed to support a body lumen.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Braided stent and method for its manufacture
InactiveUS7213495B2Improve radial strengthIncrease the diameterStentsOrnamental textile articlesInsertion stentBraided stent
A stent and method for making the stent are provided. The stent comprises regions of differing numbers of braided filaments to provide a stent with different dimensions and / or properties in different regions along the stent length. A preferred stent comprises a first and second plurality of braided filaments each braided together. The second plurality of braided filaments is braided into the first plurality of braided filaments to form a region of different properties than the first. A preferred embodiment is a stent having a narrower diameter along a more flexible region and a broader diameter along a more rigid region. Also included is a method of constructing a braided stent in accordance with the above. The method comprises the steps of braiding a first plurality of filaments to form the flexible portion, combining a second plurality of filaments to the first plurality of filaments, and then braiding the second plurality of filaments with the first plurality of filaments to form the more rigid region from the combination of the first and second plurality of filaments, wherein the second plurality of filaments are braided only in the rigid region.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
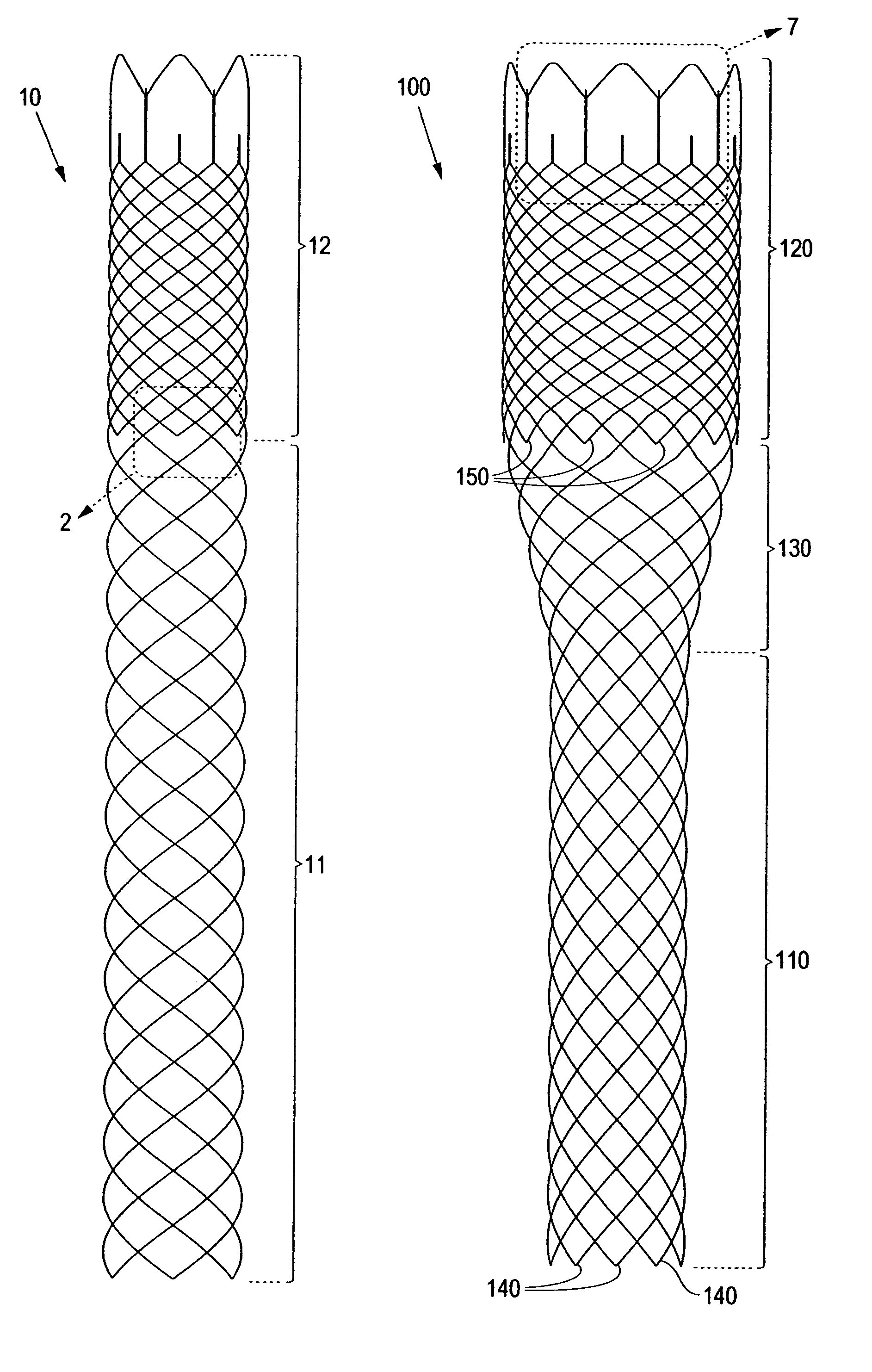
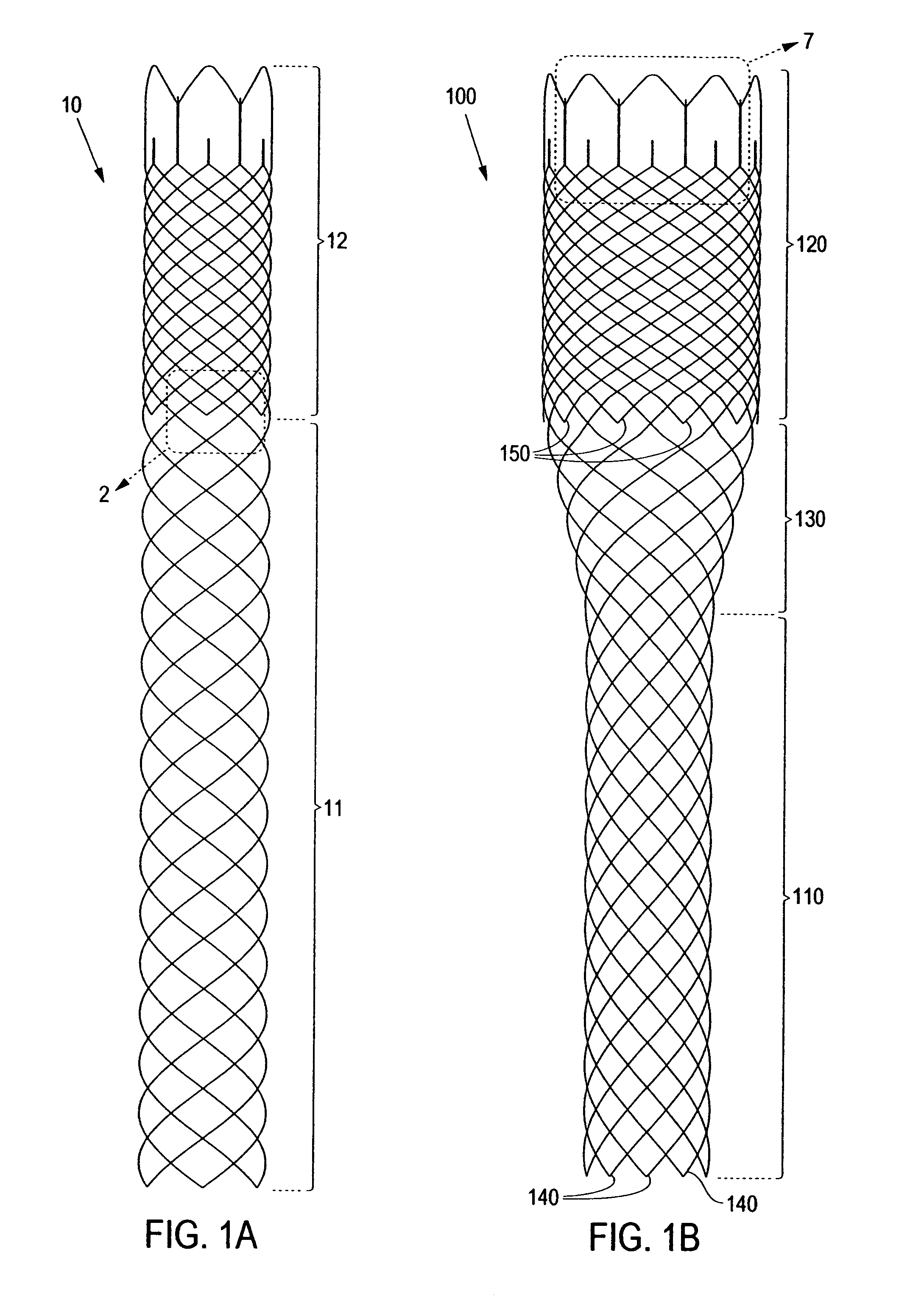
Flared stents and apparatus and methods for delivering them
ActiveUS20070073388A1Facilitate flaring outwardlyImprove radial strengthStentsCatheterInsertion stentMechanical property
Flared stents are disclosed, and apparatus and methods for delivering such stents into a bifurcation between a main vessel and a branch vessel. The stent includes a first tubular portion a second flaring portion that may be flared radially outwardly to contact the ostium. The stent may include variable mechanical properties along its length. The stent may be delivered using a catheter including proximal and distal ends, the stent overlying first and second balloons on the distal end. During use, the catheter is advanced through an ostium into the branch to place the stent within the branch. The first balloon is expanded to flare the stent to contact a wall of the ostium, thereby causing the stent to migrate partially into the ostium. The second balloon is expanded to filly expand the stent within the ostium and branch.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
Steep-taper flared stents and apparatus and methods for delivering them
ActiveUS20070067011A1Facilitate flaring outwardlyImprove radial strengthStentsCatheterInsertion stentBlood vessel
A stent includes a first portion including first and second bands of cells that flare outwardly when the stent is expanded from a contracted to a flared condition, and a second portion connected to the first portion by flexible connectors. During use, the stent is introduced into a main vessel in the contracted condition and positioned with the first portion adjacent an ostium and the second portion within a branch vessel extending from the ostium. The first portion is flared, causing first struts of the first set of cells to move from an axial towards a radial and partial circumferential orientation and causing second struts of the second set of cells to move from an axial towards a radial orientation. The stent is expanded further such that the second portion expands within the branch body lumen, and the first and second struts move towards a more circumferential orientation.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
Braided stent method for its manufacture
InactiveUS7001425B2Improve radial strengthIncrease the diameterStentsOrnamental textile articlesBraided stent
A stent and method for making the stent are provided. The stent comprises regions of differing numbers of braided filaments to provide a stent with different dimensions and / or properties in different regions along the stent length. A preferred stent comprises a first and second plurality of braided filaments each braided together. The second plurality of braided filaments is braided into the first plurality of braided filaments to form a region of different properties than the first. A preferred embodiment is a stent having a narrower diameter along a more flexible region and a broader diameter along a more rigid region. Also included is a method of constructing a braided stent in accordance with the above. The method comprises the steps of braiding a first plurality of filaments to form the flexible portion, combining a second plurality of filaments to the first plurality of filaments, and then braiding the second plurality of filaments with the first plurality of filaments to form the more rigid region from the combination of the first and second plurality of filaments, wherein the second plurality of filaments are braided only in the rigid region.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Stent deployment systems and methods
InactiveUS20060200223A1Facilitating in situ customizationImprove radial strengthStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentStent deployment
A stent deployment system includes a catheter shaft, an expandable member mounted to the catheter shaft, and one or more stents or stent segments slidably positioned on the expandable member. The stent deployment system is adapted for deployment of stents or stent segments in very long lesions and in tapered and curved vessels. The stent deployment system facilitates slidable movement of a stent in a distal direction relative to the expandable member while inhibiting slidable movement in a proximal direction relative to the expandable member.
Owner:XTENT INC
Self-sealing PTFE vascular graft and manufacturing methods
InactiveUS20040193242A1Superior assimilation capabilities and resealable propertiesImprove microporous structureBlood vesselsPorosityMedicine
An implantable microporous ePTFE tubular vascular graft exhibits long term patency, superior radial tensile strength and suture hole elongation resistance. The graft includes a first ePTFE tube and a second ePTFE tube circumferentially disposed over the first tube. The first ePTFE tube exhibits a porosity sufficient to promote cell endothelization, tissue ingrowth and healing. The second ePTFE tube exhibits enhanced radial strength in excess of the radial tensile strength of the first tube.
Owner:LIFEPORT SCI
Self-expanding pseudo-braided intravascular device
InactiveUS20100004726A1Large expansion ratioIncrease flexibilityStentsHand lacing/braidingThrombusRepair aneurysm
A self-expanding, pseudo-braided device embodying a high expansion ratio and flexibility as well as comformability and improved radial force. The pseudo-braided device is particularly suited for advancement through and deployment within highly tortuous and very distal vasculature. Various forms of the pseudo-braided device are adapted for the repair of aneurysms and stenoses as well as for use in thrombectomies and embolic protection therapy.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Thermally pliable and carbon fiber stents
A prosthesis for insertion into a body passage is disclosed. The prosthesis includes a plastic or polymer base material which is compatible with living tissue and which possesses a memory of a predetermined configuration. The base material further has a glass transition temperature at which the prosthesis can be molded intravascularly from the predetermined configuration to a larger-radius implant configuration, which is sized and shaped to conform to an internal anatomy of the body passage to expand a narrow segment of or to occlude an opening of an out pouch of the body passage. The glass transition temperature is greater than a temperature of the body passage so that the prosthesis after being molded can be allowed to cool to the temperature of the body passage.
Owner:AMIS JAMES PETER +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com